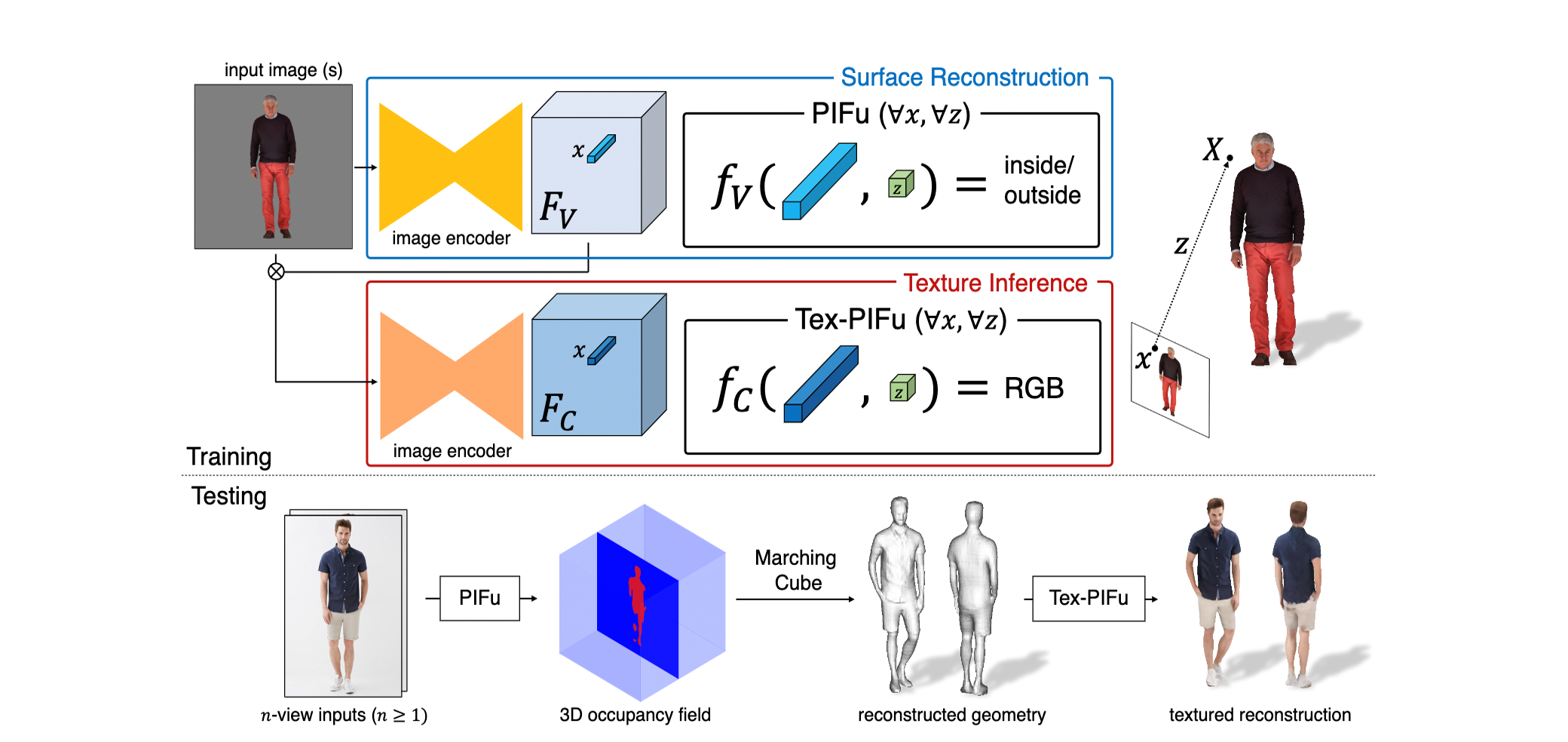
Inference pipeline
Image_input
test_image
test_image_mask
eval.py
# eval.py
if __name__ == '__main__':
evaluator = Evaluator(opt)
test_images = glob.glob(os.path.join(opt.test_folder_path, '*'))
test_images = [f for f in test_images if ('png' in f or 'jpg' in f) and (not 'mask' in f)]
test_masks = [f[:-4]+'_mask.png' for f in test_images]
print("num; ", len(test_masks))
for image_path, mask_path in tqdm.tqdm(zip(test_images, test_masks)):
try:
print(image_path, mask_path)
data = evaluator.load_image(image_path, mask_path)
evaluator.eval(data, True)
except Exception as e:
print("error:", e.args)
# class Evaluator def load_image(self, image_path, mask_path) -> dict{data}: # Name img_name = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))[0] # Calib B_MIN = np.array([-1, -1, -1]) B_MAX = np.array([1, 1, 1]) projection_matrix = np.identity(4) projection_matrix[1, 1] = -1 calib = torch.Tensor(projection_matrix).float() # Mask mask = Image.open(mask_path).convert('L') mask = transforms.Resize(self.load_size)(mask) mask = transforms.ToTensor()(mask).float() # image image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB') image = self.to_tensor(image) image = mask.expand_as(image) * image return { 'name': img_name, 'img': image.unsqueeze(0), 'calib': calib.unsqueeze(0), 'mask': mask.unsqueeze(0), 'b_min': B_MIN, 'b_max': B_MAX, }테스트 이미지를 load_image 함수에 넣어서 Tensor로 바꿔준다.
