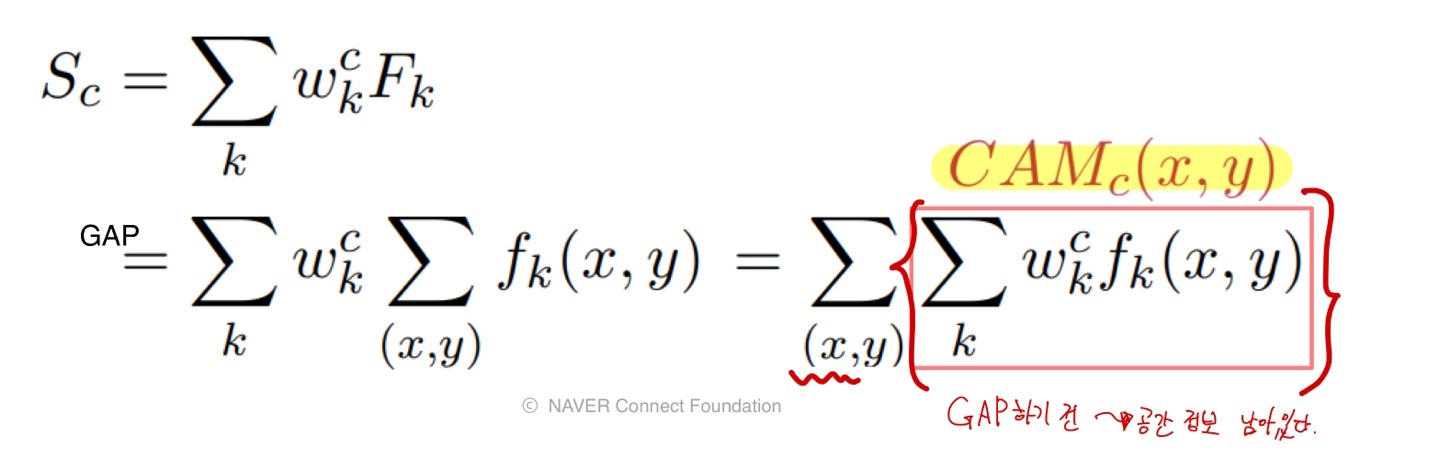학습 정리
Computer Vision & Data Visualization (2)
Computer Vision
1강 Computer Vision 이란
- Computer Vision의 간략한 소개, 앞으로의 강의 개요
- Image Classification 1
- CNN(Convolution Neural Network)의 FC(Fully Connected Layer)와의 차별성, 왜 영상 인식에 특화되어 있는가
- AlexNet
- VGGNet
2강 Data Augmentation
- Data Augmentation
- Data Augmentation의 필요성 : 대부분의 Dataset은 biased되어 있고 충분하지 않다. 학습 데이터는 실제 데이터의 극히 일부일 뿐이다. Data Augmentation을 통해 그 간극을 채운다.
- Brigtness, Rotate, Flip, Crop, Affine transformation 등을 통한 Augmentation
- CutMix : 두 이미지를 잘라 붙여 새로운 데이터 만들기 - label도 mix 해줘야 한다
- RandAugment : 랜덤하게 Augmentation 해보고 성능이 좋은걸 쓰자 - (방법과 변형 정도를 결정)
- 모델의 성능 향상에 큰 도움이 된다
- Transfer Learning
- 다른 데이터 셋으로 학습한 모델을 활용해 학습시키기, 데이터 양이 적을 때 활용하면 좋다
- pre-trained 모델의 Convolution Layer는 Freeze 시키거나 작은 Learning Rate를 부여해 파라미터 변화를 최소화시키고, 새로운 FC layer를 학습시켜 새로운 task에 대응하도록 한다.
- Knowledge Distillation (Teacher-Student Learning)
- 이미 학습된 teacher network의 지식을 더 작은 모델인 student network에 주입을 해서 학습시킨다. 모델 압축에 쓰인다. 비지도학습의 일종
- Teacher Model의 분류를 Student 모델이 모방, KL Divergence를 Loss로 설정 (Distillation Loss), Studnet Model쪽으로만 Back Propagation
- Labeled Data를 사용할 수 있다면 true label을 이용해서도 loss 측정 가능 (Student Loss)
- Distillation Loss와 Student Loss를 통해 Student Model 학습
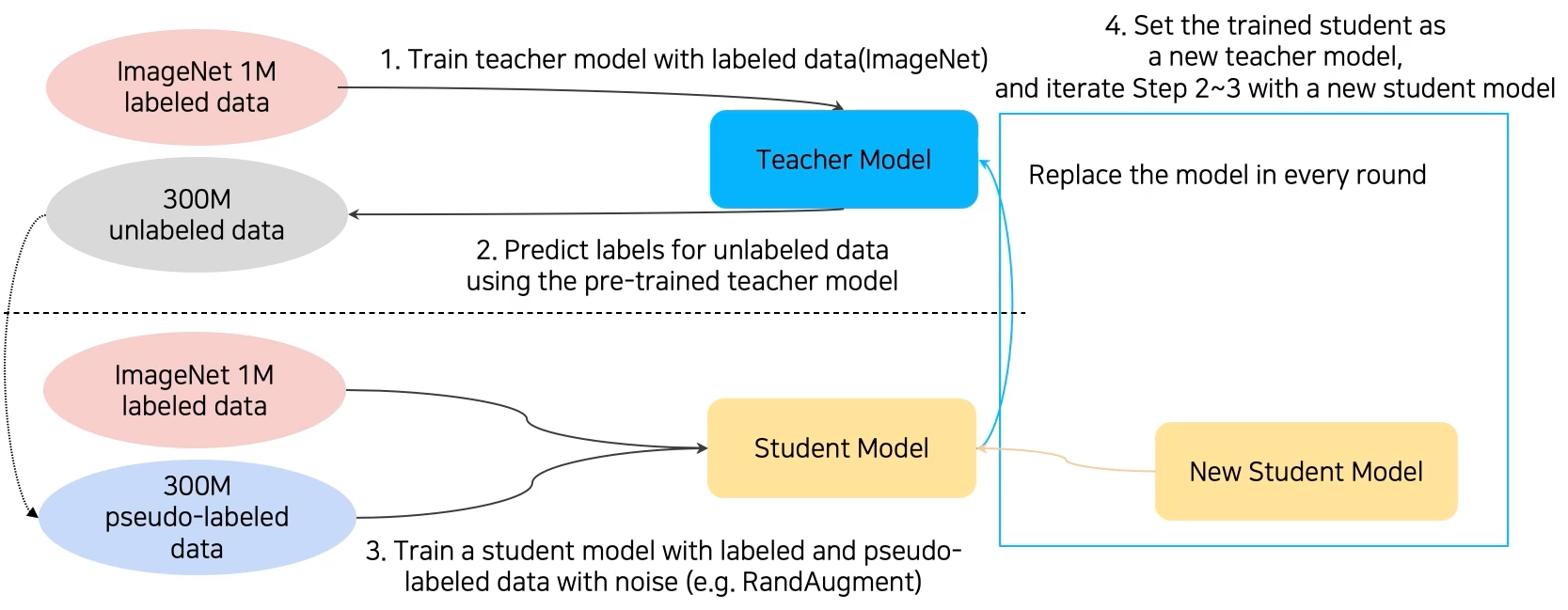
- Semi-Supervised Learning : Unsupervised (No Label) + Fully Supervised (Fully Labeled)
- Labeled Dataset으로 모델 학습, 그 모델을 통해 Pseudo Label을 잔뜩 생성해 Unlabeled Dataset을 만든다. 생성된 Unlabeled Dataset과 Labeled Datasetd으로 모델을 다시 학습시킨다.
- Self-Training : 앞선 Data Augmentation, Transfer Learning, Semi-Supervised Learning을 모두 활용해 혼자 학습시키는 방법
3강 Image Classification 2
- GoogLeNet
- ResNet
- DenseNet
- SENet : 채널간의 연관성, 중요도를 고려한 Attention 기법을 활용
- EfficientNet : width scaling, depth scaling, resolution scaling 등을 모두 고루 활용해 효율 늘림
- Deformable Convolution : Convolution시 불규칙한 sampling 활용
4강 Semantic Segmentation
- Semantic Segmentation : 이미지의 픽셀 별로 물체를 분류하는 작업 (같은 class이지만 서로 다른 물체는 고려하지 않음)
- FCN(Fully Convolutional Networks)
- 기존 CNN의 Fully Connected Layer 대신에 1x1 convolution을 사용해 공간 정보를 살림
- 결과로 저해상도의 score map을 가지게 된다. upsampling을 통해 input size의 heat map을 얻을 수 있다.
