[2022 Frontiers in Immunology] Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Score Analysis for Predicting the Expression of the Immunotherapy Biomarker PD-L1 in Lung Cancer
Paper Review
목록 보기
11/25
Introduction
- non-small cell lung cancer에서 면역치료 반응을 예측하는 데 굉장히 중요한 바이오마커 PD-L1, PD-L1 expression은 높은 연관성을 가지고 있음
- PD-L1 expression을 IHC 이미지 분석에서 추정하는데, 딥러닝 알고리즘 적용 연구가 늘고 있음
- 하지면 여전히 low PD-L1 expression에 대해서 poor specificity, accuracy tumor를 가지고 있는데, 특히 proportion score (TPS) cutoff value 1%에서 더 그렇다.
Related Works:
- Tian P, He B, Mu W, Liu K, Liu L, Zeng H, et al. Assessing PD-L1 Expression in non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Predicting Responses to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Using Deep Learning on Computed Tomography Images. Theranostics (2021) 11(5):2098–107. doi: 10.7150/thno.48027
- Wiesweg M, Mairinger F, Reis H, Goetz M, Kollmeier J, Misch D, et al. Machine Learning Reveals a PD-L1-Independent Prediction of Response to Immunotherapy ofnon-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Gene Expression Context. Eur J Cancer (2020) 140:76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.09.015
