Abstract
-
denoising diffusion model들의 생성 process는 굉장히 느린데,
이는 번거로운 신경망에 의존하는, 긴 iterative noise estimation 때문이다.- 이 때문에 edge device들에 널리 사용되지 못하는 단점이 있다.
-
이전의 연구들은 diffusion 모델의 생성 과정을 가속화하기 위해, 효율은 많이 떨어트리지 않으면서도 더 짧은 sampling trajectory를 찾았다.
- 하지만, 그 연구들은 무거운 신경망 안의 각 iteration에서의 비싼 noise estimation을 간과했다.
-
본 연구에서는, noise estimation network를 압축(compress)하는 관점으로 생성을 가속화한다.
-
diffusion model은 retraining에 어려움이 있기에,
본 연구에서는 training-aware compression 패러다임은 제외했고,
PTQ(post training quantization)을 diffusion model에 도입했다. -
하지만, noise estimation netowkrs의 output distribution이 time-step에 따라 변화하기 때문에,
이전의 PTQ methods를 diffusion model에 적용하는 것은 실패한다.
왜냐하면, single-time step 시나리오에 맞게 디자인되었기 때문이다. -
diffusion model-specific한 PTQ method를 고안하기 위해,
PTQ on DM을 세 가지 관점으로 연구했다.
1) quantization operations,
2) calibration dataset,
3) calibration metric -
본 연구는 all-inclusive investigation으로부터의 여러 발견을 사용하고 요약했으며,
이를 통해 본 연구를 수식화 했다.
이 수식은 diffusion model의 unique한 multi-time-step 구조를 타겟으로 한다.
-
-
실험적으로, 본 연구의 method는 training-free manner로 성능을 유지하거나 심지어는 향상시키키면서도,
full-precision diffusion model을 8-bit 모델로 direct하게 quantize할 수 있다.
또한 중요하게, 우리 method는 예를 들어 DDIM과 같은 fast-sampling methods에 plug-and-play module 역할을 수행할 수 있다.
Introduction
연구 동향
-
denoising process는 신경망을 통해 수천번의 timesteps로 noise estimation을 반복해야 한다.
따라서, 생성 과정을 가속화하는것은 최근 활발한 연구 분야이다.
4
29
24
40
2
18 -
diffusion model들을 가속화하기 위해서, 여러 접근들이 연구되고 있다.
주로, 더 빠른 samplig strategy를 위해 trajectory를 sampling 하는 데 집중되어 있다.
예를 들어,
본 연구의 차별성
-
본 연구는 denoising process를 느리게 만드는 두 가지 orthgonal factors를 제안한다.
1) noise로부터 image를 sampling 하기 위한 iterations
2) 각 iteration에서 noise를 예측하기 위한 신경망- 기존 diffusion model 가속화 연구들은 주로
1)에 집중하고, 2)는 간과하는 경향이 있다.
4
29
24
40
2
18
- 신경망 compression 관점에서, 많은 network quantizastion과 pruning 연구들은 다음의 간단한 파이프라인을 따른다
: original model을 training하고,
quantized/pruned compressed model을 fine-tuning한다.
17
31
- 특히, training-aware compression 파이프라인은 full training dataset을 요구하고
end-to-end back-propagation을 수행하기 위해 많은 computation resource가 필요하다.
- 기존 diffusion model 가속화 연구들은 주로
Diffusion에는 PTQ가 적합하다
-
하지만, diffusion model들은 아래 두 가지 이유로 training-aware compression이 적합하지 않다.
-
1) training data가 privacy와 commercial 문제로 언제나 ready-to-use가 아니다.
-
2) training process가 정말 expensive하다.
예를 들어, DallE2나 ImageGen 같은 text-to-image model들을 위한 training data는 접근이 불가능하다.
만약 접근이 가능하더라도, 그 데이터들을 fine-tuning하는 것은 수백 수천 GPU 시간이 소요될 것이다.
-
-
Training-free network compression 기술이 diffusion model 가속을 위해 필요한 것이다.
따라서, PTQ를 diffusion model 가속에 도입했다.
22
3
17
PTQ 방식으로 denoising 과정의 computation 속도를 높이고,
diffusion 모델의 weight을 저장하기 위한 자원을 줄일 수 있다. -
PTQ는 장점이 많지만, diffusion model 안에서의 구현은 challenging하다.
- 왜냐하면, diffusion 모델의 구조는 이전의 PTQ로 구현된 구조(예를 들어 image recognition을 위한 CNN, ViT)와는 굉장히 다르기 때문이다.
특히, noise estimation network의 output distributions는 time-step에 따라 변화하기 때문에,
single-time-step 시나리오로 고안된 이전 연구들의 PTQ 방식을 diffusion 모델에 적용하기 힘들다.
- 왜냐하면, diffusion 모델의 구조는 이전의 PTQ로 구현된 구조(예를 들어 image recognition을 위한 CNN, ViT)와는 굉장히 다르기 때문이다.
PTQ와 Diffusion Model 분석
-
본 연구는 다음 근본적인 질문에 답하려고 시도한다.
: diffusion model process를 위한 PTQ의 core ingredients 설계(e.g. quantized operation selection, calibrations set collection, and calibration metric)는
얼마나 quantized diffuion models의 성능에 영향을 미치는가?- 본 연구에서는 PTQ와 diffusion model을 각각, 그리고 연관지어서 분석한다.
- 단순히 이전의 PTQ methods들을 일반화시켜서 diffusion model에 적용하는 것은 매우 큰 성능 하락을 불러일으킨다.
denoising process에서 time-step에 따른 output distribution 차이가 크기 때문이다.
다시 말하면, noise estimation network는 time-step에 의존한다.
그리고 이 time-step에 따라 output distribution이 변화하는 것이다.
이는 이전 연구들의 PTQ calibration의 핵심 모듈을 바로 사용할 수 없다는 것을 뜻한다.