# class Evaluator """ netG = HGPIFuNet(opt, projection_mode).to(device=cuda) netC = ResBlkPIFuNet(opt).to(device=cuda) """ def eval(self, data, use_octree=False): ''' Evaluate a data point :param data: a dict containing at least ['name'], ['image'], ['calib'], ['b_min'] and ['b_max'] tensors. :return: ''' opt = self.opt with torch.no_grad(): self.netG.eval() if self.netC: self.netC.eval() save_path = '%s/%s/result_%s.obj' % (opt.results_path, opt.name, data['name']) if self.netC: gen_mesh_color(opt, self.netG, self.netC, self.cuda, data, save_path, use_octree=use_octree) else: gen_mesh(opt, self.netG, self.cuda, data, save_path, use_octree=use_octree)tex pifu(color)가 있을경우엔 mesh와 surface의 color까지 추론하고, tex pifu가 None 일 경우엔 3D geometry만 예측한다.
train_util.py
gen_mesh
def gen_mesh(opt, net, cuda, data, save_path, use_octree=True):
image_tensor = data['img'].to(device=cuda)
calib_tensor = data['calib'].to(device=cuda)
net.filter(image_tensor)
b_min = data['b_min']
b_max = data['b_max']
try:
save_img_path = save_path[:-4] + '.png'
save_img_list = []
for v in range(image_tensor.shape[0]):
save_img = (np.transpose(image_tensor[v].detach().cpu().numpy(), (1, 2, 0)) * 0.5 + 0.5)[:, :, ::-1] * 255.0
save_img_list.append(save_img)
save_img = np.concatenate(save_img_list, axis=1)
Image.fromarray(np.uint8(save_img[:,:,::-1])).save(save_img_path)
verts, faces, _, _ = reconstruction(
