모듈화란 ?
우리는 앞에서 다양한 컴포넌트에서 계속 사용되는 정보를 store 에 state 에 저장해두고 전역변수처럼 사용한다고 배웠습니다 !
근데 이런 state 에 너무 너무 다양하고 많은 값이 들어가 있으면 가독성이 떨어지겠죠 ? 여기서 나온게 바로 모듈화 의 개념입니다.
store의 단위인 모듈들을 만들어서 user 모듈엔 user 관련 state만 관리하고, post 모듈엔 post 관련 state 만 관리하자 ! 취지에서 모듈화가 등장했습니다.
모듈화 작성
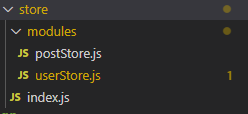
파일 구조는 이렇습니다. modules 폴더안에 store 를 작성 후, 밖의 index.js 에서 해당 store 들을 불러와 사용합니다.
👇 userStore.js
const userStore = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
userName: '도로시'
},
getters: {
GE_USER_NAME: state => state.userName
},
mutations: {
MU_USER_NAME: (state, payload) => {
/*
여기서는 payload를 객체로 받습니다.
payload를 객체로 받으면, mutation를 조금더 유연하게 사용할 수 있기는 합니다.
*/
state.userName = payload.userName
}
},
actions: {
AC_USER_NAME: ({ commit }, payload) => {
commit('MU_USER_NAME', payload)
}
}
}
export default userStore- state 에는 사용자 이름이 존재하고,
- getters 를 통해
GE_USER_NAME함수호출 시 사용자 이름을 불러옵니다. 즉 이름을 저장해두는 캐시정도가 되겠습니다. - mutations 을 통해
payload로 들어온 변수를state.userName에 매핑하는, 즉 state 의 값을 바꾸는MU_USER_NAME함수를 볼 수 있습니다. - actions 을 통해 mutations 에 접근하고 있네요.
👇 postStore.js
const postStore = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
postList: [
{
title: 'vuex 쉽게 알아보기',
author: '도로시'
},
{
title: 'axios 알아보기',
author: '도로시'
},
{
title: 'react 알아보기',
author: '토토'
}
]
},
getters: {
GE_POST_LIST: state => state.postList
},
mutations: {
MU_POST_LIST: (state, payload) => {
state.postList = payload
}
},
actions: {
AC_USER_NAME: ({ commit }, payload) => {
commit('MU_POST_LIST', payload)
}
}
}
export default postStore👇 index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 작성한 모듈을 가져옵니다.
import userStore from '@/store/modules/userStore.js'
import postStore from '@/store/modules/postStore.js'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
// 키: 값 형태로 저장됩니다.
userStore: userStore,
postStore: postStore
}
})
export default store