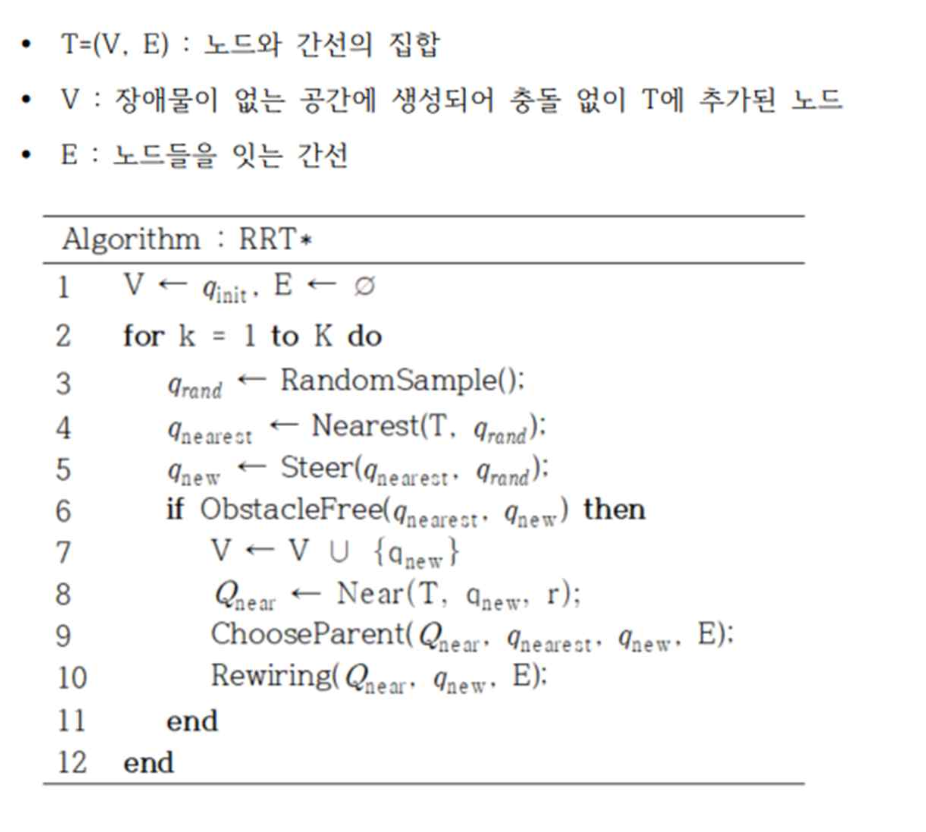
1. RRT* 알고리즘에 대하여
RRT* 알고리즘은 RRT 알고리즘과 기본 뼈대는 동일하다. 다만 RRT와 두 가지 차이점이 있는데, 첫째는 부모(parent)노드의 재선정이고, 둘째는 트리의 재구성(rewire)이다.
