모든 코드는 아래 링크에서 다운받을 수 있습니다.
https://github.com/Foxhead-Studio/NeRF-Code-Analysis/tree/main
[4] Hierarchical Sampling
1. Hierarchical Sampling이란?
- Coarse 네트워크의 인풋 데이터인(개수:)라 합시다.
- Fine 네트워크는 이 값들 중 물체가 존재할 확률이 높은 구간 에서 더 많은 샘플링을 진행하는데, 이 것이 Hierarchical Sampling 입니다.
- 이때, 확률밀도함수(PDF) 와 누적확률함수(CDF) 를 해당 구간을 파악합니다.
- 실제로 코드 상에서는 세부분할할 깊이 값으로 값들의 중간 지점들 (개수:) 이 들어갑니다.
2. 가중치 기반 확률밀도함수 (PDF, Probability Density Function)
- 수식:
- 이는 연속 분포에 대한 확률밀도함수이나, 샘플 포인트는 이항 분포를 따르므로 아래의 수식을 코드로 구현하여 사용합니다.
- 즉, 가중치가 클수록 PDF 값도 커지며, 중요한 영역에서 샘플이 더 집중적으로 생성됩니다.
- 이는 연속 분포에 대한 확률밀도함수이나, 샘플 포인트는 이항 분포를 따르므로 아래의 수식을 코드로 구현하여 사용합니다.
- 코드:
- 코드에서는
weights / torch.sum(weights, -1, keepdim=True)로 구현됩니다.
- 코드에서는
3. 누적확률함수 (CDF, Cumulative Distribution Function)
- 수식:
- 이 또한 연속 분포에 대한 누적확률함수이므로, 실제로는 아래와 같은 이항 분포에 대한 수식을 사용합니다.
- CDF는 0에서 1 사이의 값으로 정규화되며, 각 샘플 위치까지의 누적 확률을 의미합니다.
- CDF의 형태는 항상 단조 증가하며, 큰 weights를 가지는 영역 에서는 더 빠르게 증가합니다.
- 이 또한 연속 분포에 대한 누적확률함수이므로, 실제로는 아래와 같은 이항 분포에 대한 수식을 사용합니다.
- 코드:
- 코드에서는
torch.cumsum(pdf, dim=-1)로 구현됩니다. - 마지막에
torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(cdf[..., :1]), cdf], dim=-1)을 적용하여, 맨 앞에 0을 추가해형태가 되도록 설정합니다.
- 코드에서는
4. Fine 모델을 위한 역변환 샘플링 (Inverse Transform Sampling)
Fine 모델에 전달할 추가 샘플을 얻기 위해 역변환 샘플링 (Inverse Transform Sampling) 을 수행합니다.
구체적인 과정은 다음과 같습니다:
-
균등 분포에서 새로운 샘플생성
-를 따르는개의 무작위 샘플를 생성합니다. -
CDF 역변환을 이용하여 새로운값 샘플링
-를 coarse 샘플의 CDF 값들에 매핑하여 새로운 샘플링 위치을 찾습니다.- 이를 위해, CDF에서가 위치한 구간을 찾고, 이를 선형 보간하여 새로운값을 얻습니다.
torch.searchsorted(cdf, u)를 사용하여가 위치한 CDF 구간을 찾을 수 있습니다.
-
최종 샘플링된값
- 기존 coarse 샘플과 새롭게 샘플링된을 합쳐서, 최종적으로 fine 모델에 전달할값을 얻습니다.
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from adjustText import adjust_text
#---------------------
# torch.searchsorted
#---------------------
# “정렬된 1D 텐서(예: cdf) 내에서 u 값이 들어갈 인덱스”를 찾는 함수.
# 매개변수 right=True면, 동일값이면 오른쪽 인덱스 반환.
cdf_1d = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0]) # shape (5,)
u_1d = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.7, 0.9]) # shape (3,)
inds = torch.searchsorted(cdf_1d, u_1d, right=True)
# cdf_1d: 0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0
# u_1d: 0.1 -> index=1 (cdf[1]=0.2)
# 0.7 -> index=3 (cdf[2]=0.5, cdf[3]=0.8)
# 0.9 -> index=4 (cdf[4]=1.0)
# inds = [1, 3, 4]
#--------------------
# torch.gather
#--------------------
# “특정 인덱스(inds) 위치에서 값을 가져오기”
# shape가 (N_rays, N_samples)인 텐서 cdf, 그리고 (N_rays, K)인 인덱스 inds가 있을 때,
# gather로 “각 배치마다 K개 인덱스 위치”를 모아서 shape (N_rays,K) 결과를 얻는다.
cdf_2d = torch.tensor([
[0.0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0],
[0.0, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0]
]) # shape (2,4)
inds_2d = torch.tensor([
[1,3],
[0,2]
]) # shape (2,2)
# gather(cdf_2d, dim=1, index=inds_2d)
cdf_g = torch.gather(cdf_2d, 1, inds_2d)
