1. CSS 개념
- 종속형 시트 또는 캐스케이딩 스타일 시트(Cascading Style Sheets, CSS)는 마크업 언어가 실제 표시되는 방법을 기술하는 스타일 언어(style sheet language)
2. CSS 문법

3. CSS 표기 순서
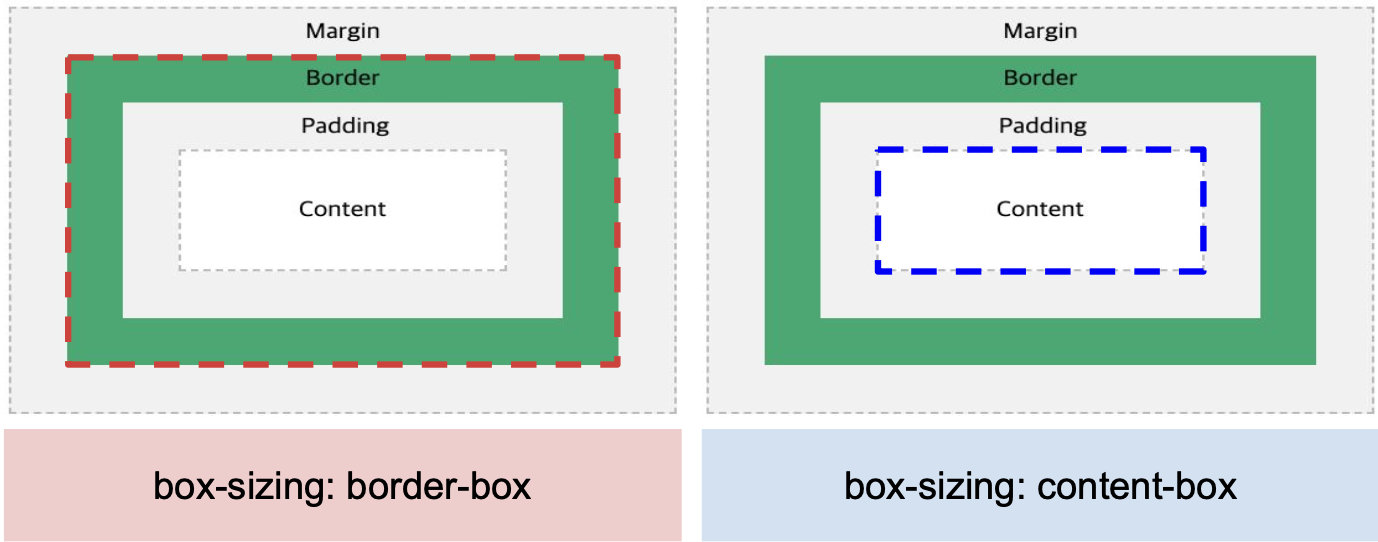
- box-sizing: border-box
- position: relative | absolute | fixed | sticky
- display: flex | block | inline | inline-block | none
- margin: 100px
- padding: 100px
- width: 100px
- height: 100px
- border: 1px solid #000
- background: #fff
- font-size: 16px
- font-weight: 300(thin) | 400(normal) | 500(medium) | 700(bold) | 900 (extra bold) color: #000
- text-align: center | left | right
- overflow: auto | scroll | hidden (사이즈보다 많은 text 기재 시 어떻게 보여줄 것인지)
- z-index: 1 (우선순위결정)
4. CSS Box Model
boxsizing : border-box; 해당 명령어를 사용하면 사이즈 수정 시 용이
1) 사용 전/후 비교
(1) 사용 전
- HTML
<div>123</div>- CSS
div{
padding : 24px;
border :10px solid #000;
width : 60px;
height : 60px;
background-color :red ;
}
![]()
(2) 사용 후
- HTML
<div>123</div>- CSS
div{
boxsizing : border-box;
padding : 24px;
border :10px solid #000;
width : 100px;
height : 100px;
background-color :red ;
}
5. Postion
ex1)
- HTML
<div>123</div>- CSS
position : relative;
top : 10px;
left : 10px;
width : 100px;
height : 100px;
background-color :red ;
}

ex2)
- HTML
<div>
<span>123</span>
</div>- CSS
div{
position : relative;
top : 10px;
left : 10px;
width : 100px;
height : 100px;
background-color :red ;
}
div span {
position : absolute;
top : 10px;
left : 10px;
}

