힙 정렬이란
자료구조인 heap을 정렬을 기반으로한 정렬 알고리즘으로
max-heaps에서 root node가 가장 큰 값이라는 점을 이용하여 정렬을 수행합니다.
힙 정렬 과정
정렬 과정을 그림과 함께 이해하는것이 빠른데
Heap Sort 그림 출처
-
먼저 array에 있는 값들을 max-heap으로 변환한다.
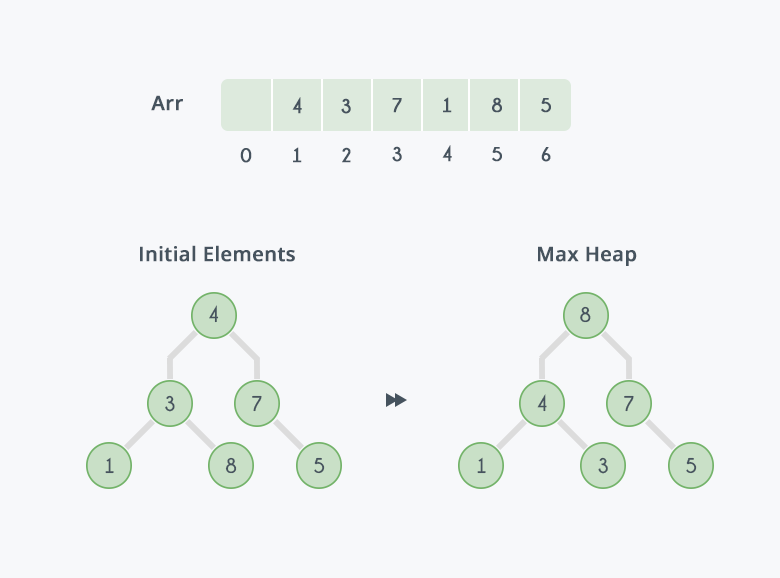
-
step들을 요약하면 root node를 제거하여 배열의 마지막 index로 보내는 것이고 이 과정을 반복하며 정렬이 이루어집니다.
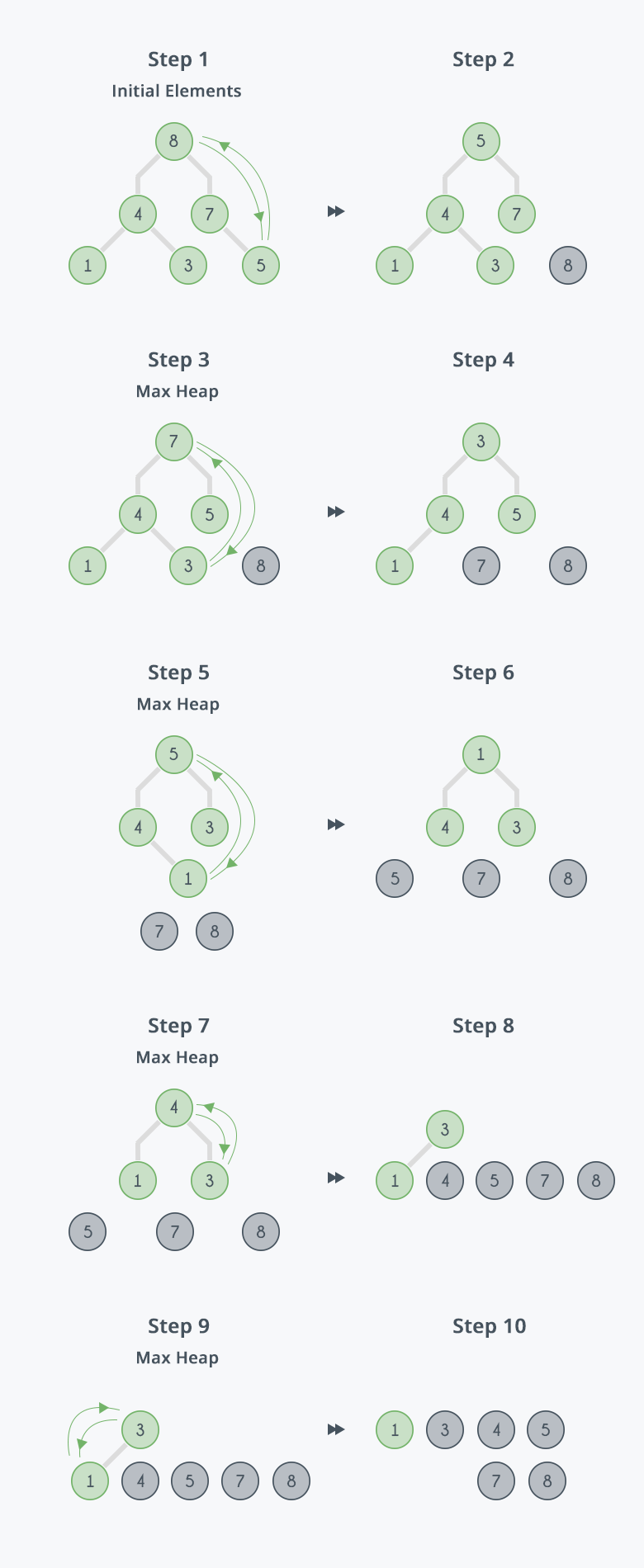
구현
다음은 C언어로 구현된 힙 정렬의 코드입니다.
#include <stdio.h>
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i
// which is an index in arr[].
void heapify(int arr[], int n, int i) {
// Initialize largest as root
int largest = i;
// left index = 2*i + 1
int l = 2 * i + 1;
// right index = 2*i + 2
int r = 2 * i + 2;
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[largest]) {
largest = l;
}
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[largest]) {
largest = r;
}
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
// Main function to do heap sort
void heapSort(int arr[], int n) {
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, n, i);
}
// One by one extract an element from heap
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// Call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// A utility function to print array of size n
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver's code
int main() {
int arr[] = {9, 4, 3, 8, 10, 2, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
heapSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array is \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}성능평가
힙 정렬의 시간 복잡도를 분석해보면, 삽입과 삭제 각각의 연산은 이며
전체 데이터의 개수가 개 라면, 이 연산을 반복해야 하므로 총 시간복잡도는 이다.
장점
-
효율적인 시간 복잡도
-
메모리 사용량 : 메모리를 거의 사용하지 않는 제자리 정렬이다.
단점
-
Costly : 내부적으로 많은 교환 작업을 요구하기 때문에 비용이 많이든다.
-
불안정성 : 기본적인 구현은 안정적이지 않아 동일한 값의 순서가 보장되지 않는다.
-
비효율적인 캐시 사용 : QuickSort와 비교 시 캐시 효율성이 떨어져 속도가 느립니다.
정리
-
힙정렬은 제자리 알고리즘이다.
(자료구조를 추가하지 않고 입력을 변환하는 알고리즘) -
일반적인 구현이 불안정적이지만 수정으로 안정적으로 만들 수 있다.
(수정 방법 : taking the position of the elements into consideration.) -
QuickSort보다 보통 2~3배 느린데 이는 힙 정렬이 지역 참조(locality of reference)가 부족하기 때문이다.