# result shape (2,2).
# cdf_g[0] = [ cdf_2d[0,1], cdf_2d[0,3] ] = [0.2,1.0]
# cdf_g[1] = [ cdf_2d[1,0], cdf_2d[1,2] ] = [0.0,0.6]def sample_pdf(bins, weights, N_samples, det=False, pytest=False):
"""
Importance Sampling으로 새로운 샘플의 z좌표(또는 깊이)를 뽑아내는 함수.
[배경]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- NeRF에서 코스(coarse) 레이어의 샘플 지점들로부터 "weights"(= a_i * T_i)를 구하고,
이를 확률분포 함수(pdf)로 삼아 더 많은 샘플을 "중요도 있게" 추가(fine 모델)하려고 함.
- 이 함수는 'Inverse Transform Sampling' 기법을 사용:
1) weights -> pdf -> cdf
2) uniform random (u) -> cdf^-1(u)
3) -> 새 z샘플(점) 추출
[입력 설명]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- bins : shape (N_rays, Coarse Model's N_samples - 1) = (N_rays, M)
코스(coarse) 모델에 입력된 샘플 포인트들(z_vals)의 중간 지점들인 z_vals_mid
* 실제론 'z_vals의 중간점'이지만, 구현 편의상 "bins"라 부름.
코스 모델의 N_samples 사이의 중간값들이므로 N_samples - 1개 존재 (이하 N_samples - 1 = M으로 칭함)
- weights: raw2outputs 함수에서 계산한 샘플별 가중치 (a_i * T_i) (N_rays, corase 모델의 N_samples)
이 때, smaple_pdf 함수에 넘겨지는 인자는 맨앞, 맨뒤 시작점을 절삭해
weighs[..., 1: -1]로 (N_rays, corase 모델의 N_samples - 2) = (N_rays, M - 1)
- N_samples: fine 모델에서 새로 추출할 샘플 개수 (Coarse Model의 N_samples와 다름에 유의!)
- det : bool
True면 '균등분할'에 따라 deterministic하게 샘플 (테스트 등),
False면 실제로 랜덤하게 뽑음.
- pytest : bool
True면 난수를 고정(np.random.seed(0))시켜 테스트 재현 가능.
[출력]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- samples : shape (N_rays, N_samples)
각 레이마다 새롭게 샘플링된 z 좌표. (importance sampling 결과)
"""
# (1) weights에 작은 수(1e-5)를 더해 NaN 방지
weights = weights + 1e-5 # prevent nans
# torch.sum(weights, -1): (N_rays, )
# torch.sum(weights, -1, keepdim=True): (N_rays, 1)
pdf = weights / torch.sum(weights, -1, keepdim=True)
# pdf: (N_rays, M - 1)
cdf = torch.cumsum(pdf, -1) # 마지막 차원 기준 누적합으로 업데이트 (N_rays, M - 1)
cdf = torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(cdf[...,:1]), cdf], -1) #맨 앞 지점의 누적 확률인 0을 concat -> (N_rays, M)
# cdf: (N_rays, M)
# Take uniform samples
# cdf에서 추출할 임의의 점의 y값이 될 u를 0부터 1까지의 값으로 생성
if det: # u를 0부터 1까지 균등 분할
u = torch.linspace(0., 1., steps=N_samples) # (N_samples, )
u = u.expand(list(cdf.shape[:-1]) + [N_samples]) # (N_rays, N_samples)
else: # u를 0부터 1까지 랜덤하게 추출
u = torch.rand(list(cdf.shape[:-1]) + [N_samples])
# u: (N_rays, N_samples)
# Pytest, overwrite u with numpy's fixed random numbers
if pytest:
np.random.seed(0)
new_shape = list(cdf.shape[:-1]) + [N_samples]
if det:
u = np.linspace(0., 1., N_samples)
u = np.broadcast_to(u, new_shape)
else:
u = np.random.rand(*new_shape)
u = torch.Tensor(u)
# Invert CDF
# weight에 따라 샘플링을 잦게 한다.
u = u.contiguous()
inds = torch.searchsorted(cdf, u, right=True)