Diffusion Model Specific Calibration Method
-
위의 관찰 결과를 바탕으로,
diffusion model specific한 calibration method인
NDTC(Normally Distributed Time-step Calibration)를 고안했다.이 방법은 skew normal distribution으로부터 a set of time-steps를 먼저 sampling하고,
denoising process를 통해 sampled time-steps에 관해서 calibration samples를 생성한다. -
이 방식으로, calibration set 안에서의 time-step 차이가 보완되고,
PTQ4DM의 성능을 향상시킨다.
정리
-
본 연구에서는 diffusion model 가속화 방법인
PTQ4DM(Post-Training for Diffusion Models)를 제안한다. -
본 논문의 contributions는 다음 세 가지다.
-
1) noise estimation networks가 direct하게 quantized되는
PTQ를 도입한 diffusion model 가속화
( training-free network compression 관점에서의 첫 번째 diffusion model 가속화 연구 )
-
2) 본 연구의 관찰 결과,
다양한 time-setps에서의 output distribution은 diffusion model에 PTQ를 적용했을 때 큰 성능 하락을 일으킴.
이 관찰 결과를 토대로, PTQ를 다른 관점에서 제안함
-
3) 큰 성능 감소 없이 pre-trained diffusion model들을 8-bit로 quantize 가능함.
plug-ang-play module로 다른 SoTA diffusion model에도 적용이 가능함.
-
Related Work
PTQ
-
QAT는 신경망 training 과정에서 quantization을 고려하는 반면,
PTQ는 training 이후 quantize한다.
PTQ가 더 적은 시간과 computation 자원을 소비하기 때문에,
신경망 배포에 널리 사용된다. -
대부분의 PTQ 연구는 각 layter에서 weights와 activation을 위한 quantization parameters를 설정한다.
-
uniform quantization을 예로 들면, quantization paramers는 scaling factor 와 zero point 를 포함한다.
fp 값 는 quantization parameters에 따라
int 값 로 quantized된다.
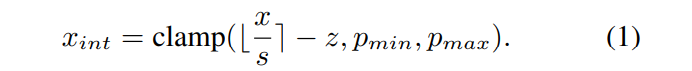
clamp 함수는 rounded value 를
범위로 자른다. -
layer안의 weight tensor와 activation tensor를 위한 quantization parameters를 설정하기 위해서,
가장 간단하고 효율적인 방법은 quantization 이전과 이후의
tensors의 MSE를 최소화하는 quantization parameter를 찾는 것이다.
다른 방법으로, L1 distance, cosine distance, KL divergence도
quantization 전후의 tensors 간의 distance를 측정하는데 사용될 수 있다.
-
-
신경망의 activations를 계산하기 위해선,
적은 수의 calibration samples가 PTQ의 input으로 사용돼야 한다.
선택된 quantization parameters는 calibration samples 선택에 의존적이다. -
ZSQ(Zero-shot quantization)는 PTQ의 특수한 케이스다.
ZSQ는 신경망에 기록된 정보(예를 들면, batch normalization layer의 mean과 var)에 따라
calibration dataset을 생성한다.
real samples의 distribution과 유사하도록 activations의 distribution을 만들기 위해서,
gradient descent를 통해 input sample을 생성한다.
diffusion 모델에서 noise로부터 image를 생성하는 과정은
오직 network inference만 사용하기 때문에,
이전의 ZSQ methods와는 꽤 다르다.
PTQ on Diffusion Models
Preliminaries
PTQ
-
well-trained network의 각 layer의 weight tensor와 activation tensor를 위한 quantization parameters를 선택한다.
-
본 연구에서는 tensor를 quantized tensor로 변환하기 위한
quantization parameter로
scaling factor 와 zero point 를 사용했다.-
quantization으로 인한 error를 최소화하는 것은
quantization parameters를 선택하기 위해 가장 널리 쓰이는 방법 중 하나이다.
quantization error는 아래와 같이 수식화된다.
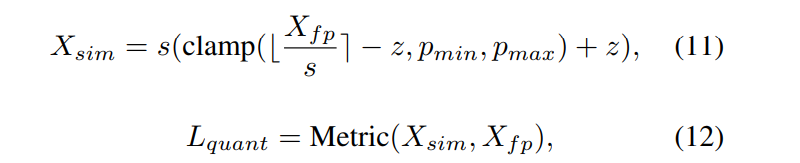
deqauntized tensor
Metric: fp tensor 와 의 distance를 측정하기 위한 metric 함수
(MSE, cosine distance, L1 distance, KL divergence는 널리 쓰이는 metric functions이다.) -
quantization 과정은 아래 같이 수식화 될 수 있다.
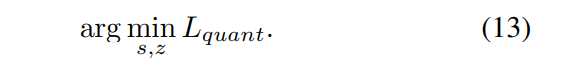
quantization error를 최소화하기 위해 weight를 direct하게 quantize할 수 있지만,
우리는 input 없이는 바로 activation tensor를 얻고 quantize 할 수는 없다.
-
따라서 fp activation tensor를 모으기 위해서,
unlabeled input samples(calibration dataset)이 input으로 사용된다.
calibration dataset의 크기는 (e.g. 128 randomly selected images) training dataset에 비해 무척 작다.
-
-
보통, PTQ는 신경망을 세 단계로 quantize한다.
-
1) 신경망에서 어떤 operation이 quantized되어야 하는지 고르고,
다른 opeartion들은 fp로 냅둔다.
예를 들어,
softmax와 GeLU와 같은 특별한 함수들은 fp로 냅둔다.
이 operation들을 quantize하면 심각하게 quantization error를 증가시킬 수 있고, 연산이 그렇게 많이 요구되지 않기 때문이다. -
2) calibration sample들을 모은다.
calibration samples에 quantization parameters가 overfitting되지 않도록 하려면,
calibration samples의 distribution은 real data의 distribution과 가능한한 가까워야 한다. -
3) weight tensors와 activation tensors를 위한
quantization paramers를 선택하기 위해 적절한 방법을 사용한다.
