4. Causal Models
4-1. Identifiability
Causal Estimand는 causal model을 통해 identification 될 수 있다.
4-2. Modularity assumption
- 에 intervene 하면, 만 변함
- 같은 표현 : modular, independent mechanisms, autonomy, invariance
- intervene한 node set가 S라면
- 만약 iS, 는 unchange
- 만약 iS, 는 1 또는 0
- modularity violation
- intervene한 node 말고 다른 노드의 까지 변화시킴.
4-3. Truncated factorization
- identification 예시
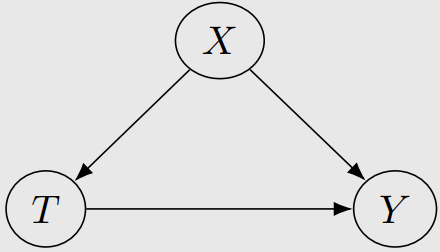

4-4. Backdoor criterion & Backdoor adjustment
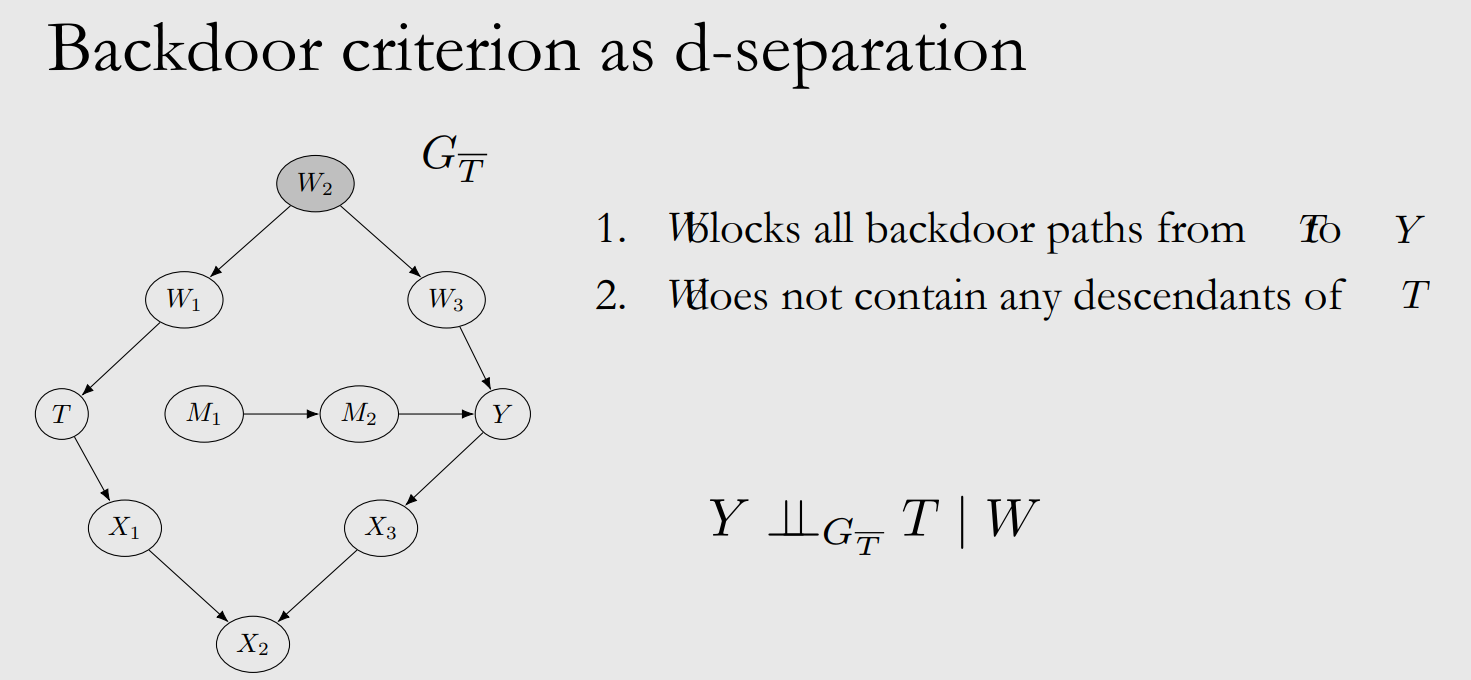
- Backdoor criterion W
- T → Y의 backdoor path를 모두 막음
- T의 descendant를 포함하지 않음
- modularity assumption과 W가 backdoor criterion을 만족하면 아래와 같이 identify할 수 있다.
