이전에 리뷰한 Swin Transformer 논문을 코드와 함께 input/output 사이즈를 중심으로 다시 리뷰해 봅시다.
Official Github -> Swin-Transformer/models/swin_transformer.py
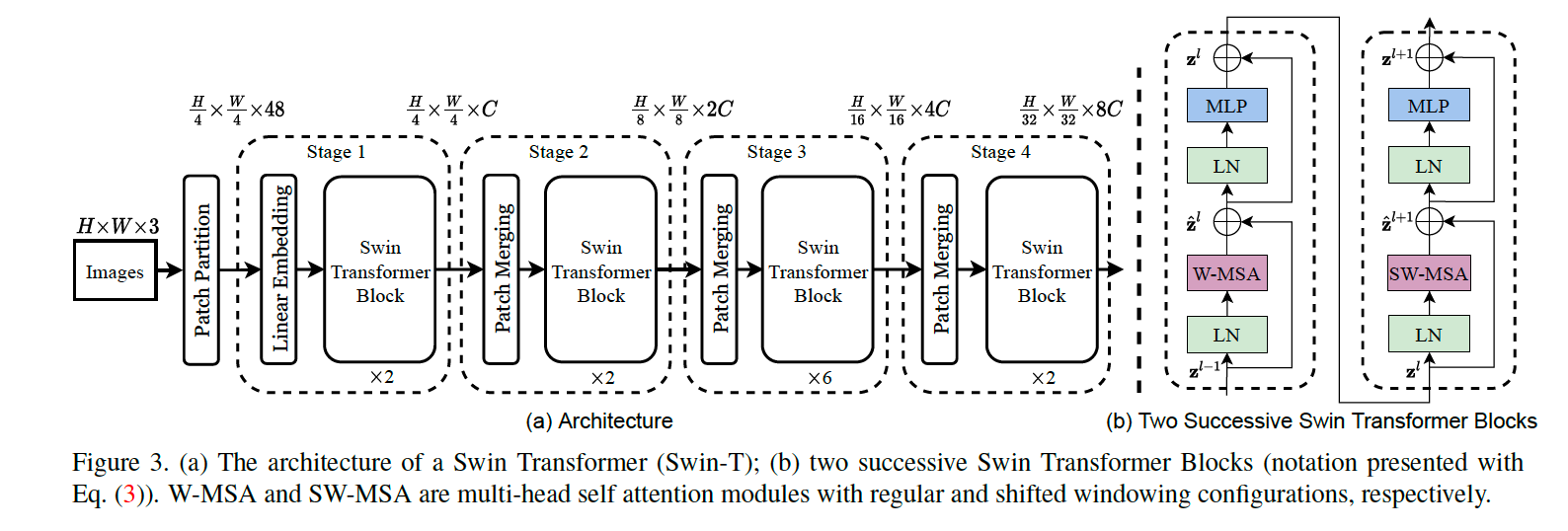
Swin Architecture
SwinTransformer
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96, depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, ape=False, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, fused_window_process=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
# ...
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
# ...
# build layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
layer = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0] // (2 ** i_layer),
patches_resolution[1] // (2 ** i_layer)),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
fused_window_process=fused_window_process)
self.layers.append(layer)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
# ...
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
if self.ape:
x = x + self.absolute_pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
x = self.norm(x) # B L C
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # B C 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
# ...코드를 보면 전체적인 흐름은 다음과 같습니다:
PatchEmbed -> BasicLayer -> norm & pooling -> Linear
이중에서 PatchEmbed 모듈은 맨 앞의 Patch Partition과 Linear Embedding block역할이고, BasicLayer 모듈은 stage 1~4의 기능을 하는 것으로 보입니다.
요 두 모듈을 중점적으로 리뷰해 봅시다.
PatchEmbed
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
r""" Image to Patch Embedding
Args:
img_size (int): Image size. Default: 224.
patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.
embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = to_2tuple(img_size)
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1]
self.in_chans = in_chans
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
else:
self.norm = None
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
# FIXME look at relaxing size constraints
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({H}*{W}) doesn't match model ({self.img_size[0]}*{self.img_size[1]})."