net, cuda, calib_tensor, opt.resolution, b_min, b_max, use_octree=use_octree)
verts_tensor = torch.from_numpy(verts.T).unsqueeze(0).to(device=cuda).float()
xyz_tensor = net.projection(verts_tensor, calib_tensor[:1])
uv = xyz_tensor[:, :2, :]
color = index(image_tensor[:1], uv).detach().cpu().numpy()[0].T
color = color * 0.5 + 0.5
save_obj_mesh_with_color(save_path, verts, faces, color)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('Can not create marching cubes at this time.')filter라는 이미지 인코더를 통해 이미지 텐서로부터 Pixel-Aligned Implicit feature를 뽑아낸다.
HGFilter
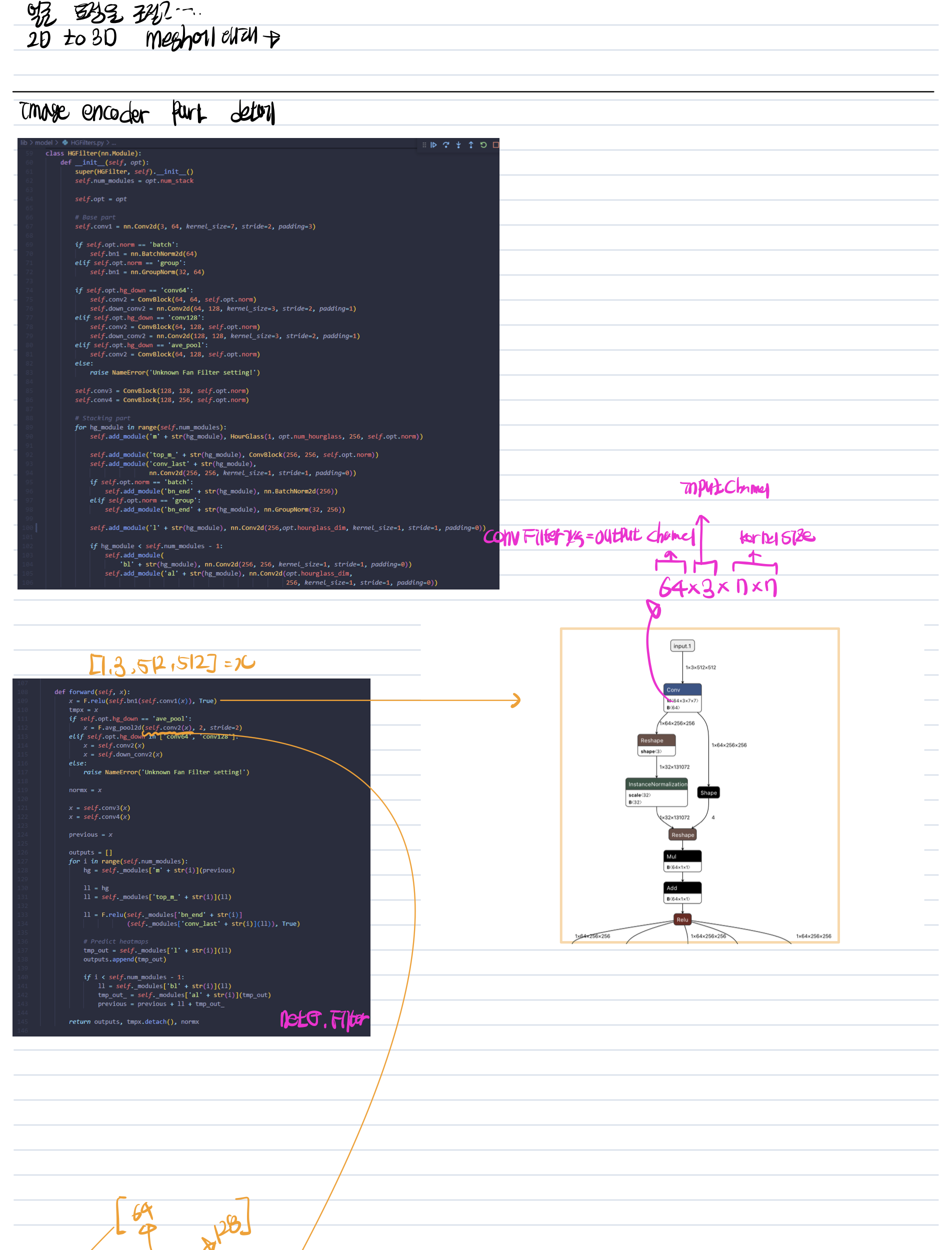
class HGFilter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, opt):
super(HGFilter, self).__init__()
self.num_modules = opt.num_stack
self.opt = opt
# Base part
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
if self.opt.norm == 'batch':
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
elif self.opt.norm == 'group':
self.bn1 = nn.GroupNorm(32, 64)
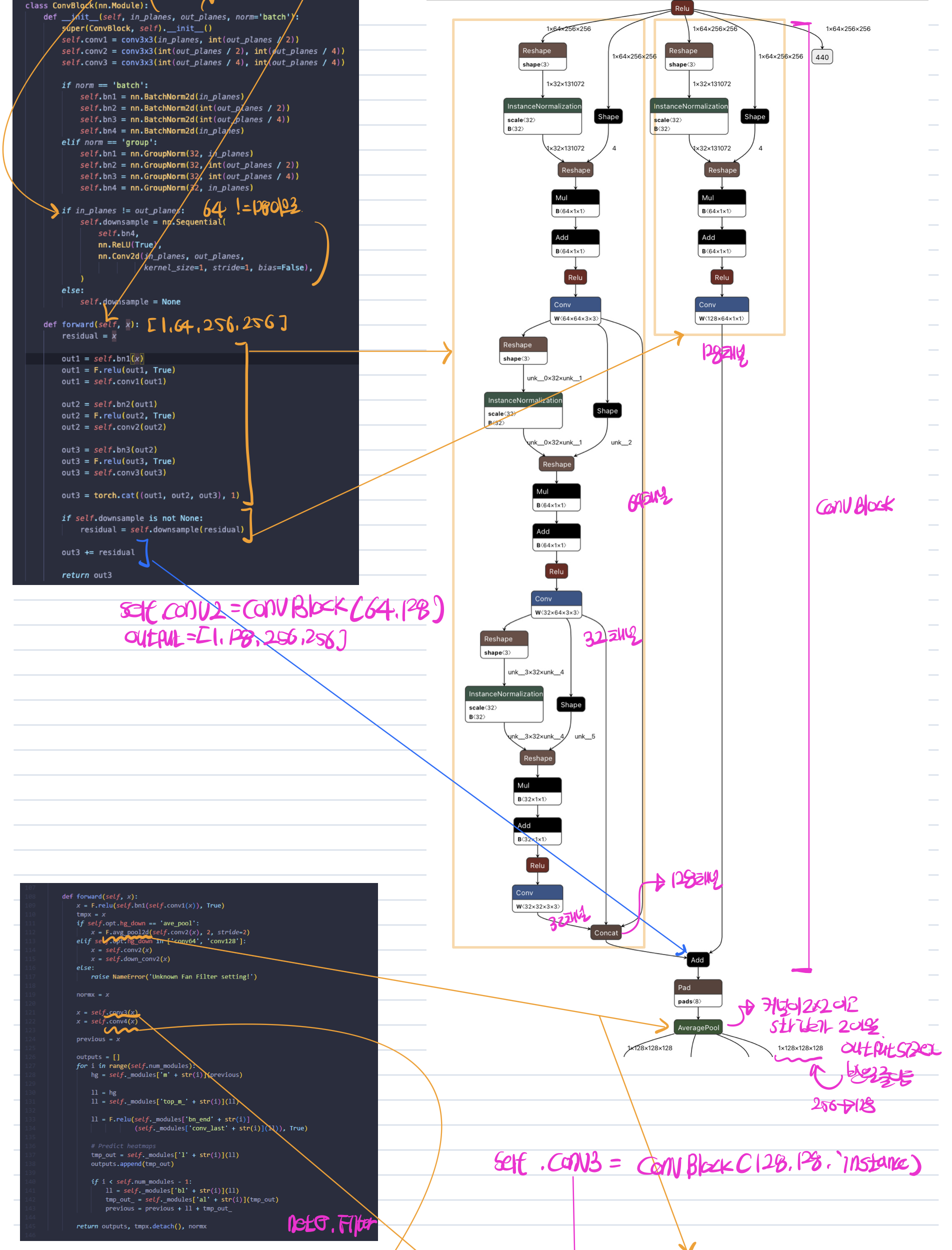
if self.opt.hg_down == 'conv64':
self.conv2 = ConvBlock(64, 64, self.opt.norm)
self.down_conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
elif self.opt.hg_down == 'conv128':
self.conv2 = ConvBlock(64, 128, self.opt.norm)
self.down_conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
elif self.opt.hg_down == 'ave_pool':
self.conv2 = ConvBlock(64, 128, self.opt.norm)
else:
raise NameError('Unknown Fan Filter setting!')