- Upsampling : 작은 activation map을 input image size로 바꿔주는 작업
- Skip Connection을 적용해 lower layer와 prediction map을 합해 두 특징 모두 활용
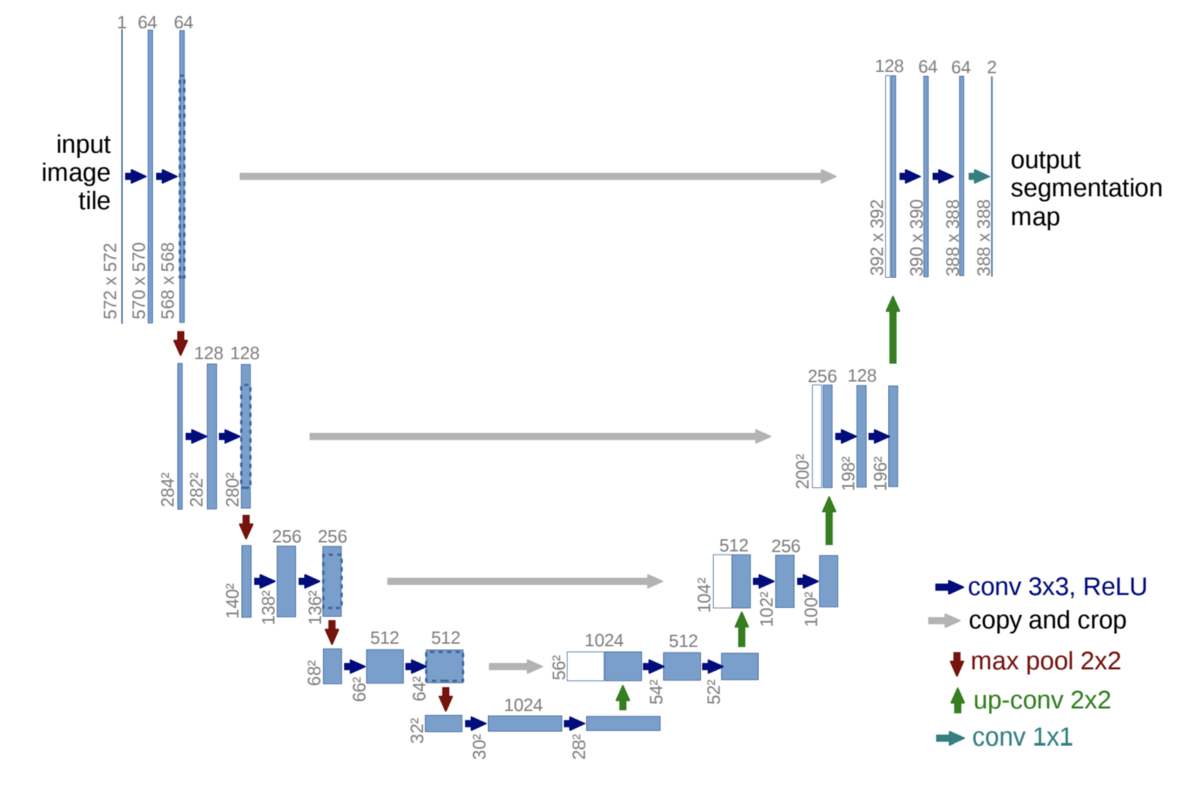
- U-Net
- FCN과 skip connection을 이용
- Contracting Path : U자의 왼쪽, 일반적인 CNN과 동일
- 3x3 convolution
- feature channel 수를 두배씩 늘려준다
- 이미지의 전체적인 context를 가져오는 과정
- Expanding Path : U자의 오른쪽, Upsampling 과정
- Contracting Path에서 오는 대칭으로 대응되는 layer와 동일하게 맞춰 낮은 층에 있는 activation map을 Concat
- 단계적으로 activation resolution은↑, channel size는↓
- 2x2 convolution
- feature channel 수를 반씩으로 줄여준다
- Concatenation의 역할 : 공간적으로 높은 해상도와 입력이 약간 바뀌는 것만으로 민감한 정보를 제공하기 때문에 경계선 혹은 공간적으로 중요한 정보들을 뒤쪽 layer에 바로 전달
- 해상도를 반씩 줄이고 두배로 늘리기 때문에 중간 feature map에서 홀수 해상도가 나오지 않도록 한다
- DeepLab
- CRFS(Conditional Random Feilds) : 픽셀과 픽셀 사이의 간계를 이어주고 regular 한 pixelmap를 그래프로 본것 => 최적화를 통해 경계를 modeling
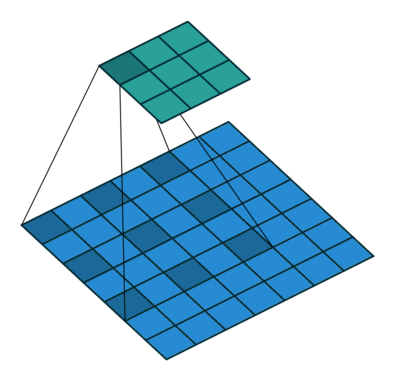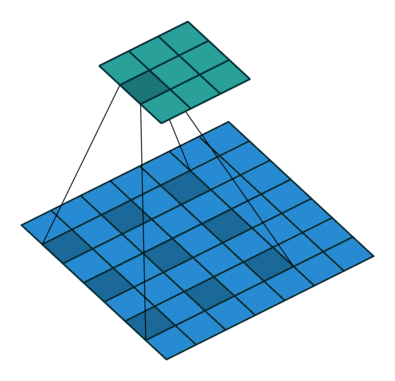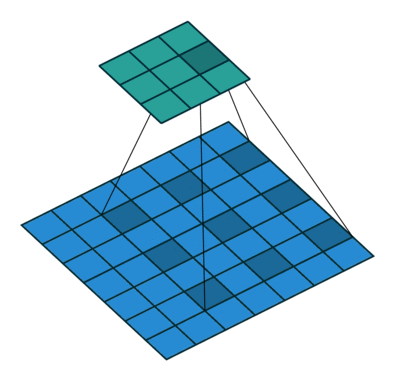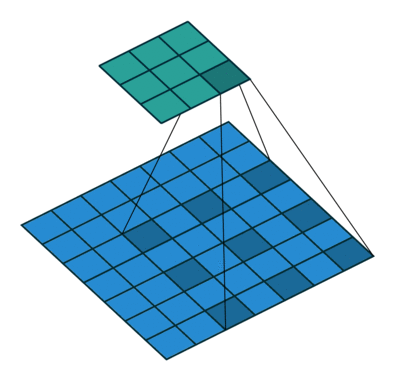
- Dilated Convolution(=Atrous Convolution) : Convolution을 할 때 한 칸씩 띄어서 계산 => 실제 convolution field 보다 더 넓은 영역을 고려, parameter 수는 동일, receptive feild는 증가
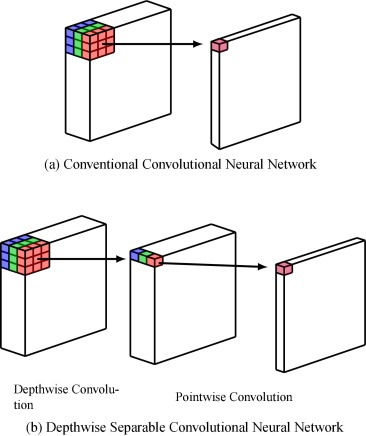
- Depthwise Separable Convolution : 기존의 convolution 연산 대신 channel별로 convolution 연산 후 1x1 convolution => 효율적인 계산 가능
5강 Object Detection
- Object Detection : Classification + Box localization
- Two-stage Detector
- Selective Search : Oversegmentation을 통해 비슷한 색끼리 잘게 분할 -> 비슷한 영역끼리 합치기 -> 합쳐진 영역들을 후보군 boxes로 설정
- R-CNN
- Selective Search로 후보군 구하기
- 적절한 사이즈로 wapring 후 CNN으로 Classification
- Fast R-CNN
- input을 CNN으로 feature map 뽑아놓고 RoI(Region of Interest)에 해당하는 feature들을 추출
- 각각의 candidate box(RoI)들을 classify & predict
- Faster R-CNN : 앞 두 방법이 Region Proposal 하는데 별도의 알고리즘을 필요로 하는 것을 개선