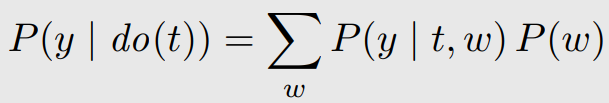
이해안됨.
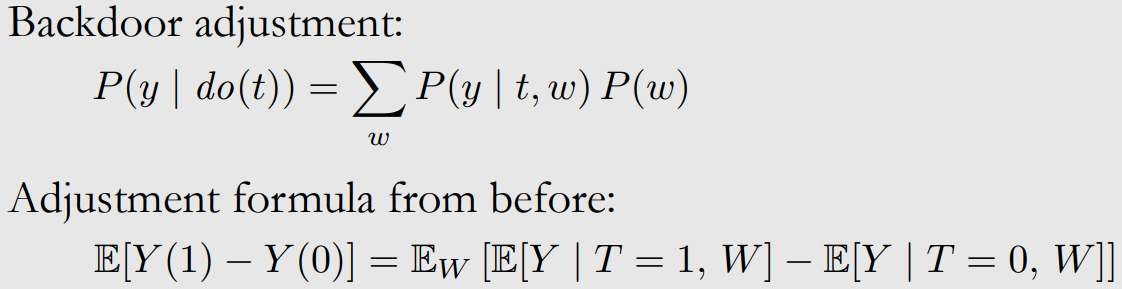
4-5. Structural equation
- A가 B의 원인일 때,
4-6. Structural causal models(SCMs)
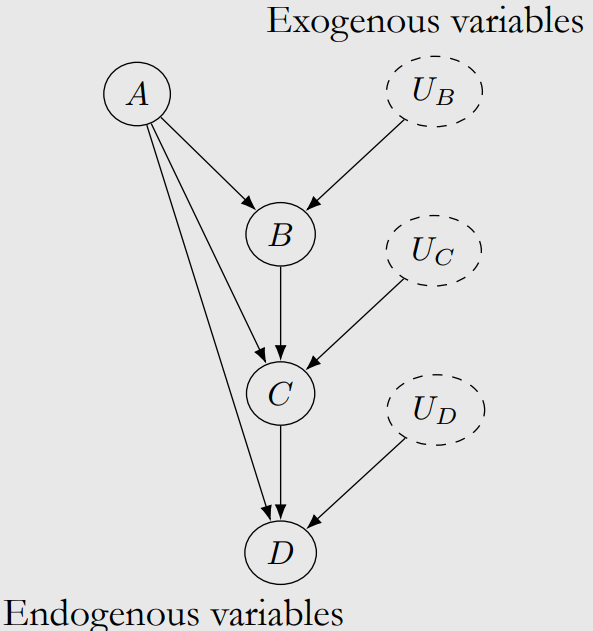
-
Exogenous variable : parent x
-
Modularity assumption for SCMs
- SCM이 M이고 interventional SCM이 Mt일때,
M과 Mt는 T의 structural equation을 제외한 모든 structural equation을 공유한다.