6. 선택자
A. 기본 선택자
*(전체), div(요소), .(클래스), #(아이디),
[attr] (특성)
ex1)
- HTML
<div>123</div>
<p>123</p>
<a href="#">123</a>
<div class="box">
<p class="text1">123</p>
<span class="text2">123</span>
</div>- CSS
.box {
color: blue;
}
.box .text1{
color : pink;
}
ex2)
- HTML
<input type="text">
<img scr="#" alt="이미지의 설명">- CSS
input[type="text"]{
border-color : red;
}
img[alt] {
border : 1px solid blue;
}
B. 그룹선택자
,
ex1)
- HTML
<div class="box1">box1</div>
<div class="box2">box2</div>- CSS
.box1, .box2 {
color: red;
}
ex2)
- HTML
<div class="box border-box">box1</div>
<div class="box bg-box">box2</div>- CSS
.box{
font-size : 20px;
}
.box.border-box {
border : 10px solid red;
}
.box.bg-box {
background-color : blue;
}.box{
font-size : 20px;
&.border-box {
border : 10px solid red;
}
&.bg-box {
background-color : blue;
}
}
C. 결합자
(자손결합자), >(자식결합자), ~(일반형제결합자), +.(인접형제 결합자)
* 자손결합자 : 보통 한 칸의 공백 문자로 표현하는 자손 결합자(" ")는 두 개의 선택자를 조합하여, 뒤쪽 선택자 요소의 조상(부모, 부모의 부모, 부모의 부모의 부모...)에 앞쪽 선택자 요소가 존재할 경우 선택합니다. 자손 결합자를 활용하는 선택자를 자손 선택자라고 부릅니다.
* 자식결합자 : 자식 결합자(>)는 두 개의 CSS 선택자 사이에 위치하여 뒤쪽 선택자의 요소가 앞쪽 선택자 요소의 바로 밑에 위치할 경우에만 선택합니다.
* 일반형제결합자 : 일반 형제 결합자(~)는 두 개의 선택자 사이에 위치하여 뒤쪽 선택자의 요소와 앞쪽 선택자 요소의 부모 요소가 같고, 뒤쪽 선택자의 요소가 뒤에 위치할 때 선택합니다. 두 요소가 서로 붙어있을 필요는 없습니다.
* 인접형제결합자 : 인접 형제 결합자(+)는 앞에서 지정한 요소의 바로 다음에 위치하는 형제 요소만 선택합니다.ex1) 자식결합자
- HTML
<div>
<span>Span #1, in the div.
<span>Span #2, in the span that's in the div.</span>
</span>
</div>
<span>Span #3, not in the div at all.</span>- CSS
span {
background-color: gray;
}
div > span {
background-color: DodgerBlue;
}
ex2) 일반형제결합자
- HTML
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>- CSS
ul {
li ~ li {
color: red;
}
}
ex3) 인접형제 결합자
- HTML
<div>
<h1>h1 title</h1>
<p>Many persons have a wrong idea of what constitutes real happiness.
It is not obtained through self-gratification,
but through fidelity to a worthy purpose.
</p>
<p>
I can give you a six-word formula for success: Think things through--then follow through.
Edward V. Rickenbacker
</p>
</div>- CSS
div{
h1 + p {
color : red;
}
}
D. 가상 클래스 선택자
:hover, :focus, :focus-visible, :active, :checked, :disabled, :not()
:first-child, :last-child, :nth-child, :only-child
* hover : 마우스 커서를 위에 놓았을 때 색깔
* focus : tap 키를 눌렀을 때 색깔
* active : 마우스 커서를 누르고 나서 떼기 직전까지 색깔
* disabled : 사용자가 사용하지 못하는 것이라고 인식을 주기 위해 default로 흐린 색깔 적용 됨
* not : 다른 선택자와 접목하여 () 괄호 안에 조건이 아닐 경우 적용ex1) :hover, :focus, :focus-visible, :active, :disabled, :not()
- HTML
<button disabled>button</button>- CSS
button:not(:disabled):hover {
background-color : red;
}
button:focus-visible {
background-color : orange;
}
button:Active{
background-color : yellow;
}
button:disabled {
}ex2) :checked
- HTML
<input type="checkbox" id="chk1">
<label for="chk1">체크</label>- CSS
input[type="checkbox"]:checked + label {
color : blue;
}
ex3) first-child, :last-child, :nth-child, :only-child
- HTMl
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>- CSS
ul {
li {
border-top: 1px solid #ddd;
&:first-child {
color: red;
}
&:last-child {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
color: blue;
}
&:nth-child(3){
color: pink;
}
&:nth-child(2)~li {
font-size: 40px;
}
}
}
5. 가상 요소 선택자
::before, ::after, ::placeholder
ex1) ::before, ::after
- HTML
<ul>
<li>이용약관</li>
<li>개인정보처리방침</li>
<li>개인정보처리방침2</li>
</ul>- CSS
ul{
display: flex;
list-style: none;
}
li + li {
&::before {
content: 'l';
margin: 8px;
}
}
ex2) ::placeholder
- HTML
<input type="text" placeholder="이름을 입력하세요">- CSS
input {
font-size: 30px;
color: black;
&::placeholder {
color: blue;
}
}