1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7570
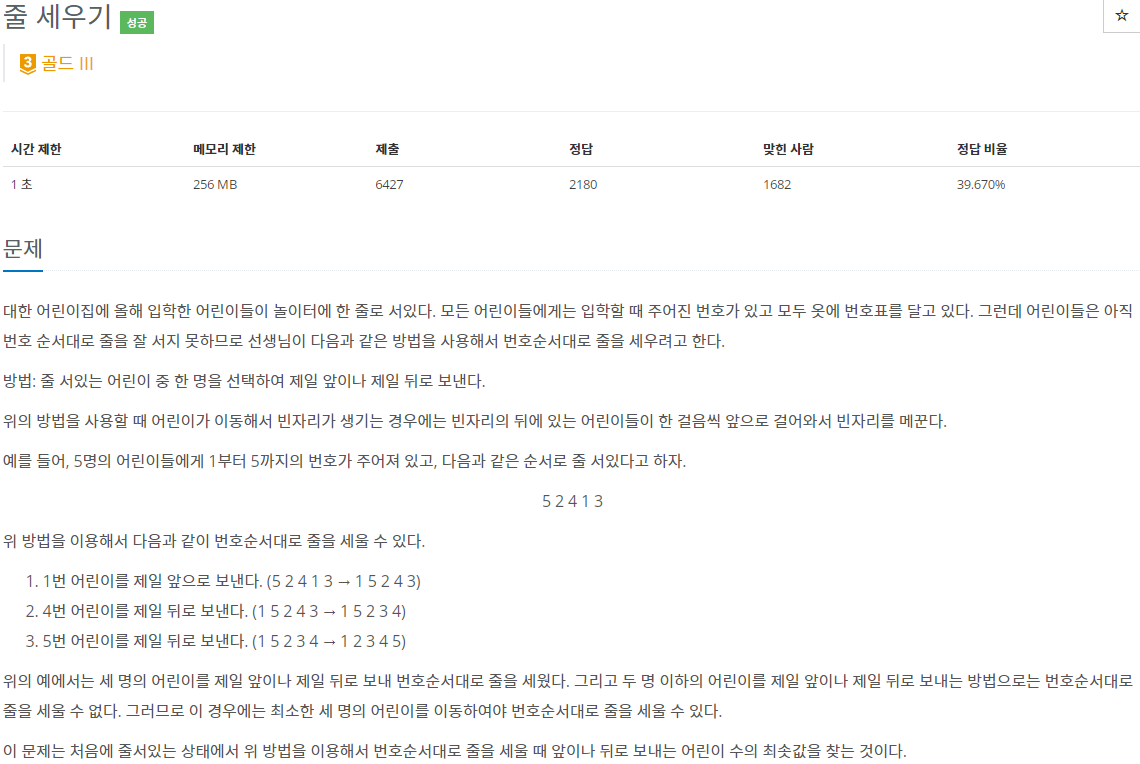
2. 문제
요약
- 모든 어린이들에게는 입학할 때 주어진 번호가 있고 모두 옷에 번호표를 달고 있습니다.
- 어린이들은 번호 순서대로 줄을 잘 서지 못하여 다음과 같은 방법을 통해 번호 순서대로 줄을 세우려고 합니다.
- 줄 서있는 어린이 중 한 명을 선택하여 제일 앞이나 제일 뒤로 보냅니다.
- 위 방법을 사용할 때, 어린이가 이동해서 빈자리가 생긴다면 빈자리의 뒤에 있는 어린이들이 한 걸음씩 앞으로 걸어와 빈자리를 메꿉니다.
- 처음에 줄서있는 상태에서 위 방법을 이용하여 번호 순서대로 줄을 세울 때, 앞이나 뒤로 보내는 어린이 수의 최솟값을 찾는 문제입니다.