- Wu J, Liu C, Liu X, Sun W, Li L, Gao N, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted System for Precision Diagnosis of PD-L1 Expression in non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mod Pathol (2021) 35(3):403–11. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00904-9
- Baxi V, Edwards R, Montalto M, Saha S. Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence in Translational Medicine and Clinical Practice. Mod Pathol (2021) 35(1):23–32. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00919-2
- Pan B, Kang Y, Jin Y, Yang L, Zheng Y, Cui L, et al. Automated Tumor Proportion Scoring for PD-L1 Expression Based on Multistage Ensemble Strategy in non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Transl Med (2021) 19(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02898-z
- Liu J, Zheng Q, Mu X, Zuo Y, Xu B, Jin Y, et al. Automated Tumor Proportion Score Analysis for PD-L1 (22C3) Expression in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci Rep (2021) 11(1):15907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95372-1
Materials And Methods
Materials
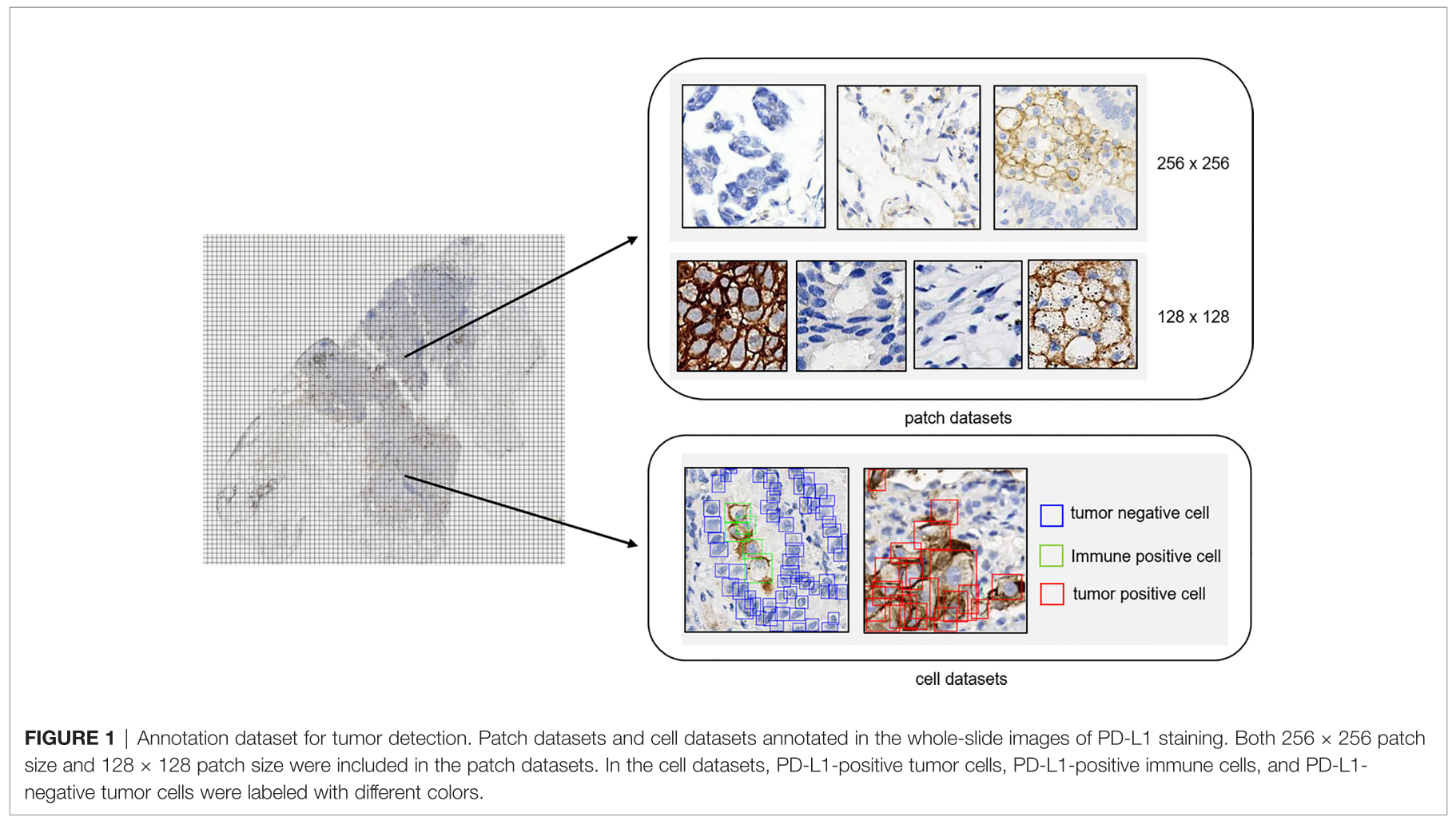
Data Collection
total 1288 FFPE Lung Cancer Samples
- 1,204 samples (stained using 22C3 assays)
- 84 samples (stained using SP263 assays)
- All slides were digitized by a KFBIO FK- Pro-120 slide scanner at ×20 magnification (0.475 mm/pixel). Furthermore, 627 PD-L1 (22C3)-staining whole-slide images (WSIs)
Data Configuration for Model Development
- training set: 627 slides (22C3) (manually annotated by two graduate students majoring in pathology, confirmed by pathologists)
- validation set: 577 slides (22C3), 84 slides (SP263)
- TPSs of all slides were estimated by one trained pathologist and confirmed by another
TPS Algorithm
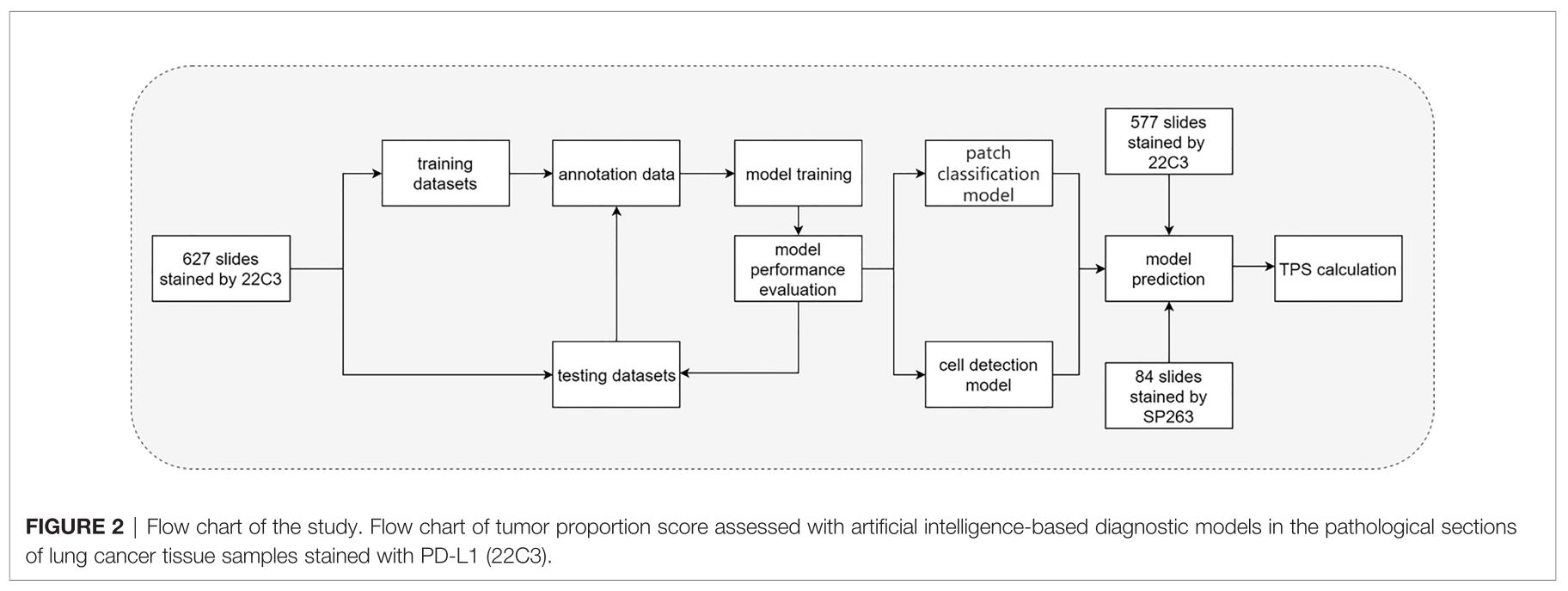
two-stage workflow based on DL