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Ph*Pw C
if self.norm is not None:
x = self.norm(x)
return x
# ...input 이미지를 patch_size로 나누고, 각 패치를 linear embedding해줍니다. 디폴트 값은 image.shape = (3,224,224), patch_size = 4, embedding_dim = 96입니다.
처음 input으로 들어오는 x는 B개의 이미지 입니다. (x.shape = (B, 3,244,244)). 위의 코드에서는 convolution layer을 이용해 patch partition과 linear embedding을 한번에 진행합니다. kernel_size = patch_size = 4, output_dim = embedding_dim로 설정해 각 convolution 연산마다 4x4x3 크기의 subimage를 입력으로 받아 크기 96의 1d embedding vector을 출력으로 얻습니다. 이때, stride = patch_size = 4로 설정하여 각각의 receptive field가 겹치지 않도록 합니다.
-> shape = (B, 96, 224/4, 224/4) = (B, 96, 56, 56)
이후에 flatten(2).transpose(1,2)를 통해 output의 shape은 (B, 56x56, 96)이 됩니다.
flatten(n): n번째 dim부터 모두 flatten
transpose(n, m): n번째 dim과 m번째 dim 순서 변경
BasicLayer
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
""" A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.
depth (int): Number of blocks.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Local window size.
#...
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False,
fused_window_process=False):
super().__init__()
# ...
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(dim=dim, input_resolution=input_resolution,
num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
fused_window_process=fused_window_process)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
if downsample is not None:
self.downsample = downsample(input_resolution, dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
self.downsample = None
def forward(self, x):
for blk in self.blocks:
if self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x)
else:
x = blk(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
# ... depth개의 SwinTransformerBlock과 downsample로 구성되어 있습니다. downsample은 각 stage의 끝에 있는 patch merging 과정입니다.
SwinTransformerBlock
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resulotion.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
fused_window_process=False):
super().__init__()
# ...
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
if self.shift_size > 0:
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
H, W = self.input_resolution
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
else:
attn_mask = None
self.register_buffer("attn_mask", attn_mask)
self.fused_window_process = fused_window_process
def forward(self, x):
H, W = self.input_resolution
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
if not self.fused_window_process:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
else:
x_windows = WindowProcess.apply(x, B, H, W, C, -self.shift_size, self.window_size)
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
if not self.fused_window_process:
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = WindowProcessReverse.apply(attn_windows, B, H, W, C, self.shift_size, self.window_size)
else:
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
x = shifted_x
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
# FFN
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
# ...현재 SwinTransformerBlock 모듈의 input shape은 (B, 56x56, 96)이다. (stage 1) normLayer을 거친 뒤에 view 함수를 통해 (B, 56, 56, 96)으로 변한다. 이후 window_partition() 함수를 거치게 된다:
def window_partition(x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windowswindow_size로 패치들 window별로 나누어 준다. 단계별로 보면 다음과 같다:
- window_partition의 input shape은 (B, 56, 56, 96)이다.
- view() -> (B, 56/7, 7, 56/7, 7, 96) = (B, 8, 7, 8, 7, 96)
- permute() -> (B, 8, 8, 7, 7, 96)
- view() -> (Bx8x8, 7, 7, 96)
따라서, window_partition() 함수는 Bx8x8개의 window마다 7x7개의 patch가 있고, 각 patch당 길이 96의 embedding vector을 같은 window끼리 partition 해주는 역할을 한다.
다시 SwinTransformerBlock코드로 돌아가서, output은 view()함수를 통해 shape이 (Bx8x8, 7x7, 96)으로 변경되고, 이후에 각 window별로 self-attention 연산이 진행된다.
self-attention연산은 input과 output이 같은 shape을 갖는다. output의 shape은 window_reverse() 함수를 거쳐 다시 (B, 56x56, 96)이 된다.
window_partition() -> (Bx8x8, 7, 7, 96) -> (Bx8x8, 7x7, 96) -> self-attention -> (Bx8x8, 7x7, 96) -> (Bx8x8, 7, 7, 96) -> window_reverse() -> (B, 56x56, 96)
Shifted-window (SW-MSA)의 경우, torch.roll() 함수를 통해 window를 구성해주고, 다시 self-attention 이후에 반대방향으로 torch.roll()함수를 이용해 원상복귀 시킨다.
