https://www.bradyneal.com/causal-inference-course
Introduction to Causal Inference라는 강의를 듣고 정리했습니다.
7. Unobserved Confounding, Bounds, and Sensitivity Analysis
7-1. Bounds
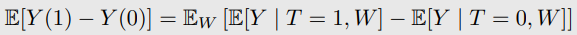
- unconfoundedness를 가정하면 point estimation이 가능
- weaker assumption을 사용하면 interval로 estimation (partial identification, set identification)
7-1-1. No-Assumptions Bound
Bounded Potential Outcomes
trivial length limit : 2
trivial length limit : 2(b-a)
Observational-Counterfactual Decomposition
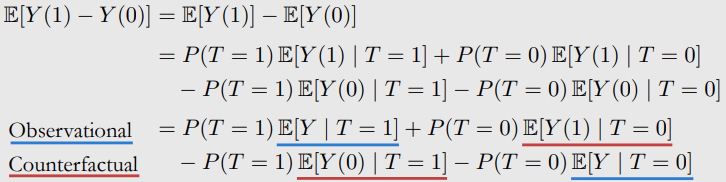

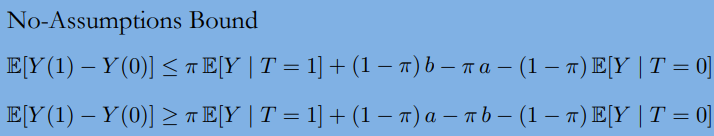
No-Assumptions Interval Length

7-1-2. Monotone Treatment Response
Nonnegative Monotone Treatment Response (MTR)
항상 treatment가 효과가 있을 때,
ITE의 평균은 non-negative ()
- 증명
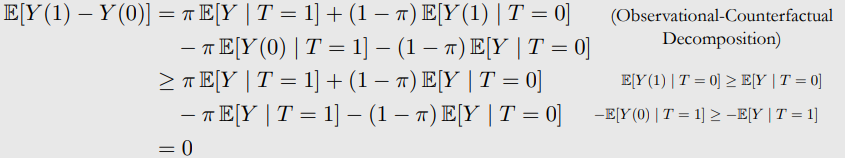
Nonpositive Monotone Treatment Response
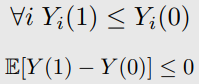