- 1 stage - DL-based classification for detecting patches containing tumor cells
- 2 stage - DL-based object detection for locating and counting the tumor cells
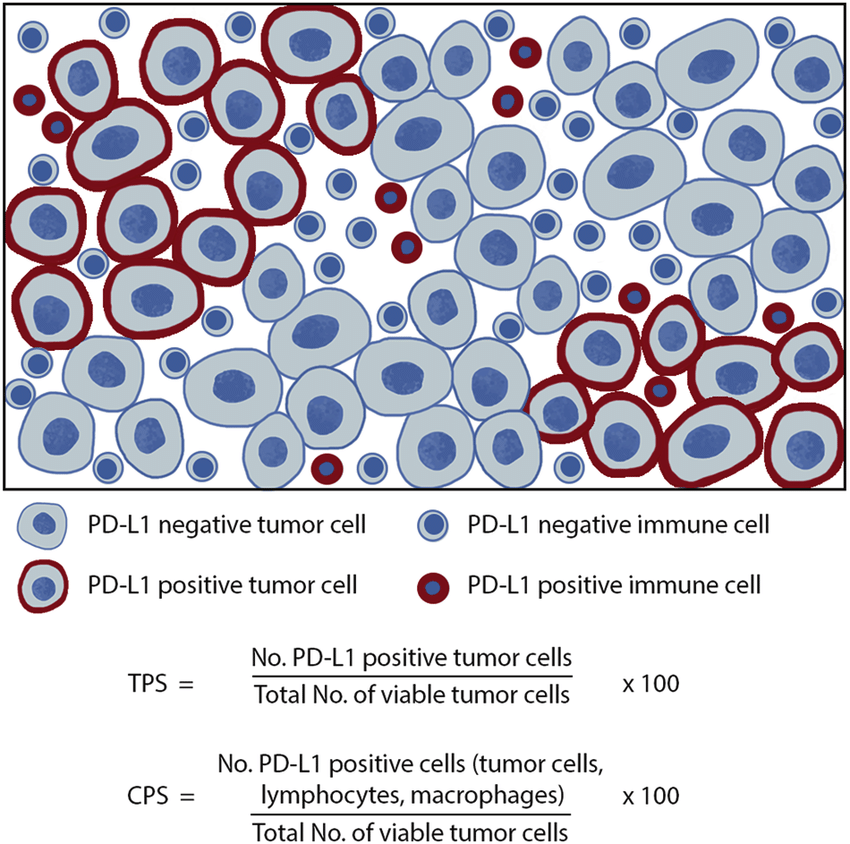
TPS, CPS 설명 그림
- de Ruiter, Emma J., et al. "Comparison of three PD-L1 immunohistochemical assays in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)." Modern Pathology 34.6 (2021): 1125-1132.
Classification Model
models
- 256 x 256 (Binary classifiers via two steps) categories
-
category 1 (124,459): 종양 세포는 있고 PD-L1 양성 면역 세포는 없는 patch들
-
category 2 (14,069): PD-L1 음성 종양세포와 PD-L1 양성 면역 세포 둘 다 있는 patch들 (macrophage와 lymphocyte 포함)
-
category 3 (131,672): 종양 세포가 없는 patch들 다양한 no-tumor 조직으로 구성됨
- negative immune cells: macrophages, lymphocytes
- hemorrhage, necrosis tissue, and stromal cellsclassification process (256 x 256)
-
1+2 vs 3 (종양세포 있니 없니) → 1 vs 2 (PD-L1 양성 면역 세포 있니 없니)
-
- 128 x 128 (Multi-class classification at Once) categories
- category 4 (37,583): PD-L1 양성 종양 세포
- category 5 (45,107): PD-L1 음성 종양세포
- category 6 (38,912): PD-L1 양성 면역 세포
