사전 지식
- 고차 함수
함수를 인수로 전달받거나, 함수를 반환받는 함수
고차 함수를 통해 외부 상태의 변경이나 가변 데이터를 피하고 불변성을 지향할 수 있다. - 콜백 함수
매개변수를 통해 다른 함수의 내부로 전달되는 함수
즉, 인수에 함수가 있는 함수는 고차함수. 이렇게 인수에 존재하는 함수는 콜백함수. 라고 정리할 수 있다.
고차 함수, 콜백 함수를 사용하는 이유
1. 함수의 효율성/가독성을 위해
함수의 기본 원칙 중에는 "하나의 함수는 하나의 역할만 담당한다" 가 있다.
함수 단위가 작아질수록, 함수의 재사용성이 높아지고, 함수의 이름을 통해 직관적으로 함수가 어떤 동작을 하는지 쉽게 유추할 수 있다.
아래의 코드를 보자.
case 1. 일반적인 함수 사용
function sum1(a,b){ console.log(a+b) } function sum2('결과는 ',a,b){ console.log(a+b) } sum1(2,3) // 5 출력 sum2(2,3) // "결과는 5" 출력
case 2. 콜백 함수를 사용
function sum(a,b,callback){ return callback(a+b) } function printData(data){ console.log(print) } function printResult(data){ console.log('결과는 ',data) } sum(2,3,(data)=>console.log(data)) // 5 출력 sum(2,3,printData) // 5 출력 sum(2,3,printResult) // "결과는 5" 출력
case 1같은 경우에는 sum1 함수가 출력과 덧셈 계산 2개를 담당하고 있다.
지금은 코드량이 적어서 큰 차이는 없지만, 나중에 코드 길이가 늘어나고 담당하는 부분이 많아질수록 높은 결합도가 생긴다.
높은 결합도는 함수를 유연하지 못하게 만든다.
함수가 유연하다는 것은 무슨 뜻일까? case 2가 대표적인 예시이다.
case 2에서 sum 함수는 연산만 담당하고, 나머지 printData, printResult 함수는 출력만 담당한다.
이렇게 역할을 분리시키면, 콜백 함수만 바꿔도 sum 결과를 마음대로 다룰 수 있다.
즉, 함수가 유연해지고 재사용성이 높아진다.
2. 비동기 처리
콜백 함수는 비동기 처리에도 많이 사용된다.
case 1
function first(){ setTimeout(() => { console.log("first") }, 300) } function second(){ console.log("second") } frist() second() // "second" 출력 => "first" 출력
case 2
function first(callback){ setTimeout(() => { console.log("first") callback() }, 300) } function second(){ console.log("second") } frist(second) // "first" 출력 => "second" 출력
case 1에서 분명 frist() 함수를 먼저 실행했는데, 출력은 second가 먼저 출력된다.
어? 자바스크립트는 위에서 아래로 실행되는거 아니였어요? 라는 의문이 생길수도 있는데, 이는 자바스크립트의 비동기 처리 방식때문에 setTimeout 함수는 가장 늦게 실행된다.
따라서 first=>second와 같이 순차적으로 코드를 실행시키고 싶으면, setTimeout의 콜백 함수 자리에 해당 함수를 넣어주면 된다.
Array.prototype.고차함수 구현하기
자 이제 드디어 본론에 왔다. 앞서의 지식들을 바탕으로 배열 고차함수를 구현할 수 있다.
Array.prototype.map()
특징
원본 배열을 변경시키지 않는, 콜백 함수의 반환값으로 구성된 새로운 배열을 반환하는 함수.