- Anchor Boxes : 각 위치에서 발생할 것 같은 box들을 미리 정의해놓는 후보군 (9개)
- RPN(Region Proposal Network) 단계에서 Object인지 아닌지를 판별 & anchor boxes 이용해서 bounding box의 위치를 regression
- NMS(Non-Maximum Suppression) : 그럴듯한 bounding box만 남겨두고 허수는 제거
- Single-stage Detector : RoI 없이 Sampling된 위치만 classification
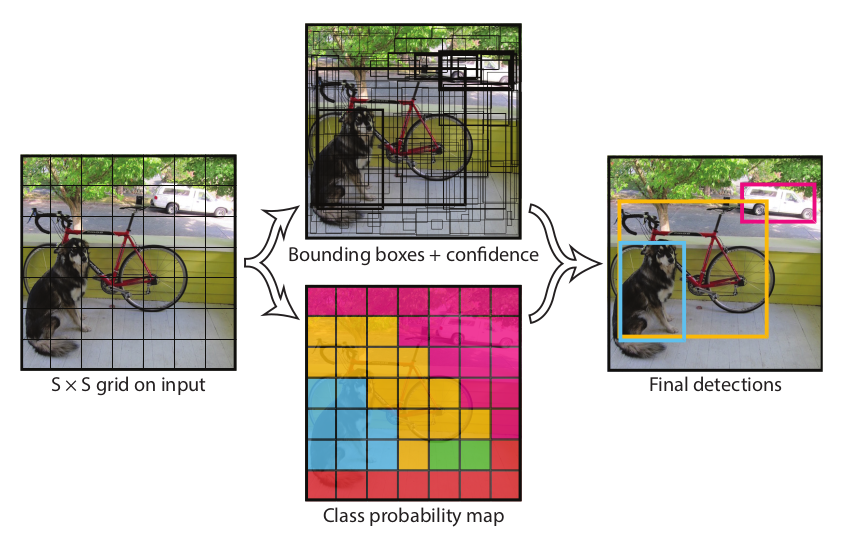
- YOLO(You Only Look Once)
- grid를 나눈 후, 각 grid에 대해 bounding boxes의 좌표와 confidence score 예측
- 동시에 각 위치에 대한 class score를 따로 예측
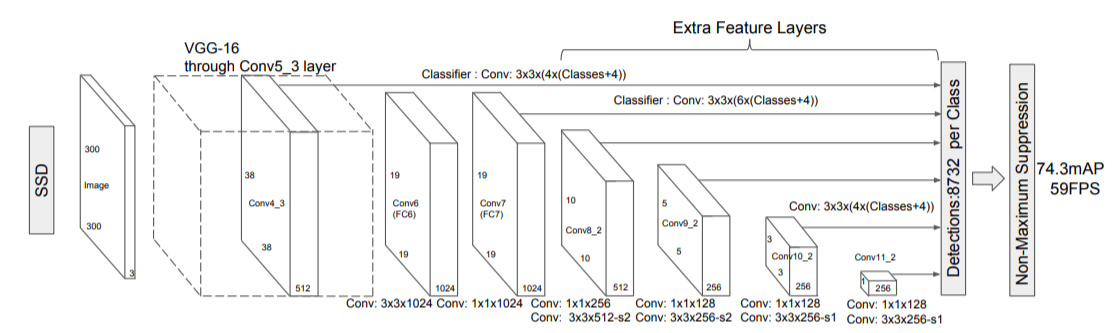
- Single Shot Multibox Detector (SSD)
- MultiScale object를 더 잘 처리하기 위해서 중간 feature map을 각 해상도에 적절한 bounding box들을 쓸 수 있도록 함
- 각 scale마다 object detection 결과를 출력하도록 디자인해서 다양한 scale의 object들에 대해서 더 잘 대응 할 수 있도록 설계
- One-stage detector VS. Two-stage detector
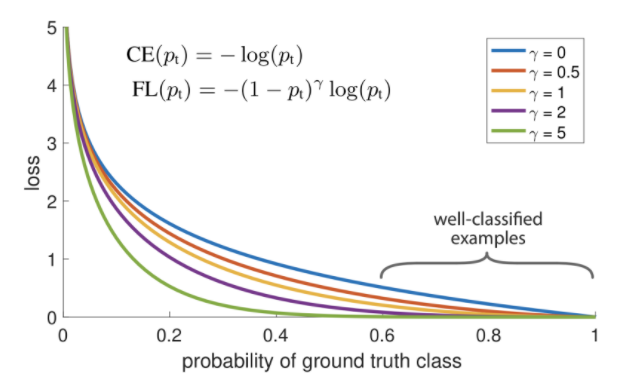
- Class Imbalance Problem : Single stage 방법들은 RoI Pooling이 없어 쓸데 없는 anchor boxes로 인한 계산이 많다 -> Focal Loss를 쓴다
- Focal Loss : 어렵고 잘못 판별된 예제들에는 더 강한 weight를 주고 쉬운 예제들에는 작은 weight를 주는 학습이 가능하게 함
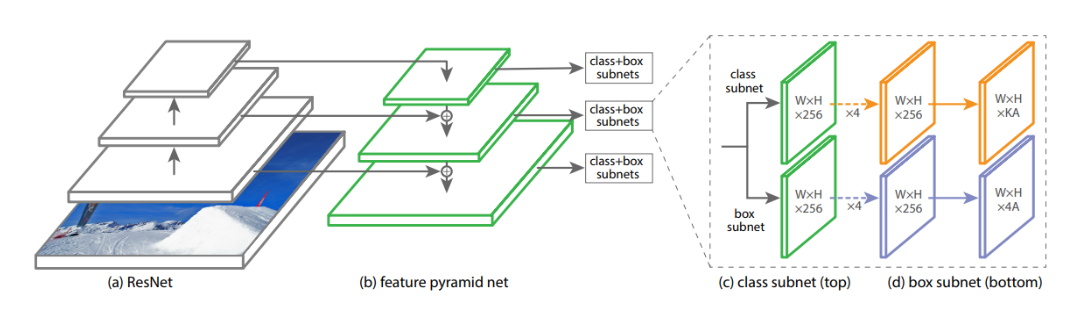
- RetinaNet : FPN(Feature Pyramid Networks) - U-Net과 유사한 구조로 Low Layer의 특지오가 High Layer 특징을 모두 활용
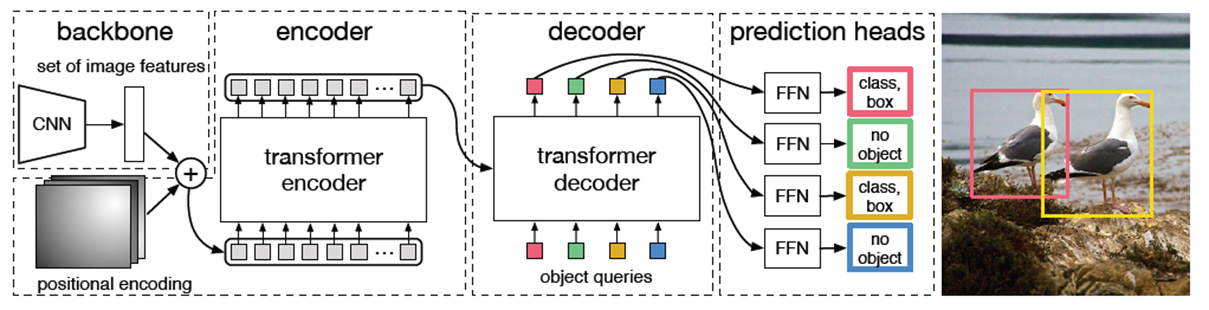
- DETR : Transformer 구조 이용한 object detection
6강 CNN Visualization
- CNN Visualization : CNN이 왜 학습이 잘 되는지 혹은 왜 잘 안되는지 원인 파악을 위해 뜯어보기
- Analysis of Model Behaviors : 모델 내부를 이해하기 위해서 시각화 및 분석
- Embedding Feature Analysis
- Nearest Neighbors in a Feature Space : Query images의 feature들을 미리 추출해서 저장 후 test 영상의 input feature와 가장 가까운 feature를 분석하는 방법
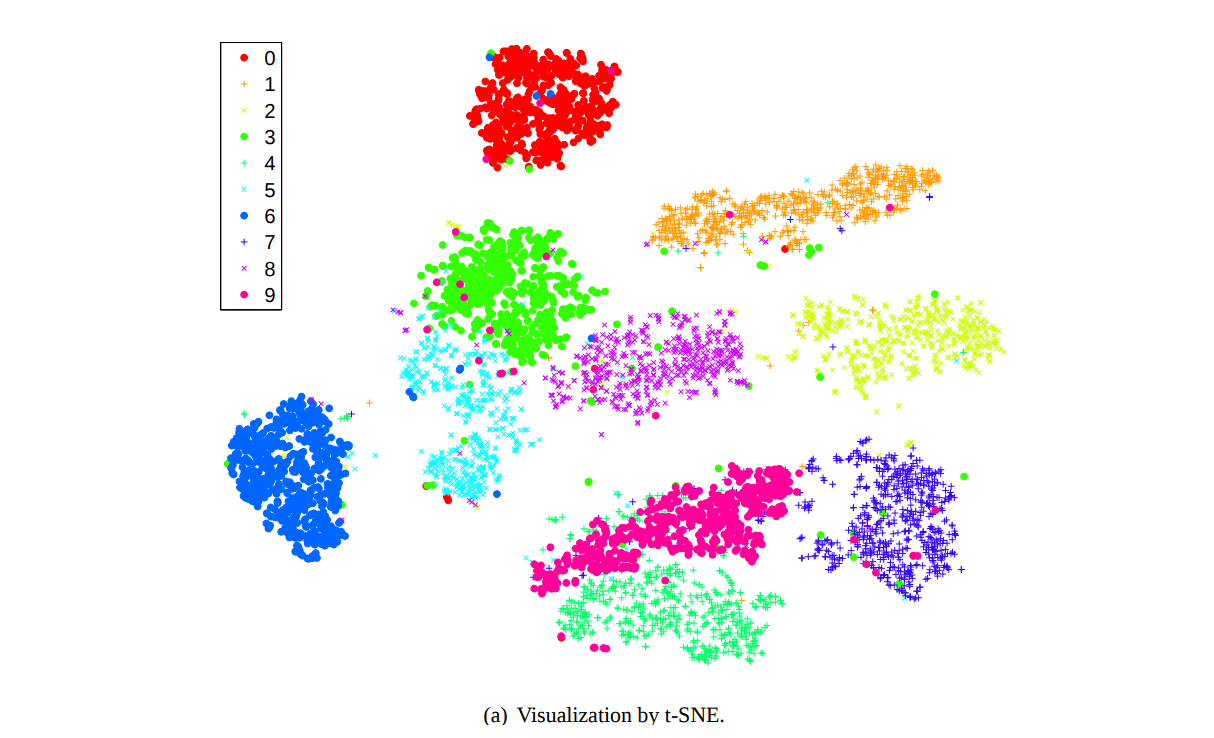
- Dimensionality reduction : 고차원의 feature를 차원 축소를 통해 2차원으로 mapping해 class마다의 feature들 간의 거리 파악 (t-SNE)
- Activation Investigation
- Layer Activation : CNN의 중간 hidden layer를 가져다가 masking을 통해 해당 layer의 hidden node의 역할을 파악 할 수 있다.