2. RRT* 알고리즘 개요
- Karaman에 의해 제안된 RRT 알고리즘에 기반하는 샘플링 기반 경로 계획 방법
- 신규 노드로 확장하는 방법이 개선
- 기존 노드 중 신규 노드의 일정 반경 내에 있는 노드들에 연결했을 때의 비용을 비교
- 가장 비용이 작은 노드를 부모 노드로 선택하여 연결
- 일정 반경 내 노드들의 비용과 신규 노드에 연결했을때의 비용을 비교
- 신규 노드에 연결했을 때의 비용이 더 작다면 트리를 재구성
- 의사코드
3. RRT* 알고리즘 순서
- Random Sampling
-상태 공간에서 무작위로 한 점()을 추출
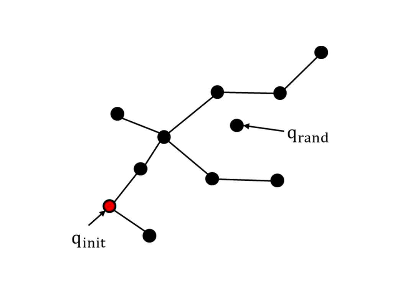
- Nearest
-트리 구조 T에서 랜덤 노드()에 가장 가까운 노드()를 탐색
- Steer
-로 부터 로의 경로 비용 도출
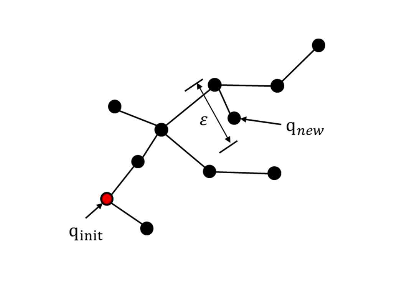
- Near
-이 추가되면, 로부터 특정 반경(r)내에 존재하는 노드의 집합 를 생성
그림에서()
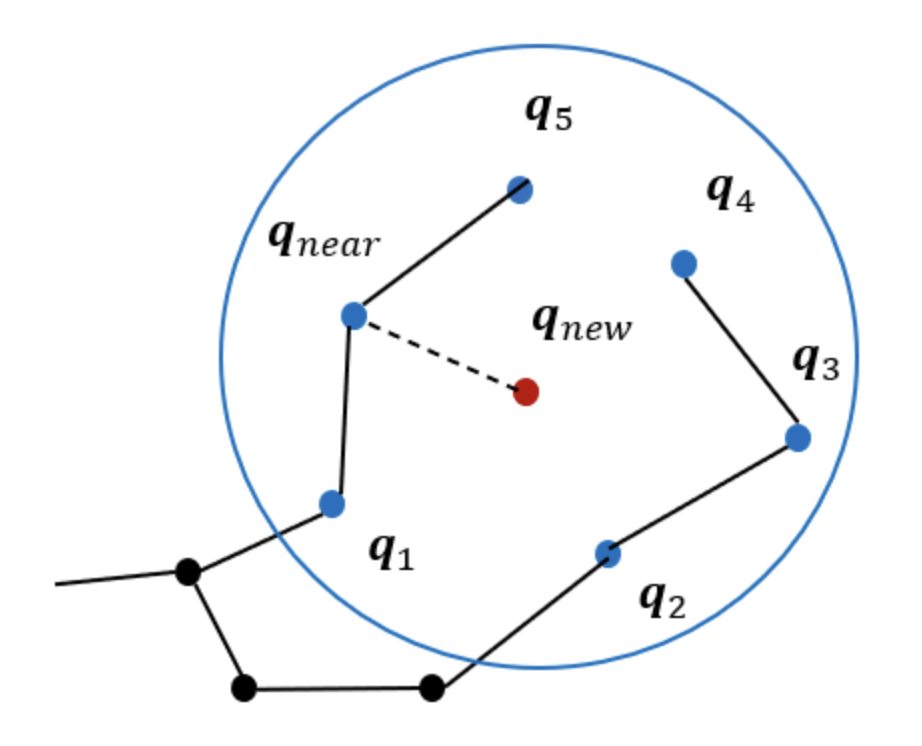
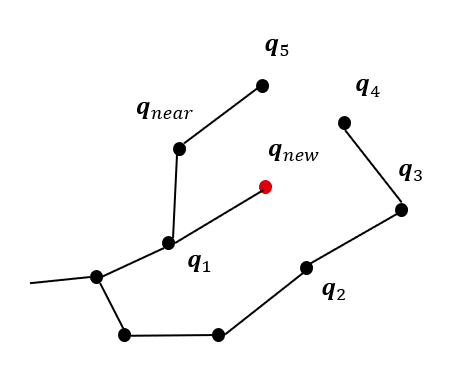
- ChooseParant
-새로운 노드 에 인접한 노드들()중, 와 연결 시 경로 비용이 최소가 되도록 하는 노드를 의 부모 노드로 설정
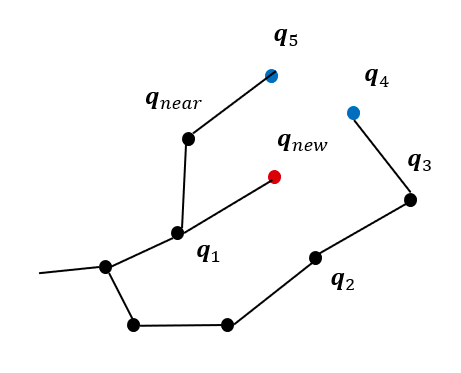
- Rewiring
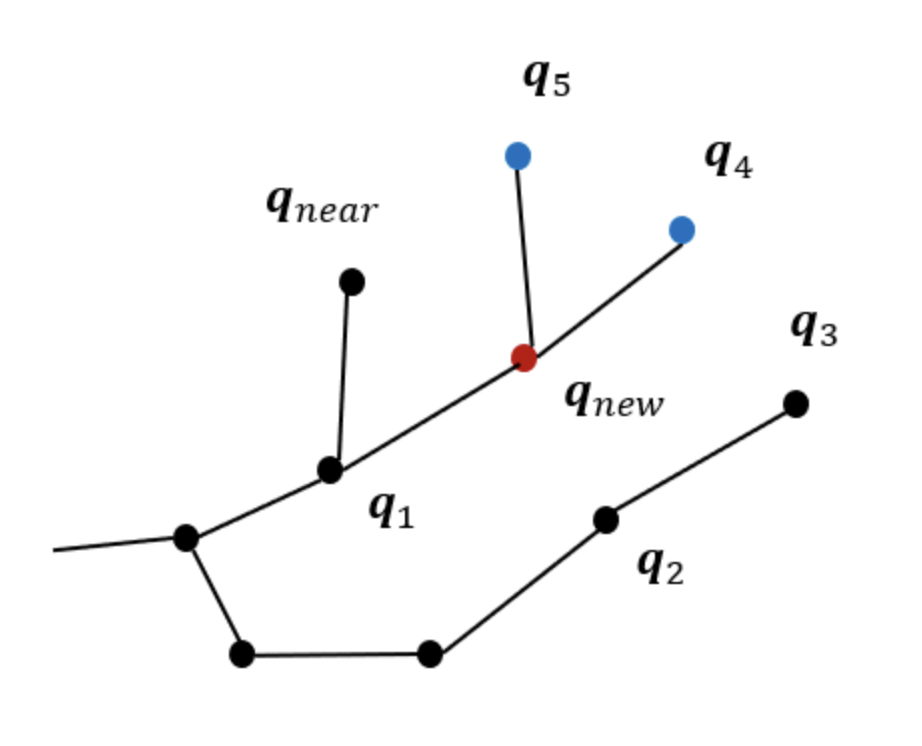
-트리의 재구성에서는 를 중심으로 일정한 반경에 있는 노드(그림)들이 새로운 노드 를 부모 노드로 설정할 때의 비용을 계산하여 기존 경로보다 에 연결할 때의 비용이 더 작다면, 해당 노드의 부모 노드를 로 수정 (그림에서 )
기존의 부모 노드와의 연결을 끊고, 의 자식 노드로 연결하여 트리를 재구성한다.(그림에서 의 부모 노드는 였지만 로 의 부모 노드는 였지만, 로 재구성 됨)
4. RRT* 알고리즘 특징
- 경로의 최적성
- 새로운 노드를 추가할 때, 경로 비용 등을 고려하여 연결 노드를 결정
- 또한, 기존의 구성된 트리 구조도 새로운 노드의 추가에 따라 경로 비용 등을 고려하여 구조를 수정
- 이로 인하여, 새로운 노드를 기존의 트리 구조에 추가하기만 하던 기존의 RRT 알고리즘 보다 적은 비용의 경로를 생성 가능
- 구현의 용이성
- 임의의 공간에서 무작위로 점을 생성하고 하나씩 연결하며 도착 지점까지 이를 반복
- 특정한 상황에서 보다 효과적으로 경로를 탐색 하도록 하는 것은 상황에 따른 설정이 필요하겠지만, 단순히 무작위로 점을 생성하고 트리를 연결하는 것은 다른 경로 계획 알고리즘들과 비교하면 상대적으로 쉽게 구현 가능
- 결과의 변동성
- RRT 및 RRT* 알고리즘은 무작위 샘플링에 기반하는 경로 계획 알고리즘
- 따라서, 같은 문제에서도 매 시행마다 다른 샘플링으로 인하여 다른 경로 계획 결과가 출력될 수 있음
5. RRT* 실습 코드
import numpy as np # 수학적 계산에 사용
import random # 난수 생성에 사용
import math # 수학 함수에 사용
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 그래프를 그리기 위해 사용
from matplotlib.patches import Circle, Rectangle # 원과 직사각형을 그리기 위해 사용
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation # 애니메이션을 만들기 위해 사용
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D # 선을 그리기 위해 사용