- category 6 (65,786): 나머지
- negative immune cells: macrophages, lymphocytes
- hemorrhage, necrosis tissue, and stromal cells
- training and validation sets in a ratio of 8:2
- MobileNetV2 (pre-trained on ImageNet) 마지막 fc layer만 dropout + dense layer로 바꿈
Cell Detection
- YOLO head 기반으로 our own object detection model을 built
- backbond으로는 CSPDarknet53을 사용하고 BiFPN을 닮은 feature network를 사용했음
- Cell tags는 128 x 128 patch 사이즈의 patch에서 labeled되었고 PD-L1 음성 종양 세포 (105,508), PD-L1 양성 종양 세포 (24,523), PD-L1 양성 면역세포 (10,429)로 그룹화되었음
- 5-fold cross validation and label smoothing (0.1) to avoid overfitting
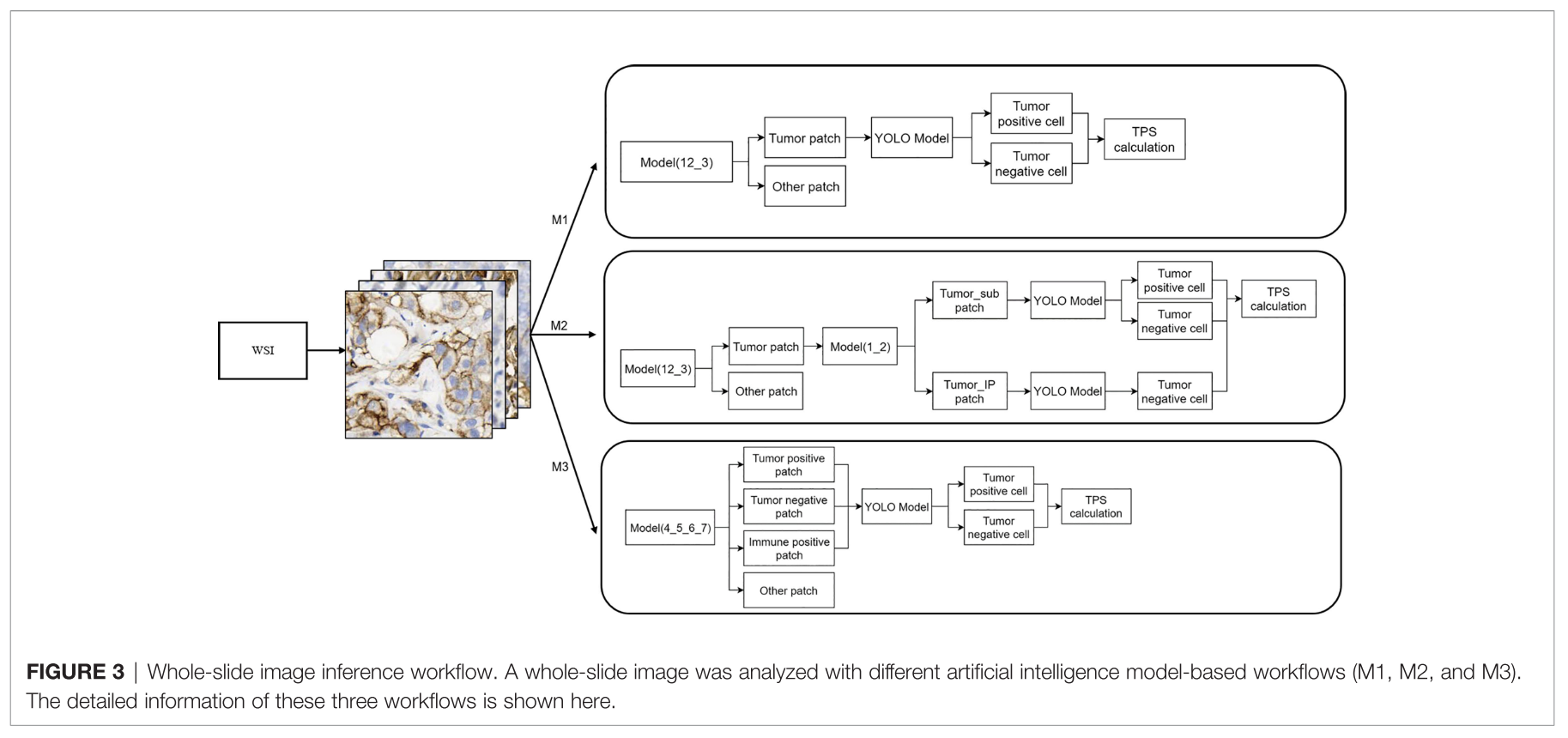
WSI Inference Workflow
3 different workflow 비교
- M1: 1+2 vs 3 → tumor patch → YOLO → tumor positive cell / tumor negative cell → TPS
- M2: 1+2 vs 3→ tumor patch → 1 vs 2 → YOLO (respectively) → tumor positive cell / tumor negative cell (1), tumor negative cell (2) → TPS
- M3: 4 / 5 / 6 / 7 → tumor positive patch, tumor negative patch, immune positive patch → YOLO → tumor positive cell / tumor negative cell → TPS
