1. 데이터 가져오기
pip install kagglehub
import kagglehub
# Download latest version
path = kagglehub.dataset_download("ashishjangra27/face-mask-12k-images-dataset")
print("Path to dataset files:", path)
# r :
Path to dataset files: ...\versions\1
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
path = '.../versions/1/Face Mask Dataset'
dataset = {
'image_path': [],
'mask_status': [],
'where': []
}
# # 주어진 경로(path) 안의 폴더를 순회
for where in os.listdir(path):
for status in os.listdir(os.path.join(path, where)):
# 주어진 경로에서 특정 패턴(*.png)에 맞는 모든 파일 경로를 찾아 리스트로 반환
for image in glob.glob(os.path.join(path, where, status, '*.png')):
dataset['image_path'].append(image)
dataset['mask_status'].append(status)
dataset['where'].append(where)
dataset = pd.DataFrame(dataset)
dataset.head()
2. 간단 EDA
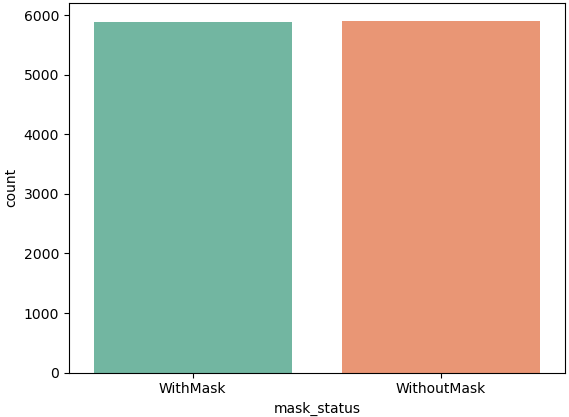
import seaborn as sns
print(dataset.value_counts('mask_status'))
# r :
mask_status
WithoutMask 5909
WithMask 5883
Name: count, dtype: int64
sns.countplot(x=dataset['mask_status'], palette='Set2')
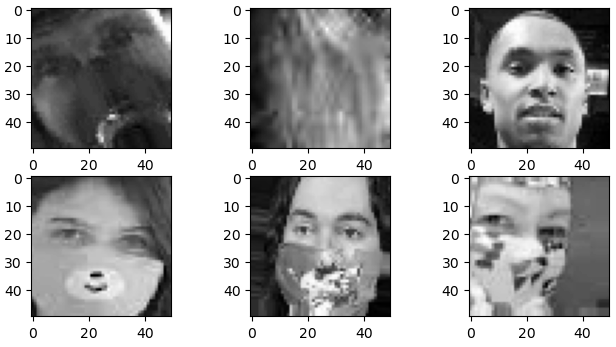
import numpy as np
import cv2 # 이미지를 읽기 위해 OpenCV를 사용
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
# 9개의 이미지를 무작위로 선택 및 시각화
for i in range(9):
random = np.random.randint(0, len(dataset))
plt.subplot(3, 3, i+1)
# cv2.imread: 경로를 가져와 이미지를 읽음
plt.imshow(cv2.imread(dataset['image_path'][random]))
plt.title(dataset['mask_status'][random])
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()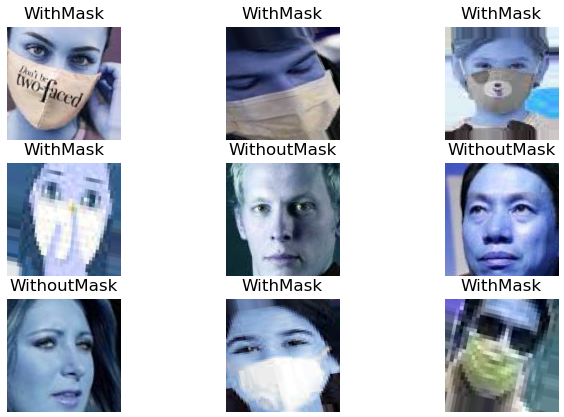
# 데이터 종류별 데이터프레임 생성
train_df = dataset[dataset['where'] == 'Train']
test_df = dataset[dataset['where'] == 'Test']
valid_df = dataset[dataset['where'] == 'Validation']
# 데이터 종류별 countplot 생성
plt.figure(figsize=(15,4))
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
sns.countplot(x = train_df['mask_status'], palette='Set2')
plt.title('Train')
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
sns.countplot(x = test_df['mask_status'], palette='Set2')
plt.title('Test')