# 노드 클래스 정의
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y, parent=None, cost=0.0):
self.x = x # 노드의 x 좌표
self.y = y # 노드의 y 좌표
self.parent = parent # 부모 노드
self.cost = cost # 비용
# 유클리드 거리 계산 함수 정의
def euclidean_distance(node1, node2):
node_to_node_distance = math.sqrt((node1.x - node2.x)**2 + (node1.y - node2.y)**2) # 유클리드 거리 계산, 점과 점사이 거리 계산 공식
return node_to_node_distance
# 랜덤 노드 생성 함수 정의
def get_random_node(x_max, y_max):
x = random.uniform(0, x_max) # x 좌표를 0부터 x_max까지 랜덤하게 선택
y = random.uniform(0, y_max) # y 좌표를 0부터 y_max까지 랜덤하게 선택
return Node(x, y)
# 가장 가까운 노드 찾기 함수 정의
def get_nearest_node(rrt_nodes, rand_node):
min_distance = float('inf') # 최소 거리를 무한대로 초기화
nearest_node = None # 가장 가까운 노드
for node in rrt_nodes:
distance = euclidean_distance(node, rand_node) # 현재 노드와 랜덤 노드 사이의 거리 계산
if distance < min_distance:
min_distance = distance # 최소 거리 업데이트
nearest_node = node # 가장 가까운 노드 업데이트
return nearest_node
# 새로운 노드 생성 함수 정의
def create_new_node(nearest_node, rand_node, step_size):
theta = math.atan2(rand_node.y - nearest_node.y, rand_node.x - nearest_node.x) # 직선의 각도 계산
dist = min(step_size, euclidean_distance(nearest_node, rand_node)) # 직선의 길이 계산
new_x = nearest_node.x + dist * math.cos(theta) # 새로운 노드의 x 좌표 계산
new_y = nearest_node.y + dist * math.sin(theta) # 새로운 노드의 y 좌표 계산
new_node = Node(new_x, new_y) # 새로운 노드 생성
new_node.parent = nearest_node # 새로운 노드의 부모 설정
return new_node
# 목표에 도달했는지 확인하는 함수 정의
def goal_reached(goal_node, current_node, goal_radius):
return euclidean_distance(goal_node, current_node) < goal_radius # 목표와 현재 노드 사이의 거리가 목표 반경 내에 있는지 확인
# 원형 장애물 클래스 정의
class ObstacleCircle:
def __init__(self, x, y, radius):
self.x = x # 원의 중심 x 좌표
self.y = y # 원의 중심 y 좌표
self.radius = radius # 원의 반지름
def contains(self, point):