- Maximally Activating Patches : hidden layer의 한 채널을 가져왔을 때 가장 큰 값을 가진 위치의 주변 patch를 원본 입력 영상에서 뜯어낸 후 시각화, 해당 hidden node가 어떤걸 찾는지 알 수 있음
- Class Visualization : 한 class에 대해 네트워크가 내재하고 있는 이미지가 어떤 것인지 분석, Gradient Ascent 와 Back Propagation 이용해서 어떤 입력이 해당 class의 target class score가 높아지는지 찾는 과정
- Model Decision Explanation : 네트워크가 특정 입력 data를 어떤 방식으로 바라보는지
- Saliency test
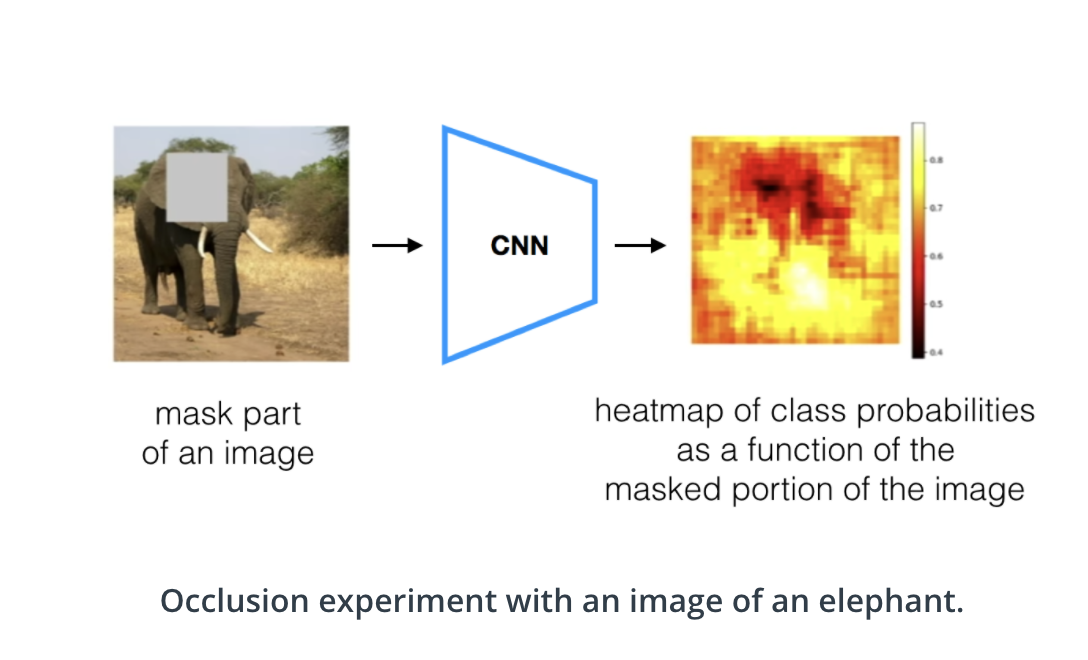
- Occlusion Map : 입력 이미지의 특정 patch를 가렸을 때 score차이를 통해 어느 부분을 중요하게 바라보고 있는지 파악
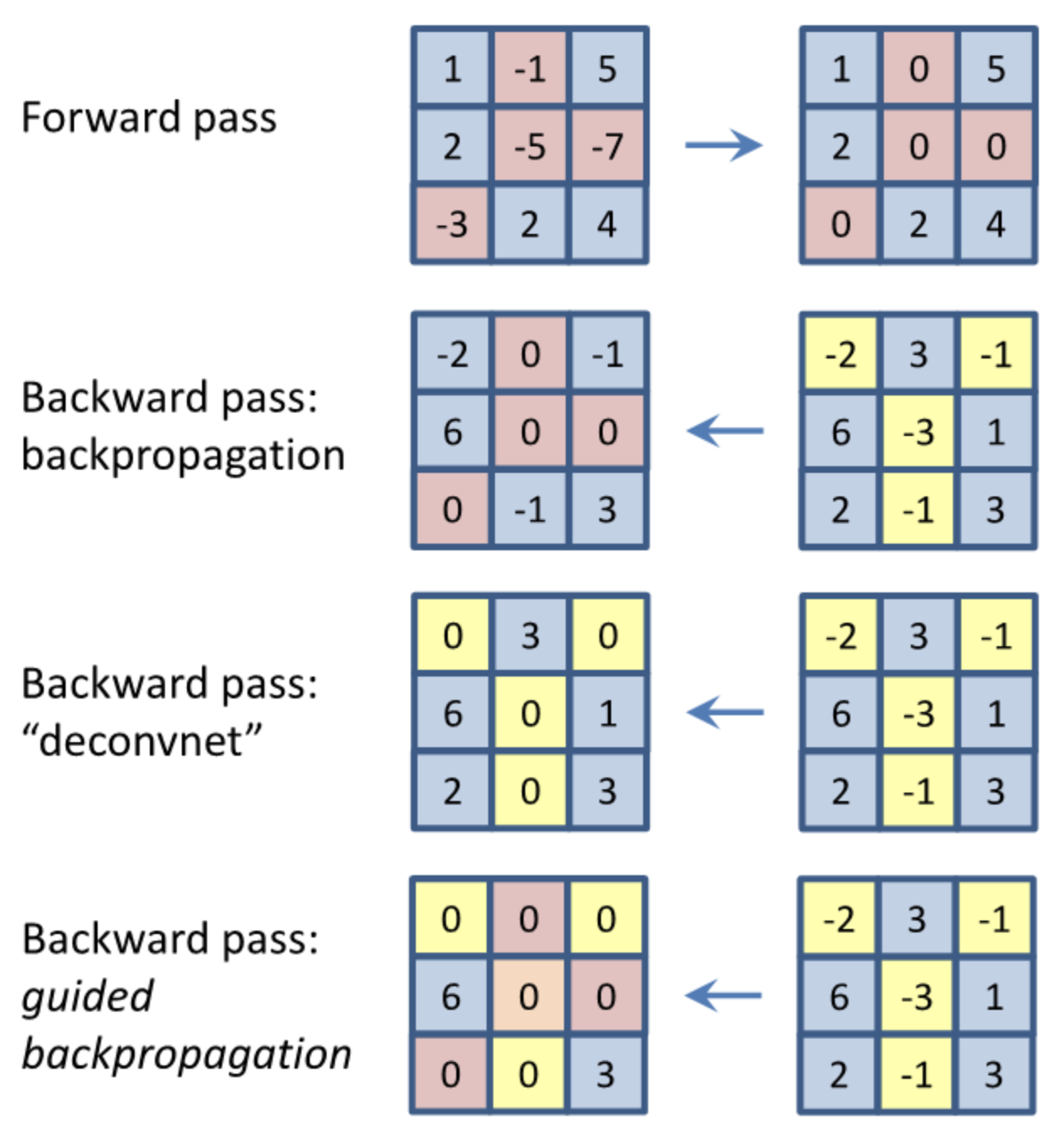
- Back Propagation 이용 : 특정 이미지를 classification 해보고 최종 결론이 나온 class에 결정적으로 영향을 미친 부분이 어디인지 heatmap 형태로 표현, 입력 도메인까지 back propagation 을 통해 얻어진 gradient들을 이미지 형태로 출력
- Guided Backpropagation : Backpropagation 시에 forward의 relu와 backward의 deconvNet의 masking을 모두 적용(? 맞게 이해한건지 모르겠다), 두 masking을 같이 썼을때 forward와 backward에서 모두 class 결정에 도움이 되는 부분만 추출
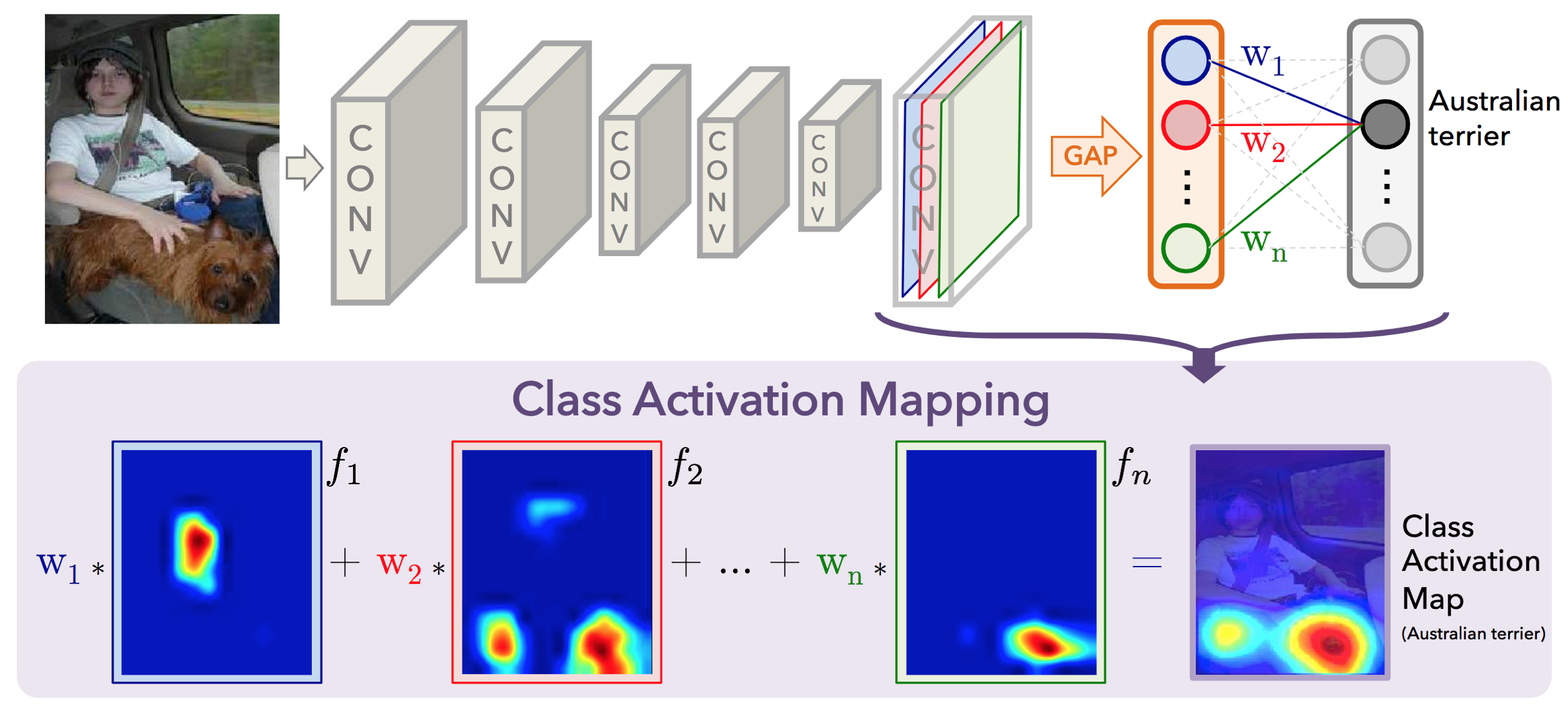
- Class Activation Mapping(CAM) : 이미지의 어떤 부분이 class 결정에 영향을 미치는지 시각화
(아래와 같다는데 완벽히 이해하지 못해 설명 생략...)
