1. 토픽
ROS2의 메시지 통신에 대해 설명할때 토픽에 대해 설명하였지만 다시 개념을 짚고 넘어가겠다.
토픽(Topic)은 비동기식 단방향 메시지 송수신 방식으로 메시지를 퍼블리시하는 퍼블리셔(Publisher)와 메시지를 서브스크라이브하는 서브스크라이버(Subscriber) 간의 통신이다. 이는 1:1 통신을 기본으로 하지만 복수의 노드에서 하나의 토픽을 송수신하는 1:N 도 가능하고, 그 구성 방식에 따라 N:1 , N:N 통신도 가능하다. 이는 ROS 메시지 통신에서 가장 널리 사용되는 통신 방법이다.
우리는 이번 장에서는 아래 그림과 같이 토픽을 생성한 시간과 연산에 사용할 변수 a, b 를 퍼블리시하는 토픽 퍼블리셔와 이를 서브스크라이브하는 토픽 서브스크라이버를 작성할 것이다. 만약 토픽에 대한 개념이 부족하다면
위 링크를 참고하면 된다.
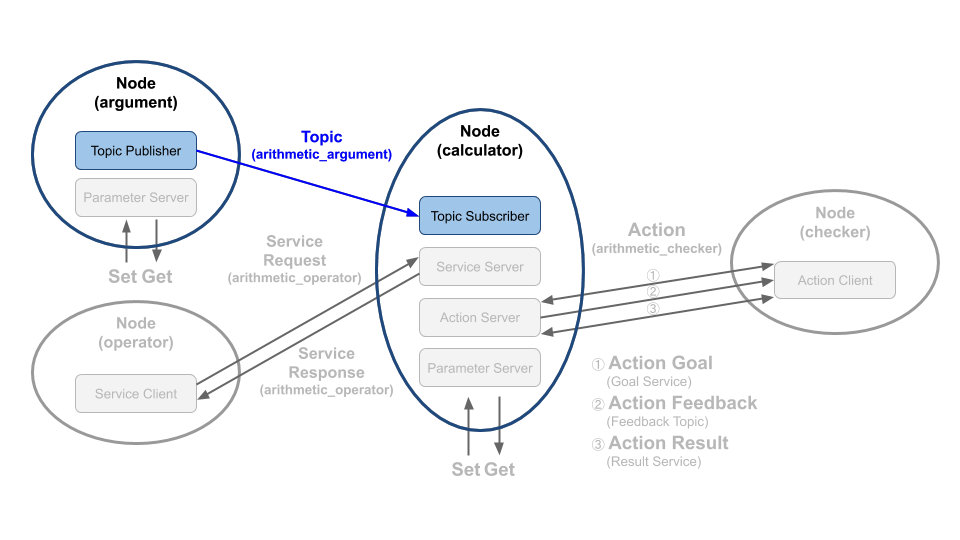
2. 토픽 퍼블리셔 코드
토픽 퍼블리셔의 전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
import random
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.msg import ArithmeticArgument
from rcl_interfaces.msg import SetParametersResult
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.parameter import Parameter
from rclpy.qos import QoSDurabilityPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSHistoryPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from rclpy.qos import QoSReliabilityPolicy
class Argument(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('argument')
self.declare_parameter('qos_depth', 10)
qos_depth = self.get_parameter('qos_depth').value
self.declare_parameter('min_random_num', 0)
self.min_random_num = self.get_parameter('min_random_num').value
self.declare_parameter('max_random_num', 9)
self.max_random_num = self.get_parameter('max_random_num').value
self.add_on_set_parameters_callback(self.update_parameter)
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher = self.create_publisher(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
QOS_RKL10V)
self.timer = self.create_timer(1.0, self.publish_random_arithmetic_arguments)
def publish_random_arithmetic_arguments(self):
msg = ArithmeticArgument()
msg.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
msg.argument_a = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
msg.argument_b = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher.publish(msg)
self.get_logger().info('Published argument a: {0}'.format(msg.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Published argument b: {0}'.format(msg.argument_b))
def update_parameter(self, params):
for param in params:
if param.name == 'min_random_num' and param.type_ == Parameter.Type.INTEGER:
self.min_random_num = param.value
elif param.name == 'max_random_num' and param.type_ == Parameter.Type.INTEGER:
self.max_random_num = param.value
return SetParametersResult(successful=True)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
argument = Argument()
try:
rclpy.spin(argument)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
argument.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
argument.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()차근차근 코드에 대해 알아보자.