7-1-3. Monotone Treatment Selection (MTS)
-
가정 : 좋은 outcome을 내는 units은 treatment group으로 self selection된다.

-
MTS
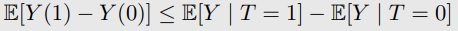
7-1-4. Optimal Treatment Selection
-
가정 : individual은 그들에게 도움되는 treatment를 항상 받게 되어있음

-
OTS

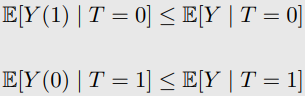
-
OTS Upper Bound 1
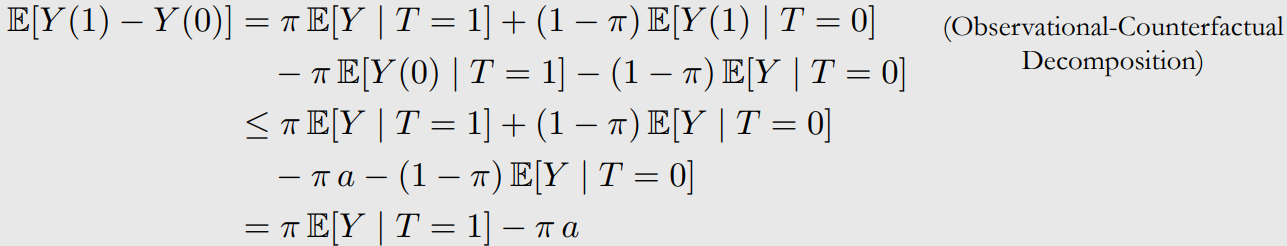
-
OTS Lower Bound 1
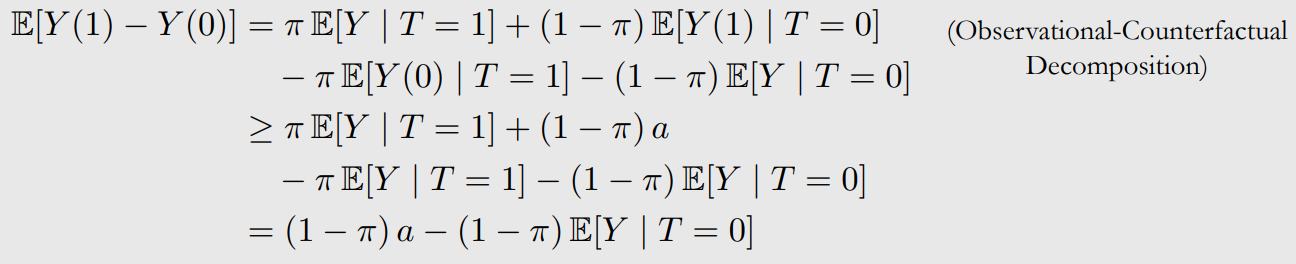
-
OTS Complete Bound 1
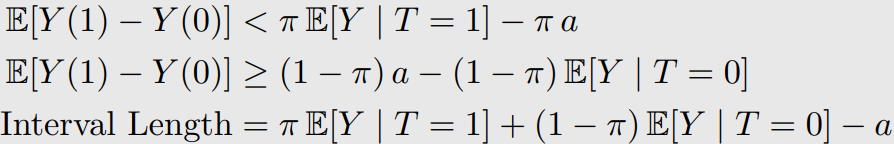
-
OTS Complete Bound 2
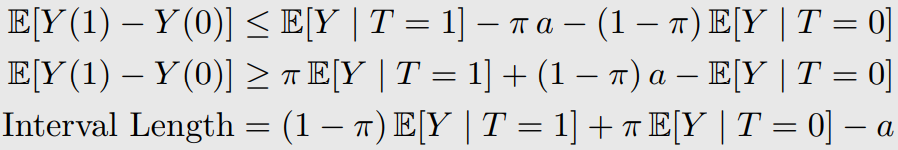
-
OTS Bound 1과 OTS Bound 2를 합쳐서 사용한다.
7-2. Sensitivity Analysis
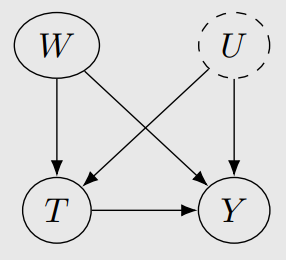
U가 unobserved confounder일 때,
U를 adjust하지 않은 거랑 실제 U를 adjust한 것과 얼마나 차이가 있는지를 분석하는 것이다.
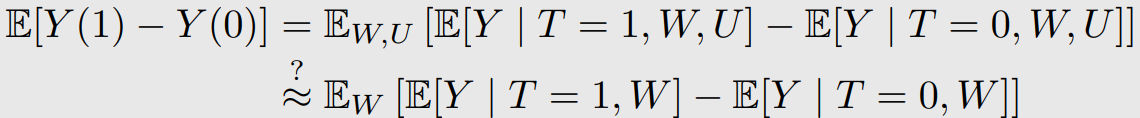
7-2-1. Linear Single Confounder
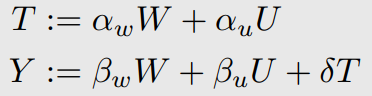
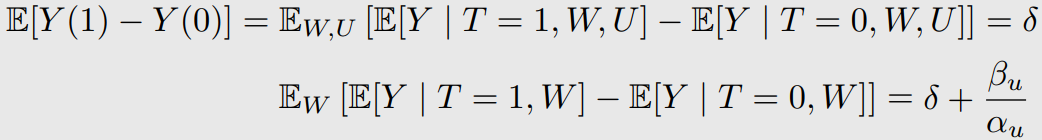
위와 같이 bias가 생긴다.