distance = euclidean_distance(point, self) # 장애물 중심과 점 사이의 거리 계산
return distance <= self.radius # 점이 장애물 안에 있는지 여부 반환
# 직사각형 장애물 클래스 정의
class ObstacleRectangle:
def __init__(self, x, y, width, height):
self.x = x # 직사각형의 왼쪽 상단 모서리 x 좌표
self.y = y # 직사각형의 왼쪽 상단 모서리 y 좌표
self.width = width # 직사각형의 너비
self.height = height # 직사각형의 높이
def contains(self, point):
return (self.x < point.x <= self.x + self.width and self.y <= point.y <= self.y + self.height) # 점이 직사각형 안에 있는지 여부 반환
# 점이 장애물 내에 있는지 확인하는 함수 정의
def is_point_in_obstacle(point, obstacle):
if isinstance(obstacle, ObstacleCircle):
return obstacle.contains(point) # 원형 장애물인 경우 점이 원 안에 있는지 여부 반환
elif isinstance(obstacle, ObstacleRectangle):
return obstacle.contains(point) # 직사각형 장애물인 경우 점이 직사각형 안에 있는지 여부 반환
return False
# 경로가 충돌이 없는지 확인하는 함수 정의
def is_collision_free(new_node, nearest_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max):
num_point = int(euclidean_distance(new_node, nearest_node) // 0.1) # 두 노드 사이의 점 개수 계산
vector = np.array([new_node.x - nearest_node.x, new_node.y - nearest_node.y]) / num_point # 두 노드 사이의 벡터 계산
point = np.array([nearest_node.x, nearest_node.y], dtype=np.float64) # 시작 점 설정
for i in range(num_point):
point += vector # 다음 점 위치 계산
if not (0 <= point[0] <= x_max and 0 <= point[1] <= y_max): # 경계를 벗어나는 경우
return False # 경계 밖으로 벗어남
for obstacle in obstacles: # 각 장애물에 대해
if is_point_in_obstacle(Node(point[0], point[1]), obstacle): # 장애물 내에 점이 있는지 확인
return False # 충돌이 발생함
return True # 충돌이 발생하지 않음
# RRT* 경로 계획 함수 정의
def rrt_star_path_planning(start_node, goal_node, x_max, y_max, step_size, goal_radius, max_iterations, obstacles, search_radius):
rrt_nodes = [start_node] # RRT 노드들을 저장할 리스트 초기화
for i in range(max_iterations): # 최대 반복 횟수만큼 반복
rand_node = get_random_node(x_max, y_max) # 랜덤 노드 생성
nearest_node = get_nearest_node(rrt_nodes, rand_node) # 랜덤 노드에 가장 가까운 노드 찾기