Data Visualization
이전 주차에서 이어집니다
4강 통계와 차트
- Seaborn : Matplotlib 기반 통계 시각화 라이브러리
import seaborn as sns # 왜 sns인지는 아무도 모른다고 한다...
Categorical API
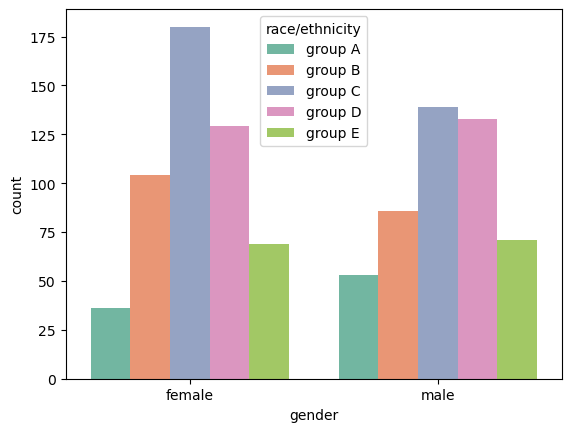
countplot: 범주를 이산적으로 세서 막대 그래프로 그려주는 함수sns.countplot(x='gender', # y= 'gender' 로 하면 y축에 데이터 표현 data=student, # 데이터 정해주기 hue='race/ethnicity', # 'race/ethnicity' 컬럼을 기준으로 데이터를 구분해서 시각화 hue_order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique()), # hue_order로 색상의 순서도 정해 줄 수 있다 #color='red', # 단일 색상을 지정해주면 연속적인 색상으로 표현해준다 palette='Set2' # 컬러팔레트 바꾸기 )
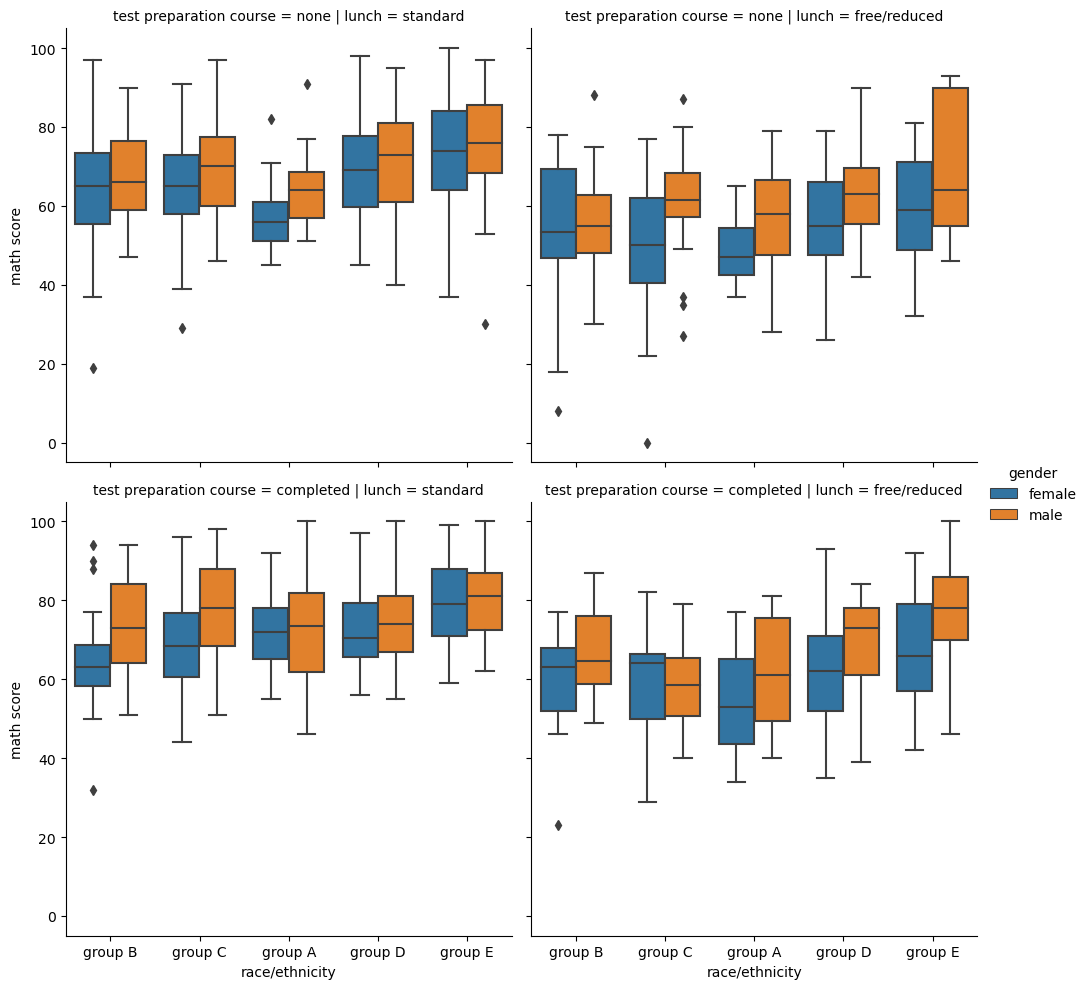
boxplot: 분포를 살피는 대표적인 시각화 방법fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(10, 5)) sns.boxplot(x='race/ethnicity', y='math score', # x 별로 y에 대한 boxplot data=student, hue='gender', # 'gender'에 따라도 나눠달라 order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique()), # 순서 지정 ax=ax) plt.show()
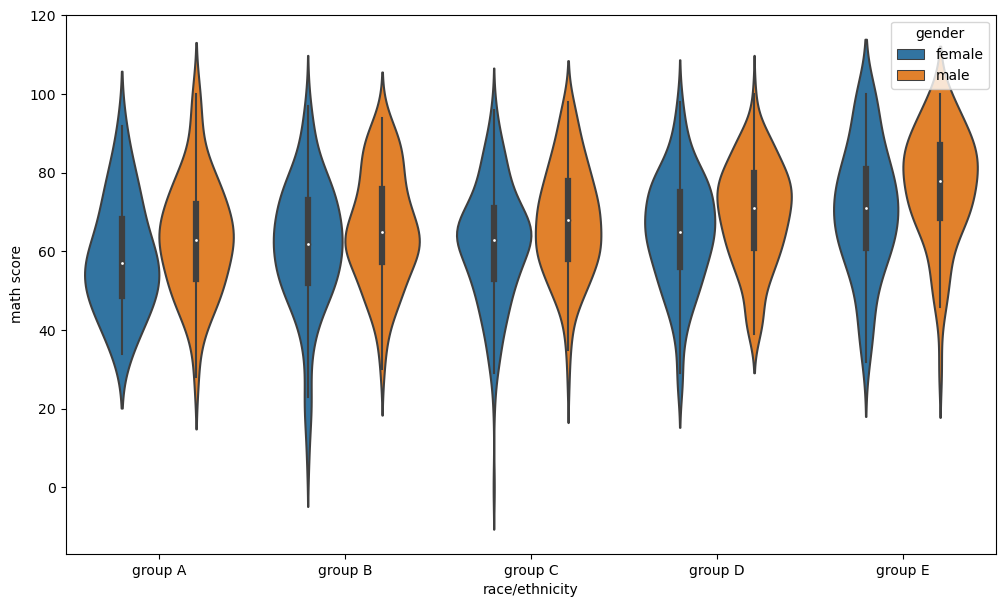
violinplot: 분포를 곡선으로 표현fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(12, 7)) sns.violinplot(x='race/ethnicity', y='math score', # x 별로 y에 대한 boxplot data=student, ax=ax, hue='gender', order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique()) ) plt.show()그 외 :
bw: 분포 표현을 얼마나 자세하게 보여줄 것인가 - ‘scott’, ‘silverman’, float
cut: 끝부분을 얼마나 자를 것인가? - float
inner: 내부를 어떻게 표현할 것인가 - “box”, “quartile”, “point”, “stick”, None
scale: 바이올린의 종류 - 바이올린 크기가 정보를 얼마나 반영하냐 - “area”, “count”, “width”
split: 동시에 비교 - 반쪽씩 나눠서 - True, False
ETC
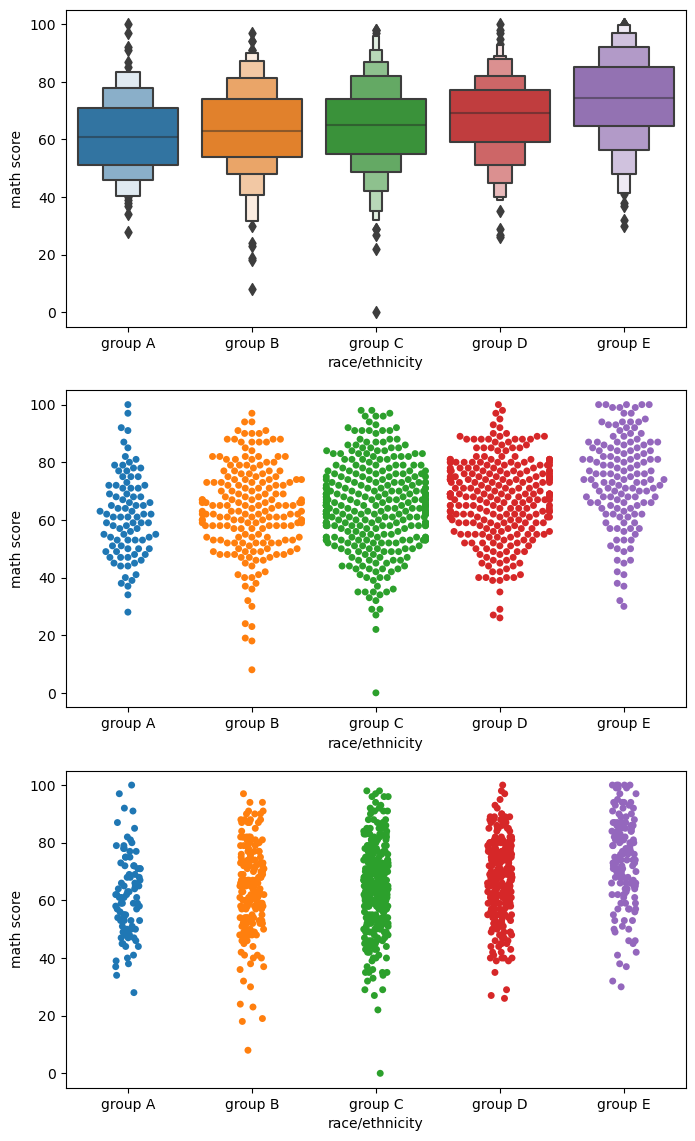
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3,1, figsize=(12, 21)) sns.boxenplot(x='race/ethnicity', y='math score', data=student, ax=axes[0], # boxplot + violinplot 느낌 -> 잘 안쓴다 order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique())) sns.swarmplot(x='race/ethnicity', y='math score', data=student, ax=axes[1], # 각각의 데이터를 하나의 점으로 scatterplot 한 느낌, 밀도와 양적인 정보를 표현 간,ㅇ, violinplot과 같이 사용 order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique())) sns.stripplot(x='race/ethnicity', y='math score', data=student, ax=axes[2], # 직선 막대에 점을 뿌려놓은 느낌, 점의 밀도를 확인 가능 order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique())) plt.show()
Distribution API : 분포 시각화
Univariate Distribution
