Dataset
우리가 다룰 Dataset은 CelebA (Celebrity Attributes) Dataset이다. 이 데이터 셋은 10,000명 이상의 유명인사 얼굴 이미지 200,000장 이상을 가지고 있다.
CV작업을 위한 연구 및 실험에 자주 사용된다. 데이터 셋의 사용은 연구목적으로 제한되며, 상업적 사용은 불가하다.
다양한 포즈와 배경이 포함된 얼굴 이미지가 많아, 성능을 평가하기에 적합하다.

이렇게 생겼다. 데이터 불러오는 코드는 생략하겠다.
image.shape은 (218,178,3)이다. 각각 h = 218px, w = 178px, RGB를 담기 위한 3개의 layer이다.
Dataset class 정의
# dataset class
class CelebADataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, file):
self.file_object = h5py.File(file, 'r')
self.dataset = self.file_object['img_align_celeba']
pass
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def __getitem__(self, index):
if (index >= len(self.dataset)):
raise IndexError()
img = numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg'])
return torch.cuda.FloatTensor(img) / 255.0
def plot_image(self, index):
plt.imshow(numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg']), interpolation='nearest')
pass
passCelebA 데이터셋을 불러오고 처리하기 위한 CelebADataset 클래스를 정의한다. 이 클래스는 PyTorch의 Dataset 추상 클래스를 상속받아 구현되며, 이미지 데이터를 불러오고 전처리하는 기능을 제공한다. 아래는 클래스의 주요 메서드들에 대한 설명이다:
- init(self, file)
이 메서드는 CelebADataset 클래스의 인스턴스를 초기화한다. file 매개변수로 데이터셋이 저장된 HDF5 파일의 경로를 받는다.
h5py.File(file, 'r')을 사용해 HDF5 파일을 읽기 모드로 열고, self.file_object에 파일 객체를 저장한다.
self.dataset에는 HDF5 파일 내 img_align_celeba 데이터그룹에 접근해 이미지 데이터셋을 저장한다. - len(self)
이 메서드는 데이터셋의 총 이미지 개수를 반환한다. len(self.dataset)을 사용해 데이터셋 내 이미지의 수를 반환한다. - getitem(self, index)
이 메서드는 주어진 index에 해당하는 이미지 데이터를 불러와 전처리한 후 반환한다.
먼저 index가 유효한 범위 내에 있는지 확인한다. 만약 index가 데이터셋의 범위를 벗어나면 IndexError를 발생시킨다.
HDF5 데이터셋에서 해당 index의 이미지를 불러와 NumPy 배열로 변환한다 (numpy.array(self.dataset[str(index)+'.jpg'])).
이미지 데이터를 PyTorch의 텐서로 변환하고 (torch.cuda.FloatTensor(img)), GPU를 사용할 수 있게 .cuda()를 호출한다. 그리고 모든 픽셀 값을 [0, 1] 범위로 정규화하기 위해 255로 나눈다. - plot_image(self, index)
이 메서드는 주어진 index에 해당하는 이미지를 matplotlib을 사용하여 화면에 표시한다.
plt.imshow() 함수를 사용해 이미지를 화면에 출력한다. interpolation='nearest' 매개변수는 이미지가 확대될 때 픽셀 사이의 보간 방법을 지정한다.
Discriminator
다 비슷비슷해서 이것만 보자.
self.model = nn.Sequential(
View(218*178*3),
nn.Linear(3*218*178, 100),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.LayerNorm(100),
nn.Linear(100, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
100개의 노드를 연결하는 Linear Layer 하나 있다.
LeakyReLu ActivFunc사용
정규화
마지막 sigmoid.
View(2181783)은 218 x 178 x 3 텐서를 116,412의 1차원 tensor로 바꾸고 FClayer로 드간다.
나머지는 전 과정과 똑같다.