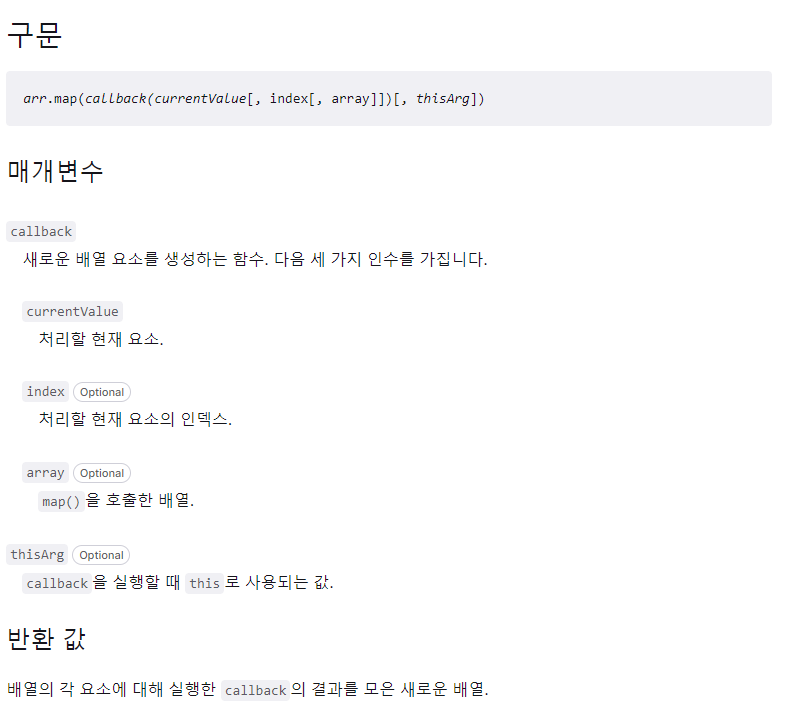
1차 구현(without thisArg)
currentValue,index,array,thisArg를 모두 처리해야 한다.
구현하기 전 우선 우리가 쓰던 map 함수가 어떤 형태였는지 다시 한 번 확인해보자.
['a','b','c','d'].map((el,i,arr)=>console.log(el,i,arr))
// a 0 ['a','b','c','d']
// b 1 ['a','b','c','d']
// c 2 ['a','b','c','d']
// d 3 ['a','b','c','d']구현하기 전 생각했던 것들
-
평소에는 무심코 지나쳤는데, 알고보니 map은 콜백 함수를 가지고 있는 고차함수였다.
콜백 함수에 들어가는 인자 => currentValue, index, array
-
map은 배열을 순회하는 함수이기 때문에 for문의 사용이 필요해보인다.
-
map은 새로운 배열은 반환해야 하므로, 함수 내부에서 배열을 만들고, 이를 return해야 할 것 같다.
구현
const customMap = function(callback){
const arr = [];
for(let i=0;i<this.length;i++){
callback(this[i],i,this);
arr.push(this[i]);
}
return arr;
}
Array.prototype.customMap = customMap;
['a','b','c','d'].customMap((el,i,arr)=>console.log(el,i,arr)) // 기존 map과 같은 결과 나옴-
배열을 순회하면서 callback() 함수가 실행되는데, 이는
console.log(el,i,arr)부분이다. -
배열을 순회하면서 customMap 내부의 arr에
this[i](여기서 this는 customMap을 호출한 객체인 ['a','b','c','d'])를 넣어준다.
2차 구현(with thisArg)
첫 번째로 구현했을 때에는, thisArg를 넣지 않았다.
그 이유는 thisArg에 대한 이해가 부족했기 때문인데, 여기서 thisArg를 설명하며 Array.prototype.map 구현까지 마무리짓도록 하겠다.
thisArg
callback을 실행할 때 this로 사용하는 값.
쉽게 풀이하자면 thisArg 자리에 들어가는 객체에 this를 바인딩하겠다(in 콜백 함수)는 뜻이다.
더 빠른 이해를 위해 예제를 들어보겠다.
const user = {name:'jamong',age: 23}
[1,2,3,4].map(function(){console.log(this)})
/* Window {0: Window, window: Window, self: Window, document: document, name: '', location: Location, …}
... 출력 */만약, thisArg 인자를 주지 않으면 콜백 함수 내부의 this는 전역 객체를 가리킨다.
const user = {name:'jamong',age: 23}
[1,2,3,4].map(function(){console.log(this)})
/* {name: 'jamong', age: 23}
... 출력 */하지만 만약 thisArg에 user를 넣으면 해당 객체에 this가 바인딩되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
구현하기 전 생각했던 것들
-
this 바인딩을 위해서는
Function.prototype.bind()를 사용할 필요가 있어보인다. -
콜백 함수 내부 this가 thisArg에 바인딩되어야 하므로,
callback.bind(thisArg)();와 같이 사용하면 될듯하다.