# cdf 함수의 특징
# 1. 단조증가 함수이므로 정렬된 자료에만 쓸 수 있는 seachsorted() 함수를 사용해 y = u에와 대응하는 단 하나의 x값을 가짐.
# 2. 0부터 1까지의 값을 가지므로 모든 y = u에 일대일 대응하는 x값을 가짐.
# inds: y = u와 y=cdf의 교점의 x좌표 집합 (N_rays, N_samples)
# 인덱스들의 최대 한계
below = torch.max(
torch.zeros_like(inds-1), # inds-1과 같은 차원의 0으로 이루어진 텐서
inds-1 # inds의 모든 원소에서 1을 뺀 값.
)
# 이 두 텐서 중 최대 값을 골라 (inds[i,k]-1)이 음수가 될 수 있으면(예: inds=0 → inds-1=-1), 그것을 0으로 클램프(clamp)하는 효과.
above = torch.min(
# cdf.shape[-1] = M
# cdf.shape[-1]-1: M - 1 (즉 최고 인덱스)
(cdf.shape[-1]-1)*torch.ones_like(inds), # 차원이 inds와 동일하고, 모든 원소가 최고 인덱스로 이루어진 텐서
inds # 실제 인덱스 텐서
)
# 이 둘 중 최소값을 골라냄
# below: (N_rays, N_samples) … “구간 하한 인덱스”.
# above: (N_rays, N_samples) … “구간 상한 인덱스”.
# 이 두 텐서(below[i,k], above[i,k])는, i번째 광선, k번째 샘플에 대해 CDF 상에서 “인접 두 인덱스 (lower, upper)”를 담고 있음.
# 예) inds = 1: below = 0, above = 1
# 예) inds = 0: below = 0, above = 0
inds_g = torch.stack([below, above], -1)
# <shape>
# below.shape = (N_rays, N_samples)
# above.shape = (N_rays, N_samples)
# torch.stack([...], -1) → 마지막 축(-1)에 2개를 쌓음.
# ⇒ inds_g.shape = (N_rays, N_samples, 2).
# <세부 구분>
# inds_g[i,k,0] = below[i,k]
# inds_g[i,k,1] = above[i,k]
# inds_g에 해당하는 cdf, bin값을 얻는다.
matched_shape = [inds_g.shape[0], inds_g.shape[1], cdf.shape[-1]] # [N_rays, N_samples, M]의 리스트.
cdf_g = torch.gather(cdf.unsqueeze(1).expand(matched_shape), 2, inds_g)
# cdf: (N_rays, M)
# cdf.unsqueeze(1): (N_rays, 1, M)
# cdf.unsqueeze(1).expand(matched_shape): (N_rays, N_samples, M)
# inds_g: (N_rays, N_samples, 2)
# torch.gather(...): 해당 함수를 사용할 수 있도록 cdf의 1, 2차원을 맞춰준 뒤, 3차원에 대하여 inds_g의 인덱스에 해당하는 값 두 개(하한, 상한)을 뽑아온다.
bins_g = torch.gather(bins.unsqueeze(1).expand(matched_shape), 2, inds_g)
# inds_g의 인덱스에 해당하는 bins 값을 상한, 하한으로 가져온다.
# 즉, 특정 값 u를 포함하는 cdf(i), cdf(i + 1)과 bins(i), bins(i + 1)을 각각 cdf_g, bins_g에 담는다.
denom = (cdf_g[...,1]-cdf_g[...,0]) #below와 above의 차이를 분모로 사용한다
denom = torch.where(denom<1e-5, torch.ones_like(denom), denom) # denom이 너무 작아지면 분자를 1로 두도록
t = (u-cdf_g[...,0])/denom # 분자는 u에서 below를 뺀 값
# 즉, t = cdf(i)에서 u까지의 증가량 / cdf(i)에서 cdf(i + 1) 까지의 증가량
samples = bins_g[...,0] + t * (bins_g[...,1]-bins_g[...,0])