plt.subplot(1,3,3)
sns.countplot(x = valid_df['mask_status'], palette='Set2')
plt.title('Validation')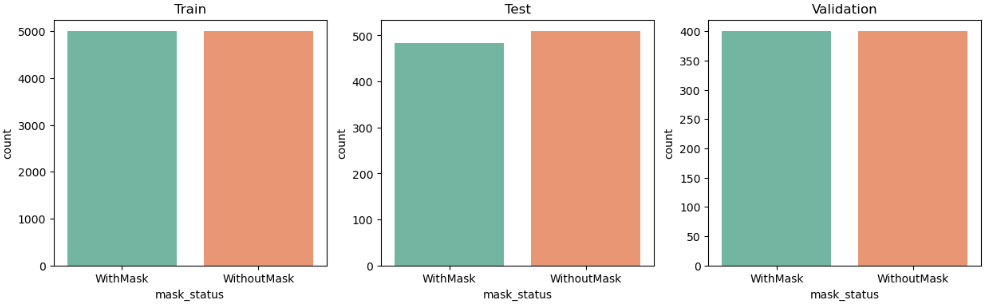
3. Train 데이터 전처리
- cv2.imread : 메모리 효율을 위해 이전에 읽은 이미지를 저장하지 않고 필요할 때마다 새로 읽음
train_df = train_df.reset_index(drop=True)
# data는 이미지 데이터와 라벨(0 또는 1)을 저장하기 위한 리스트
data = []; image_size = 50
for i in range(len(train_df)):
# 이미지를 흑백으로 읽음 (1채널)
# 반환되는 배열은 2차원 형태 (높이, 너비)
# Numpy 배열(numpy.ndarray)로 이미지를 저장
img_array = cv2.imread(train_df['image_path'][i], cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 이미지 리사이징
new_img_array = cv2.resize(img_array, (image_size, image_size))
# 리스트 형태로 라벨(1 또는 0)과 함께 묶어 모델 학습에 적합하도록 구조화
if train_df['mask_status'][i] == 'WithMask':
data.append([new_img_array,1]) # 라벨 1 (마스크 착용)
else:
data.append([new_img_array, 0]) # 라벨 0 (마스크 미착)
# 첫 번째 값
data[0]
# r :
# 50x50 = 2500개의 픽셀 값
[array([[238, 238, 238, ..., 187, 194, 197],
[237, 240, 239, ..., 177, 194, 193],
[238, 238, 238, ..., 174, 184, 189],
...,
[235, 234, 233, ..., 146, 150, 151],
[235, 235, 233, ..., 149, 152, 152],
[235, 234, 234, ..., 150, 151, 152]], dtype=uint8), 1]
# 리스트 형태의 데이터를 추출해서 Numpy 배열로 변환
X = np.array([item[0] for item in data]) # 이미지 배열만 추출
y = np.array([item[1] for item in data]) # 라벨만 추출
print(X.shape) # 결과: 3차원 Numpy 배열 (데이터 개수, 50, 50)
print(y.shape) # 결과: 1차원 Numpy 배열 (데이터 개수,)
# r :
(10000, 50, 50)
(10000,)4. Train 데이터 시각화
# 셔플
np.random.shuffle(data)
# 행렬 형태로 정렬된 데이터를 시각화
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,3, figsize=(10,6))
for row in range(2):
for col in range(3):
ax[row][col].imshow(data[row*3+col][0], cmap='gray') # 이미지
ax[row][col].set_title(data[row*3+col][1]) # 레이블
plt.show()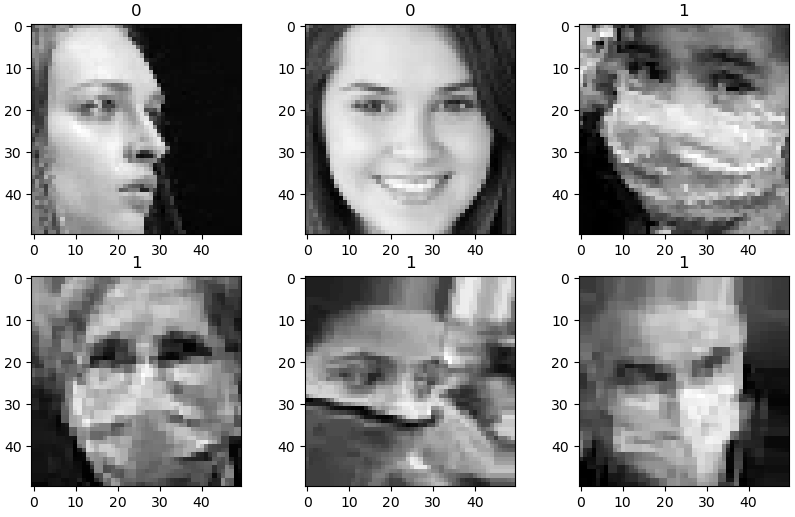
5. 입력 데이터와 라벨 분리 / Numpy 배열 변환
<배열로 바꾸는 이유>
- 머신러닝/딥러닝 모델이 데이터를 처리할 수 있는 형태로 변환하기 위해
- 모델 학습은 리스트가 아니라 Numpy 배열이나 텐서(Tensor)와 같은 고정된 형태의 데이터 구조를 요구
- 리스트 형식의 데이터를 직접 처리할 수 없으므로, 배열로 변환이 필수적
- Numpy 배열은 벡터화 연산을 지원, 대규모 데이터 연산에 적합
<데이터 준비 과정 요약>
- 데이터 수집: 데이터는 보통 리스트 형태로 관리됩니다.