-
Exploration on Operation Selection
-
diffusion model에서 어떤 operations가 quantized되어야 하는지 image generation procss를 분석했다.
-
diffusion model은 iterative하게 로부터 를 생성한다.
각 timestep에서, 신경망의 inputs는 , 이고
outpus는 mean 와 variance 이다.
은 아래 수식에서 정의된 distribution으로부터 sampling 된다.
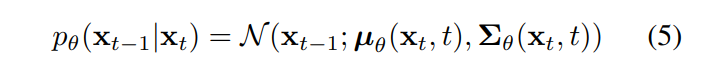
Figure. 2와 같이, diffusion model의 신경망은 UNet 형태의 CNN 구조를 갖는다.
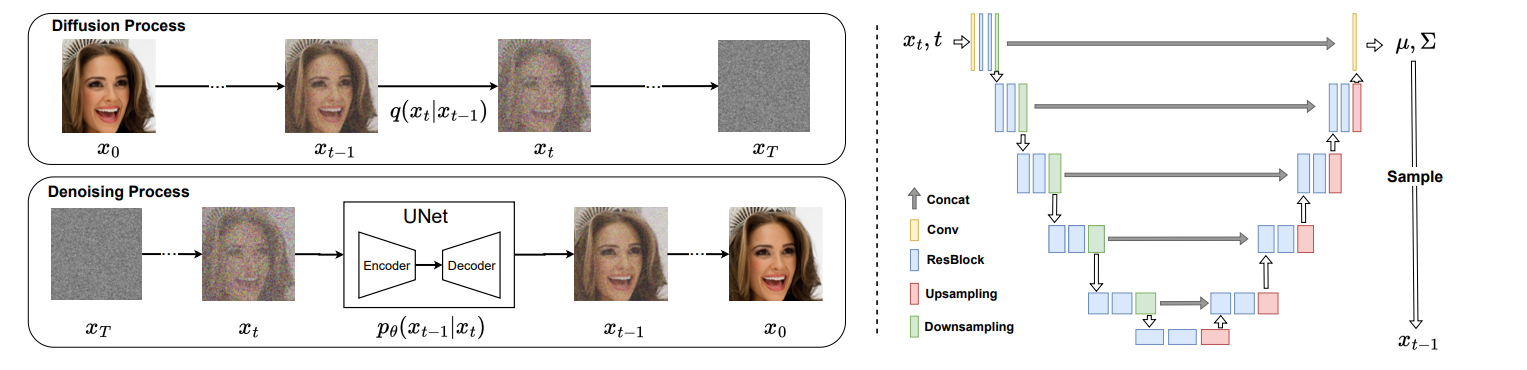
이전 PTQ 연구들과 같이, computation-intesive conovlution layers와 fully-connected layers는 quantized되어야 한다.
batch normalization은 convolution layer안에 포함될 수 으며,
SiLU와 softmax같은 특수한 함수는 full-precision으로 유지된다. -
diffusion model에 두 가지 질문이 더 있다.
- 신경망의 output인 와 가 quantized될 수 있을까?
- sampled image 이 quantized될 수 있을까?
이에 대해 답하기 위해서,
우리는 오직 , 또는 을 생성하는 operation을 quantize한다.
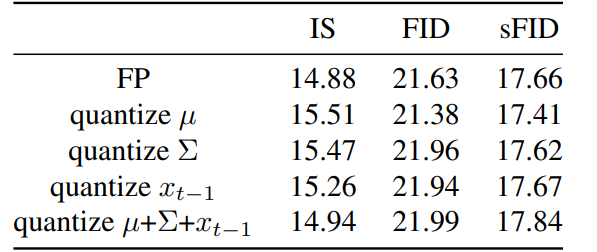
Table 1과 같이, , 또는 들은 quantization에 민감하지 않음을 관찰했고,
quantized될 수 있음을 알 수 있었다.
Exploration on Calibration Dataset
-
두 번째 단계는 diffusion model을 quantize하기 위한 calibration sample들을 모으는 것이다.
calibration samples는 training dataset으로부터 얻어질 수 있으며, 다른 networks를 quantize하는데 사용된다.
하지만, diffuion model의 training dataset은 로, network's의 input이 아니다.
실제 input은 genrated smaples 이다.또한, 우리는 diffusion process의 generated samples를 사용해야 할까?
또는 denoising process의 generated samples를 사용해야 할까?어떤 time-step 에서, generated samples를 뽑아야 할까?
이 section은 어떻게 좋은 calibration dataset을 만들 수 있는지 살펴본다.
-
여러 PTQ baseline들을 조사하여 네 가지 유의미한 관찰(아래 Analysis on PTQ calibrations and DMs)을 얻어서, 본 연구의 설계에 참고했다(아래 Noramlly Distributed Time-step Calibration).
PTQ4DM calibration을 통해, 8-bit PTQ diffusion model은 full-precision 모델과 동일한 성능을 가짐을 실험을 통해 알 수 있었다.
(8-bit DM 23.9 FID, 15.8 IS
32-bit DM 21.6 FID, 14.9 IS)
Analysis on PTQ Calibration and DMs
-
우리는 뽑은 calibration sample들의 distribution이 real data의 distribution과 가능한한 가깝길 원한다.
calibration set이 quantization error를 줄이도록 quantization을 supervise할 수 있기 때문이다.이전의 연구들은 single-time-step 시나리오에서 구현되었기 때문에,real training dataset으로부터 networks를 quantizing하기 위한 sample들을 직접 추출할 수 있었다.
calibration dataset은 굉장히 작은 규모이기 때문에, colletcion은 굉장히 sensitive하다.
만약 뽑은 calibration dataset의 분포가 real dataset을 잘 표현(반영)하지 못한다면, calibration task에 overfitting을 초래할 수 있다.