histplot: 히스토그램kdeplot: Kernel Density Estimateecdfplot: 누적 밀도 함수rugplot: 선을 사용한 밀도함수fig, axes = plt.subplots(2,2, figsize=(12, 10)) axes = axes.flatten() sns.histplot(x='math score', data=student, ax=axes[0], # binwidth=50, # 막내 너비 조정 # bins=50, # 막대의 갯수 조정 # element='poly', # 다른 표현 방식도 있다 - step, poly -> 기본은 'bar' # multiple='stack' # 여러개의 분포 나타내기 - layer, dodge, stack, fill ) sns.kdeplot(x='math score', data=student, ax=axes[1] # 곡선을 통한 보간으로 분포를 나타내는 방식 # fill=True, # 내부를 채워 표현 # bw_method=0.05, # 분포가 자세한 정도 조정 # cumulative=True # 데이터 점진적으로 쌓아서 보여준다 ) sns.ecdfplot(x='math score', data=student, ax=axes[2] # 히스토그램을 점진적으로 쌓아서 0~1까지의 누적 분포를 나타냄 # stat='count', # proportion은 비율, count는 양 # complementary=True # 0에서 시작할건지 1에서 시작할건지 ) sns.rugplot(x='math score', data=student, ax=axes[3]) # 막대로 실제 데이터가 어디 있는지, 밀도 확인 plt.show()
Bivariate Distribution : 2개 이상 변수를 동시에 분포 표현, 결합 확률 분포
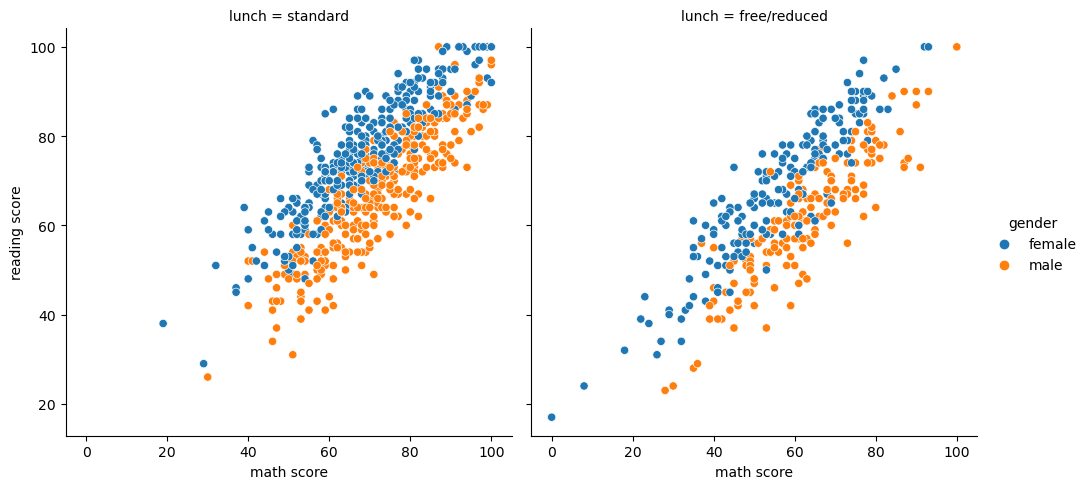
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(12, 7)) ax.set_aspect(1) axes[0].scatter(student['math score'], student['reading score'], alpha=0.2) sns.histplot(x='math score', y='reading score', # 특정 구간으로 나눠서 밀도를 표현하는게 더 좋다 data=student, ax=axes[1], color='orange', # 색 조정 cbar=True, bins=(10, 20), # reading은 10개로 나누고 math는 20로 나누겠다 ) plt.show()
- Relation & Regression API
scatterplotfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7)) sns.scatterplot(x='math score', y='reading score', data=student, style='gender', markers={'male':'s', 'female':'o'}, # 동그라미와 네모로 성별 구분 hue='race/ethnicity', # size='writing score', # 크기에 따라 정보 표현 가능 ) # 다같이 쓰면 가독성 떨어지니 따로 따로 하는게 더 좋다 plt.show()
lineplotfig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1,figsize=(12, 7)) sns.lineplot(x='year', y='Jan',data=flights_wide, ax=ax)
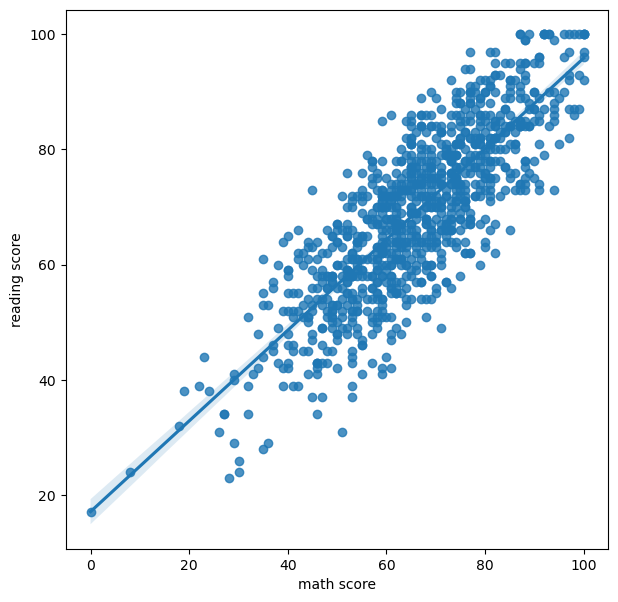
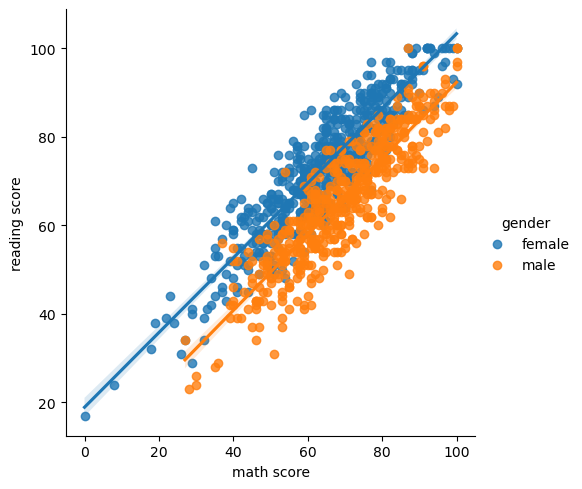
regplotfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7)) sns.regplot(x='math score', y='reading score', data=student, ) plt.show()
Matrix API
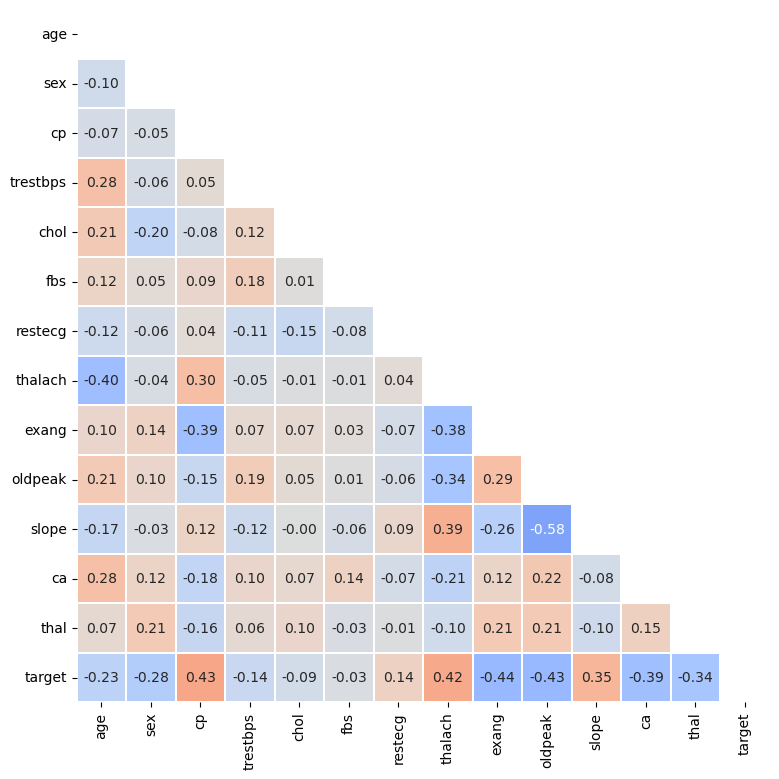
Heatmap
- Correlation 시각화
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1 ,figsize=(10, 9)) mask = np.zeros_like(heart.corr()) mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True # 아래 삼각행렬만 보겠다 sns.heatmap(heart.corr(), ax=ax, # correlation 시각화 vmin=-1, vmax=1, center=0, # center 지정 cmap='coolwarm', # color map 지정 annot=True, fmt='.2f', linewidth=0.1, square=True, cbar=False, # 실제 값을 적어줄 수 있다. mask=mask # 아래 삼각행렬만 보겠다 ) plt.show()
- Advanced
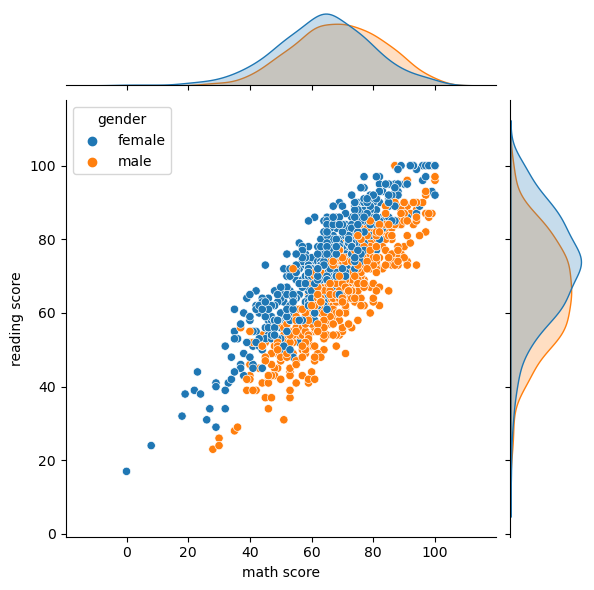