Evaluation Metrics and Statistical Analyses
- linear correlation coefficient (LCC) → TPS 비교 (AI vs pathologist)
- Cohen’s kappa → 일치도 비교 (AI vs pathologist)
- Specificity, Sensitivity, Precision, Accuracy, and F1 score → Accuracy evaluation
- Statistical significance, <0.05
Results
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients With Lung Cancer
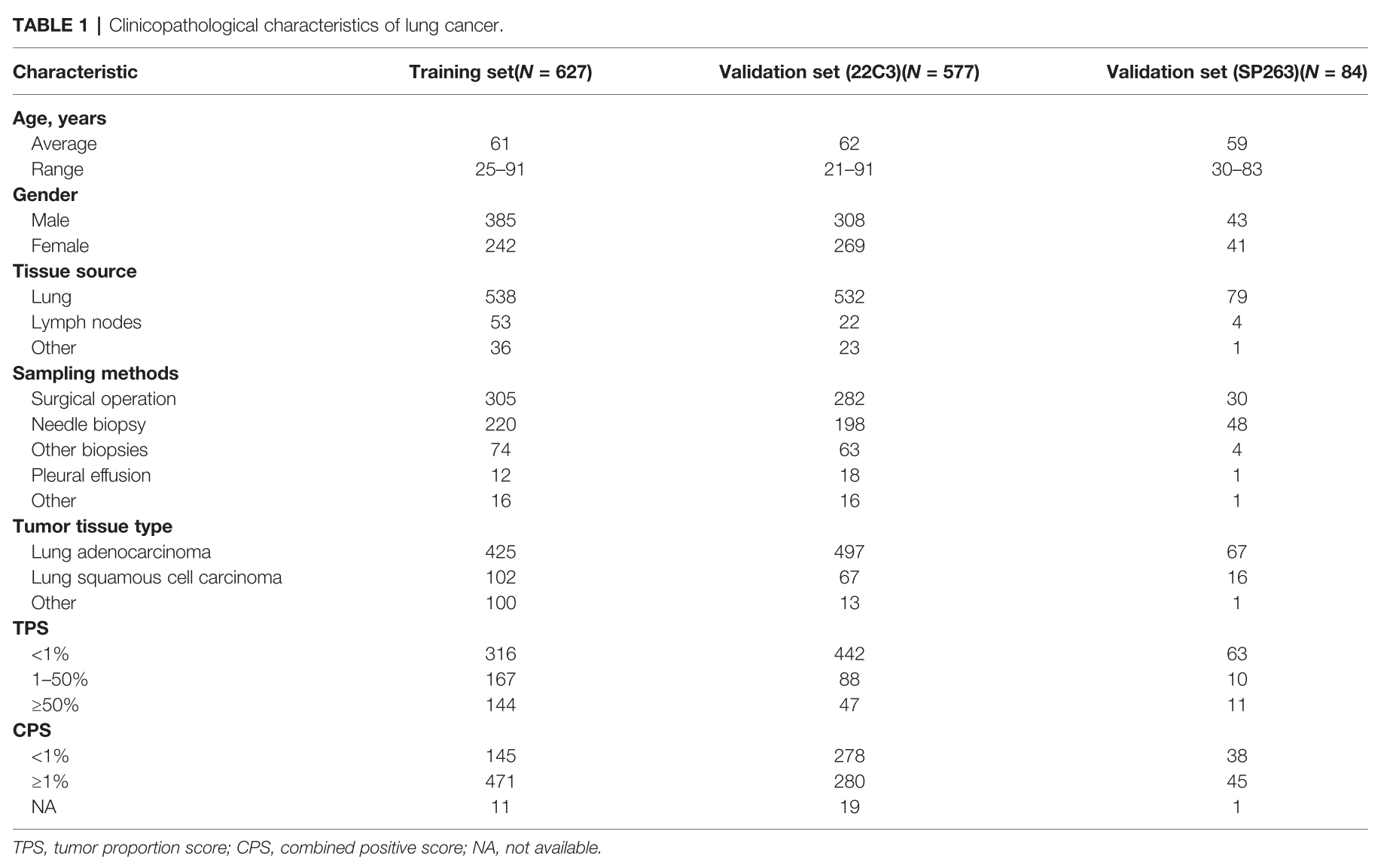
- 57.1% from male patients, 42.9 % from female patients
- surgical operation (617), needle biopsy (466), other biopsy (141), pleural effusion (31)
- adenocarcinoma (989), squamous cell carcinoma (185)
- PD-L1 TPS (<1, 1-49 and ≥ 50%) and combined positive score (CPS) (<1 and ≥ 1%)
DL Model Performance Evaluation in the 22C3 and SP263 Assays
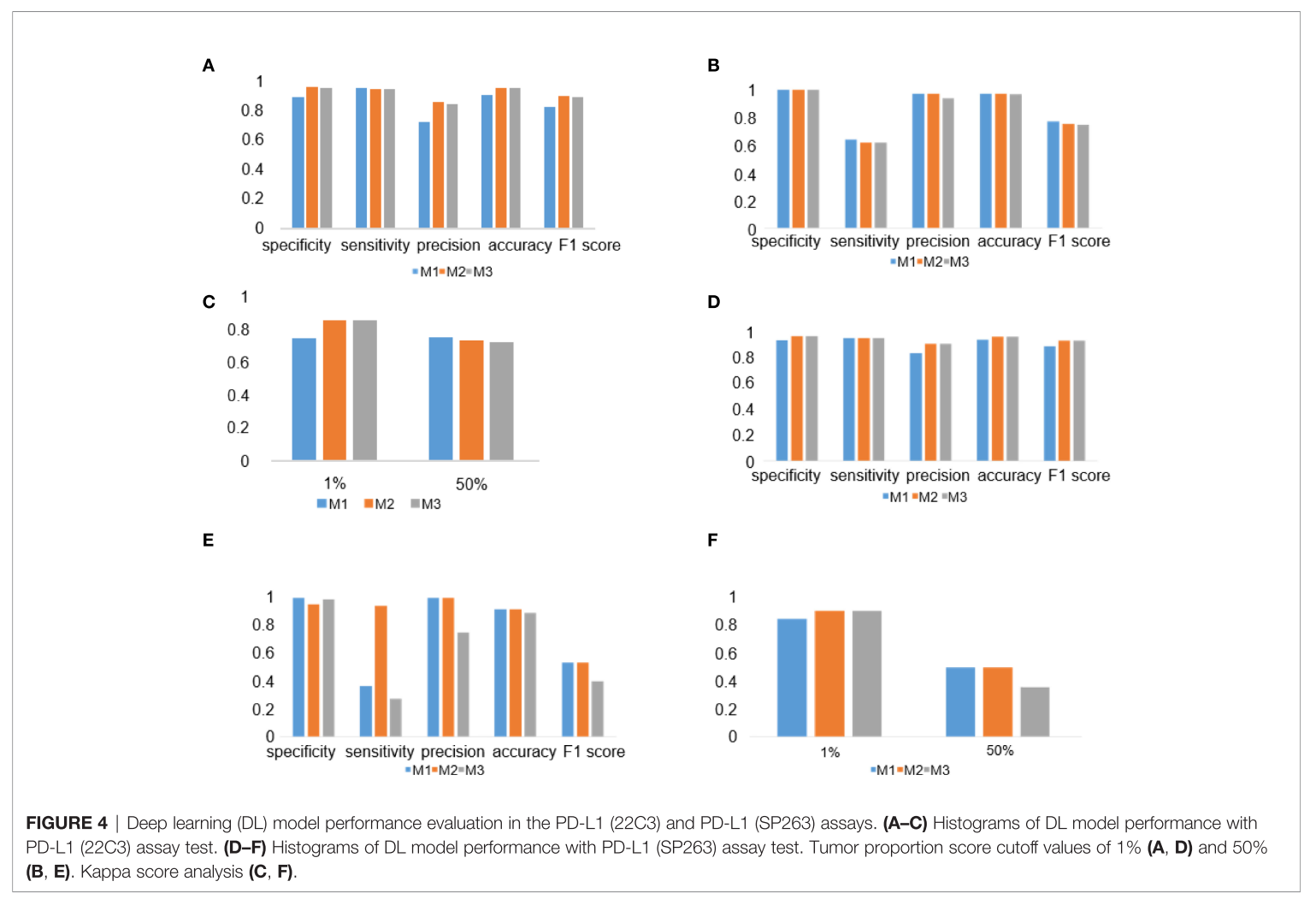
- M2와 M3가 TPS calculation에서 성능을 개선함
LCC (Linear Correlation Coefficient) in 22C3 and SP263 Assays

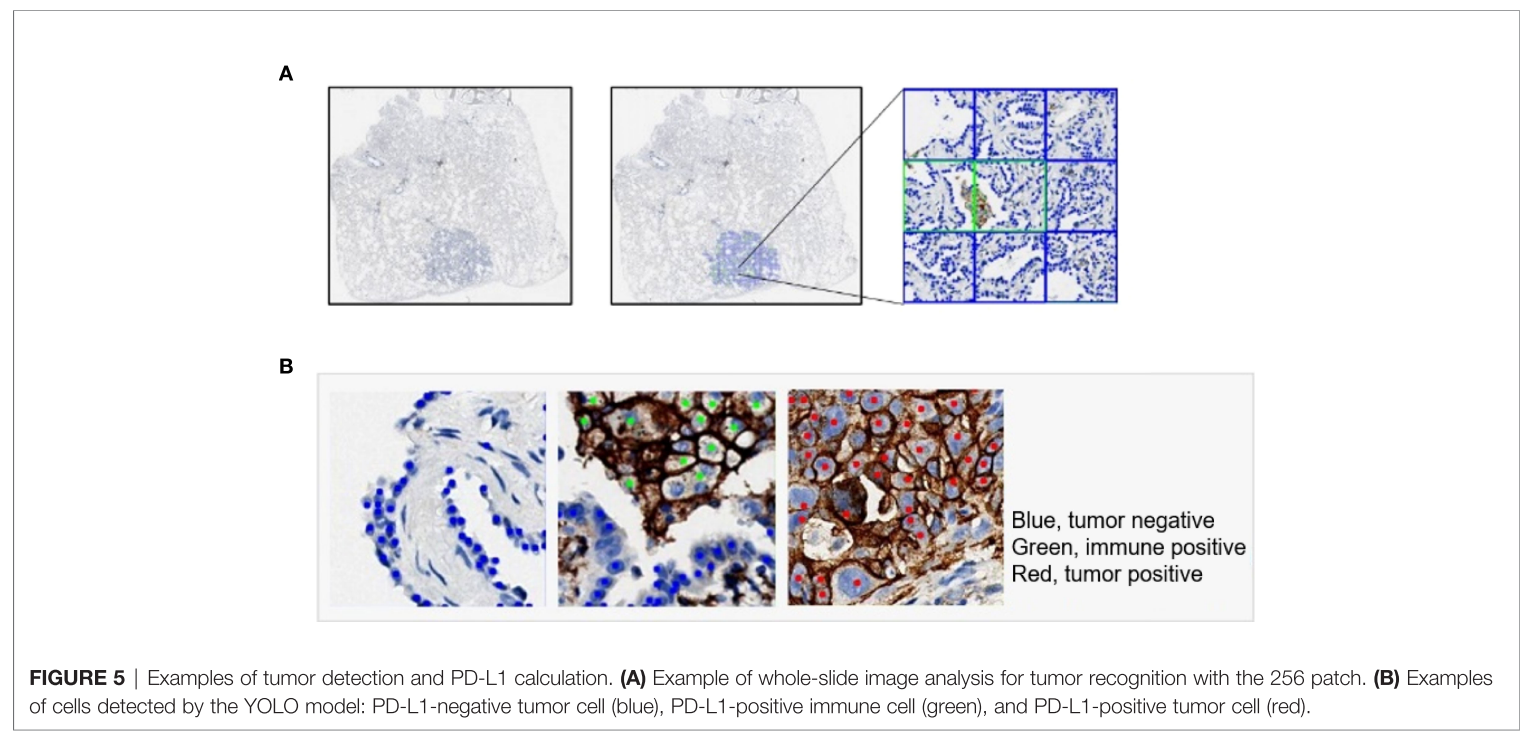
Examples of Tumor Detection and PD-L1
PD-L1-Positive Immune Cell Patch Filter Module