new_node = create_new_node(nearest_node, rand_node, step_size) # 새로운 노드 생성
if is_collision_free(new_node, nearest_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max): # 충돌이 발생하지 않는 경우
nearby_nodes = get_nearby_nodes(rrt_nodes, new_node, search_radius) # 근접한 노드들 찾기
min_cost_node = choose_min_cost_node(nearby_nodes, new_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max) # 최소 비용 노드 선택
if min_cost_node is not None: # 최소 비용 노드가 존재하는 경우
new_node.parent = min_cost_node # 새로운 노드의 부모 설정
new_node.cost = min_cost_node.cost + euclidean_distance(min_cost_node, new_node) # 새로운 노드의 비용 계산
rewire_nodes(nearby_nodes, new_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max) # 근접한 노드들의 부모를 새로운 노드로 설정
rrt_nodes.append(new_node) # 새로운 노드를 RRT 노드 리스트에 추가
if goal_reached(goal_node, new_node, goal_radius): # 목표에 도달한 경우
goal_node.parent = new_node # 목표 노드의 부모 설정
goal_node.cost = new_node.cost + euclidean_distance(new_node, goal_node) # 목표 노드의 비용 계산
print("Goal reached!") # 목표에 도달했다는 메시지 출력
return rrt_nodes, new_node # RRT 노드 리스트와 마지막 노드 반환
print("Max Iteration reached, goal not found") # 최대 반복 횟수에 도달했지만 목표에 도달하지 못한 경우
return rrt_nodes, None # RRT 노드 리스트와 None 반환
# 근처에 있는 노드들을 찾는 함수 정의
def get_nearby_nodes(rrt_nodes, new_node, search_radius):
nearby_nodes = [] # 근처에 있는 노드를 저장할 리스트 초기화
for node in rrt_nodes: # 각 노드에 대해
if euclidean_distance(node, new_node) < search_radius: # 주어진 반경 내에 있는 경우
nearby_nodes.append(node) # 근처에 있는 노드로 추가
return nearby_nodes # 근처에 있는 노드들을 리스트로 반환
# 최소 비용 노드 선택하는 함수 정의
def choose_min_cost_node(nearby_nodes, new_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max):
min_cost = float('inf') # 최소 비용을 무한대로 초기화
min_cost_node = None # 최소 비용 노드
for node in nearby_nodes: # 각 노드에 대해
if is_collision_free(new_node, node, obstacles, x_max, y_max): # 충돌이 발생하지 않는 경우
