=== Block Coding for Error Detection/CorrectionI(이어서) ===
2. Linear block codes
• Pick any two codewords from the set
• XOR them
• The result codeword is in the codeword set
• If this is satisfied, this codeword set is called linear block codes
코드워드의 set을 block code라고 부른다. 그중에서도 block code중에 linear block code라는 것이 존재한다. 아무 2개 codeword를 고른다음 XOR한다. 그 결과가 다른 codeword set의 codeword가 된다. 이 조건을 만족하면 linear block code라고 부른다.
• Is this linear block codes?

위와 같이 어떠한 codeword와 xor 해도 다른 codeword가 나오기에 linear block code라고 볼 수 있다.
• Is this linear block codes?

MHD of linear block codes
• Exclude codeword with all zeros
• Count 1s for all other codewords
• The minimum number of 1s is the MHD of the codeword set
linear block코드의 특징 : 모두 0인 것은 제외한다. 제외되지 않은 것중에서 1의 갯수를 계산하여 최솟값을 구하면 MHD를 구할 수 있다.
• What is the MHD of this codeword set?

Simple Parity Check Codes
• k-bit dataword -> (k+1)-bit codeword
– Add 1 bit (parity bit)
• The parity bit should make the codeword have even number of 1s.Introduction to Computer Networks
첫번째로 볼 것은 Parity이다. Parity code의 특징은 k-bit dataword에서 1bit를 더해서 (k+1)-bit codeword를 만든다. 이것을 parity bit이라고 부른다.
parity bit는 추가됨으로써 codeword의 1의 갯수가 짝수가 되도록 parity bit를 결정해준다.
parity bit를 짝/홀수로 만드는 건 개인의 선택이다.
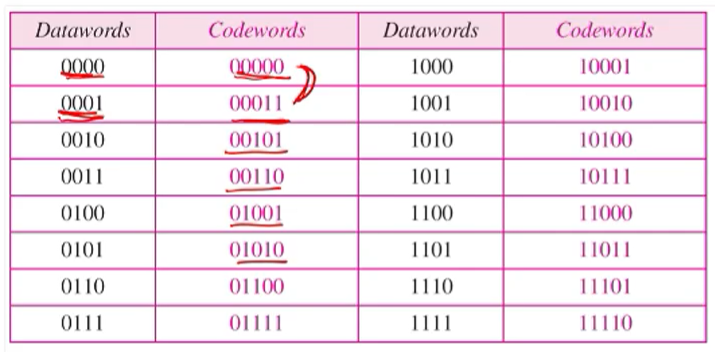
• n = k + 1
• dmin = 2
0000은 0을 붙이고 0001은 1을 하나 붙여서 짝수개의 1이 되도록 만든다. MHD는 반드시 2가 될수 밖에 없는거을 쉽게 알 수 있다. 그리고 redundancy는 1이 추가된것이다.
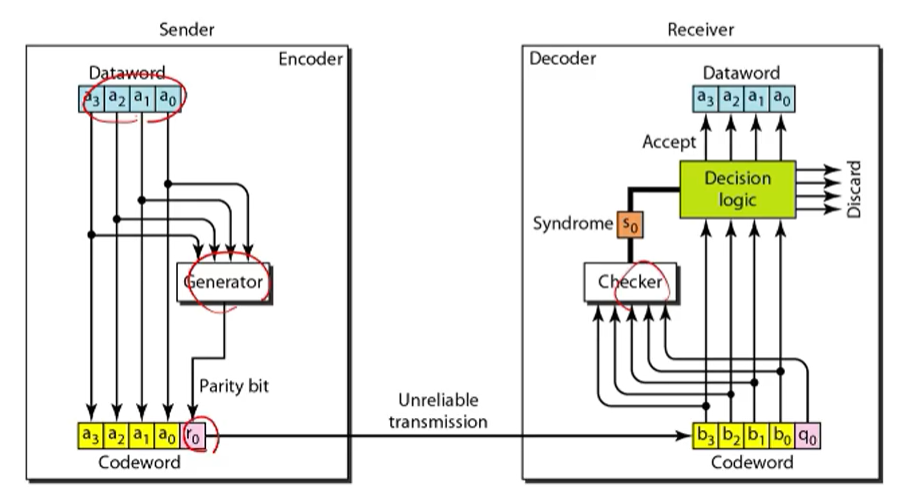
Example
• Sender sends dataword ‘1011’ using parity check codes.
