기수 정렬은 숫자를 구성하는 각 자릿수를 기준으로 정렬하는 선형 정렬 알고리즘으로 크기가 고정되어있는 문자나 숫자 정렬에 유용합니다.
기수 정렬의 단계
설명을 위해 {170, 45, 75, 90, 803, 24, 2, 66} 라는 배열이 있다고 가정하고

해당 배열에서 자릿수가 가장 큰 값을 확인하고 그 자릿수를 key값으로 정렬합니다.
LSD 방식으로 정렬한다면
먼저 1의자리 숫자를 기준으로 정렬합니다.
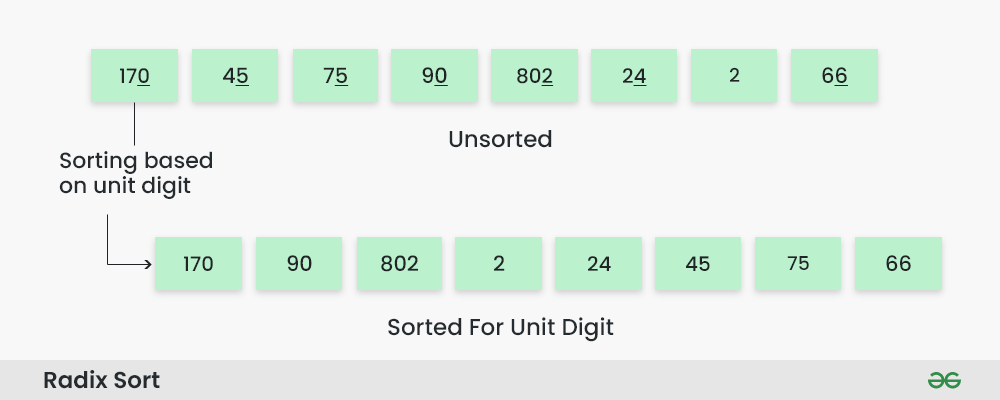
만약 같은 값이 존재한다면 Unsorted 배열에서 우선순위대로 정렬합니다.
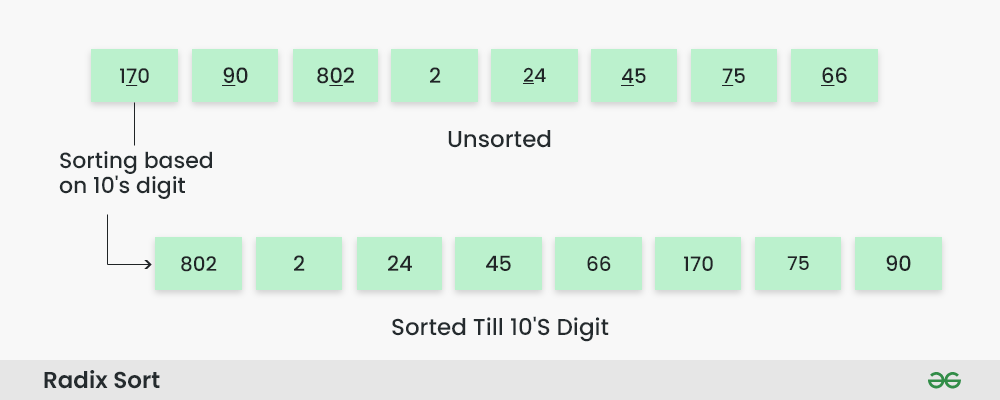
그 다음 10의 자리수로 정렬을하면
(n의 자리 수가없으면 0으로 표시합니다.)
이제 마지막으로 100의 자리 수로 정렬을 진행하면
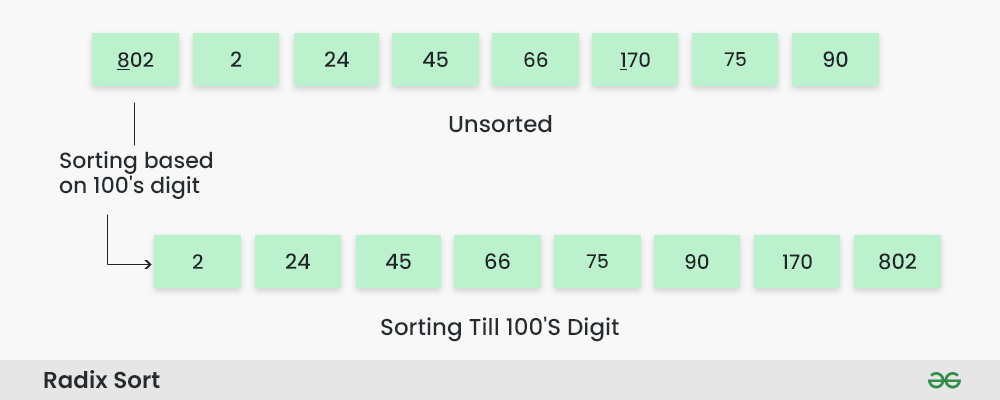
이렇게 오름차순으로 정렬이 됩니다.
기수 정렬 예시 코드
c언어로 구현 코드입니다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_NUM 1000000
void countingSort(int arr[], int n, int exp) {
int output[n];
int count[10] = {0};
// Count occurrences of each digit
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
// Calculate cumulative frequencies
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Build output array
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
// Copy output array back to original array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
void radixSort(int arr[], int n) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > max)
max = arr[i];
// Do counting
sort for every digit.
for (int exp = 1; max / exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countingSort(arr,
n, exp);
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
radixSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted
array: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
return
0;
}성능평가
복잡도는
b는 최대값의 자릿수에 따라 달라집니다.
장점
-
Fast when the keys are short i.e. when the range of the array elements is less.
-
Used in suffix array constuction algorithms like Manber's algorithm and DC3 algorithm.
단점
-
Since Radix Sort depends on digits or letters, Radix Sort is much less flexible than other sorts. Hence , for every different type of data it needs to be rewritten.
-
The constant for Radix sort is greater compared to other sorting algorithms.
-
It takes more space compared to Quicksort which is inplace sorting.
정리
- Since Radix Sort depends on digits or letters, Radix Sort is much less flexible than other sorts. Hence , for every different type of data it needs to be rewritten.
- The constant for Radix sort is greater compared to other sorting algorithms.
- It takes more space compared to Quicksort which is inplace sorting.