-
DM을 위한 PTQ를 calibration할 때는 더 많은 challenge가 존재한다.
quantize될 networks의 input들이 generated samples 이다.DM을 quantize하기 위해선 calibration dataset collection method를 특정한 multi-time-step 시나리오에서 고안해야 한다.
이 연구에선 PTQ calibraion과 DMs를 모두 조사한 후, 다음과 같은 관찰을 얻을 수 있었다.
Observation 0: Distributions of activation changes along with time-step chaning.
-
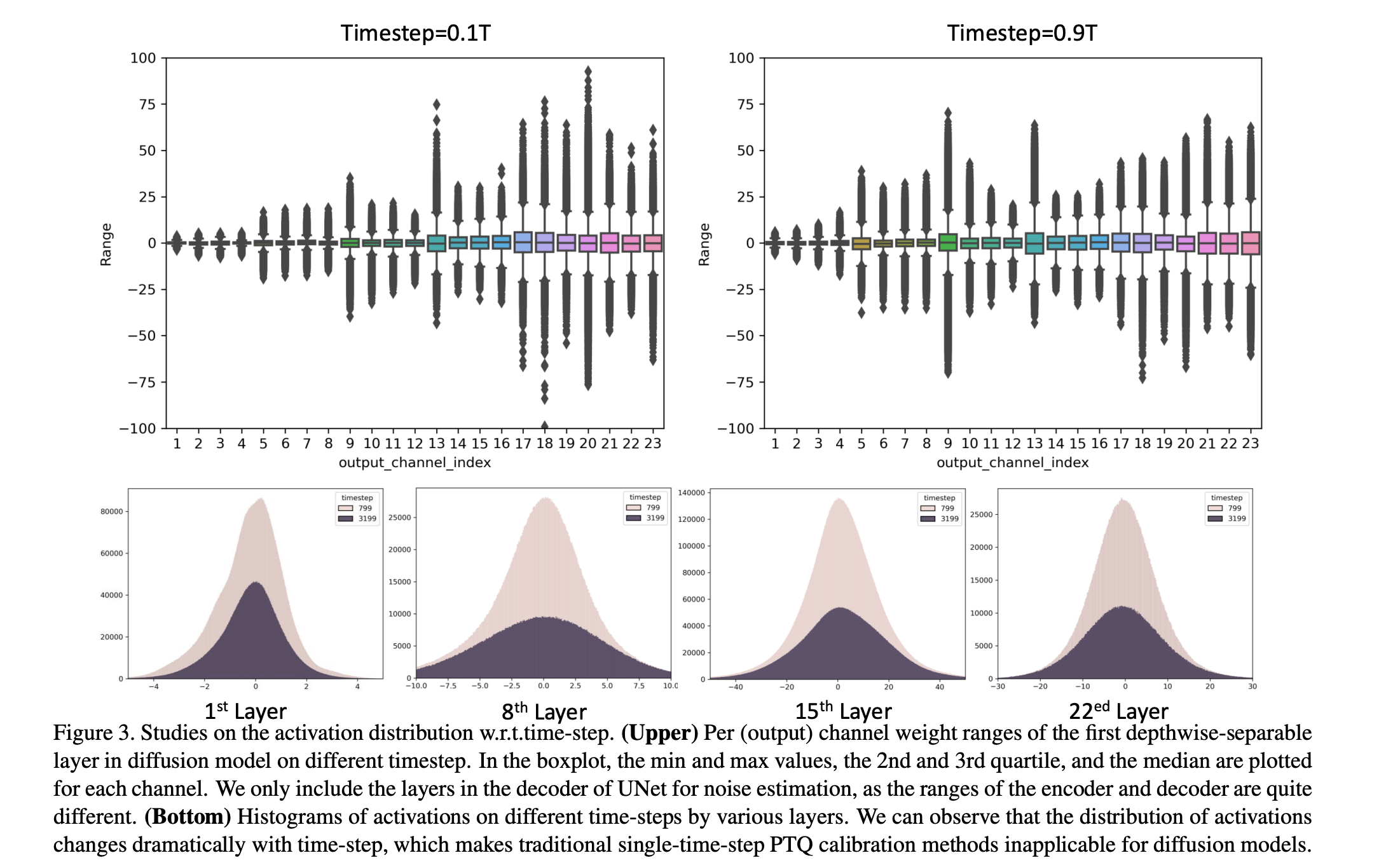
diffusion model들의 output distribution 변화를 이해하기 위해, time-step에 따른 activation distribution을 조사했다.
time-step에 달라짐에 따라 output distribution이 어떻게 변화하는지, 예를 들어
와 가 주어졌을 때,
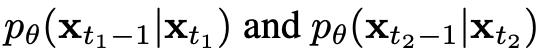 의 output activation distribution을 분석하고자 했다.
의 output activation distribution을 분석하고자 했다.이론적으로, time-step에 따라 distribution이 변화한다면,
이전의 PTQ calibration methods들은 temporally-invariant calibration으로 제안되었기 때문에 적용하기에는 어려움이 있다.먼저 noise estimatio network의 overall activation distribution을 boxplot을 통해 분석했다.
그 후 histogram을 통해 layer-wise distributions를 면밀히 살펴봤다.
그 결과는 다음 Fig 3과 같다.
각기 다른 time-steps에서 대응되는 activation distributions는 큰 차이를 갖고있음을 알 수 있었고,
이전의 PTQ calibration methods들을 DM과 같은 multi-time-step models에 적용이 어려움을 알 수 있었다.