# 이 증가량을 bins(i)부터 bins(i + 1)까지의 증가량에 곱하여 선형적인 비율을 구한 후 bins (i)에 더해준다.
# 이로써 u가 정확히 어디 있는지 파악
return samplesdef sample_pdf_debug(bins, weights, N_samples=5, det=False, do_plot=False):
"""
Args:
bins: (M,) 구간 경계(또는 중간점) 좌표
weights: (M-1,) 각 구간에 대한 가중치
N_samples: 새로 뽑을 샘플 개수
det: True면 균등분할, False면 난수
do_plot: True면 matplotlib 그래프를 표시
Returns:
samples: (N_samples,) shape
새로 샘플링된 z좌표
"""
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1) weights -> pdf -> cdf
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 작은 숫자 더해 NaN 회피
weights = weights + 1e-5
pdf = weights / weights.sum() # pdf = weights / sum(weights) (M-1,)
# cdf는 pdf 누적합 => shape (M-1,)
cdf = torch.cumsum(pdf, dim=0) # (M-1,)
# 맨 앞에 0을 붙여 (M,)로 확장
cdf = torch.cat([torch.zeros(1), cdf], dim=0) # (M,)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2) uniform 샘플(u) 생성
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
if det: # 균등하게 0~1 분할하여 샘플링
u = torch.linspace(0., 1., steps=N_samples)
else: # 난수 샘플링
u = torch.rand(N_samples) # (N_samples,)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3) searchsorted(cdf, u) -> inds
# => u가 cdf의 어느 구간에 속하는지 인덱스
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# inds: 각 u에 대해 cdf 어디 구간인지
inds = torch.searchsorted(cdf, u, right=True)
# print(f"{'Variable':<10} {'Values'}")
print("=" * 30, "Variable Value", "=" * 30)
print(f"{'cdf':<10} {cdf}")
print(f"{'u':<10} {u}")
print(f"{'inds':<10} {inds}", end = "\n\n")
# => inds: u가 cdf의 몇 번째 인덱스로 삽입될 수 있는가
# 하한 인덱스, 상한 인덱스
below = torch.clamp(inds - 1, min=0)
above = torch.clamp(inds, max=cdf.shape[0]-1)
print(f"{'below':<10} {below}")
print(f"{'above':<10} {above}", end = "\n\n")
# -----------------------------
# 4) cdf, bins에서 아래/위 값
# -----------------------------
cdf_below = cdf[below] # (N_samples,)
cdf_above = cdf[above] # (N_samples,)
bins_below = bins[below] # (N_samples,)
bins_above = bins[above] # (N_samples,)
print(f"{'cdf_below':<10} {cdf_below}")
print(f"{'cdf_above':<10} {cdf_above}")
print(f"{'bins_below':<10} {bins_below}")
print(f"{'bins_above':<10} {bins_above}", end = "\n\n")
# 0나눗셈 회피
denom = (cdf_above - cdf_below)
denom = torch.where(denom < 1e-5, torch.ones_like(denom), denom)
print(f"{'denom':<10} {denom}")
# 선형 보간
t = (u - cdf_below) / denom
print(f"{'t':<10} {t}")
samples = bins_below + t * (bins_above - bins_below)
print(f"{'samples':<10} {samples}")
# => (N_samples,)
# -----------------------------
# (옵션) 그래프 디버그
# -----------------------------
if do_plot:
bins_np = bins.detach().cpu().numpy()
pdf_np = pdf.detach().cpu().numpy() # (M-1,)
cdf_np = cdf.detach().cpu().numpy() # (M,)
u_np = u.detach().cpu().numpy() # (N_samples,)
samp_np = samples.detach().cpu().numpy()
# figure
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