구현
const customMap = function(callback,thisArg){
const arr = [];
for(let i=0;i<this.length;i++){
callback.bind(thisArg)(this[i],i,this);
arr.push(this[i]);
}
return arr;
}
const user = {name: 'jamong'}
Array.prototype.customMap = customMap;
['a','b','c','d'].customMap(function(el,i,arr){console.log(el,i,arr,this)},user) // 기존 map과 같은 결과 나옴❗ 주의할 점
만약 콜백 함수가화살표 함수로 작성되었다면, thisArg는 아무 작업도 수행하지 않는다.
"화살표 함수의 this는 언제나 상위 스코프의 this를 가리킨다" 는 특징으로 인해 화살표 함수에서는 call, apply, bind 메소드를 사용해 this를 변경할 수 없다.
Array.prototype.filter()
특징
원본 배열을 변경시키지 않는, 콜백 함수의 테스트를 통과하는 모든 요소를 모아 새로운 배열로 반환하는 함수
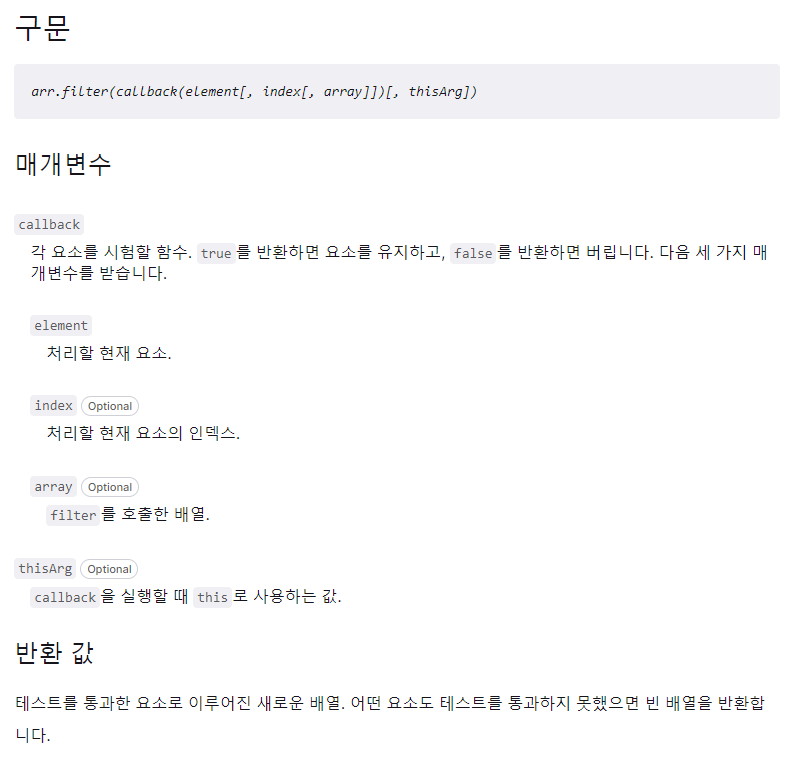
구현
구현하기 전 생각했던 것들
- 앞서 구현했던 map을 응용해 테스트 결과인 true/false에 따라 true만 배열에 넣어주면 될 것 같다.
구현
const customFilter = function(callback,thisArg){
const arr = [];
for(let i=0;i<this.length;i++){
callback.bind(thisArg)(this[i],i,this) && arr.push(this[i]);
}
return arr;
}
Array.prototype.customFilter = customFilter;
const user = { name: "b", age: 23 };
let arr = ['a','b','c','d'].customFilter(function(el,i,arr){return el===this.name},user)
console.log(arr) // ["b"] 출력- this.name은 'b'이므로,
el===this.name은 el이 'b'일 때 true가 된다.
