1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17616
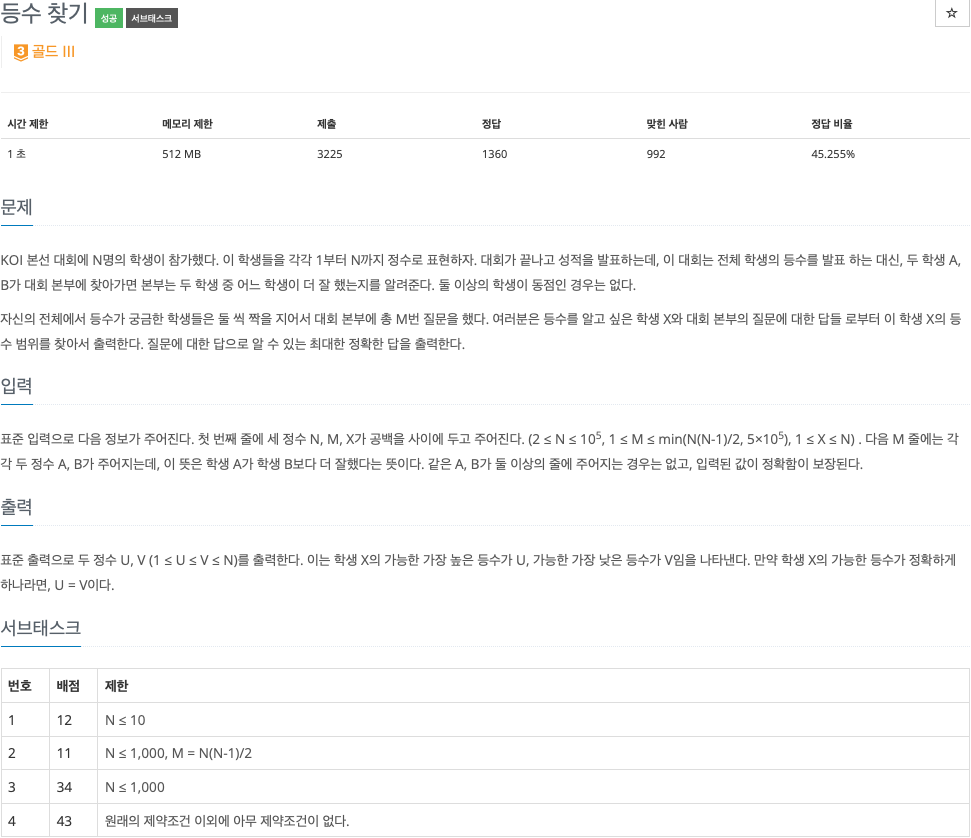
2. 문제

3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int studentCount;
static int questionCount;
static int targetStudent;
static Set<Integer> higherStudents;
static Set<Integer> lowerStudents;
static Map<Integer, List<Integer>> higherRelations;
static Map<Integer, List<Integer>> lowerRelations;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
studentCount = scanner.nextInt();
questionCount = scanner.nextInt();
targetStudent = scanner.nextInt();
higherStudents = new HashSet<>();
lowerStudents = new HashSet<>();
higherRelations = new HashMap<>();
lowerRelations = new HashMap<>();
for (int student = 1; student <= studentCount; student++) {
higherRelations.put(student, new ArrayList<>());
lowerRelations.put(student, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int question = 0; question < questionCount; question++) {
int higher = scanner.nextInt();
int lower = scanner.nextInt();
higherRelations.get(lower).add(higher);
lowerRelations.get(higher).add(lower);
}
}
/*
* 주어진 두 학생 사이의 점수 비교 정보를 통해 자신보다 등수가 높은 학생을 저장하는 Map 하나, 자신보다 등수가 낮은 학생을 저장하는 Map 하나를 생성한다
* 두 정보를 이용해 등수 범위를 찾고 싶은 학생에 대해 자신보다 등수가 높은 학생들, 자신보다 등수가 낮은 학생들을 BFS를 통해 찾는다
*
* 위 작업을 통해 자신보다 등수가 높은 학생들의 수, 자신보다 등수가 낮은 학생들의 수를 알 수 있으니
* 가장 높은 등수는 (자신보다 등수가 높은 학생들의 수 + 1)이 될 것이고
* 가장 낮은 등수는 (총 학생의 수 - 자신보다 등수가 낮은 학생들의 수)가 될 것이다
*/
static void solution() {
bfs(targetStudent, higherStudents, higherRelations);
bfs(targetStudent, lowerStudents, lowerRelations);
int higherStudentCount = higherStudents.size();
int lowerStudentCount = lowerStudents.size();
System.out.println((higherStudentCount + 1) + " " + (studentCount - lowerStudentCount));
}
static void bfs(int start, Set<Integer> result, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> relations) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[studentCount + 1];
queue.offer(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int student : relations.get(cur)) {
if (!visited[student]) {
visited[student] = true;
result.add(student);
queue.offer(student);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