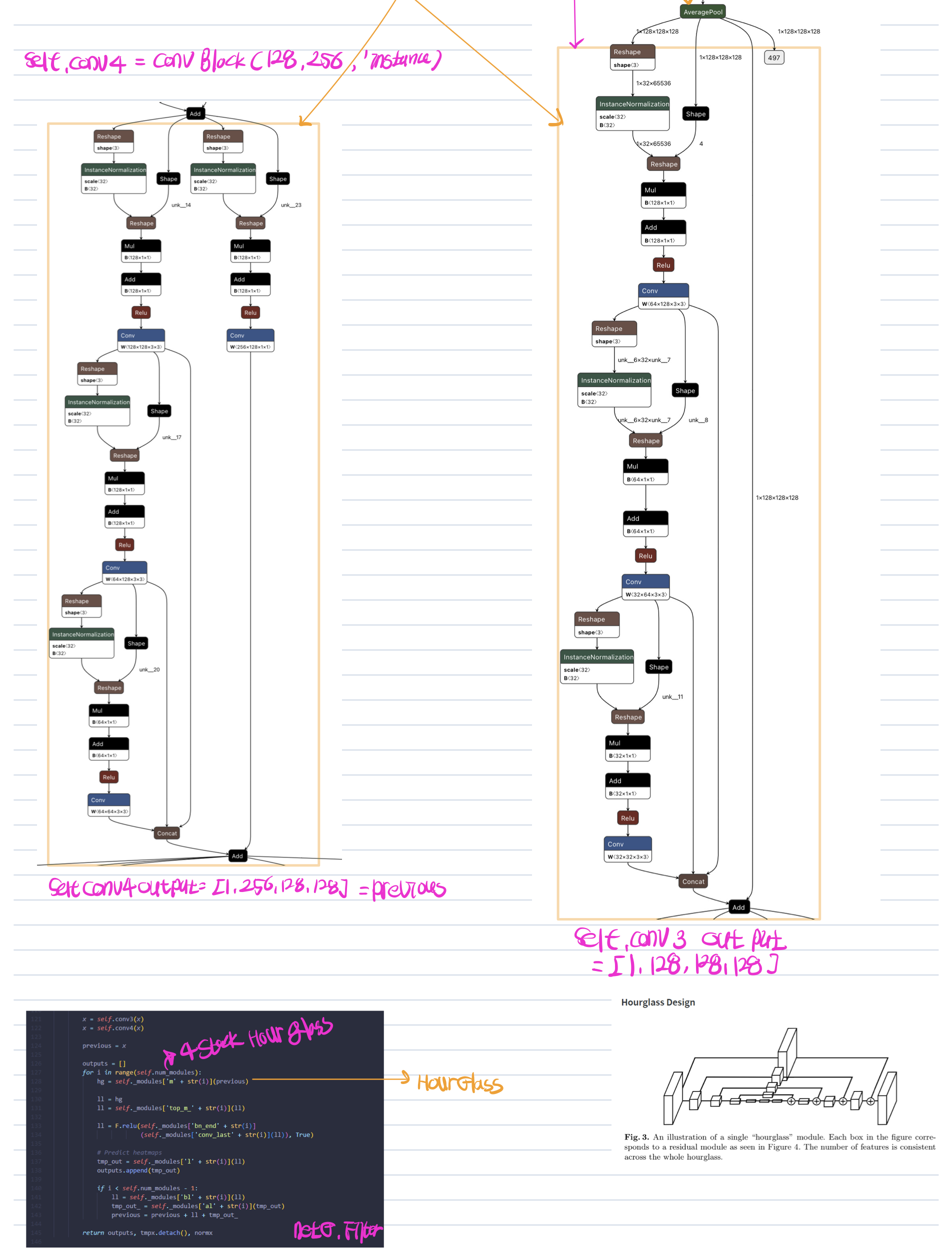
self.conv3 = ConvBlock(128, 128, self.opt.norm)
self.conv4 = ConvBlock(128, 256, self.opt.norm)
# Stacking part
for hg_module in range(self.num_modules):
self.add_module('m' + str(hg_module), HourGlass(1, opt.num_hourglass, 256, self.opt.norm))
self.add_module('top_m_' + str(hg_module), ConvBlock(256, 256, self.opt.norm))
self.add_module('conv_last' + str(hg_module),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0))
if self.opt.norm == 'batch':
self.add_module('bn_end' + str(hg_module), nn.BatchNorm2d(256))
elif self.opt.norm == 'group':
self.add_module('bn_end' + str(hg_module), nn.GroupNorm(32, 256))
self.add_module('l' + str(hg_module), nn.Conv2d(256,opt.hourglass_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0))
if hg_module < self.num_modules - 1:
self.add_module(
'bl' + str(hg_module), nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0))
self.add_module('al' + str(hg_module), nn.Conv2d(opt.hourglass_dim,
256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0))
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)), True)
tmpx = x
if self.opt.hg_down == 'ave_pool':
x = F.avg_pool2d(self.conv2(x), 2, stride=2)
elif self.opt.hg_down in ['conv64', 'conv128']:
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.down_conv2(x)
else:
raise NameError('Unknown Fan Filter setting!')