따라서 콜백 함수가 true를 return 하면 arr에 해당 값이 추가되도록 구현하였다.
Array.prototype.forEach()
특징
원본 배열을 변경시키지 않는, 주어진 함수를 배열 요소 각각에 대해 실행하는 함수
map과 forEach의 큰 차이점으로는 map 메서드는 콜백 함수의 반환값들로 구성된 새로운 배열을 반환하는 반면, forEach 메서드는 언제나 undefined를 반환한다는 점이다.
즉, forEach는 단순히 배열 대체 고차함수이다.
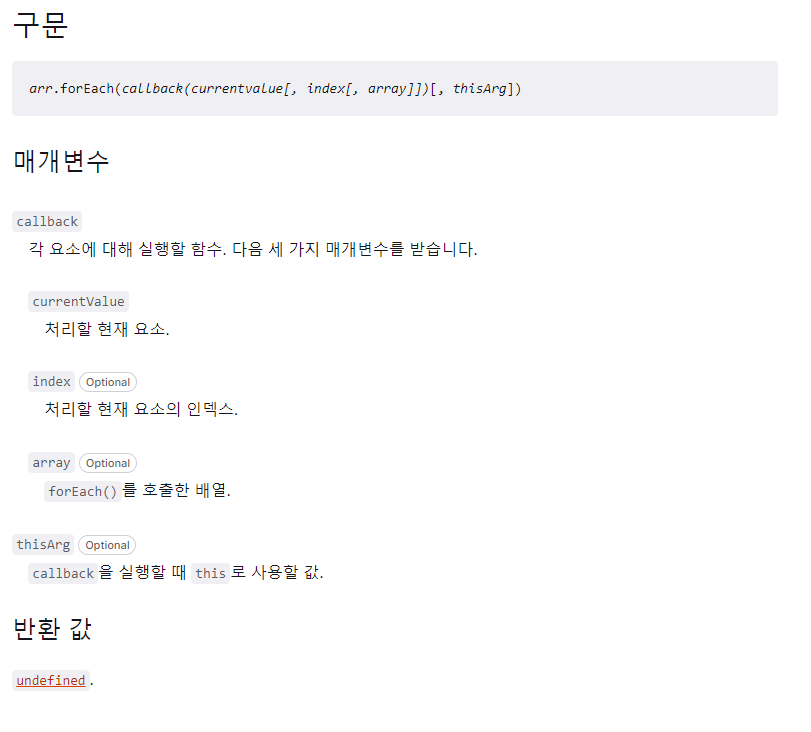
구현
구현하기 전 생각했던 것들
- map의 return 부분을 undefined로 해주면 forEach가 될 것 같다.
구현
const customForEach = function(callback, thisArg) {
const arr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
callback.bind(thisArg)(this[i], i, this);
arr.push(this[i]);
}
return undefined;
}
const user = {name: 'jamong'}
Array.prototype.customForEach = customForEach;
['a','b','c','d'].customForEach(function(el, i, arr) {
console.log(el, i, arr, this)
}, user) // 기존 forEach와 출력 동일- 고차함수 return 부분을 undefined 처리해줌
Array.prototype.reduce()
특징
원본 배열을 변경시키지 않는, 배열의 각 요소에 대해 reducer 함수를 실행하고 결과값을 반환하는 함수
reducer 함수
누적해서 값을 처리해나가는 함수
인자: (누산기, 현재 값, 현재 인덱스, 원본 배열)
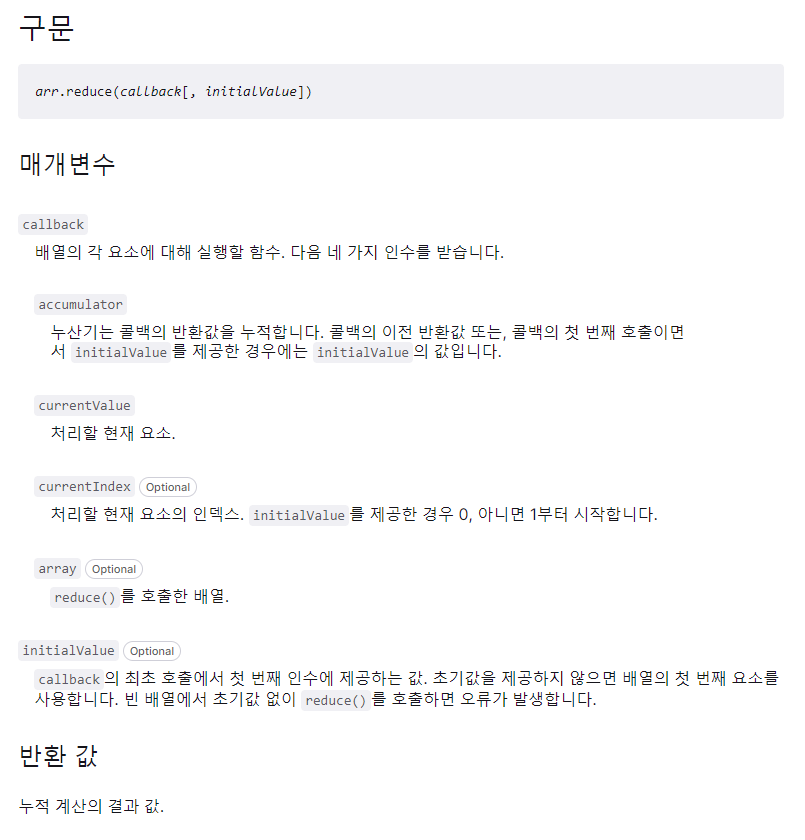
구현
구현하기 전 생각했던 것들
-
reduce()의 매개변수에
initialValue가 있으면[initialValue,...기존 배열]에서의 첫 인덱스부터 누적값을 구한다.
initalValue가 없으면기존 배열의 첫 인덱스부터 시작해 누적된 값을 구한다. -
콜백함수의 return 값을 계속해서 누적합해야 한다.
1차 구현
const customReduce = function(callback, initialValue) {
if(this
let acc = initialValue ? callback(initialValue, this[0], 0, this) : this[0]
if(this.l
