React에서 무시되는 값들
React에서 null, undefined, true, false와 같은 값들은 무시되어 아무것도 렌더링되지 않는다.
function App() {
const IGNORE_VALUES = [null, undefined, true, false];
return (
<div>
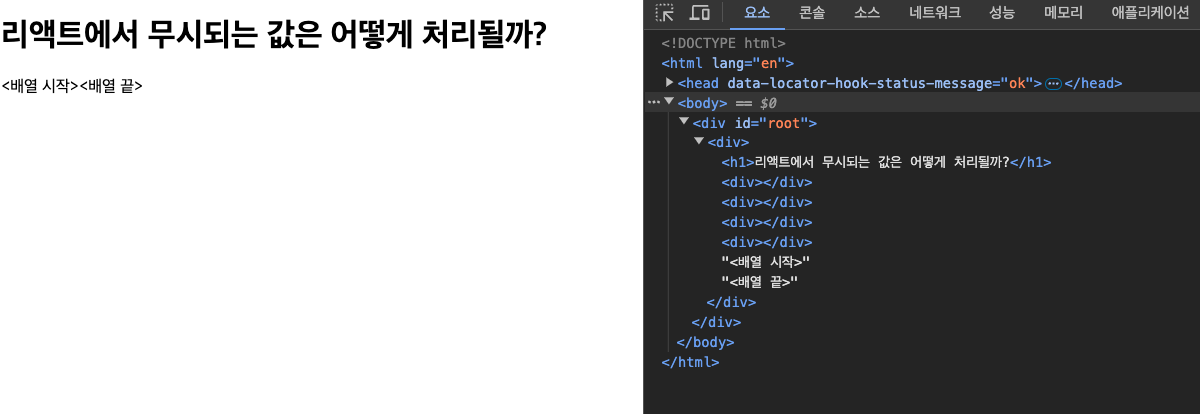
<h1>리액트에서 무시되는 값은 어떻게 처리될까?</h1>
{IGNORE_VALUES.map((value, idx) => (
<div key={idx}>{value}</div>
))}
{["<배열 시작>", ...IGNORE_VALUES, "<배열 끝>"]}
</div>
);
}map을 통해 배열을 순회하여 개별로 값을 처리할 때는 빈div태그만 렌더링되고, 배열에서도 무시되는 값들은 렌더링되지 않는 것을 볼 수 있다.
React에서 이 값들을 어떻게 처리하길래 무시되는걸까?
React가 무시되는 값들을 처리하는 방식
이 값들은 독립적인 컴포넌트가 아니라 다른 컴포넌트의 자식으로만 존재한다. 따라서 reconcileChildren이 사용된다.
export function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
nextChildren: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
if (current === null) { // 초기 렌더링 O
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
} else { // 초기 렌더링 X
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
}
}// 초기 렌더링과 같은 상황에서 불필요한 작업을 피하기 위해 부작용(side effect)을 추적하지 않는다.
export const mountChildFibers: ChildReconciler = createChildReconciler(false);
export const reconcileChildFibers: ChildReconciler = createChildReconciler(true);두 함수는 부작용(side effect)을 추적할지 여부라는 한 가지 차이점을 제외하면 동일하다.
createChildReconciler 함수는 deleteChild, deleteRemainingChildren와 같은 함수들을 포함하고 있다.
(실제 함수 내부에는 아래 코드보다 더 많은 함수들이 포함되어 있다. 실제 코드 보기)
function createChildReconciler(
shouldTrackSideEffects: boolean
): ChildReconciler {
// returnFiber는 부모 Fiber 노드를 의미한다.
function deleteChild(returnFiber: Fiber, childToDelete: Fiber): void {
if (!shouldTrackSideEffects) {
return;
}
const deletions = returnFiber.deletions; // 삭제될 자식들의 목록
if (deletions === null) {
// 목록이 없다면
returnFiber.deletions = [childToDelete]; // 새로 생성
returnFiber.flags |= ChildDeletion; // 플래그 설정(삭제될 자식이 있음을 알린다)
} else {
deletions.push(childToDelete); // 목록이 있다면 자식 추가
}
}
function deleteRemainingChildren(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null
): null {
if (!shouldTrackSideEffects) {
return null;
}
let childToDelete = currentFirstChild;
while (childToDelete !== null) {
// 모든 형재 Fiber를 순회
deleteChild(returnFiber, childToDelete); // deleteChild 호출
childToDelete = childToDelete.sibling; // 다음 형제로 이동
}
return null;
}
// another code...
return reconcileChildFibers;
}
내부에서 여러 함수들을 포함하고 있고 최종적으로는 reconcileChildFibers 함수를 리턴하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
// React 컴포넌트들의 자식 요소들을 재조정하는 역할을 한다.