# discriminator class
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
View(218*178*3),
nn.Linear(3*218*178, 100),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.LayerNorm(100),
nn.Linear(100, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# create loss function
self.loss_function = nn.BCELoss()
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
outputs = self.forward(inputs)
# calculate loss
loss = self.loss_function(outputs, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
if (self.counter % 1000 == 0):
print("counter = ", self.counter)
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))
pass
pass- init(self)
클래스 인스턴스를 초기화한다. 여기서는 PyTorch의 nn.Module 기본 클래스를 초기화하고, 판별자의 신경망 구조를 정의한다. - self.model은 신경망의 순차적인 레이어를 정의한다. 이 구조는 입력 이미지를 1차원 벡터로 변환하고, 하나의 출력 노드로 연결된 여러 선형 레이어(nn.Linear)와 비선형 활성화 함수(nn.LeakyReLU), 그리고 정규화 레이어(nn.LayerNorm)를 포함한다. 최종 출력은 nn.Sigmoid를 통해 0과 1 사이의 값으로 변환된다.
- self.loss_function은 손실 함수로, Binary Cross Entropy Loss(nn.BCELoss)를 사용한다. 이는 판별자가 출력한 확률이 실제 레이블과 얼마나 잘 일치하는지를 측정한다.
- self.optimiser는 최적화 알고리즘으로, Adam 최적화 기법을 사용한다. 학습률(lr)은 0.0001로 설정된다.
- self.counter와 self.progress는 학습 과정을 모니터링하기 위한 변수들이다.
forward(self, inputs) - 판별자 모델을 입력 데이터에 적용한다. 이 메서드는 주어진 입력에 대해 모델의 예측 결과를 반환한다.
- train(self, inputs, targets)
모델의 학습 과정을 정의한다. 이 메서드는 모델의 예측(outputs)을 계산하고, 이를 실제 레이블(targets)과 비교하여 손실을 계산한다. 그런 다음, 손실에 대한 역전파를 수행하여 모델의 가중치를 업데이트한다. - self.counter를 사용해 일정 간격마다 학습 과정에서의 손실을 기록하고, 1000번째 마다 현재까지의 카운터 값을 출력한다.
Generator
D와 반대임.
이하 생략.
# generator class
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(100, 3*10*10),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.LayerNorm(3*10*10),
nn.Linear(3*10*10, 3*218*178),
nn.Sigmoid(),
View((218,178,3))
)
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, D, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
g_output = self.forward(inputs)
# pass onto Discriminator
d_output = D.forward(g_output)
# calculate error
loss = D.loss_function(d_output, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))
pass
pass마지막 view()는, 1차원을 3차원으로 바꿈
Train
%%time
# create Discriminator and Generator
D = Discriminator()
D.to(device)
G = Generator()
G.to(device)
epochs = 1
for epoch in range(epochs):
print ("epoch = ", epoch + 1)
# train Discriminator and Generator
for image_data_tensor in celeba_dataset:
# train discriminator on true
D.train(image_data_tensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# train discriminator on false
# use detach() so gradients in G are not calculated
D.train(G.forward(generate_random_seed(100)).detach(), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0]))
# train generator
G.train(D, generate_random_seed(100), torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))
pass
pass판별자 학습
판별자는 진짜 이미지(image_data_tensor)에 대해 "진짜"라고 판단하도록 학습된다(torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0])는 진짜 레이블을 의미한다).
생성자가 생성한 가짜 이미지에 대해 판별자를 학습시킨다. .detach() 메서드는 생성자의 가중치에 대한 그래디언트 계산이 이루어지지 않도록 한다(즉, 판별자 학습 시에만 가중치가 업데이트된다).
torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0])는 가짜 레이블을 의미한다.
생성자 학습
생성자는 판별자를 속이도록 학습된다. 생성자는 판별자가 생성자의 출력을 "진짜"로 분류하도록 유도하는 방향으로 가중치를 업데이트한다.
G.train() 메서드는 생성된 이미지를 판별자에게 제공하고, 판별자의 반응을 기반으로 생성자의 손실을 계산하여 업데이트한다. "진짜" 레이블(torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0]))을 사용한다.