normx = x
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
previous = x
outputs = []
for i in range(self.num_modules):
hg = self._modules['m' + str(i)](previous)
ll = hg
ll = self._modules['top_m_' + str(i)](ll)
ll = F.relu(self._modules['bn_end' + str(i)]
(self._modules['conv_last' + str(i)](ll)), True)
# Predict heatmaps
tmp_out = self._modules['l' + str(i)](ll)
outputs.append(tmp_out)
if i < self.num_modules - 1:
ll = self._modules['bl' + str(i)](ll)
tmp_out_ = self._modules['al' + str(i)](tmp_out)
previous = previous + ll + tmp_out_
return outputs, tmpx.detach(), normx
HGfilter는 pifu의 image encoder로써 Unet과 비슷한 구조인 HourGlass라는 컨볼루션 블록이 반복되는 형태를 보여주고 있다.
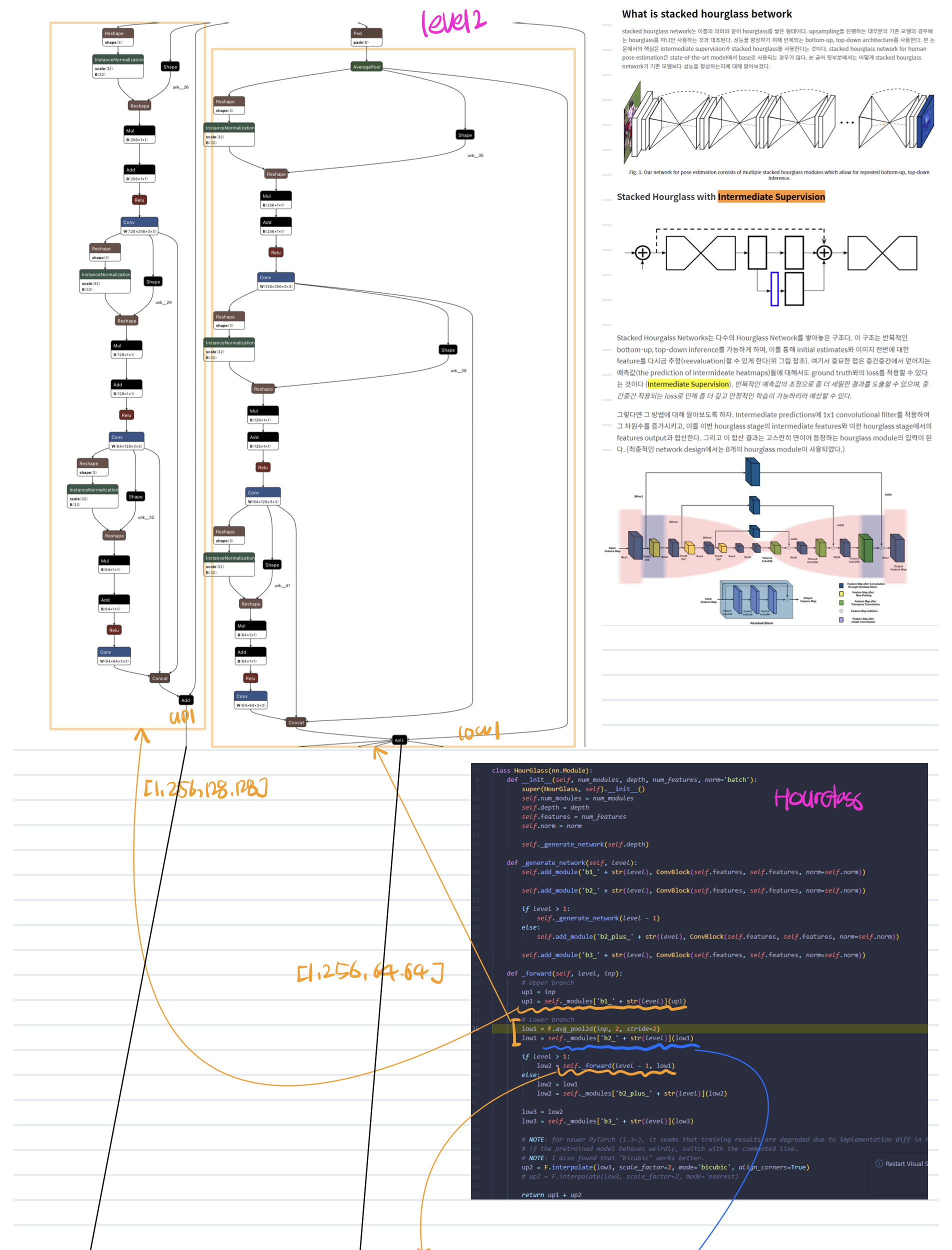
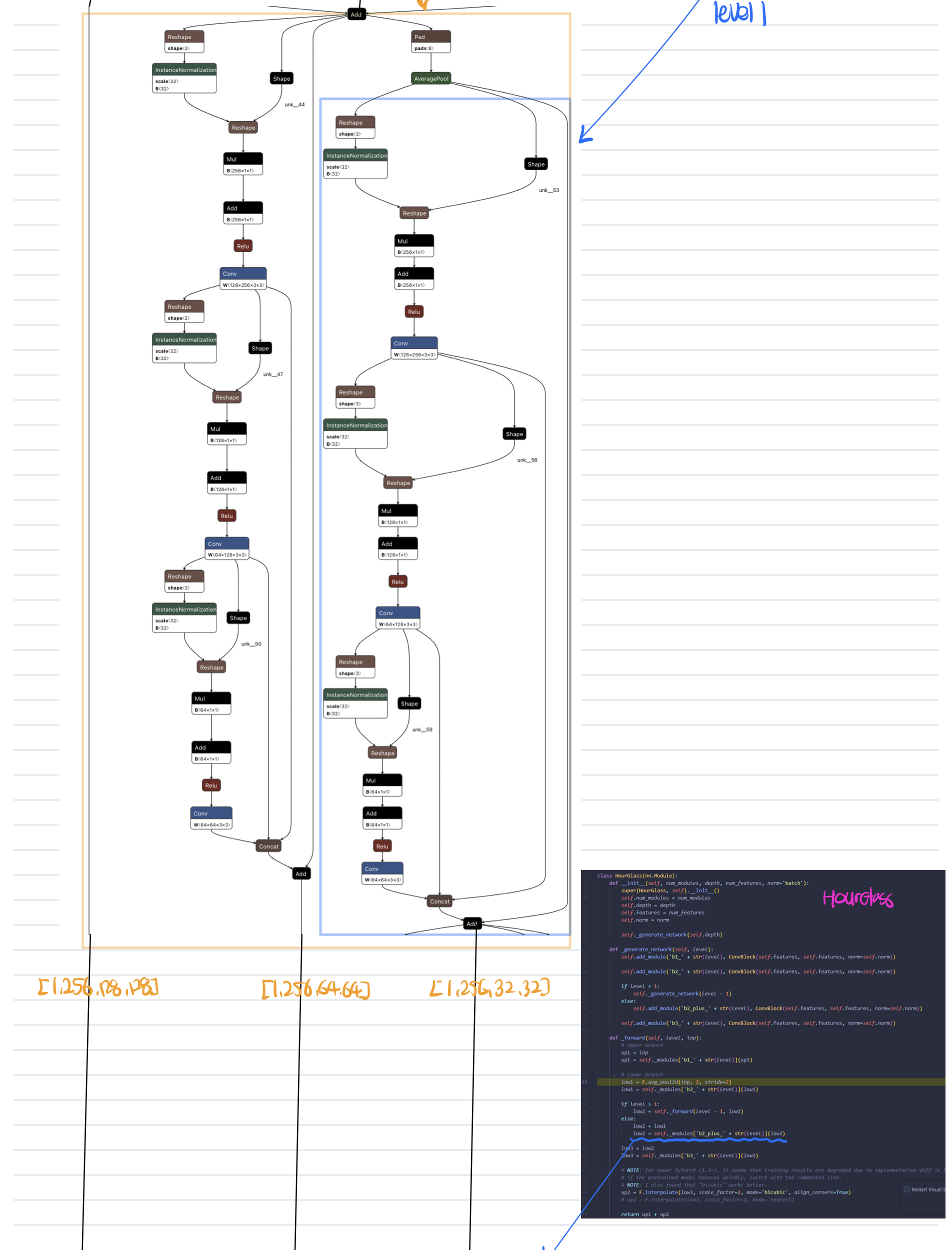


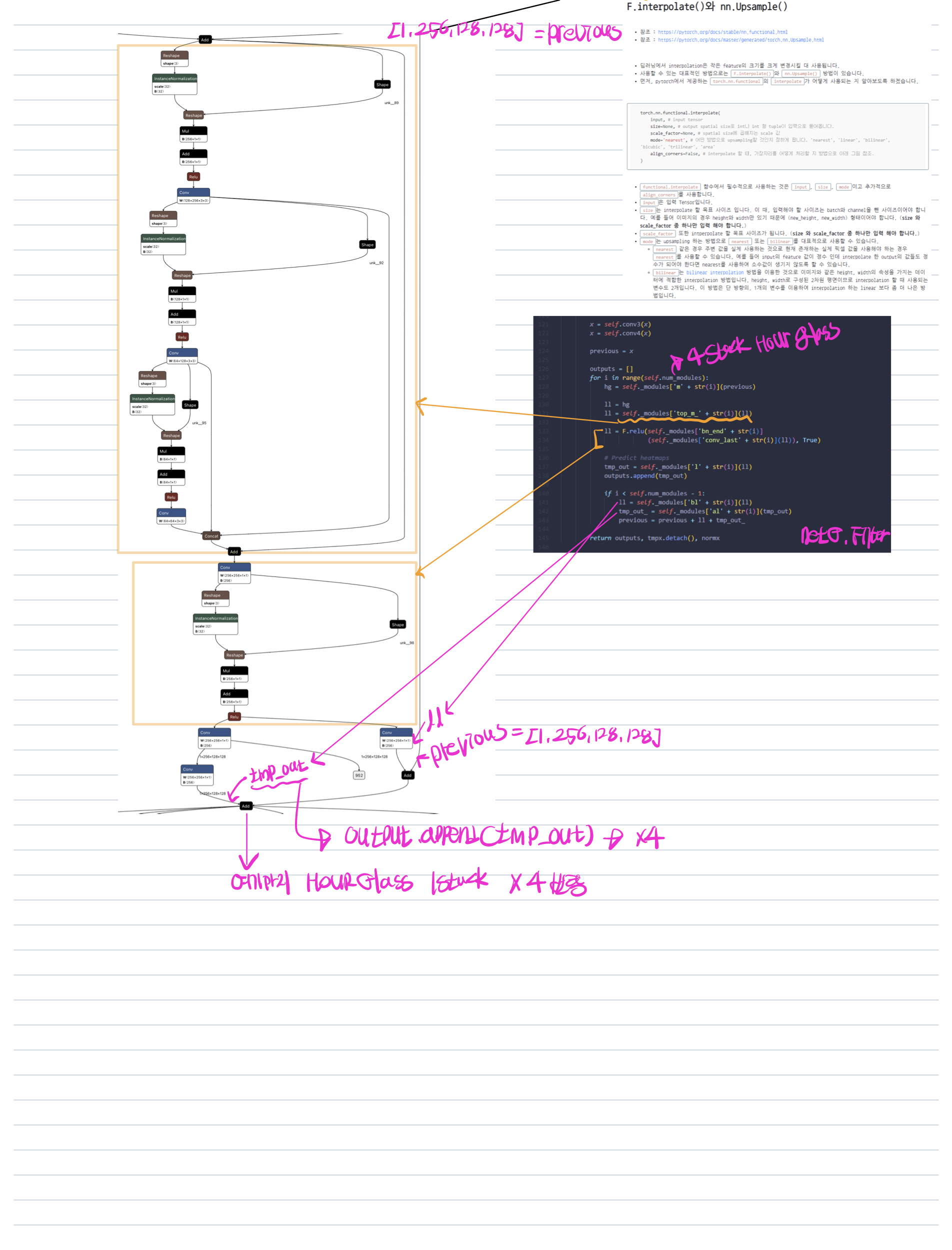
SurfaceClassifier
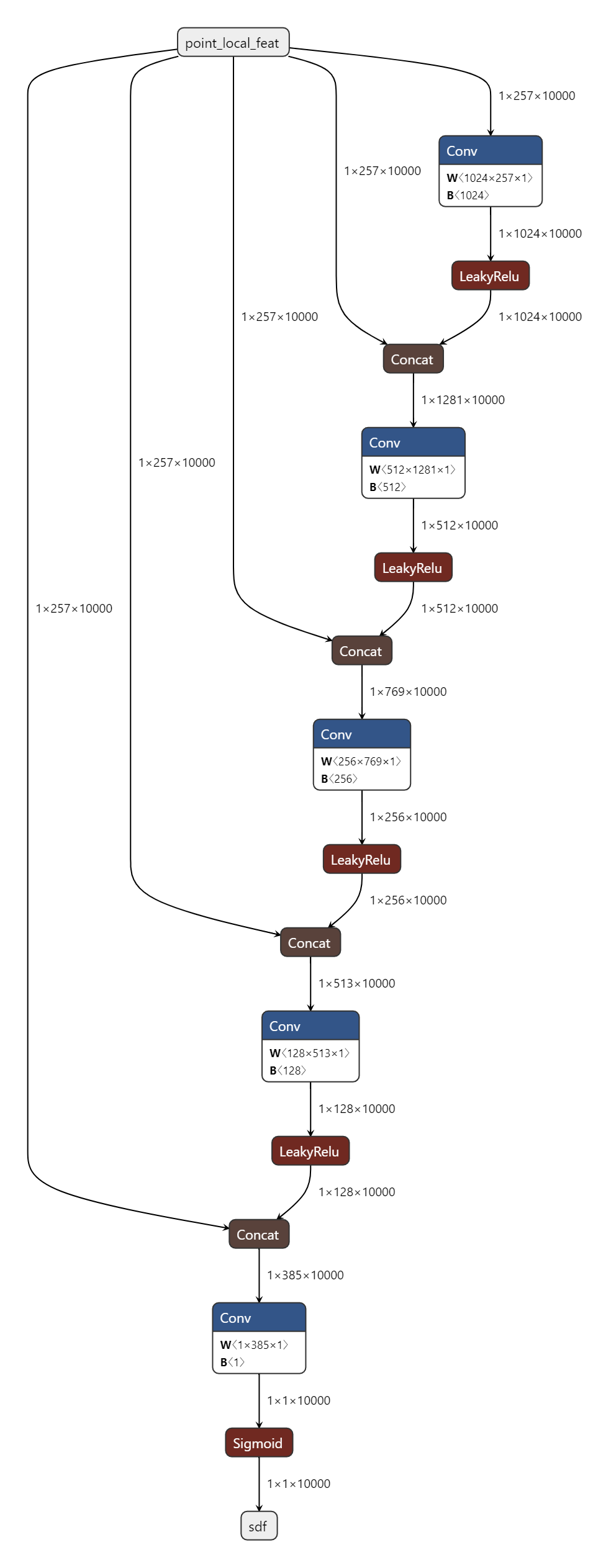
'''
class HGPIFuNet(BasePIFuNet)
'''
def query(self, points, calibs, transforms=None, labels=None):
'''
Given 3D points, query the network predictions for each point.