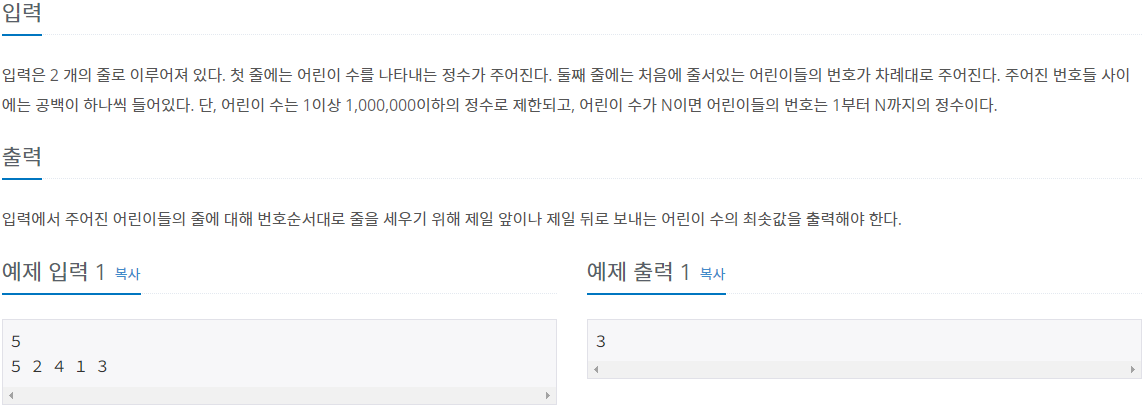
- 입력: 첫 번째 줄에 1보다 크거나 같고 1,000,000보다 작거나 같은 정수인 어린이 수가 주어지고 두 번째 줄에 처음에 줄 서있는 어린이들의 번호가 차례대로 주어집니다. 어린이의 수가 N이면 어린이들의 번호는 1부터 N까지의 정수입니다.
- 출력: 첫 번째 줄에 주어진 어린이들의 줄에 대해 번호 순서대로 줄을 세우기 위해 제일 앞이나 제일 뒤로 보내는 어린이 수의 최솟값을 출력합니다.
3. 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int[] consecutiveLISNum;
static void input() {
Reader scanner = new Reader();
N = scanner.nextInt();
consecutiveLISNum = new int[N + 1];
// 연속된 수들로 이루어진 LIS의 길이를 구한다
for(int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++) {
int num = scanner.nextInt();
consecutiveLISNum[num] = consecutiveLISNum[num - 1] + 1;
}
}
static void solution() {
// 정렬을 하여 가장 긴 연속된 수들로 이루어진 LIS의 길이를 찾는다
Arrays.sort(consecutiveLISNum);
// 연속된 수들로 이루어진 LIS에 포함되는 번호들은 제일 앞이나 뒤로 보낼 필요가 없다
// 그러므로 그러한 번호들의 개수를 전체 어린이 수에서 빼주면 그 값이 움직여야 할 번호들의 수가 된다
System.out.println(N - consecutiveLISNum[N]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
solution();
}
static class Reader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public Reader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}4. 접근
- 어린이를 제일 앞 또는 제일 뒤로만 보낼 수 있기 때문에 현재 줄 서있는 아이들의 번호에서 연속된 수들의 LIS들을 구하여 그 중 가장 긴 LIS에 속한 번호들을 제외한 나머지 번호들을 앞 또는 뒤로 보내면 가장 적은 수의 아이들을 앞 또는 뒤로 보낼 수 있습니다.
- 어린이들을 제일 앞 또는 뒤로 보내기 때문에 중간에 있는 번호는 앞 또는 뒤로 보내진 어린이의 번호만 제외하고 같은 형태를 띄게 됩니다.
- 즉, 연속되지 않는 번호의 어린이를 이동시켜 연속된 번호를 만들어야 순서대로 줄을 서게 할 수 있습니다.
- 이 때, 연속되지 않은 번호의 어린이를 최소로 이동시키려면 가장 긴 증가하는 연속된 번호들의 부분 수열을 찾아 그 번호만 남기고 다른 번호들을 이동시키는 것이 최소로 어린이들을 이동시키는 방법이 될 것입니다.
- consecutiveLISNum이라는 배열을 하나 선언하고, 입력으로 어린이의 번호를 받을 때마다 연속된 번호의 LIS 길이를 구합니다.
- 연속된 번호에 대한 LIS를 구하는 것이기 때문에 입력으로 번호가 들어오면 자신의 바로 앞 번호까지의 연속된 번호의 LIS 길이를 가져와 거기에 1을 더해주면 현재 번호까지의 연속된 번호의 LIS 길이를 구할 수 있습니다.
- consecutiveLISNum 배열을 정렬하여 가장 긴 연속된 번호의 LIS 길이를 찾고 전체 어린이의 수인 N에서 해당 길이를 빼주어 이동할 어린이의 수를 구합니다.