jointplot: 2개 피처의 결합확률 분포와 함께 각각의 분포도 살필 수 있는 시각화를 제공sns.jointplot(x='math score', y='reading score',data=student, hue='gender')
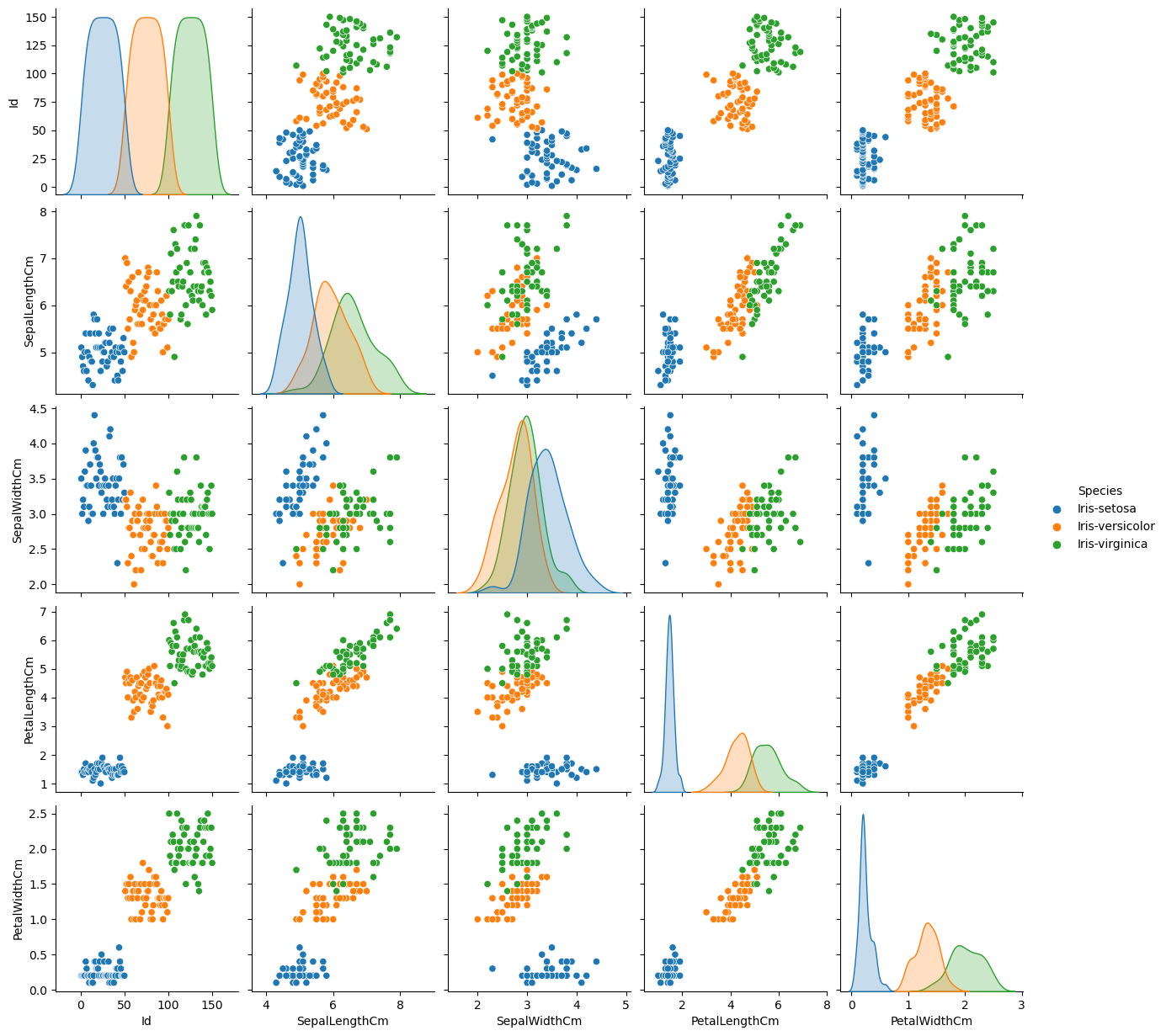
pairplot
kind: 전체 서브 플롯 조정, {‘scatter’, ‘kde’, ‘hist’, ‘reg’}diag_kind: 대각 서브플롯을 조정, {‘auto’, ‘hist’, ‘kde’, None}sns.pairplot(data=iris, hue='Species') # 종으로 나눠서 시각화
- Facet Grid : feature's category-feature's category의 관계 살펴볼 수 있음
catplot: Categoricalsns.catplot(x="race/ethnicity", y="math score", hue="gender", data=student, kind='box', col='lunch', row='test preparation course' ) # 각각 feature에 대해 분리해서 여러 catplot을 그려준다displot: Distribution
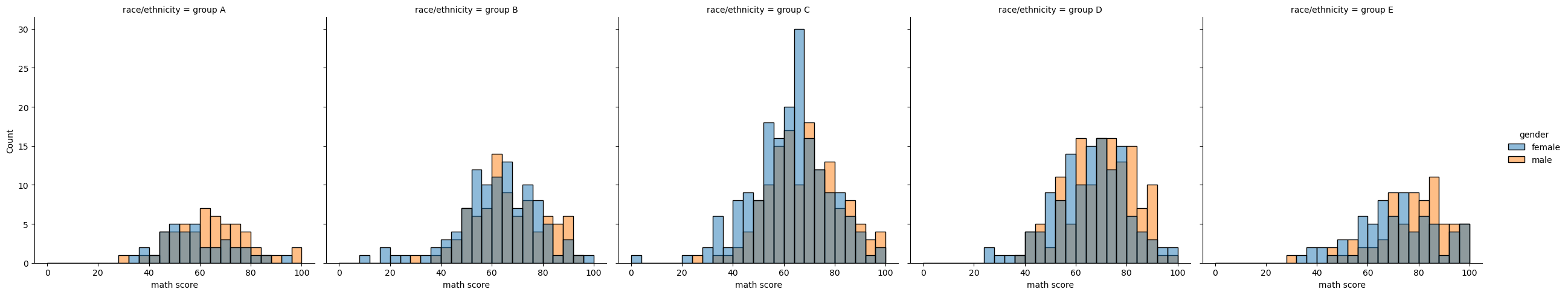
histplot()(withkind="hist"; the default)kdeplot()(withkind="kde")ecdfplot()(withkind="ecdf"; univariate-only)sns.displot(x="math score", hue="gender", data=student, col='race/ethnicity', # kind='kde', fill=True col_order=sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique()) # col의 순서도 정해 줄 수 있다. )relplot: Relational
scatterplot()(withkind="scatter"; the default)lineplot()(withkind="line")sns.relplot(x="math score", y='reading score', hue="gender", data=student, col='lunch')lmplot: Regressionsns.lmplot(x="math score", y='reading score', hue="gender", data=student)
5강 다양한 시각화 방법론
Polar Coordinate
극좌표계
ax.set_rmax: 좌표계 반지름 조정ax.set_rmin: 최소값도 지정하는데 시작점(중심)이 1로 바뀌는거임 (도넛형태 X)ax.set_sticks: 반지름 표기 grid 조정, 원하는 간격에다가 label 지정 가능set_rlabel_position: 반지름 label이 적히는 위치의 각도 조정set_thetamin(): 각도의 min값 (각도 조절하여 부채꼴 모양 사용)set_thetamax(): 각도의 max값 (각도 조절하여 부채꼴 모양 사용)scatter(): 기존 산점도와 같음 (theta, r 순서)N = 100 r = 2 * np.random.rand(N) theta = 2 * np.pi * np.random.rand(N) area = 200 * r**2 colors = theta fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='polar') c = ax.scatter(theta, r, c=colors, s=area, cmap='hsv', alpha=0.75) plt.show()
plot(): 선 그리기N = 10 r = np.linspace(0, 1, N) theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, N) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='polar') ax.plot(theta, r) plt.show()
fill(): 선이 그려져있는곳 아래 채우기Radar Chart
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='polar') # 극좌표계를 사용 values = pokemon.iloc[0][stats].to_list() values.append(values[0]) # 마지막 끝 값 포함해줘서 선 끝까지 그려주기 ax.plot(theta, values) # 선 그리고 ax.fill(theta, values, alpha=0.5) # 그 아래 채우기 ax.set_thetagrids([n*60 for n in range(6)], stats) # 각도에 따른 그리드 및 ticklabels 변경 ax.set_theta_offset(np.pi/2) # 시작 각도 조정해주기 plt.show()