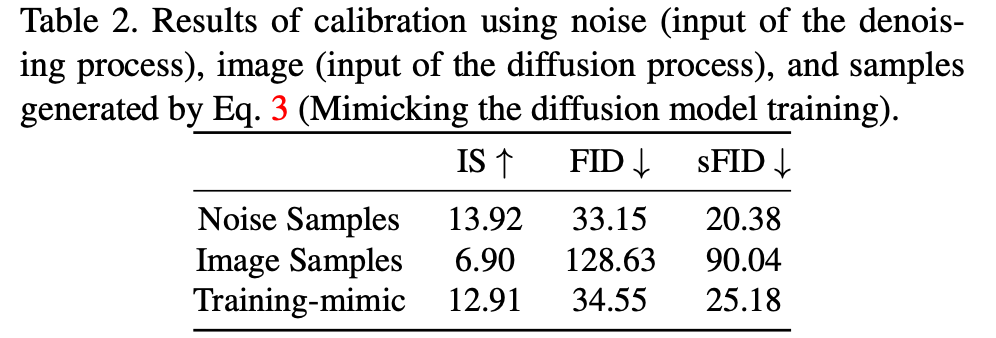
Observation 1: Generated samples in the denoising preocss are more constructicve for calibration
-
보편적으로, diffusion에서 PTQ calibration을 위한 sample들을 생성하는 데는 두 방향이 있다.
1) raw images as input for diffusion process
2) noise as input for denoising process이전의 PTQ methods들은 raw image들을 사용했는데,
raw images는 training set의 distribution을 대표할 수 있는 GT 역할을 할 수 있기 때문이다.본 연구는 각각 raw images for diffusion process와
Gaussian noise for denoising process로 이루어진 두 가지 calibration sets로 quantized model들을 calibrate하는 비교 실험을 진행했다.또 다른 유사한 baseline은 diffusion process의 training samples를 calibration data로 사용한다.
구체적으로 말하면, 우리는 각 image 에 대해 timestep 를 랜덤하게 생성하고,
아래 수식을 사용해 를 생성한다.
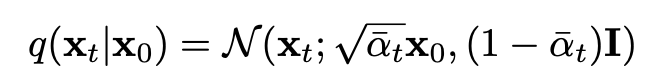
다르게 말하면, Image + Gaussian 에서 calibration samples를 추출하는 것이다.
이를 training-mimic baseline으로 명명했다.실험 결과는 아래 Tab. 2.에 나와있다.
이 실험을 통해 diffusion process의 input noise가 quantized DMs를 calibration하는데 더 효율적임을 알 수 있었다.
Observation 2: Sample close to real image is more benefical for calibration.
-
위 관찰을 바탕으로, 각 time-step 의 samples로 calibrated되는 quantized diffusion model인
DM을 위한 PTQ calibration baseline을 만들었다.
이때, [Loss aware post-training quantization] 논문을 기반으로 했다.
이 straight-forward한 접근을 naive PTQ-for-DM baseline으로 명명했다.구체적으로, Gaussian noise 가 주어질 때,
calibration set을 로
생성하기 위해, 아래 Eq. 5의 full-precision noise estimation network 를 사용하는 diffusion model을 사용했다.
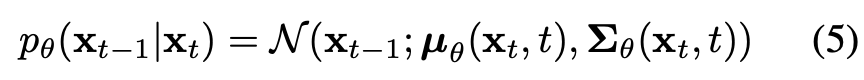
그 후, calibration set을 사용해서 우리의 quantized noise estimation network, 를 calibrate하기 위해 사용했다.
(여기서 은 quantized paramters를 뜻한다.) -
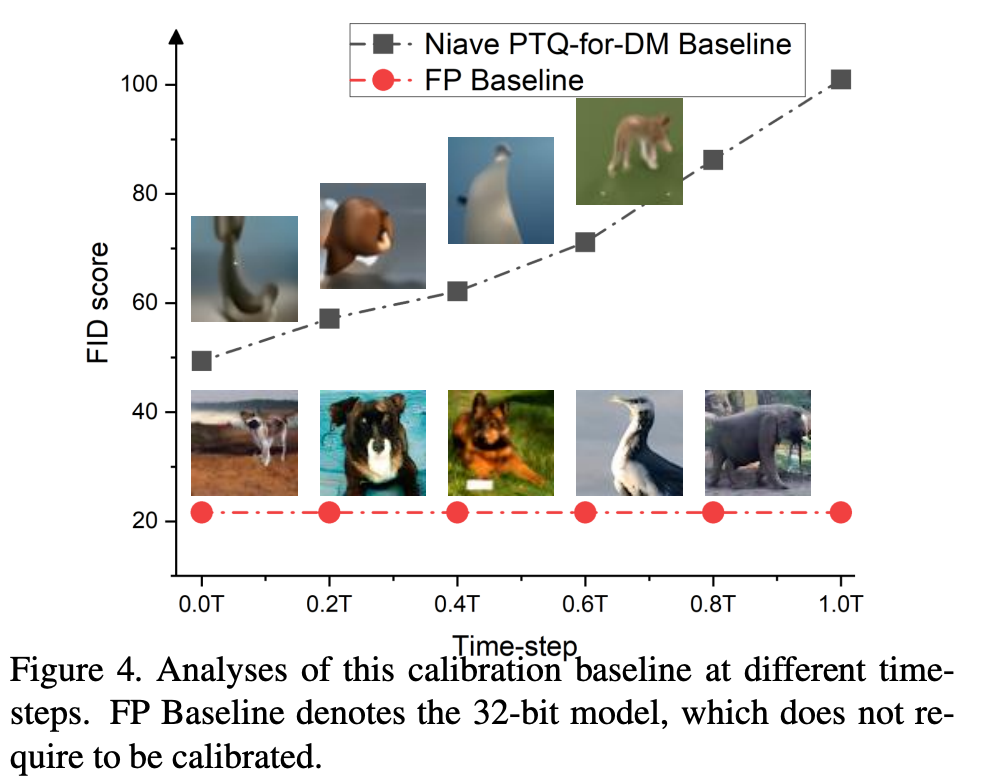
이 calibration baseline과 함께 각기 다른 time-steps에서 일련의 실험을 진행했다.
where : total denoising time steps.이 실험의 결과는 아래 Fig.4와 같다.
naive baseline으로 calibrated된 8-bit 모델은 만족할만한 image를 정성적으로나 정량적으로 생성하지 못함을 확인할 수 있다.