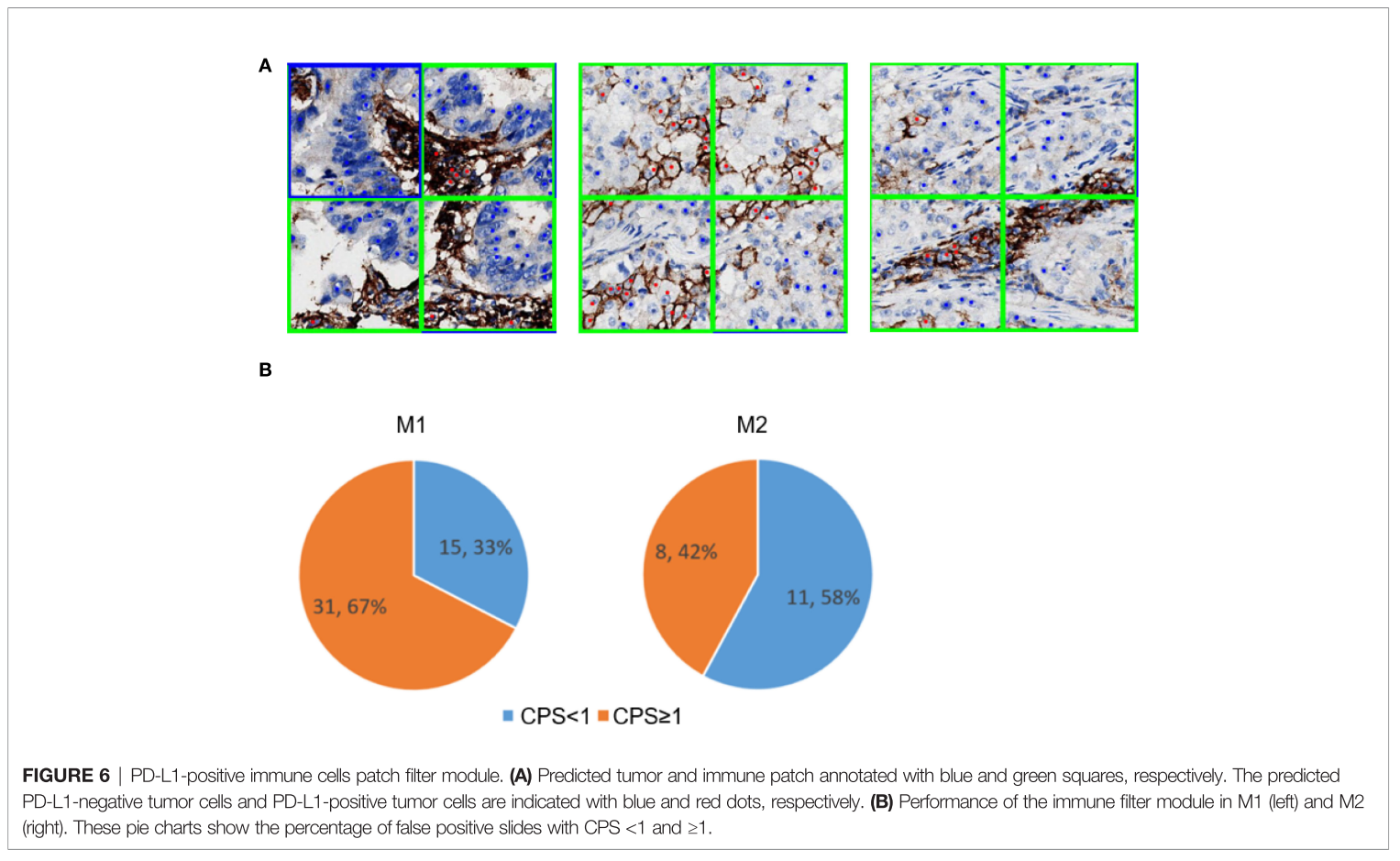
- M2 (1+2 vs 3 → 1 vs 2), immune cell filter module이 있어서 PD-L1 positive immune cell이 tumor cell로 혼동되는 걸 줄여준 것을 보여줌
- false positive가 많아지고 CPS >= 1 도 늘었음
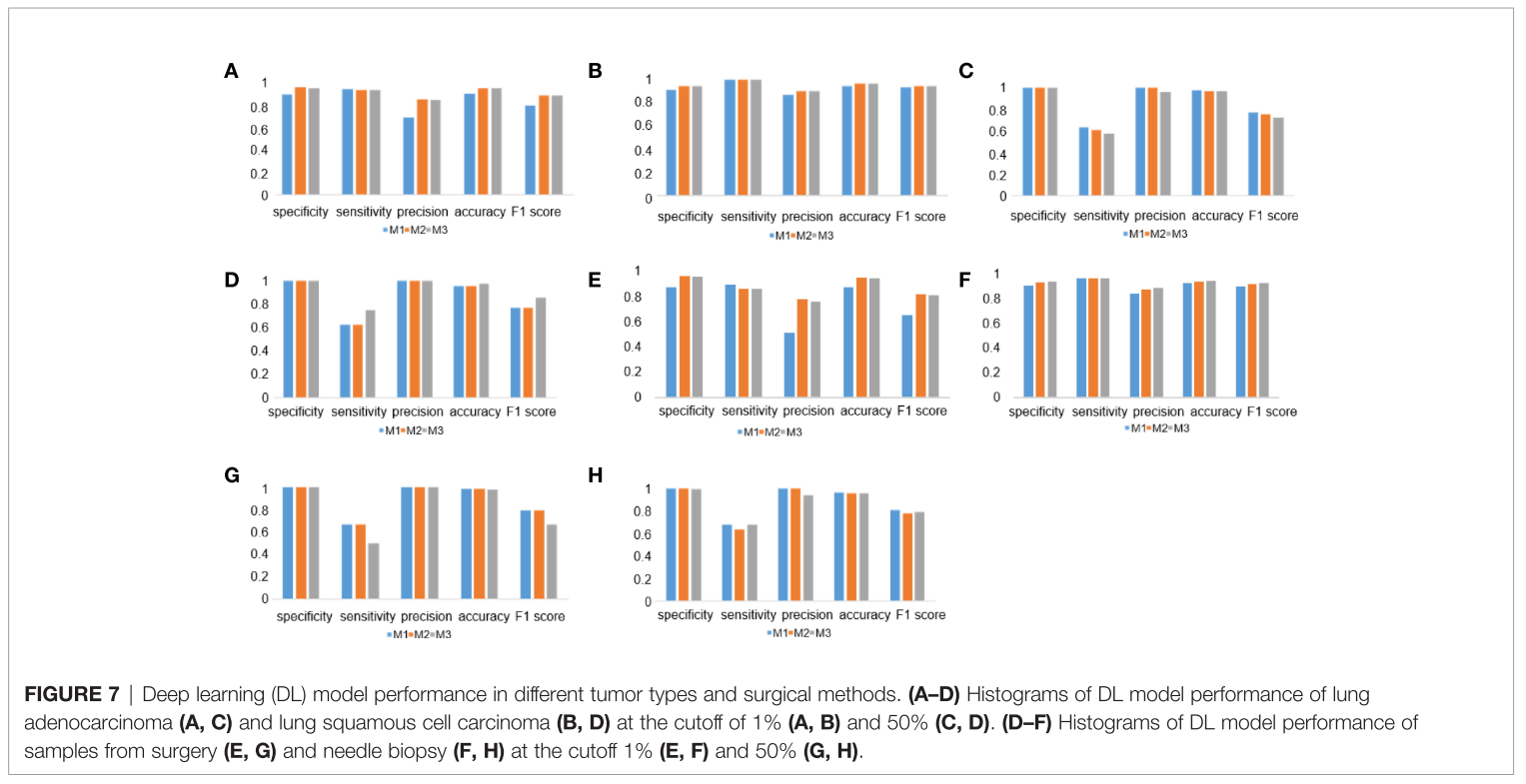
DL Model Performance in Different Tumor Types and Surgical Methods
Discussion & Conclusion
- 2 stage workflow를 3가지 classifiaction 시나리오로 실험해 비교하였음
- M1: tumor vs no-tumor
- M2: tumor vs no-tumor -> tumor positive/no immune positive vs tumor negative/immun positive로 쉬운 문제에서 어려운 문제로 binary classifier를 tree 형태로 설계하는 방식
- c-MET 쪽에서도 tumor positive/tumor negative를 하나의 tumor로 segmentation하면서 tumor negative에 대한 성능과 덩달아 tumor positive에 대한 성능도 저하하는데, 이런 식의 접근 방식을 응용해보는 아이디어도 나쁘지 않을 것 같음
- 다만, 2개의 network를 개발한다는 비용이 발생 ㅠ
- M3: tumor positive/tumor negative/immune positive/others로 한 번에 풀어버리는 multi-classification 문제로 설계하는 방식을 비교했는데, 둘 다 괜찮은 성능을 보였음
- class imbalance에 더 취약할 가능성이 있음
- 우리 쪽엔 immune을 고려하지 않고 있긴 한데, 추후에 고려해야될 것 같기도 하다.
- 둘 다 잘 나왔는데, M1과 M2를 비교하며 immnue filter module의 효과를 분석하고 최종적으로 M2가 좀 더 성능을 올렸다고 결론 짓고 있음