– Codeword is ‘10111’.
4bit를 5bit로 바꾸는 parity인 것이다. 1이 3개이니 1이 하나더 붙인다.
• Receiver receives ‘10111’. What happens? 제대로 받은거니 그냥 올린다.
• Receiver receives ‘10011’. What happens? 한 비트가 잘못되어서 왔으면 discard시킨다.
• Receiver receives ‘10110’. What happens? 이것도 비트가 홀수이니 버린다.
• Sender sends ‘10111’.
• Receiver receives ‘00110’. What happens? : 두개가 틀린경우 오류이지만 오류가 아니라고 판단한다.
• Receiver receives ‘01011’. What happens? : 세개가 틀린경우 버린다.
Performance of parity check codes
어떤 경우에라도 에러를 검사할 수 있어야 한다.
• Can parity check codes detect 1-bit errors? error detection이 된다고 볼 수 있다.
• Can parity check codes detect 2-bit errors? 안된다.
• Can parity check codes detect 3-bit errors? detect가 된다.
• Can parity check codes detect 4-bit errors? 안된다.
Performance of parity check codes
• Parity check codes can detect odd-bit errors. : 홀수 비트를 검출 할 수 있는게 parity check code이다.
• Pretty good!Introduction to Computer Networks
2-dimensional parity

위와 같이 x, y축에 대해서 패리티 비트를 넣어주는 것을 이야기 한다.

1-bit error가 난 경우 1->0이 되었다고 생각해보자 그럼 그 비트의 row, col의 parity error난 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이때 좋은 점이 어디에서 에러가 났는지 확인을 할 수 있다. 단 주의할점은 여기에서는 1-bit만 에러가 났다고 가정한다.
그러나 2-bit에러가 난 경우 col은 맞지가 않지만 row는 맞게 된다. 그래서 detection은 된다. error correction은 하기 힘들다. 왜냐하면 어떤 col인지 확인이 불가능하기 때문이다.
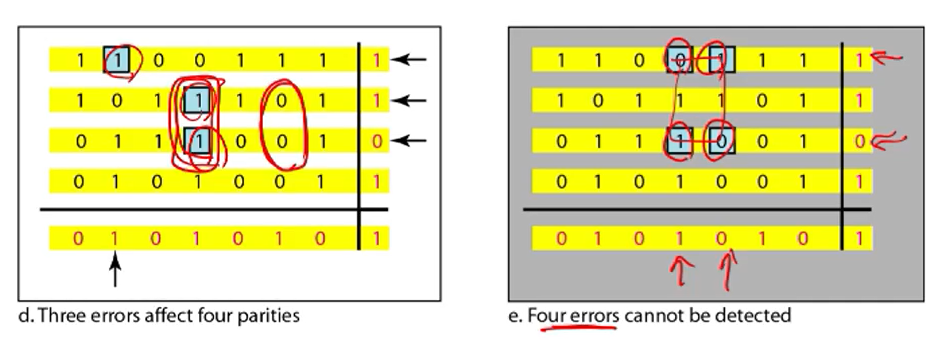
3bit error가 난 경우 detect는 되는데 correct는 하기 힘들다.
4bit인 경우 하필 겹치어서 에러가 난 경우 error detection도 하기 힘들다.
Performance of 2-D parity
• 1-bit errors: detect & correct
• 2-bit errors: detect
• 3-bit errors: detect
• 4-bit errors: cannot detect
• 2-D parity can detect some of 4-bit errors, but cannot detect all 4-bit errors.