cost = node.cost + euclidean_distance(node, new_node) # 노드까지의 비용 계산
if cost < min_cost: # 최소 비용보다 작은 경우
min_cost = cost # 최소 비용 업데이트
min_cost_node = node # 최소 비용 노드 업데이트
return min_cost_node # 최소 비용 노드 반환
# 근접한 노드들의 부모를 새로운 노드로 설정하는 함수 정의
def rewire_nodes(nearby_nodes, new_node, obstacles, x_max, y_max):
for node in nearby_nodes: # 각 노드에 대해
if is_collision_free(new_node, node, obstacles, x_max, y_max): # 충돌이 발생하지 않는 경우
cost_through_new_node = new_node.cost + euclidean_distance(new_node, node) # 새로운 노드를 거쳐서 가는 비용 계산
if cost_through_new_node < node.cost: # 새로운 비용이 더 작은 경우
node.parent = new_node # 부모 노드를 새로운 노드로 설정
node.cost = cost_through_new_node # 비용 업데이트
# RRT 경로를 그리는 함수 정의
def plot_rrt(rrt_nodes, start_node, goal_node, obstacles, path_node):
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # 새로운 figure와 axes 생성
ax.set_xlim(0, x_max) # x 좌표 범위 설정
ax.set_ylim(0, y_max) # y 좌표 범위 설정
ax.grid(True) # 그리드 활성화
plot_obstacles(obstacles, ax) # 장애물 그리기
for node in rrt_nodes: # 각 노드에 대해
if node.parent: # 부모 노드가 있는 경우
ax.add_line(Line2D([node.parent.x, node.x], [node.parent.y, node.y], linewidth=1, color='black')) # 부모 노드와 현재 노드를 잇는 선 그리기
temp_node = path_node # 경로 노드 초기화
while temp_node: # 경로 노드가 있는 동안 반복
if temp_node.parent: # 부모 노드가 있는 경우
ax.add_line(Line2D([temp_node.parent.x, temp_node.x], [temp_node.parent.y, temp_node.y], linewidth=3, color='red')) # 부모 노드와 현재 노드를 잇는 빨간 선 그리기
temp_node = temp_node.parent # 부모 노드로 이동
nearest_node = get_nearest_node(rrt_nodes, goal_node) # 목표에 가장 가까운 노드 찾기
ax.add_line(Line2D([nearest_node.x, goal_node.x], [nearest_node.y, goal_node.y], linewidth=3, color='blue')) # 해당 노드와 목표를 잇는 파란 선 그리기
ax.scatter([start_node.x], [start_node.y], c='blue', s=50, label='Start') # 시작 노드 그리기
ax.scatter([goal_node.x], [goal_node.y], c='green', s=50, label='Goal') # 목표 노드 그리기
plt.legend() # 범례 표시