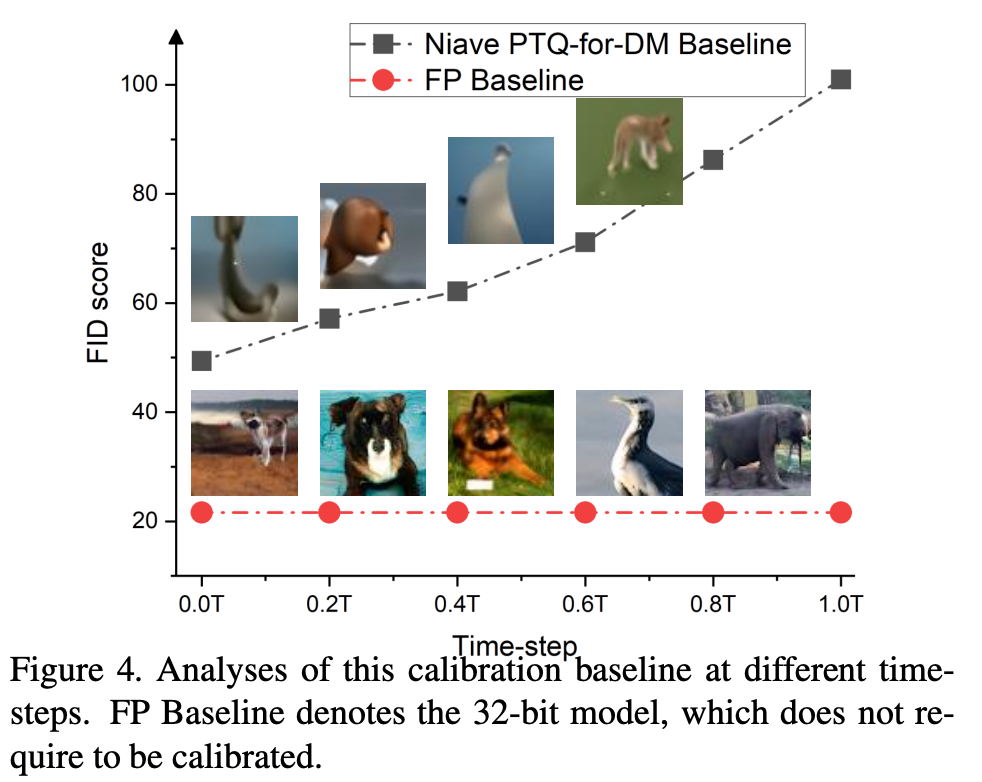
다행히도, 이 실험을 진행하면서 PTQ calibration이 time-step 가 real image 에 다가가면서 더 도움이 된다는 점을 알 수 있었다.
이 현상에 대한 직관적인 설명을 해보자면,
denoising process에서 가 줄어들면서, network 의 output의 distribution은 real image의 distribution과 유사해지기 때문이다.
Observation 3: Instead of a set of samples generated at the same time-step, calibration samples should be generated with varying time-steps.
-
대부분의 methods들은 single-time-step 시나리오를 위해 제안되었지만,
본 연구의 calibration dataset은 multi-time-step 시나리오를 위해 뽑았다.본 연구에서는 diffusion model의 calibration dataset은 다양한 time-stpe의 sample stem을 포함해야 한다고 가정했다.
time-step에 따른 sample의 차이를 반영해야 된다고 생각했기 때문이다.
가장 직관적으로 이 가정을 실험해볼 수 있는 방법은 time-steps의 범위에서 uniform하게 를 sampling하는 것이다.
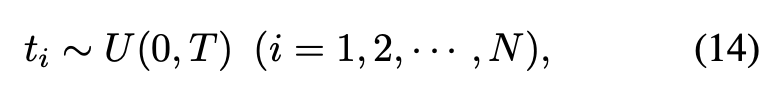
여기서 : uniform distribution between 0 and T,
: size of calibration set,
: # of time-steps in denoising process
주어진 Gaussian noise 와 에 대해서,
full-precision noise estimation network 로 diffusion model을 사용하여,
를 생성한다.
최종적으로, calibration set 을 얻게 된다.
따라서 위 calibration sample은 넓은 범위의 time steps를 커버할 수 있다.