• If a codeword is said to detect n-bit errors, it should
detect all of n-bit errors.
정말 운없는 4-bit가 아닌 경우를 제외하고는 detect가 되기 때문에 상당히 좋은 detecting방법이다.
3. Hamming Code
• A family of error detection codes invented by Richard Hamming in 1950.
• dmin = 3
– detect up to 2-bit errors
– correct up to 1-bit errors
Hamming distance를 3으로 만든다.
• Hamming (n,k) code
– convert a k-bit dataword into an n-bit codeword
k가 dataword이고 n이 codeword이다. (7,4) = 7-bit의 codeword를 4-bit의 dataword로 바꾸는 Hamming code이다.
Hamming (7,4) code
• Convert 4-bit datawords into 7-bit codewords
※ Note
– There are different ways to generate Hamming (7,4) code
– If you have textbooks, the coding method will be different from the slides
– I suggest that you should follow the slides (not the textbook)
- 방법
• Number the bits from the left.
• If the index of the bit is a power of 2, it is a check bit.
– 1st, 2nd, 4th bit
• If the index of the bit is not a power of 2, it is a data bit.
– 3rd, 5th, 6th, 7th bitIntroduction to Computer Networks
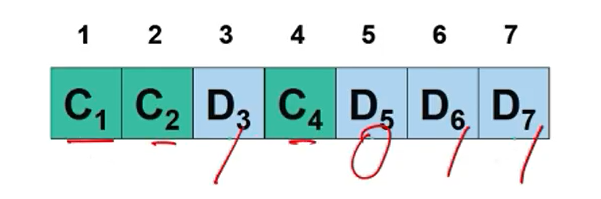
7비트중에 3개가 check bit, 4개가 data bit이다.
이때 parity bit가 들어가는 위치가 1, 2, 4번 위치이다.
Hamming (7,4) code
• The 4 bits of the dataword go into the data bits
– If dataword is “1011”
– D3= 1
– D5= 0
– D6= 1
– D7= 1
data bit만 check bit가 아닌 위치에 적어주면 된다.
- Check bits
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- &: bitwise AND
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- 1st bit: XOR values of 3rd, 5th, and 7th bits
- 001 & 011 = 011, 001 & 101 = 001, 001 & 111 = 001

이를 계산하기 위해 첫번째 위치 j = 001이고 3번먼저 보면 3(k) = 011이다. 두개를 &하면 001이 되기 때문에 3은 1에 영향을 준다.
동일하게 5, 7(6제외)는 영향을 미치는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
그럼 1번 비트에 영향을 주는 비트들을 알게 되었다. 그럼 3, 5, 7번의 비트들을 XOR한다. 지금 보면 101로 1이 짝수개이다. 그러므로 C1의 값은 0이 된다.
- Check bits
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- &: bitwise AND
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- 2nd bit: XOR values of 3rd, 6th, and 7th bits
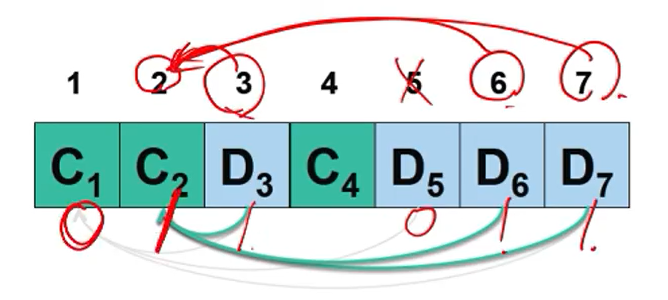
2번은 3,6,7번에 의해서 영향을 받는다. 3, 6, 7은 111이기 떄문에 2번은 1이 된다.