Patch Merging
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
r""" Patch Merging Layer.
Args:
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Resolution of input feature.
dim (int): Number of input channels.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, input_resolution, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.dim = dim
self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)
def forward(self, x):
"""
x: B, H*W, C
"""
H, W = self.input_resolution
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
assert H % 2 == 0 and W % 2 == 0, f"x size ({H}*{W}) are not even."
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 C
x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # B H/2 W/2 4*C
x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # B H/2*W/2 4*C
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.reduction(x)
return x
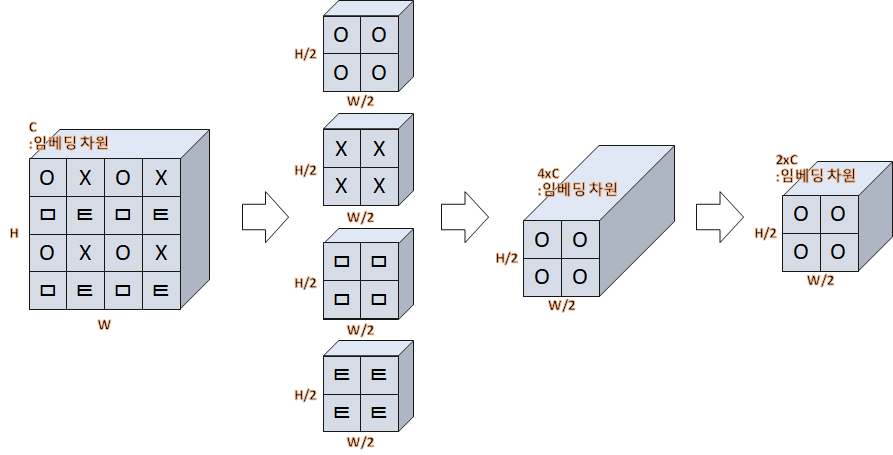
# ...input의 shape은 (B, H, W, C) 이고, 이 input을 4개로 쪼개 주는데, 아래의 그림과 같이 H, W 부분을 한칸씩 띄어서 4개로 나누어 준다. 그 후, embedding vector 차원 기준으로 4개를 concat한다. (B, H/2, W/2, 4C). 마지막으로 x2 downsampling을 통해 block의 최종 output shape은 (B, H/2, W/2, 2C) 가 된다.
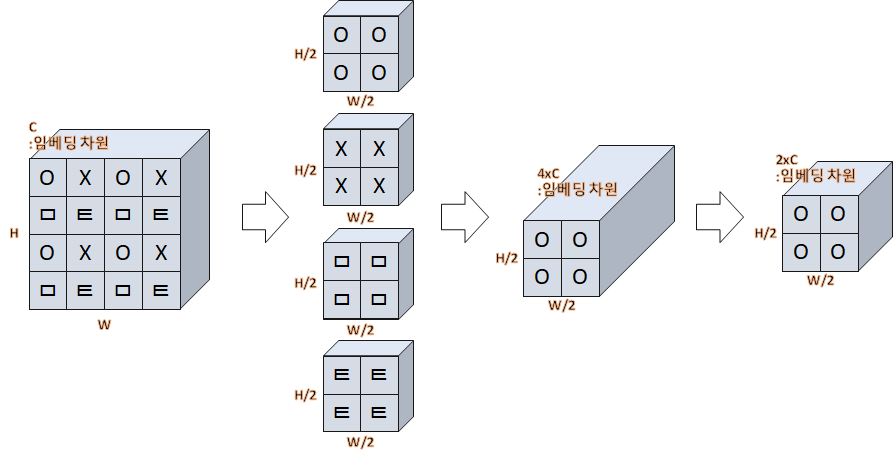
(B, 56x56, 96) -> (B, 56, 56, 96) -> (B, 56/2, 56/2, 96x4) -> (B, 56/2, 56/2, 96x2)
Reference
https://byeongjo-kim.tistory.com/36
글 잘 봤습니다, 감사합니다.