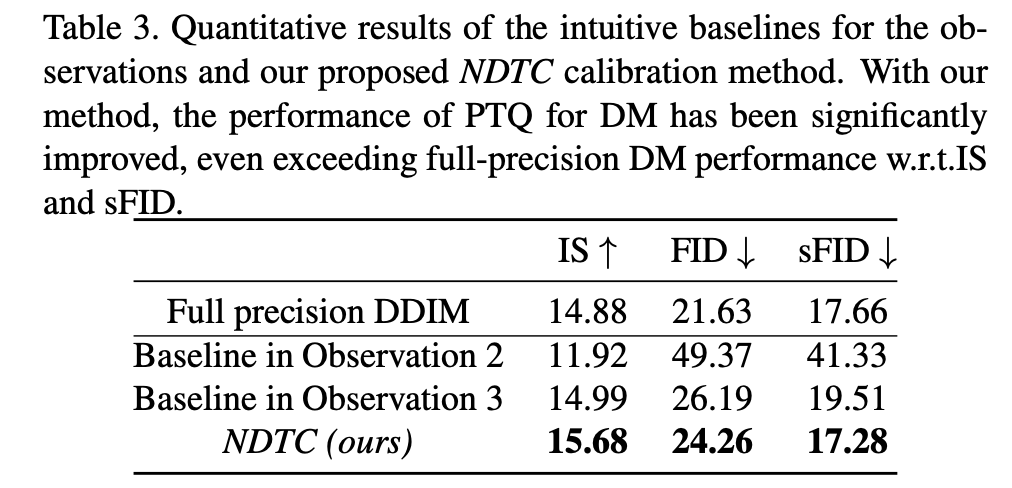
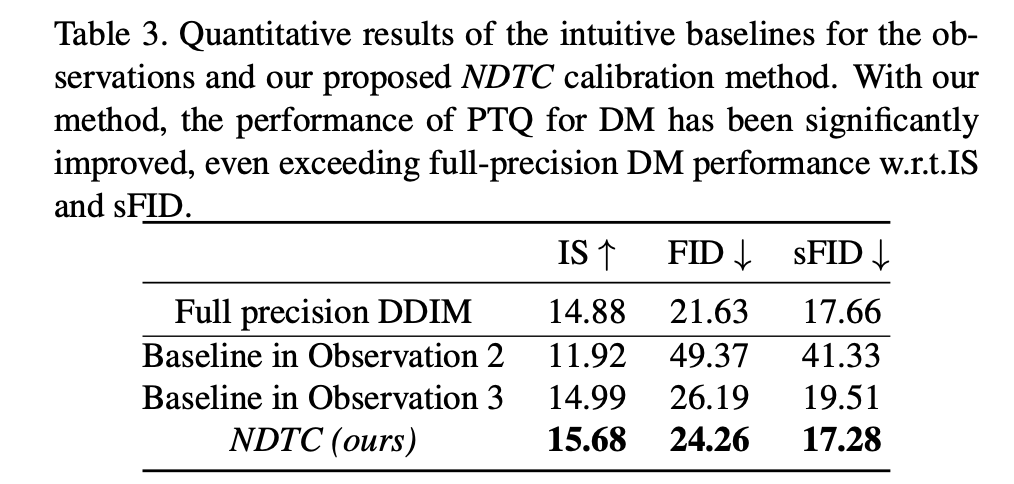
이 collection method의 효율성을 테스트한 결과는 Tab. 3과 같다.
결과적으로 time-step discrepancy를 반영하는 calibration sample들을 validate하는 결과를 얻었다.
Normally Distributed Time-step Calibration
-
위에서 증명한 calibration baseline과 observation을 바탕으로, calibration sample이 다음을 만족하길 원한다.
1) full-precision diffusion model로 denoising process에 의행 생성되는 calibration samples
2) 에 상대적으로 가깝고,
로부터 멀리 떨어진 calibration samples.
3) 다양한 time-steps를 커버한 calibration sampels.하지만 위의 2), 3) 조건은 trade-off 관계로, 동시에 수행될 수 없다.
모든 조건을 고려하여, DM-specifig calibration set collection method를 제안하는데,
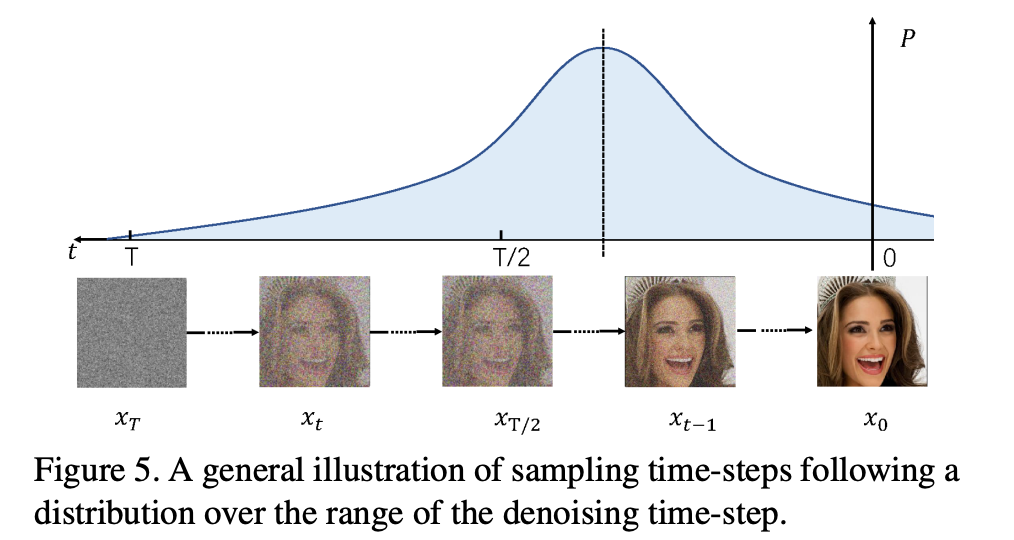
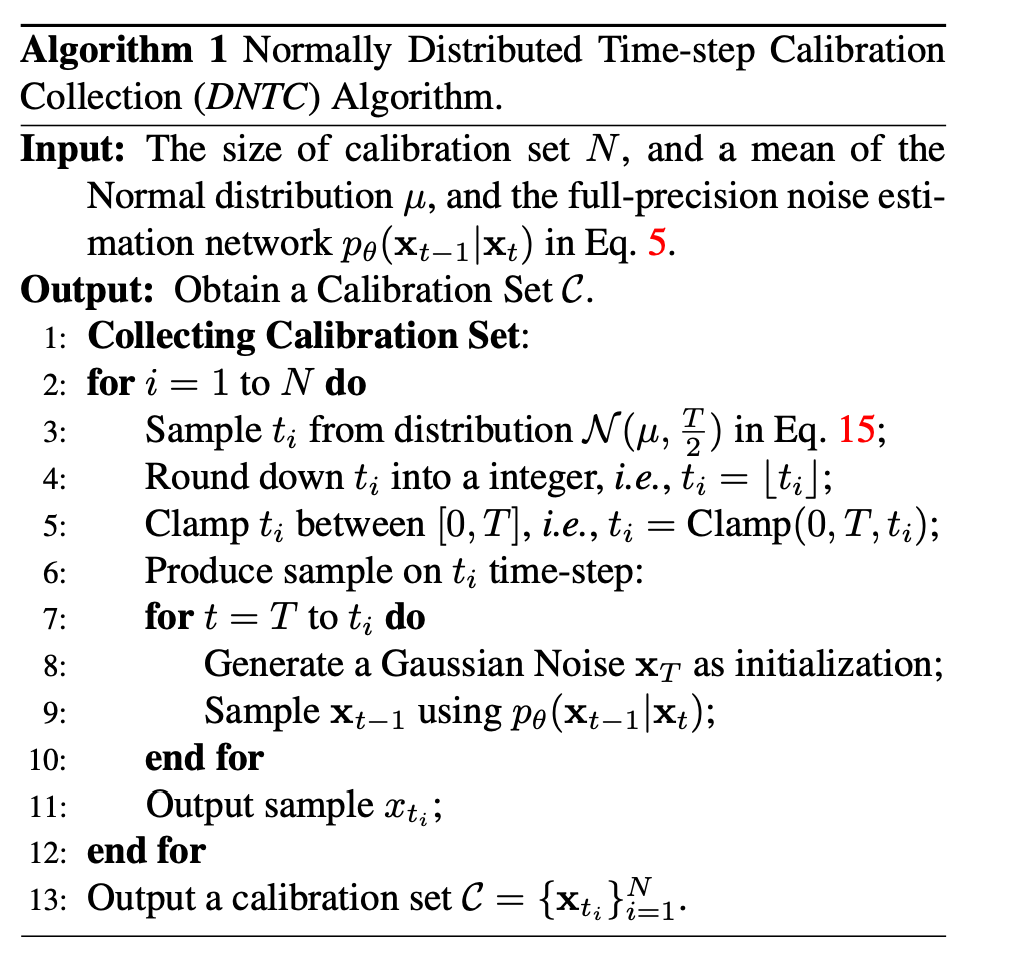
그 이름은 Normally Distributed Time-step Calibration(NDTC)이다.이 method는 calibration set 가 denoising pocess에 의해 생성되고(조건 1),