Argument 클래스는 rclpy.node 모듈의 Node 클래스를 상속받고 있으며 생성자를 통해 노드 이름을 argument 로 초기화했다. 그 뒤 rclpy.qos 모듈의 QoSProfile 클래스를 이용하여 퇵 퍼블리셔에 사용할 QoS 설정을 해주었다.
class Argument(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('argument')
(일부 코드 생략)
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)제일 중요한 설정은 arithmetic_argument_publisher 선언이다. 이는 Node 클래스의 create_publisher 함수를 이용하여 퍼블리셔를 선언하는 부분으로 토픽의 타입은 ArithmeticArgument , 토픽의 이름은 arithmetic_argument , QoS는 위에서 설정한 QoS_RKL10V 를 사용하였다.
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher = self.create_publisher(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
QOS_RKL10V)그리고 마지막 줄에서는 create_timer 함수를 이용해 1초마다 publish_random_arithmetic_arguments 함수를 실행시키도록 설정하였다. 이전 설정들은 퍼블리시를 위한 기본 설정이고 실제 토픽 퍼블리시가 이루어지는 부분은 publish_random_arithmetic_arguments 함수임을 알아두자.
self.timer = self.create_timer(1.0, self.publish_random_arithmetic_arguments)다음으로 publish_random_arithmetic_arguments 함수를 알아보자. 이 함수는 지정 타이머로 동작하는 콜백함수이며, 우선 msg 변수를 지난 시간에 작성한 msg 인터페이스의 ArthmeticArgument() 클래스로 생성한다. msg.stamp 변수는 get_clock().now().to_msg() 함수를 통하여 토픽이 생성된 시간을 기록해두고, 랜덤 함수를 통해 0~9까지의 정수를 float 타입으로 변환하여 msg.argument_a 와 msg_argument_b 에 저장하였다.
그 뒤 이어지는 arithmetic_argument_publisher.publish(msg) 함수가 실제로 토픽을 퍼블리시 하는 함수로 퍼블리시한 시간 및 변수 a, b 를 저장한 메시지를 퍼블리시한다는 의미이다.
마지막으로 get_logger().info()난 주로 디버깅에 사용되는 함수로 노드를 실행한 터미널 창에 특정 값을 표시하게 된다. 여기서는 토픽으로 보낸 변수 a, b 값을 표시하고 있다.
def publish_random_arithmetic_arguments(self):
msg = ArithmeticArgument()
msg.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
msg.argument_a = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
msg.argument_b = float(random.randint(self.min_random_num, self.max_random_num))
self.arithmetic_argument_publisher.publish(msg)
self.get_logger().info('Published argument a: {0}'.format(msg.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Published argument b: {0}'.format(msg.argument_b))3. 토픽 서브스크라이버 코드
토픽 서브스크라이브 역할을 하는 calculator 노드의 소스코드는 다음과 같다.
import time
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.action import ArithmeticChecker
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.msg import ArithmeticArgument
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.srv import ArithmeticOperator
from rclpy.action import ActionServer
from rclpy.callback_groups import ReentrantCallbackGroup
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import QoSDurabilityPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSHistoryPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from rclpy.qos import QoSReliabilityPolicy
class Calculator(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('calculator')
self.argument_a = 0.0
self.argument_b = 0.0
self.argument_operator = 0
self.argument_result = 0.0
self.argument_formula = ''
self.operator = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
self.callback_group = ReentrantCallbackGroup()
self.declare_parameter('qos_depth', 10)
qos_depth = self.get_parameter('qos_depth').value
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)
self.arithmetic_argument_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
self.get_arithmetic_argument,
QOS_RKL10V,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
self.arithmetic_service_server = self.create_service(
ArithmeticOperator,
'arithmetic_operator',
self.get_arithmetic_operator,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
self.arithmetic_action_server = ActionServer(
self,
ArithmeticChecker,
'arithmetic_checker',
self.execute_checker,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
def get_arithmetic_argument(self, msg):
self.argument_a = msg.argument_a
self.argument_b = msg.argument_b
self.get_logger().info('Timestamp of the message: {0}'.format(msg.stamp))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument a: {0}'.format(self.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument b: {0}'.format(self.argument_b))
def get_arithmetic_operator(self, request, response):
self.argument_operator = request.arithmetic_operator
self.argument_result = self.calculate_given_formula(
self.argument_a,
self.argument_b,
self.argument_operator)
response.arithmetic_result = self.argument_result
self.argument_formula = '{0} {1} {2} = {3}'.format(
self.argument_a,
self.operator[self.argument_operator-1],
self.argument_b,
self.argument_result)
self.get_logger().info(self.argument_formula)
return response
def calculate_given_formula(self, a, b, operator):
if operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.PLUS:
self.argument_result = a + b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MINUS:
self.argument_result = a - b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MULTIPLY:
self.argument_result = a * b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.DIVISION:
try:
self.argument_result = a / b
except ZeroDivisionError:
self.get_logger().error('ZeroDivisionError!')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
else:
self.get_logger().error(
'Please make sure arithmetic operator(plus, minus, multiply, division).')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
def execute_checker(self, goal_handle):
self.get_logger().info('Execute arithmetic_checker action!')