D 손실값
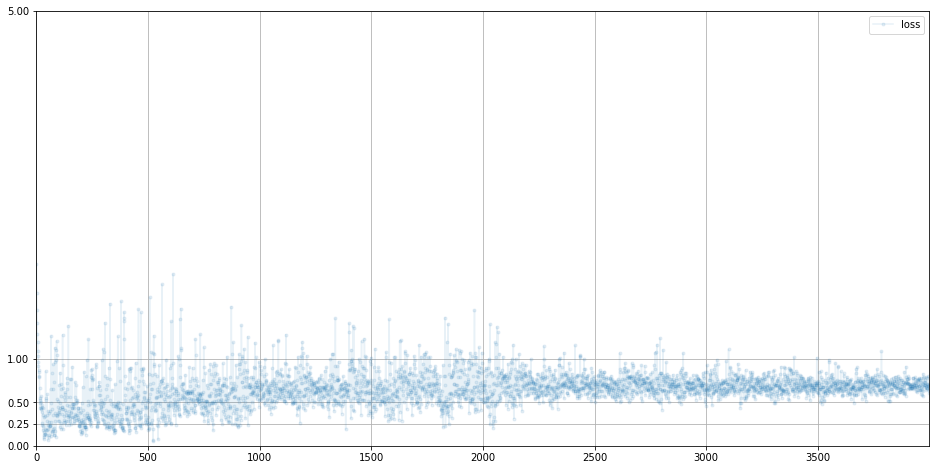
깔꼼하다. 적당한 값으로 수렴하고 있다.
G 손실값
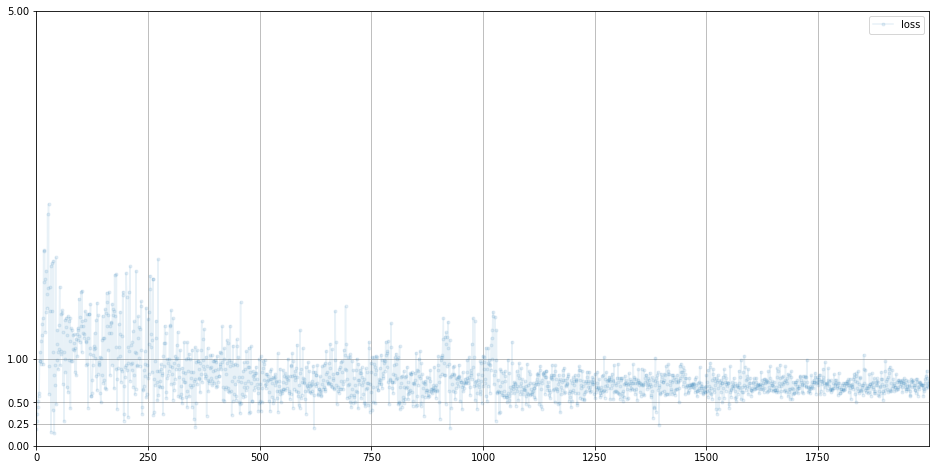
ㄱㅊㄱㅊ 0.69 = ln(2)에 수렴하는 아주 좋은 현상
결과물!
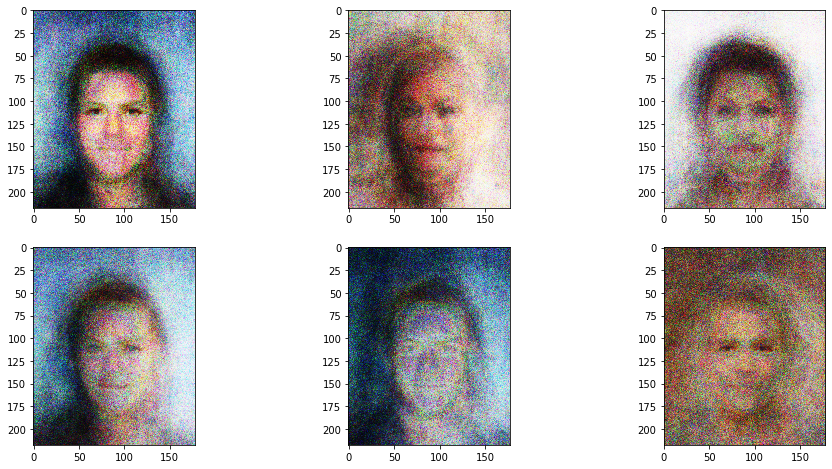

good
에폭 좀 더 돌리면 더 깔끔해질듯
결론
RGB의 shape은 (H,W,3)이다.
HDF는 계층적 구조라 효율적이다.
GAN은 훈련데이터를 기억하지 않는다. 확률분포를 파악하고 이를 재현한 데이터를 생성하기 위해 노력한다.