Contour Plots for Sensitivity to Confounding
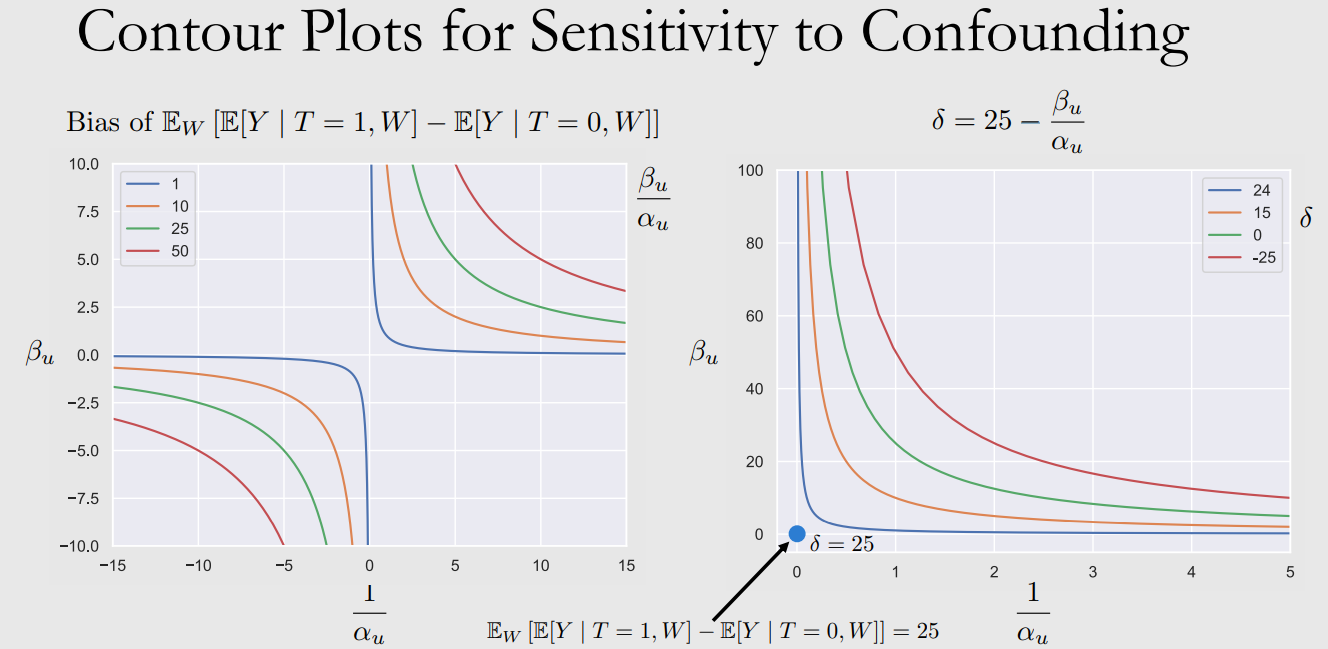
이해 안됨.
Bias in Simple Linear Setting 계산
Linear SCMs이 되면 이렇게 bias를 계산할 수 있다.
Linear이 아니면 방법이 없나?
여기서 bias의 의미가 뭐지?
