AWS Overview
AWS is the world's most comprehensive and boardly adopted cloud platform
Cloud: On-demand, Pay as you go, Network-accessible
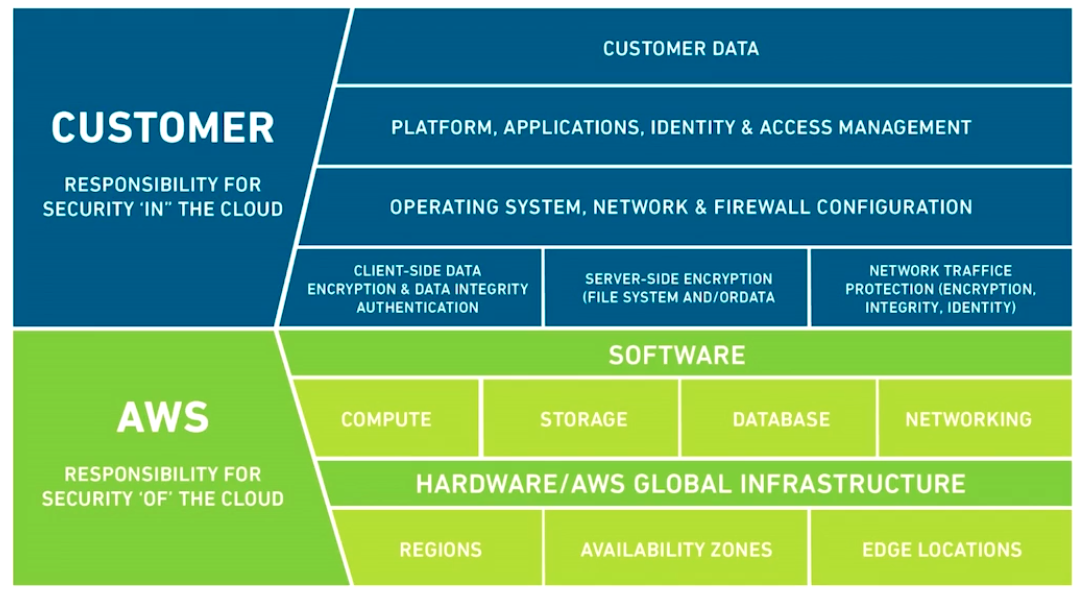
Shared Responsibility Model
Shared responsibilities for the ownership of different parts of the infrastructure, the services, the features, and resources that are launched into the AWS ecosystem.
AWS
- Provide security OF the cloud itself (servers, storage, network hardware, physical data-centers, etc.)
- Making sure that the requested task through service API is executed faithfully
Customer
- Security IN the cloud (securitiy of the individual resources deployed in the cloud)
Diagram for Shared Responsibility
IAM) Identity and Acess Management
Performs Authentication and Authroization.
Identity-based access control
Allows cross-account access
Root Account Email
This is the Root Account that has access to all the functionalities within AWS console.
Cautions
- Use a distribution list (corporate) for email notifications
- Use an alias (personal), there are many AWS features that cannot be tested unless you have multiple AWS accounts. Alias enables you to create mutiple accounts within the same email.
- Root account properties can only be changed by the root user.
- If you close the account, that root email cannot ever be used again as a root account
- Don't enable API keysTasks
- Change account settings
- Change AWS support plan
- Activate access to the billing and cost management Console
- View billing tax invoices
- Restore IAM User permissions for only IAM adminIAM Users
A principal identity
Associated with permissions [ group, in-line, managed ]
Associated with a permission boundary
Container for credentials
Don't perform all your actions in Root Account. Rather, create an IAM User for admin.
Example User
Username: tony
Sign-in credentials
API keys
Profile: DevopsCreating an IAM User
For each user that needs access to the AWS console, create a user with corresponding permissions
Creating an IAM Group
- Collection of IAM Users
- IAM Group cannot be nested
Permissions
Permission Policy
- Identity-based policies: associated directed to an identity
- Resource-based policies: associated with resources
- Session policies: binded to the sessionPermission boundaries
- IAM permissions boudaries
- AWS Oganizations Service Control Policies (SCPs)
Effective permissions
Identity + Resources-based policies -> UNION of policies
Identity + Permissions boundary -> INTERSECTION of policies
Policy Evaluation Logic
- Assume AWS denies all action
- Is the account part of AWS Organization with an SCP with allowed boundaries? (boundaries cannot grant permissions)
a. No, implicit Deny
b. Yes, go to #3 - Does the destination resource have an associated policy?
a. No, go to #4
b. Yes, allow - Does the principal have a permission boundary?
a. No, go to #5
b. Yes, look for implicit allow - Is the principal using a session-based policy?
a. No, go to #6
b. Yes, allow (session policies override all other policies) - Does the principal use identity-based policies?
a. No, deny
b. Yes, allow
Policy Format