# (A) 상단 subplot: PDF vs midpoints
ax1 = plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.title("PDF")
width = (bins_np[-1] - bins_np[0]) * 0.03 # bar 너비 대략
plt.bar(bins_np, np.insert(pdf_np, 0, 0), width=width, alpha=0.6, label='pdf')
# bins_np (M, 1)이므로, pdf_np를 동일 차원으로 맞춰주기 위해 0번 인덱스에 0의 값을 추가
plt.xlabel("Z")
plt.ylabel("PDF")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# (B) 하단 subplot: CDF vs bins + 샘플 표시
ax2 = plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.title("CDF")
# cdf 라인: x=bins_np, y=cdf_np
plt.plot(bins_np, cdf_np, '-o', label='CDF')
# 텍스트 리스트 저장
texts = []
# u_i 값마다, 수평선 y=u_i, 교차점 x=samp_i
# 교점 시각화(수직선+수평선+점)
for k in range(N_samples):
yk = u_np[k] # u의 y 좌표
xk = samp_np[k] # u의 y 좌표와 CDF 함수가 만나는 교점의 x 좌표
# 수평선: y=yk, x from bins[0] to xk
ax2.hlines(yk, bins_np[0], xk, color='red', linestyles='dashed', alpha=0.6)
# 수직선: x=xk, y from 0 to yk
ax2.vlines(xk, 0, yk, color='red', linestyles='dashed', alpha=0.6)
# 교점(X)
ax2.scatter([xk],[yk], color='red', marker='x', zorder=5)
# 좌표 표시
text = ax2.text(xk, yk, f"(sample z = {xk:.2f}, u = {yk:.2f})", fontsize=10, ha='left', va='bottom', color='red')
texts.append(text)
adjust_text(texts, ax=ax2, expand_points=(2, 2), force_points=(0.2, 0.2))
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel("z")
plt.ylabel("CDF")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return samples
# 테스트 / 예시
if __name__ == "__main__":
# bins = (M,) => 여기서 M=4
# => 실제 구간 4개 => weights.shape=(4,)
# bins: z 구간 경계
bins_example = torch.tensor([2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5], dtype=torch.float32) # (4,)
# weights: bins 사이의 구간 3개 => shape=(3,)
weights_example = torch.tensor([0.05, 0.90, 0.05], dtype=torch.float32)
samples = sample_pdf_debug(bins_example, weights_example, N_samples=6,
det=False, do_plot=True)
print("samples:", samples)
============================== Variable Value ==============================
cdf tensor([0.0000, 0.0500, 0.9500, 1.0000])
u tensor([0.4663, 0.4623, 0.1814, 0.0709, 0.8433, 0.1471])
inds tensor([2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
below tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
above tensor([2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
cdf_below tensor([0.0500, 0.0500, 0.0500, 0.0500, 0.0500, 0.0500])
cdf_above tensor([0.9500, 0.9500, 0.9500, 0.9500, 0.9500, 0.9500])
bins_below tensor([3.5000, 3.5000, 3.5000, 3.5000, 3.5000, 3.5000])
bins_above tensor([4.5000, 4.5000, 4.5000, 4.5000, 4.5000, 4.5000])
denom tensor([0.9000, 0.9000, 0.9000, 0.9000, 0.9000, 0.9000])
t tensor([0.4625, 0.4581, 0.1459, 0.0233, 0.8814, 0.1079])
samples tensor([3.9625, 3.9581, 3.6459, 3.5233, 4.3814, 3.6079])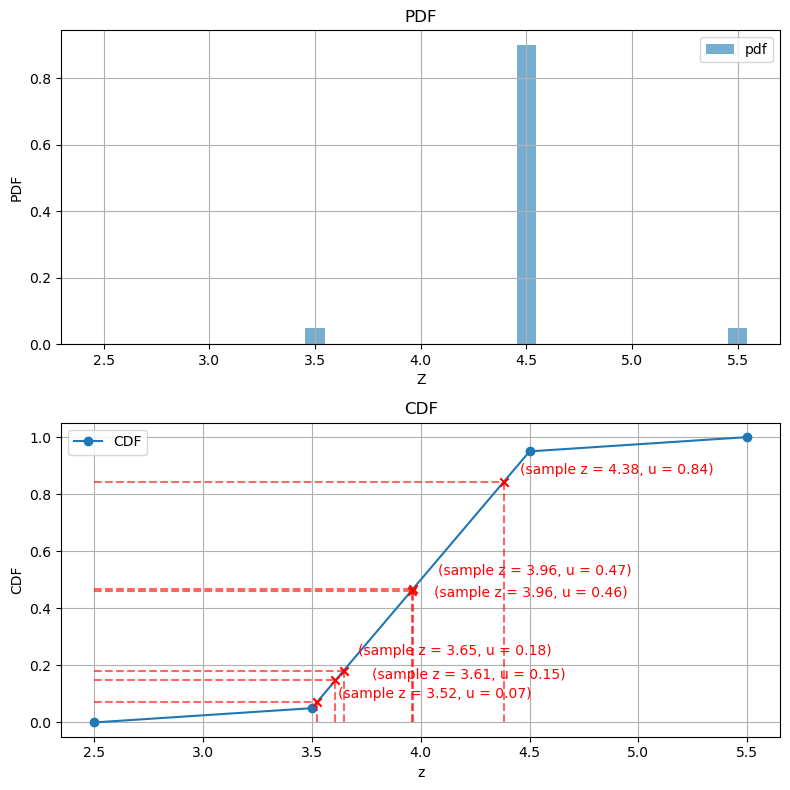
samples: tensor([3.9625, 3.9581, 3.6459, 3.5233, 4.3814, 3.6079])