이때 time-step 는 skew Normal distribution으로부터 샘플링된다.
(조건 2와 3의 균형을 맞추기 위해서)구체적으로, time-step 범위에서 skew normal distribution을 따르는 sampled 를 생성한다.
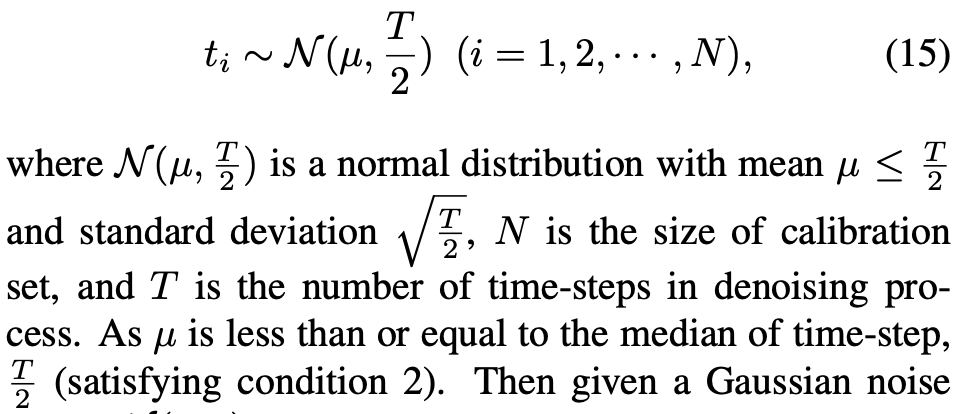
이후, 주어진 Gaussian noise 와 로,
full-precision noise estimation network와 함께 diffusion model을 사용하여, 를 생성한다.
최종적으로, 우리는 calibration set 을 얻게된다.
자세한 collection 알고리즘은 아래와 같다.
NDTC의 효율성은 PTQ baseline과 full-precision DM 간의 비교를 통해 평가했으며,
결과는 Tab.3, Fig.6와 같다.

Exploration on Parameter Calibration
-
calibration sample들이 collected되면,
세 번째 step은 diffusion mdoel의 tensor들을 위한 quantization parameter를 선택하는 것이다. -
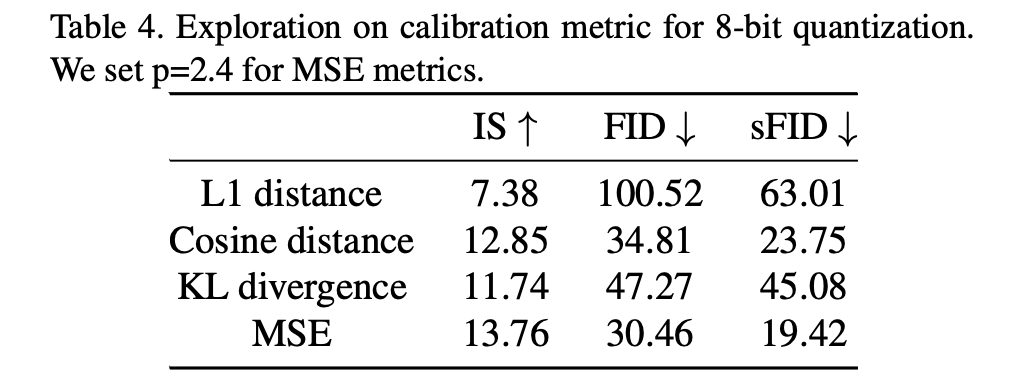
Table 4에서 볼 수 있듯,
MSE가 L1 distance, cosine distance, KL divergence보다 보다 더 나은 것을 확인했고
MSE를 diffusion model을 quantize하는 metric으로 사용했다.