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
acc = callback(acc, this[i], i, this);
}
return acc;
}
Array.prototype.customReduce = customReduce;
[0,1,2,3,4].customReduce((acc,cur,i,arr)=>{
console.log(acc,cur,i,arr)
return acc + cur},10)- reduce 함수 내부에 acc를 선언하고, 이를 누적값으로서 사용했다.
- initialValue 존재 유무에 따라 초기값을 세팅해주었다.
2차 구현
첫 번째 구현을 마치고 reduce에 대한 MDN 문서를 다시 천천히 읽어보니 예외 처리를 하지 않은 부분이 있었다. 따라서 해당 예외처리를 추가로 해주었다.
const customReduce = function(callback, initialValue) {
if(this.length===0){
if(initialValue!==undefined){
return initialValue
}else{
return console.error('Uncaught TypeError: Reduce of empty array with no initial value')
}
}
let acc = initialValue ? callback(initialValue, this[0], 0, this) : this[0]
if(this.length>1){
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
acc = callback(acc, this[i], i, this);
}
}
return acc;
}
Array.prototype.customReduce = customReduce;
[0,1,2,3,4].customReduce((acc,cur,i,arr)=>{
console.log(acc,cur,i,arr)
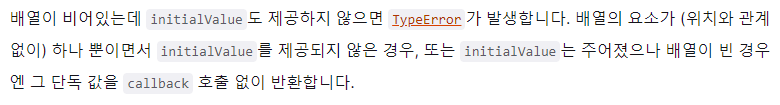
return acc + cur},10)- 주어진 배열이 비어있을 때,
- initialValue가 없을 경우 => TypeError 발생
- initialValue가 있을 경우 => callback 호출 없이
initialValue 출력
참고
https://solveaproblem.dev/javascript-callback-function/
https://www.daleseo.com/js-async-callback/
https://ktpark1651.tistory.com/215
https://tesseractjh.tistory.com/175