feedback_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Feedback()
feedback_msg.formula = []
total_sum = 0.0
goal_sum = goal_handle.request.goal_sum
while total_sum < goal_sum:
total_sum += self.argument_result
feedback_msg.formula.append(self.argument_formula)
self.get_logger().info('Feedback: {0}'.format(feedback_msg.formula))
goal_handle.publish_feedback(feedback_msg)
time.sleep(1)
goal_handle.succeed()
result = ArithmeticChecker.Result()
result.all_formula = feedback_msg.formula
result.total_sum = total_sum
return result이 소스코드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버를 모두 포함하고 있어서 매우 길다. 이 장에서는 전체 소스코드중 토픽 서브스크라이버와 관련된 코드만 살펴보겠다.
우선 Calculator 클래스인데 토픽 퍼블리셔 노드와 마찬가지로 rclpy.node 모듈의 Node 클래스를 상속하고 있으며, 생성자를 통해 노드 이름을 calculator 로 초기화했다. 그 뒤 위에서와 마찬가지로 rclpy.qos 모듈의 QoSProfile 클래스를 이용하여 토픽 서브스크라버에서 사용할 QoS 설정을 해주었다. 여기서 QoS는 앞서 설명한 토픽 퍼블리셔 노드와 동일하게 RELIABLE, KEEP_LAST, DEPTH 10, VOLATILE로 설정하였다
class Calculator(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('calculator')
self.argument_a = 0.0
self.argument_b = 0.0
self.callback_group = ReentrantCallbackGroup()
(일부 코드 생략)
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)제일 중요한 설정은 arithmetic_argument_subscriber 선언이다. 이는 Node 클래스의 create_subscriber 함수를 이용하여 서브스크라이버를 선언하는 부분으로 토픽으 타입은 퍼블리셔와 동일하게 ArithmeticArgument 으로 선언하였고, 토픽 이름은 arithmetic_argument, QoS는 위에서 설정한 QOS_RKL10V를 사용하였다.
여기까지는 퍼블리셔와 비슷한데 퍼블리셔와 다른점은 get_arithmetic_argument 콜백 함수를 두어 퍼블리셔로부터 메시지를 서브스크라이브할 때마다 실행되는 함수를 지정한 것이다. 그리고 callback_group을 ReentrantCallbackGroup으로 지정했는데 콜백함수를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게 해주며 뒤에서 설명할 MultiThreadedExecutor와 함께 사용되곤 한다.
좀더 자세히 callback_group을 설명하자면 원래 callback_group을 지정하지 않게 되면 MutuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup이 기본 설정으로 사용된다. MutuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup 설정은 한 번에 하나의 콜백 함수만 실행하도록 허용하는 것이다. 이에 반해 ReentrantCallbackGroup 설정은 제한 없이 콜백 함수를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게 해준다. 이러한 callback_group 설정은 create_subscription(), create_service(), ActionServer(), create_timer() 에서 사용됨을 알아두도록 하자.
self.arithmetic_argument_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
self.get_arithmetic_argument,
QOS_RKL10V,
callback_group=self.callback_group)get_arithmetic_argument 함수는 앞서 콜백 함수라 설명하였다. 이 함수는 arithmetic_argument 토픽으로 ArithmeticArguemt 타입의 메시지를 서브스크라이브하게 되면 실행된다. 서브스크라이브한 메시지의 argument_a 와 argument_b를 멤버 변수에 저장하고 get_logger().info() 함수를 이용하여 토픽으로 받은 시간, 변수 a, b 값을 화면에 표시하게 된다.
def get_arithmetic_argument(self, msg):
self.argument_a = msg.argument_a
self.argument_b = msg.argument_b
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed at: {0}'.format(msg.stamp))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument a: {0}'.format(self.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument b: {0}'.format(self.argument_b))4. 토픽 퍼블리셔, 서브스크라이버 정리
1) 토픽 퍼블리셔 (데이터를 송신하는 프로그램)
1) Node 설정
2) QoS 설정
3) create_publisher 설정
4) 퍼블리시 함수 작성
2) 토픽 서브스크라이버 (데이터를 수신하는 프로그램)
1) Node 설정
2) QoS 설정
3) create_subscription 설정
4) 서브스크라이브 함수 작성
5. 노드 실행 코드
이번에는 이 실행 노드를 어떻게 설정해야 사용이 가능하게 되는지 알아보자. 이번 장에서 사용할 두개의 노드 실행 명령어는 다음과 같다. caculator 가 토픽 서브스크라이버 노드이고, argument 는 토픽 퍼블리셔 노드이다.