- 그리고 다양한 subtype에 대해서 성능을 비교하려고 노력했음
- Staining Type: 22C3 염색에서만 훈련시켰는데, 22C3, SP263 염색 둘 다에서 좋은 성능을 냈다
- 두 stain에 대한 stain 차이가 얼마나 나는 지 보여주면 좋았을 것 같다
- stain normalization이 적용 안 된 것 같은데, 그게 필요없을 정도로 비슷했을런지..
- Patch Size: 128/256 패치 사이즈 비교했고 128 사이즈가 같은 타입일 확률이 커서? tumor cell이 있는 patch에서 stromal cell에 대한 오진단을 낮출거라 예상했는데, 실제론 둘 다 잘 나오더라
- network가 해당 task의 pattern을 효과적으로 학습하는 차원에서 local context만으로도 판단가능한 task면 slide에서 추출하는 patch size를 충분히 줄여도 되지만, 그것을 모두 훈련에 사용하는 것이 옳은 지는 또 생각해봐야할 문제다.
- slide에서 patch를 어느 크기로 뽑을 지는 sample의 수, GPU 메모리에 올리는 batch size가 줄어드는 양적인 trade-off가 존재한다.
- tumor area segmentation은 좀 더 global context를 봐야한다고 생각하여 256 -> 512로 키우고 sampling하는 방식을 256 grid에서 1024 grid, 512 random crop으로 바꿨는데, 훈련 속도도 훨씬 빨랐고 성능도 괜찮은 경험이 있다.
- Tuomr Type: adenocarcinoma/squamous caner cell 둘에 대해서도 성능 차이가 별로 없었음
- Sampling Type: pleural effusion sample이 적다보니 18개중 4개의 negative sample가 FP, 1개의 positive sample이 FN이 발생함
- Staining Type: 22C3 염색에서만 훈련시켰는데, 22C3, SP263 염색 둘 다에서 좋은 성능을 냈다