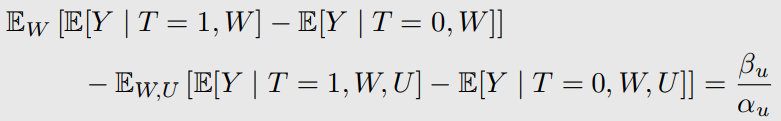
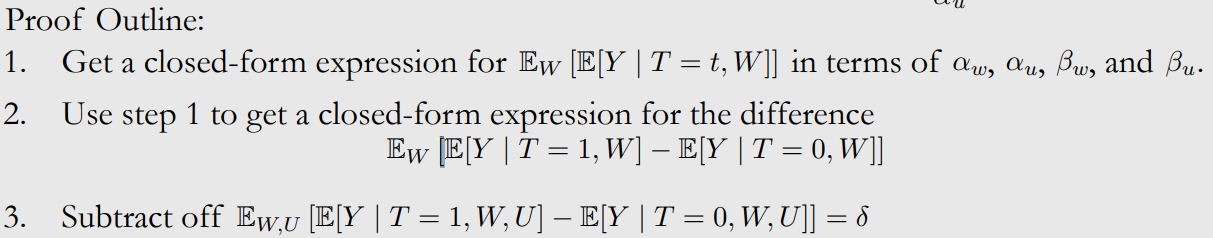
-
close-form expression 계산
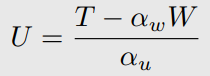
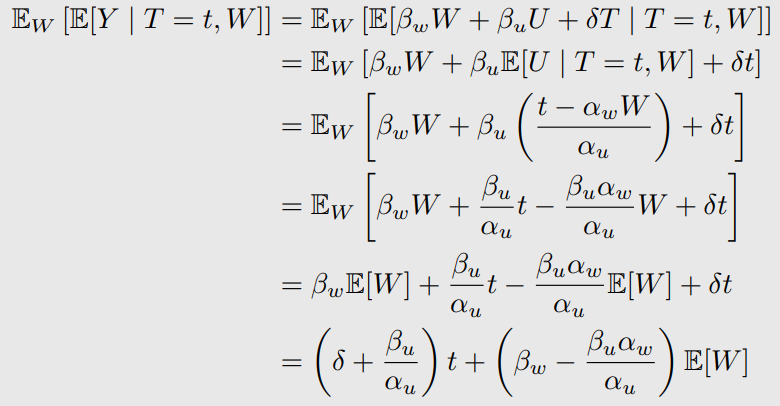
-
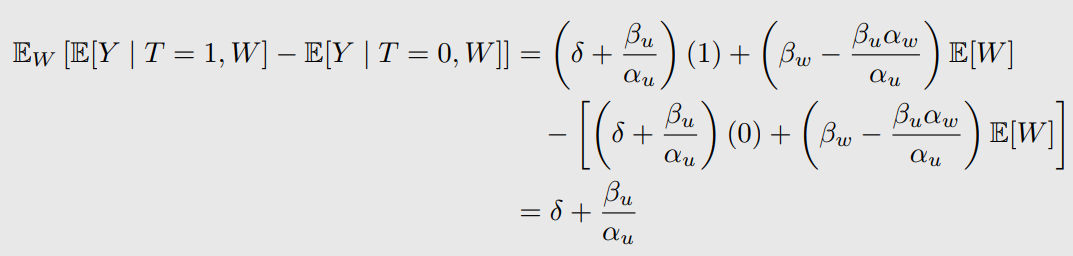
-
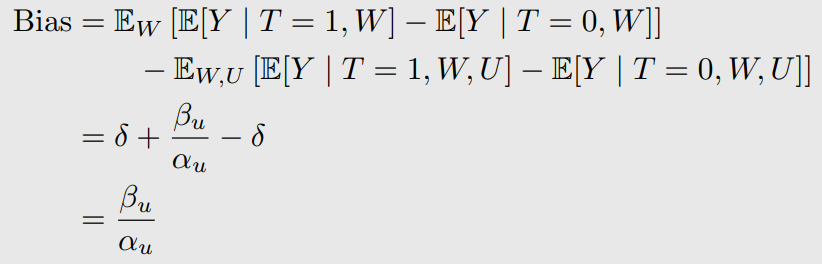
여기서 는 아래와 같다.
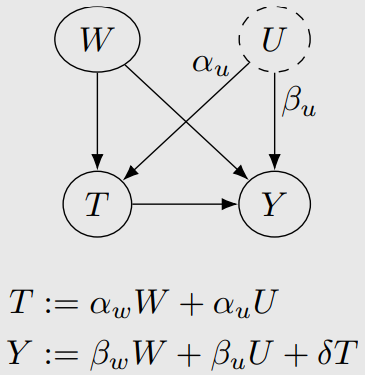
7-2-2. Towards More General Settings
위처럼 계산되는 것은 binary treatment일때
- T가 simple parametric form
- Y가 simple parametric form
- U가 binary, scalar
