Introduction
In this work we propose the Transformer, a model architecture eschewing recurrence and instead relying entiredly on an attention mechanism to draw dependencies between input and ouput.
Background
In the Transformer this(the number of operations required to relate signals from two arbitrary input or output positions grows
in the distance between positions) is reduced to a constant number of operations, albeit at the cost of reduced effective resolution due to averaging attention-weighted positions, an effect we counteract with Multi-Head Attention.
Self-attention, sometimes called intra-attention is an attention mechanism relating different positions of a single sequence in order to compute a representation of the sequence.
End-to-end memory networks are based on a recurrent attention mechanism and have been shown to perform well on simple-language question answering and language model tasks.
Model Architecture
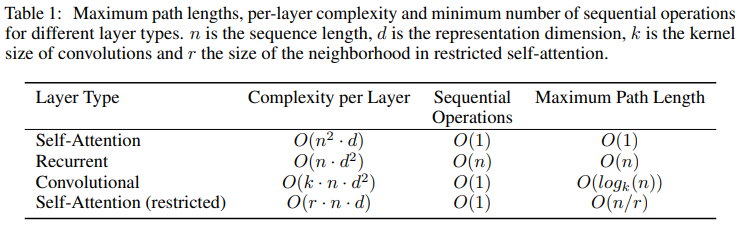
The encoder maps an input sequece of symbol representations to a sequence of continuous representations . Given z, the decoder then generates an output sequence of symbols one element at a time. At each step the model is auto-regressive, consuming the previously generated symbols as additional input when generating the next.
Encoder and Decoder Stacks
Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple position-wise fully connected feed-forward network.
Decoder: In addition to the two sub-layers in each encoder layer, the decoder inserts a third sub-layer, which performs multi-head attention over the output of the encoder stack.
Attention
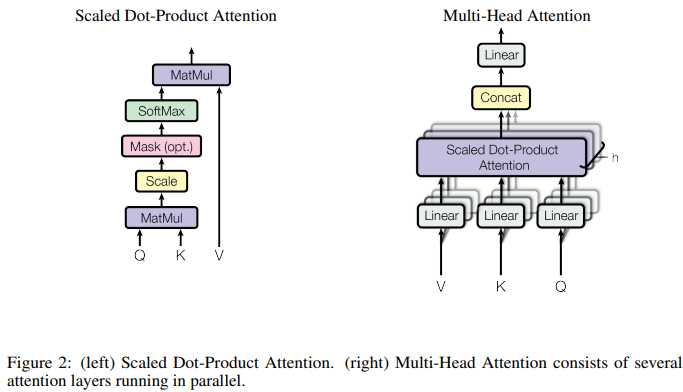
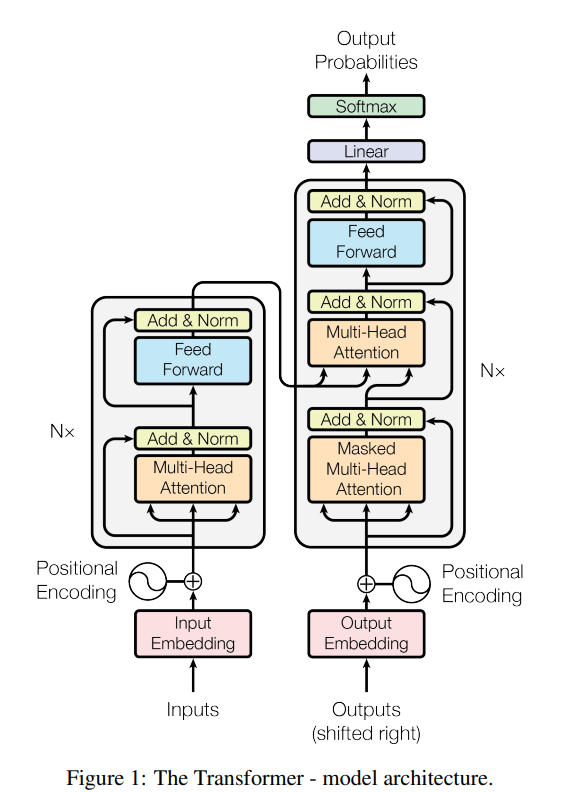
The query, keys, values, and output are all vectors. The output is computed as a weighted sum of the values, where the weight assigned to each value is computed by a compatibility function of the query with the corresponding key.
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
: keys of dimension : values of dimension
Multi-Head Attention
Instead of performing a single attention function with -dimensionl keys, values and queries, we found it beneficial to linearly project the queries, keys, and values times with different, learned linear projections to and dimensions, respectively.
\
Multi-head attention allows the model to jointly atten to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. With a single attention head, averaging inhibits this.
Applications of Attention in our Model
- In encoder-decoder attention layers,This allows every position in the decoder to attend over all positions in the input sequence.
- The encoder contains self-attention layers.Each position in the encoder can attend to all positions in the previous layer of the encoder.
- Similarly, self-attention layers in the decoder allow each position in the decoder to attend to all positions in the decoder up to aand including that position.
Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks
Embeddings and Softmax