function reconcileChildFibersImpl(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChild: any,
lanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
// 키가 없는 최상위 Fragment를 처리
const isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment =
typeof newChild === "object" &&
newChild !== null &&
newChild.type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE &&
newChild.key === null;
if (isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment) {
// Fragment의 자식들을 직접 처리하기 위해 newChild를 Fragment의 children으로 교체
validateFragmentProps(newChild, null, returnFiber);
newChild = newChild.props.children;
}
// Fragment, Portal, Lazy 컴포넌트, 배열 등등 처리
if (typeof newChild === "object" && newChild !== null) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE: {
// 단일 React 앨리먼트 처리
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo(newChild._debugInfo);
const firstChild = placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes
)
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE: // 포탈 처리
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSinglePortal(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newChild, lanes)
);
case REACT_LAZY_TYPE: {
// Lazy 컴포넌트 처리
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo(newChild._debugInfo);
let result;
const payload = newChild._payload;
const init = newChild._init;
result = init(payload);
const firstChild = reconcileChildFibersImpl(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
result,
lanes
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
}
if (isArray(newChild)) {
// 배열
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo(newChild._debugInfo);
const firstChild = reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
if (getIteratorFn(newChild)) {
// 이터러블 자식 처리
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo(newChild._debugInfo);
const firstChild = reconcileChildrenIteratable(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
// 비동기 이터러블 자식 처리
if (
enableAsyncIterableChildren &&
typeof newChild[ASYNC_ITERATOR] === "function"
) {
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo(newChild._debugInfo);
const firstChild = reconcileChildrenAsyncIteratable(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
if (typeof newChild.then === "function") {
// Thenable 객체 처리
const thenable: Thenable<any> = (newChild: any);
const prevDebugInfo = pushDebugInfo((thenable: any)._debugInfo);
const firstChild = reconcileChildFibersImpl(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
unwrapThenable(thenable),
lanes
);
currentDebugInfo = prevDebugInfo;
return firstChild;
}
if (newChild.$$typeof === REACT_CONTEXT_TYPE) {
// Context 처리
const context: ReactContext<mixed> = (newChild: any);
return reconcileChildFibersImpl(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
readContextDuringReconciliation(returnFiber, context, lanes),
lanes
);
}
throwOnInvalidObjectType(returnFiber, newChild);
}
// 텍스트 노드 처리
if (
(typeof newChild === "string" && newChild !== "") ||
typeof newChild === "number" ||
typeof newChild === "bigint"
) {
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
"" + newChild,
lanes
)
);
}
// 나머지 경우는 모두 비어 있는 것으로 처리
return deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild);
}이 함수는 다양한 타입의 자식 요소들을 처리한다.
-
React 앨리먼트: 일반적인 React 컴포넌트 처리
-
Portal: React 트리 외부의 Dom 노드에 자식을 렌더링할 때 사용
-
Lazy 컴포넌트: 동적으로 불러오는 컴포넌트 처리
-
배열: 여러 자식 요소를 포함하는 배열 처리
-
이터러블 객체: 배열과 유사하게 여러 자식 요소를 포함할 수 있는 이터러블 객체 처리
-
비동기 이터러블: 비동기적으로 자식 요소를 생성하는 객체 처리
-
Thenable 객체: Promise와 유사한 객체 처리
-
context 객체: Context API를 사용할 때 처리
-
문자열, 숫자, BigInt: 텍스트 노드로 처리된다.
null, undefined, true, false는 위의 어떤 케이스에도 해당되지 않아 deleteRemainingChildren 함수에 의해 처리된다. 이 함수는 이러한 값들을 비어있는 것으로 간주하고 실제로 아무것도 렌더링하지 않는다.
무시되는 값 활용하기(조건부 렌더링)
무시되는 값들을 활용하면 조건부 렌더링을 사용할 수 있다.
function App() {
const emptyArray = [];
return (
<div>
<h1>리액트에서 무시되는 값 활용하기</h1>
<h2>배열의 길이가 1 이상일 때 Hello 렌더링하기</h2>
<div>첫 번째 결과: {emptyArray.length && "Hello"}</div>
<div>두 번째 결과: {emptyArray.length > 0 && "Hello"}</div>
</div>
);
}이렇게 하면 배열의 길이가 1 이상일 때는 문제가 없지만 위 코드처럼 배열의 길이가 0인 경우에 원하는 동작이 일어나지 않는다.
지금 원하는 동작은 배열의 길이가 1이상일 때 Hello를 렌더링하고 1 미만이라면 렌더링하지 않아야 하는데,
첫 번째 결과에서는 0을 렌더링하는 것을 볼 수 있다.

그 이유는 위에서 알아봤듯이 0(배열의 길이)은 무시되는 값이 아니기 때문에 텍스트 노드에서 0이 렌더링 처리가 되어 원하는 동작을 할 수 없기 때문에 배열의 길이로 조건부 렌더링을 해야하는 상황에서는 emptyArray.length > 0와 같이 표현식이 boolean 값을 가질 수 있도록 해주어야 한다.
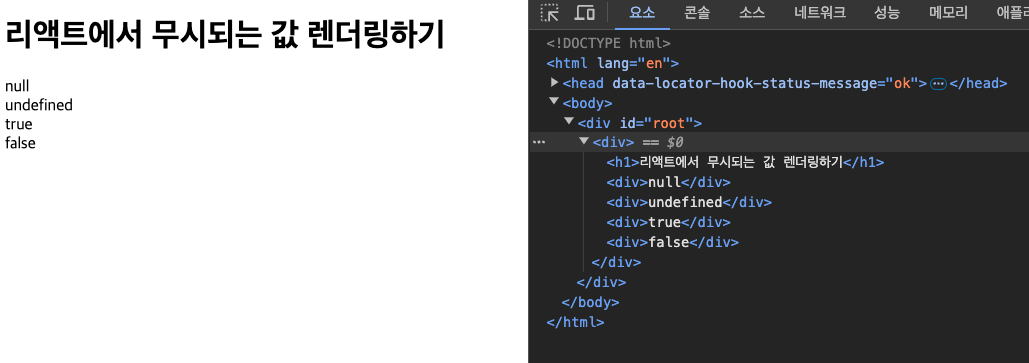
무시되는 값 렌더링하기
React에서 무시되는 값을 렌더링하려면 문자열로 바꾸면 된다.
🙃 도움이 되었던 자료들
How does React handle empty values(null/undfined/Booleans) internally?
Booleans, Null, and Undefined Are Ignored - React 공식 문서(구버전)