- Check bits
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- &: bitwise AND
- jth bit: select kth bits where j & k = j
- 4th bit: XOR values of 5rd, 6th, and 7th bits
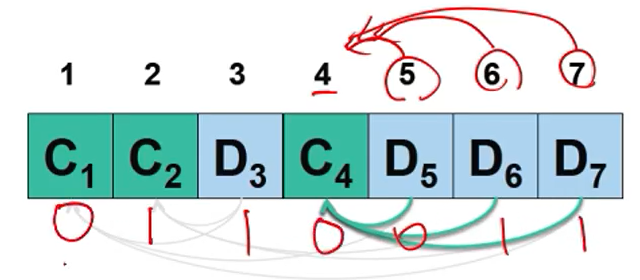
3번은 4라는 숫자가 100이기 때문에 영향을 미치지 않는게 확정이다. 그래서 5,6,7번을 검사해보니 5,6,7번이 영향을 미치는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
따라서 완성된 코드는 0110011이 된다는 것을 알 수 있다.
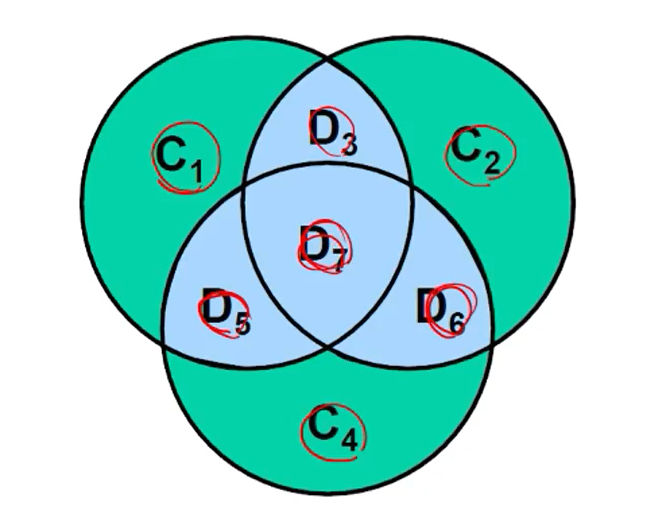
정리해보면 위와 같은 다이어그램을 만들 수 있을 거이다.
Hamming (7,4) code
• Exercise
• 0000 -> xx0x000 -> 0000000
• 0011 -> xx0x011 -> 100011
• 1010 -> xx1x010 -> 1011010
• 1110 -> xx1x110 -> 0010110
0011과 1010의 hamming distance는 3이 된다.
0011과 1110의 4이다. 따라서 MHD는 3이다.
• What is the MHD of Hamming (7,4) code?
그런데 왜 MHD가 3이 될까?
D3 하나가 바뀌는 순간 C1, C2가 바뀌게 된다.
• Why?

0000 -> 1000으로 바뀌는 순간 C1, C2가 바뀌게 된다. C4는 바뀌지 않는다. 그렇다면 Dataword 하나 바뀌니 checkbit 2개가 바뀌니 distance는 3이 된다.
0000 -> 0001이 바뀌면 C1, C2, C4가 다 바뀌게 되기 떄문에 distance가 4이다.
그래서 MHD가 3이 될 수 있는 것이다.
• Why (7,4)?
왜 (7,4)로 하는가? 앞의 7은 앞의 hamming distance의 codeword를 2^m - 1 이 될 수 있도록 만든 것이다. 그러면 7, 15, 31, 63이 있다.
• Suppose we use n-bit codeword, where n = 2^m - 1 for a natural number m.
• Suppose the dataword is k bits, so that
• k = n – log2(n+1)
k는 위의 공식이 될 수있도록 만든 것이다.
• Is there a better way to correct 1-bit errors?
한 비트를 고치기 위해서 얼마만큼의 데이터가 필요한지를 생각해 보자
• To correct a 1-bit error in an n-bit codeword, the receiver should be able to correctly pick one of the following cases:
– No error
– 1st bit is error
– 2nd bit is error
– 3rd bit is error
– …
– (n-1) th bit is error
– n th bit is error
• How many cases? n+1
• For a n-bit codeword, n+1 pieces of information is needed in order to correct a 1-bit error.
n bit codeword를 구분짓기 위해서는 n+1가지의 경우를 고려해줄 수 있어야 1-bit error을 고칠 수 있다.