- SCM이 M이고 interventional SCM이 Mt일때,
-
treatment의 descendant를 condition하면 안되는 이유
-
mediator : causal association을 block
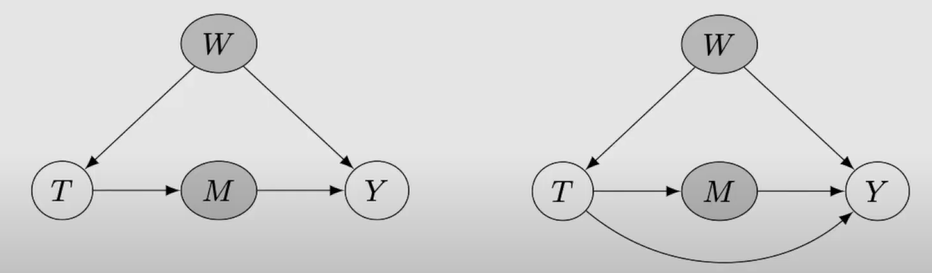
-
새로운 post-treatment association을 유발(collider bias)
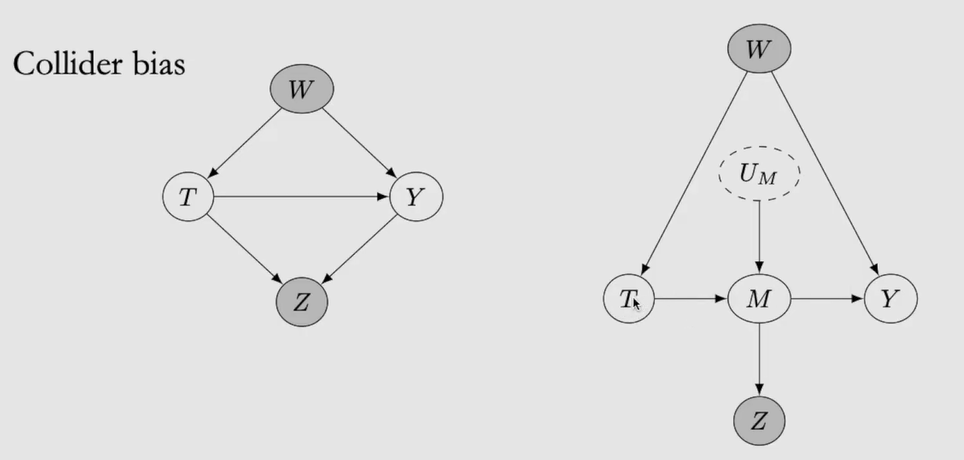
-
-
treatment의 descendant를 condition한 것이 아니지만 collider bias를 관찰하게 되는 상황
-
M-bias : 새로운 pre-treatment association을 유발
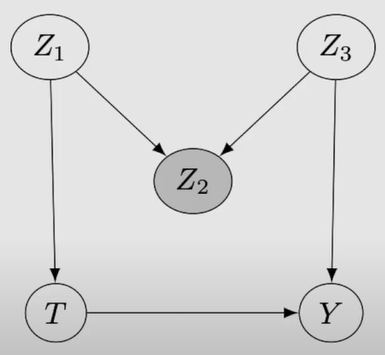
Example : Sodium intake → blood pressure
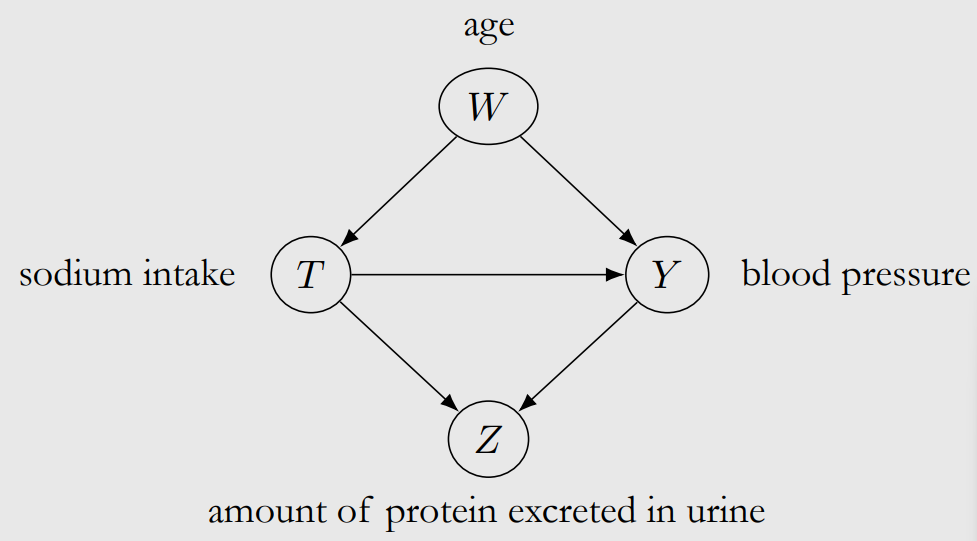

-