Majority of the permissions are in Statement
All Resources can Terminate EC2 instances if the source IP does not originate from aws:SourceIp.
Identity Policy generation
You can filter by type to check for AWS managed policies or customer managed policies.
However, if much customization is not required, AWS managed - job fucntion will suffice.
Say you want to generate a policy that gives accesss to the S3 bucket.
From policy generator, search for S3 and click.
Actions will show different options for read. It currently shows 53 access levels. However, a basic user only requires GetObject access.
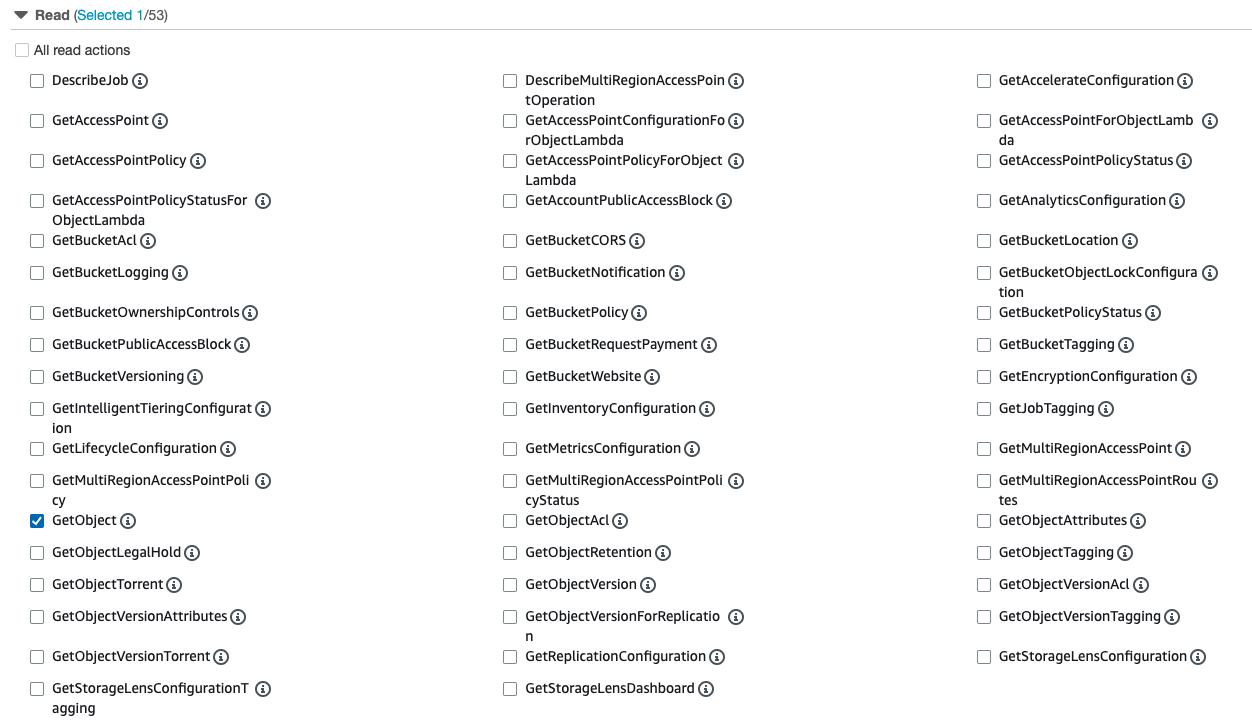
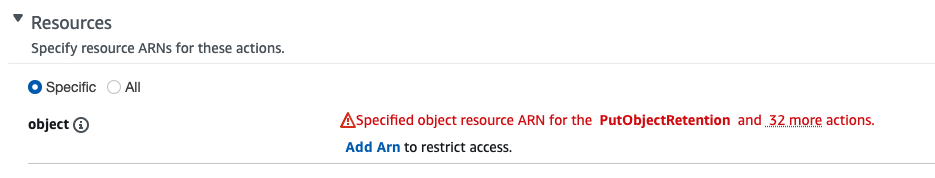
In resources, we don't want to give them access to all.
So add an ARN to restrict access.
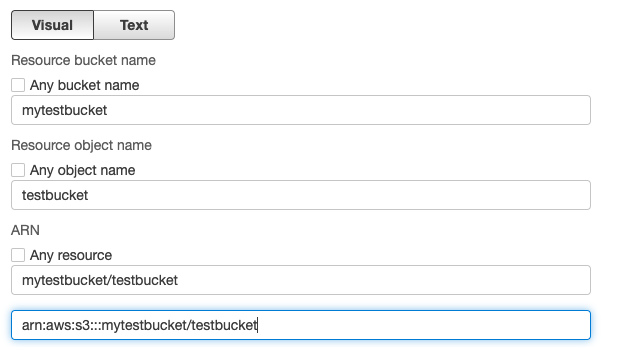
By specifying the ARN, notice how ARN changes!
Resource Policy
Principal: This element is there as an extra mechanism for defining what external identities can gain access to the resource in question.
Many resource policies are optional, but others are going to be required. For example, an S3 bucket has a bucket policy as a resource based policy. The default policy is entirely empty because it is optional.

Session Policy
A policy document that is pased as a parameter during the creation of a temporary session that has an actual expiration date
IAM Roles
Associated with permissions.
Similar to IAM Users, but roles define temporary permissions and it is assumed by other principals.
Think of right clicking on exe file and run as admin that's equivalent to running something with an IAM Role permission.
Role trust policy can link which entities can assume this role and on its permissions based on the pricipal.
Example,

You see the principal is ec2.amazonaws.com. That means that this role can be applied to EC2 instances and then they could be granted the permissions that are associated with the role.

Here you can assign expiry date range for the role.
Generate User in CLI
In the shell that you've configured your AWS CLI, run
$ aws sts get-session-token --duration-second 900
This will generate a temp credential that will only last 900 seconds.
Disclaimer
This summary is made possible by Oreilly's AWS, 3rd Edition - Chad Smith.
If the above post violates any copyright permissions, please let me know!