Image features should be pre-computed before this call.
store all intermediate features.
query() function may behave differently during training/testing.
:param points: [B, 3, N] world space coordinates of points
:param calibs: [B, 3, 4] calibration matrices for each image
:param transforms: Optional [B, 2, 3] image space coordinate transforms
:param labels: Optional [B, Res, N] gt labeling
:return: [B, Res, N] predictions for each point
'''
if labels is not None:
self.labels = labels
xyz = self.projection(points, calibs, transforms)
xy = xyz[:, :2, :]
z = xyz[:, 2:3, :]
in_img = (xy[:, 0] >= -1.0) & (xy[:, 0] <= 1.0) & (xy[:, 1] >= -1.0) & (xy[:, 1] <= 1.0)
z_feat = self.normalizer(z, calibs=calibs)
if self.opt.skip_hourglass:
tmpx_local_feature = self.index(self.tmpx, xy)
self.intermediate_preds_list = []
for im_feat in self.im_feat_list:
# [B, Feat_i + z, N]
point_local_feat_list = [self.index(im_feat, xy), z_feat]
if self.opt.skip_hourglass:
point_local_feat_list.append(tmpx_local_feature)
# torch.Size([1, 257, 10000])
point_local_feat = torch.cat(point_local_feat_list, 1) # Concatenates the given sequence of seq tensors in the given dimension.
# out of image plane is always set to 0
pred = in_img[:,None].float() * self.surface_classifier(point_local_feat)
self.intermediate_preds_list.append(pred)
self.preds = self.intermediate_preds_list[-1]안의 self.surface_classifier 가 sdf 이고 이 sdf를 근사하는 네트워크 구조가 위의 그림
HGPIFuNet 의 query 함수는 시스템 시작시 지정했던 resolution대로 셈플링된 point들의 sdf를 판단하는데 사용
'''
def reconstruction(net, cuda, calib_tensor,
resolution, b_min, b_max,
use_octree=False, num_samples=10000, transform=None):
'''
def eval_func(points):
points = np.expand_dims(points, axis=0)
points = np.repeat(points, net.num_views, axis=0)
samples = torch.from_numpy(points).to(device=cuda).float()
net.query(samples, calib_tensor)
pred = net.get_preds()[0][0]
return pred.detach().cpu().numpy()
### eval grid
if use_octree:
sdf = eval_grid_octree(coords, eval_func, num_samples=num_samples)
else:
sdf = eval_grid(coords, eval_func, num_samples=num_samples)
### marching cubedef eval_grid_octree(coords, eval_func,
init_resolution=64, threshold=0.01,
num_samples=512 * 512 * 512):
resolution = coords.shape[1:4]
sdf = np.zeros(resolution)
dirty = np.ones(resolution, dtype=np.bool)
grid_mask = np.zeros(resolution, dtype=np.bool)
reso = resolution[0] // init_resolution
while reso > 0:
# subdivide the grid
grid_mask[0:resolution[0]:reso, 0:resolution[1]:reso, 0:resolution[2]:reso] = True # reso만큼의 간격으로 점을 뽑음
# test samples in this iteration
test_mask = np.logical_and(grid_mask, dirty)
#print('step size:', reso, 'test sample size:', test_mask.sum())
points = coords[:, test_mask] # coords : 3 256 256 256 (i, j, k 의 정보가 각각 256 256 256 행렬에 들어있음 ) 이고 mask 가 256 256 256 이므로 (마스크는 bool 행렬임) 마스크의 reso 만큼 grid의 점들이 선택되어짐
sdf[test_mask] = batch_eval(points, eval_func, num_samples=num_samples)
dirty[test_mask] = False
# do interpolation
if reso <= 1:
break
for x in range(0, resolution[0] - reso, reso):
for y in range(0, resolution[1] - reso, reso):
for z in range(0, resolution[2] - reso, reso):
# if center marked, return
if not dirty[x + reso // 2, y + reso // 2, z + reso // 2]:
continue
v0 = sdf[x, y, z]
v1 = sdf[x, y, z + reso]
v2 = sdf[x, y + reso, z]
v3 = sdf[x, y + reso, z + reso]
v4 = sdf[x + reso, y, z]
v5 = sdf[x + reso, y, z + reso]
v6 = sdf[x + reso, y + reso, z]
v7 = sdf[x + reso, y + reso, z + reso]
v = np.array([v0, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7])
v_min = v.min()
v_max = v.max()
# this cell is all the same
if (v_max - v_min) < threshold:
sdf[x:x + reso, y:y + reso, z:z + reso] = (v_max + v_min) / 2
dirty[x:x + reso, y:y + reso, z:z + reso] = False
reso //= 2
return sdf.reshape(resolution)