Pie Chart
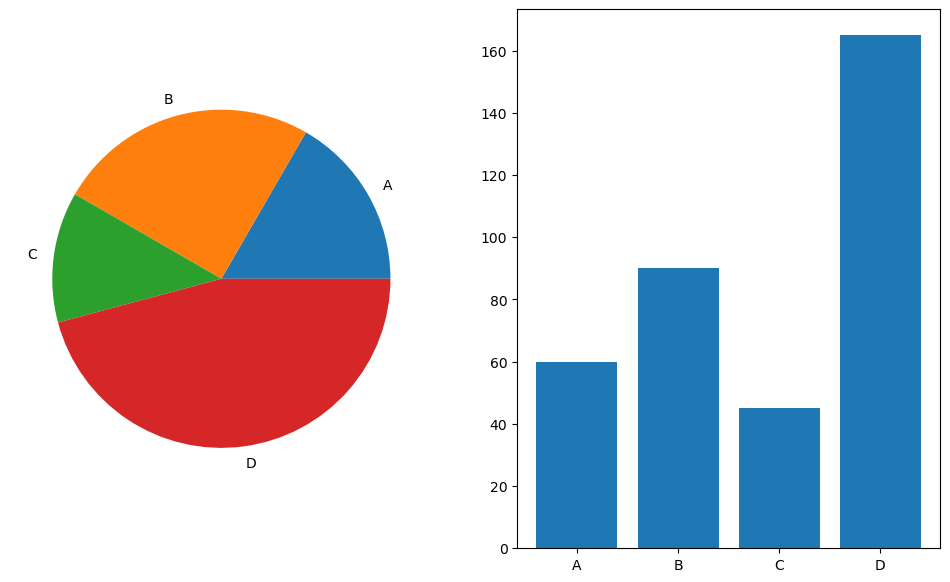
Pie Chart vs Bar Chart
- 장점 : 비율 정보에 대한 정보를 제공할 수 있다.
- 단점 : 구체적인 양의 비교가 어렵다. (비슷한 값들에 대해서는 비교가 어렵다)
labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] data = np.array([60, 90, 45, 165]) # total 360 fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 7)) axes[0].pie(data, labels=labels) # 라벨이 없어도 그릴 수 있음, 라벨을 추가하면 붙여준다 axes[1].bar(labels, data) plt.show()
startangle: 차트의 시작 각도 지정 (0도는 3시방향에서 출발)explode: 튀어나올 놈 지정 (몇퍼센트 튀어나갈 것인가)shadow: 그림자 넣기 (3D 느낌 주기)autopct: 각 데이터의 퍼센트 비율 알려주기labeldistance: 레이블이 차트와 떨어진 거리 조정rotatelabels: 글자를 중심점 기준으로 각도 회전counterclock: 시계 반대 방향 순서로 그리기 (default임)radius: 원 자체의 크기 조정pctdistance: label 위치 지정fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(7, 7)) explode = [0, 0, 0.2, 0] ax.pie(data, labels=labels, explode=explode, startangle=90, shadow=True, autopct='%1.1f%%', labeldistance=1.15 # rotatelabels=90 ) plt.show()
여러 라이브러리
MissingNo : 결측치를 matrix로 나타내어 흰 부분으로 표시
import missingno as msno msno.matrix(titanic)
Treemap
import squarify values = [100, 200, 300, 400] squarify.plot(values) # 1:2:3:4 비율로 사각형 나눠준다
Waffle Chart
from pywaffle import Waffle fig = plt.figure( FigureClass=Waffle, # matplotlib의 FigureClass와 연동된다 rows=5, columns=10, values=[48, 46, 6], # 왼쪽부터 48, 46, 6 -> 비율 시각화(정확한 값은 아님) figsize=(5, 3) ) plt.show()
Venn
- 01 : 1번째 Set에 들어갈 내용
- 10 : 2번째 Set에 들어갈 내용
- 11 : 교집합에 들어갈 내용
from matplotlib_venn import venn2 venn2(subsets = (3, 2, 1))
6강 인터랙티브 시각화
- Interactive Visualization : 동적 시각화
MatPlotlib,Plotly,Plotly Express,Bokeh,Altair등의 라이브러리로 사용 가능
7강 주제별 시각화와 사용법
- Custom Matplotlib Theme : 다양한 색과 테마로 시각화 효율을 극대화 할 수 있음
- Image & Text Visualization Techniques
회고
- 이번주도 Computer Vision과 Data Visualization의 두 강의가 병렬적으로 진행되었다. 그렇다보니 강의량이 많아 금요일까지 강의를 완벽하게 듣지는 못했다. Data Viz 강의를 주말에 들어야했다.
- 이번주부터 도메인마다 강의를 따로 듣게 되었다. 더욱 더 자세한 내용에 대해 배워갈 수 있어 좋았고 앞으로도 기대가 된다.
- 앞선 강의에서 잘 이해가 되지 않았던 부분들이 이번주 CV 강의에서 다시 언급 되는 경우가 많았다. 앞서 잘 모른채로 넘어갔는데 이번 강의들에서 설명이 더해지면서 점점 내용이 머릿속에 들어오는 것 같다.
- 강의를 평소보다 꼼꼼하게 들었다. 아무래도 CV도메인에 대한 자세한 이론 강의이다 보니 놓치고 지나가면 안될 것 같았다. 그래도 이해가 안되는 부분이 있었지만 대부분 이해하고 넘어갈 수 있었던 것 같다. 그렇다보니 강의를 듣는데 시간이 굉장히 많이 걸렸다. 30분 강의를 한 번 듣는데 2시간이 걸려서 모든 강의를 5일 내에 듣는데 실패했다.
- 이번주부터 Level2와 Level3를 함께할 팀원들을 찾는 시기가 되었다. 다른 캠퍼분들과 이야기를 나누어야하지만 많은 이야기를 나누지 못한 것이 아쉬웠다. 다음주에는 다른 캠퍼분들과 연락을 하여 이야기를 나눠보도록 해야겠다.