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example caculator$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example argument이 두 개의 노드는 앞전의 setup.py 의 entry_points 부분에서 이미 설명하였던 부분이다. entry_points는 설치하여 사용할 실행 가능한 콘솔 스크립트의 이름과 호출 함수를 기입하도록 되어 있는데 우리는 4개의 노드를 작성하고 ros2 run 과 같은 노드 실행 명령어를 통하여 각각의 노드를 실행할 예정이기에 하기와 같이 entry_points를 추가했었다.
argument 노드는 topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 arithmetic 폴더에 argument.py의 main문에 실행 코드가 담겨져 있고, calculator 노드는 topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 calculator 폴더에 main.py의 main문에 실행 코드가 담겨져있다. 약간 다름에 주의하도록하자.
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'argument = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.argument:main',
'operator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.operator:main',
'calculator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.main:main',
'checker = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.main:main',
],
},우선 argument 노드부터 살펴보자. main 함수 안에서 rclpy.init 함수로 프로그램을 초기화한다. 그리고 앞에서 작성한 Argument 클래스를 argument 객체로 생성한 다음 rclpy.spin() 함수를 이용해 생성한 노드를 spin 시킴으로서 선언된 콜백 함수가 호출될 수 있도록 했다. (spin은 그냥 토픽을 퍼블리시해주는 장치라고 생각하면됨)
그리고 종료(Ctrl + c)와 같은 인터럽트 시그널 예외 상황에서는 argument 노드를 소멸시키고 rclpy.shutdown 함수로 프로그램을 종료하게 된다.
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
argument = Argument()
try:
rclpy.spin(argument)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
argument.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
argument.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()다음으로 아래의 calculator 노드를 살펴보자. main 함수로 rclpy.init를 이용하여 초기화하고 위에서 작성한 Calculator 클래스를 calculator라는 이름으로 생성한 다음 MultiThreadedExecutor로 스레드 4개를 사용하는 executor를 생성하였다.
여기서 생소한 MultiThreadedExecutor이 나왔는데 MultiThreadedExecutor는 스레드 풀(thread pool)을 사용하여 콜백을 실행하는 것이다. num_threads로 스레드 수를 지정 가능하며 이를 지정되지 않은 경우 multiprocessing.cpu_count()를 통해 시스템에서 가용한 스레드 수를 지정받게 된다. 이 둘 모두 해당되지 않는다면 단일 스레드를 사용하게 된다. 이 Executor는 콜백이 병렬로 발생하도록 허용하여 앞서 설명한 ReentrantCallbackGroup와 함께 사용하면 콜백함수를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게된다. 그 말인즉슨 create_subscription(), create_service(), ActionServer(), create_timer() 등의 함수를 이용하여 설정한 토픽 퍼블리셔의 콜백함수, 서비스 서버의 콜백함수, 액션 서버의 콜백함수, 특정 타이머의 콜백함수 등의 병렬 처리를 설정하는 방법이라고 보면 된다. --> 한개의 노드에서 여러개의 토픽, 서비스, 액션을 처리해야하기때문에 사용
이어서 설명하면 MultiThreadedExecutor으로 선언된 executor에 calculator 노드를 추가하고 executor.spin() 이용하여 생성한 노드를 spin시켜 지정된 콜백함수가 실행될 수 있도록 하고 있다. 그리고 종료 Ctrl + c와 같은 인터럽트 시그널 예외 상황에서는 executor, calculator의 액션 서버(액션 서버는 별도로 소멸시켜야함), calculator를 소멸시키고 rclpy.shutdown 함수로 노드를 종료하게 된다.
import rclpy
from rclpy.executors import MultiThreadedExecutor
from topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.calculator import Calculator
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
calculator = Calculator()
executor = MultiThreadedExecutor(num_threads=4)
executor.add_node(calculator)
try:
executor.spin()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
calculator.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
executor.shutdown()
calculator.arithmetic_action_server.destroy()
calculator.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()ROS2 토픽 프로그래밍에 대해 알아보았다. 다음에 이어지는 장에서는 서비스 프로그래밍 코드를 분석해보는 시간을 가져보겠다.