• To embed n+1 pieces of information, we need log2(n+1) bits
8개의 다른 케이스를 구분하기 위해서는 3bit가 필요하다. 이를 공식으로 나탄내면 log_2(n+1)의 식이 생기게 된다.
• Thus Hamming code uses minimum cost to correct 1-bit errors. There cannot be a better way.
– Hamming code is described as a perfect code.
7 bit가 있을때 1bit 에러가 나는 상황. 그 case는 8가지의 케이스로 에러가 날 수 있다. 그래서 8가지를 구분할 수 있어야 1bit error을 에러를 고칠 수 있다.
(6,4)는 redundancy가 2이니 4가지를 가려낼 수 있어서 7가지 경우를 가려내는 것을 모두 구분할 수 없다.
(7,3)은 redundancy가 4이니 16가지를 가려낼 수는 있으나 8가지 경우를 다루기에는 너무 많다.
(8,5)는 8가지를 가려낼 수 있으나 9가지 경우를 다루기에는 너무 적다.
그래서 적절한 숫자는 (7,4)이다. 앞에 있는 값은 2^m - 1이 되도록, 뒤에 오는 것은 redundancy가 log_w2(15+1)이기 떄문에 redundancy가 4이다. 따라서 (15,11)은 가능하다.
중요한것은 해밍코드보다 더 잘할 수가 없다.
Voting
• The simplest way to increase hamming distance
• Convert ‘0’ into N number of ‘0’s
– If n = 3, ‘0’ -> ‘000’,‘1’ -> ‘111’
• Makes hamming distance N
• If receiver receives ‘010’, it is interpreted as 0 because the codeword has more 0s than 1s -> voting
약간 0이 많은것 1이 많은 것으로 나뉘어서 Voting방식이라고 부르기도 한다.
Voting (N=3) vs. Hamming (7,4)
• Efficiency of voting = 1/3 = 33.3%
• Efficiency of hamming (7,4) = 4/7 = 57.1%
Hamming이 Voting보다 가능성이 높다.
Hamming Codes
• Recall that to correct 1-bit error in 7-bit codeword, we need 3 control bits
– 8 pieces of information
• In general, suppose we have a (2^k-1)bit codeword.
Then, to correct 1-bit error we need k control bits
• If k=4, we obtain Hamming (15, 11) code
• If k=5, we obtain Hamming (31, 26) code
k가 높아질 수록 확률이 높아진다. 하지만 그렇게 할 경우 에러가 날 확률이 높아진다.
• The efficiency rate increases with k
Hamming (15,11) Code
• Dataword is 10110001011
• Convert dataword into codeword using hamming (15,11) code
• What is the efficiency rate? – 11/15 = 73.3%
ㅁㅁ1ㅁ011ㅁ0001011
1 = 001 이기에 3,5,7,9,11,13,15 번이 영향을 비친다. 따라서 여기에 들어올 값은 1이다.
2 = 010 이기에 3,6,7,10,11,14,15가 영향을 미친다. 5개가 1이니 여기에 들어올 값은 1이다.
4 = 0100 이기에 5,6,7,12,13,14,15가 영향을 미친다. 1이다.
8 = 1000이기에 나머지 뒤에가 다영향을 미친다. 1이다.
효율성은 15개중 11개이니 73.3%이다.
Hamming Codes: Summary
• Size of the control bits = k
• Size of the codeword = 2^k-1
• Size of the dataword = 2^k-1-k
• Efficiency rate = (2^k-1-k) / (2^k-1)
• As k increases, efficiency rate increases
• However, as the dataword becomes longer, the possibility of having 2 or more bit-errors increases -> detection rate decrease