- Numpy 배열로 변환: 연산 효율성과 딥러닝 프레임워크 호환성을 위해 Numpy 배열로 변환.
- 모델 입력 준비:
- 데이터 정규화 (예: 픽셀 값을 0~1 범위로 변환).
- 데이터 차원 재구성 (CNN 등 모델 입력 요구사항에 맞춤).
X=[]; y=[]
for image in data:
X.append(image[0]) # 이미지 배열을 X 리스트에 추가
y.append(image[1]) # 라벨 값을 y 리스트에 추가
# 리스트를 Numpy 배열로 변환
X = np.array(X) # 3차원 배열 (데이터 개수, 이미지 높이, 너비)
y = np.array(y) # 1차원 배열 (데이터 개수,)
# 데이터 정규화 (정규화 유/무에 따른 퍼포먼스 비교 필요)
X = X/255.6. 모델 형성 / Compile - CNN 모델
<CNN 모델의 구조>
- 합성곱(Conv2D): 이미지의 특징을 추출.
- Pooling: 크기를 줄이며 중요한 정보를 유지.
- Flatten: 2D 데이터를 1D 벡터로 변환.
- Dense: 완전 연결 층으로 출력 계산.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=4)
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
model = models.Sequential([
# 32개의 (5x5) 필터를 사용
layers.Conv2D(32, (5,5), strides=(1,1), padding='same', activation='relu',
input_shape=(image_size, image_size, 1)),
# pool_size : 한 번에 2x2 영역(4개의 값)을 처리
# strides : 윈도우가 겹치지 않고 2칸씩 이동
layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (2,2), activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)),
# 과적합을 방지하기 위해 25%의 뉴런을 무작위로 비활성화
layers.Dropout(0.25),
# 2D 특성 맵을 1D 벡터로 변환해 밀집 층(Dense Layer) 연결 준비
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(1000, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
model.summary()
# r :
Model: "sequential_1"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ conv2d_3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 50, 50, 32) │ 832 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ max_pooling2d_2 (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 25, 25, 32) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_4 (Conv2D) │ (None, 25, 25, 64) │ 8,256 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ max_pooling2d_3 (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 12, 12, 64) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dropout_1 (Dropout) │ (None, 12, 12, 64) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ flatten_1 (Flatten) │ (None, 9216) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dense_2 (Dense) │ (None, 1000) │ 9,217,000 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dense_3 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 1,001 │
└──────────────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴─────────────────┘
Total params: 9,227,089 (35.20 MB)
Trainable params: 9,227,089 (35.20 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
# 모델 컴파일
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])7. Train & Evaluate
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1, image_size, image_size, 1)
X_val = X_val.reshape(-1, image_size, image_size, 1)
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5, validation_data=(X_val, y_val))
# r :
Epoch 5/5
250/250 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 38s 152ms/step - accuracy: 0.9699 - loss: 0.0701 - val_accuracy: 0.9740 - val_loss: 0.0743
model.evaluate(X_val, y_val)
# r :
[0.07427990436553955, 0.9739999771118164]8. Confusion_matrix , Classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
prediction = (model.predict(X_val) > 0.5).astype('int32')
print(classification_report(y_val, prediction))
print(confusion_matrix(y_val, prediction))
# r :
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.99 0.96 0.98 1053
1 0.96 0.99 0.97 947
accuracy 0.97 2000
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 2000
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 2000
[[1015 38]
[ 14 933]]9. Wrong Result
wrong_result = []
for n in range(len(y_val)):
if prediction[n] != y_val[n]:
wrong_result.append(n)
len(wrong_result)
# r :
38
import random
samples = random.choices(wrong_result, k=6)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(2,3, i+1)
plt.imshow(X_val[samples[i]], cmap='gray')
plt.show()