plt.show() # 그래프 출력
# 장애물 그리기 함수 정의
def plot_obstacles(obstacles, ax):
for obstacle in obstacles: # 각 장애물에 대해
if isinstance(obstacle, ObstacleCircle): # 원형 장애물인 경우
circle = Circle((obstacle.x, obstacle.y), obstacle.radius, color='gray', alpha=0.5) # 원 그리기
ax.add_patch(circle) # 원 추가
elif isinstance(obstacle, ObstacleRectangle): # 직사각형 장애물인 경우
rectangle = Rectangle((obstacle.x, obstacle.y), obstacle.width, obstacle.height, color='gray', alpha=0.5) # 직사각형 그리기
ax.add_patch(rectangle) # 직사각형 추가
# 경로의 비용 계산 함수 정의
def calculate_cost(path_node):
path = [path_node] # 경로 노드 리스트 초기화
while path_node != start_node: # 시작 노드에 도달할 때까지 반복
path_node = path_node.parent # 부모 노드로 이동
path.append(path_node) # 경로 노드 리스트에 추가
cost = 0 # 비용 초기화
for i in range(len(path) - 1): # 각 노드에 대해
cost += euclidean_distance(path[i], path[i + 1]) # 노드 간의 거리를 누적하여 비용 계산
return cost # 총 비용 반환
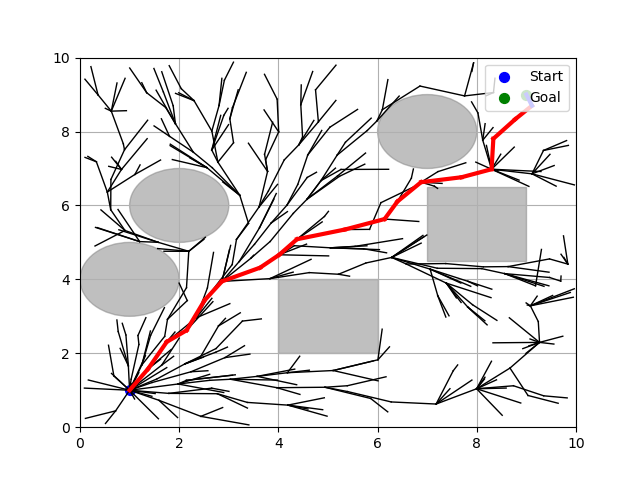
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 시작 노드, 목표 노드, 좌표 범위, 단계 크기, 목표 반경, 최대 반복 횟수, 장애물, 탐색 반경 설정
start_node = Node(1, 1) # 시작 노드 생성
goal_node = Node(9, 9) # 목표 노드 생성
x_max, y_max = (10, 10) # x, y 좌표의 최대값 설정
step_size = 0.5 # 단계 크기 설정
goal_radius = 0.5 # 목표 반경 설정
max_iterations = 1000 # 최대 반복 횟수 설정
# 장애물 생성
obstacles = [
ObstacleCircle(2, 6, 1),
ObstacleCircle(7, 8, 1),
ObstacleCircle(1, 4, 1),
ObstacleRectangle(4, 2, 2, 2),
ObstacleRectangle(7, 4.5, 2, 2)
]
# RRT* 경로 계획
rrt_nodes, path_node = rrt_star_path_planning(start_node, goal_node, x_max, y_max, step_size, goal_radius, max_iterations, obstacles, 2 * step_size)
if path_node: # 경로가 존재하는 경우
cost = calculate_cost(path_node) # 경로의 비용 계산
print("Cost of the final path : {0}".format(cost)) # 경로의 비용 출력
else: # 경로가 없는 경우
print("No path found") # 경로가 없다는 메시지 출력
# RRT 경로 그리기
plot_rrt(rrt_nodes, start_node, goal_node, obstacles, path_node)