INDEX
- part1
- greates common divisor
- (extended) Euclid's Algorithm
- Modular Arithmetic
- Euler's Totient Function
- Fermat's Theorem
- Euler's Theorem
- part2
- randomness
- true random nubmer
- pseudo-random number
- cryptographic pseudo-random number
prime number
prime number
-
prime number = 소수 = only have divisors of 1 and self
- cannot be written as a product of other number
- 1 is prime, but is generally not of interest
-
Prime Factorization
: All numbers can be expressed as a unique products of primes. (모든 수는 prime num들의 곱으로 표현될 수 있다)
n = a X b X c- ex) 10 = 25 , 20 = 22*5
- factoring a number is relatively hard!
- relatively prime numbers
- a와 b가 common divisor가 1을 제외하고 없을때, a와 b는 relatively prime이다
GCD
-
greatest common divisor
-
by comparing their prime factorizations & using the least common powers(가장 큰 공약수) -> we can determine the GCD
- ex) gcd(273, 399)
273 = 3*7*13, 399 = 3*7*19.
gcd(273, 399) = 3*7=21
- ex) gcd(273, 399)
-
Euclid Algorithm
gcd를 구할 수 있다!- 수도코드
def Euclid_GCD(a,b) : # Assume a and b are nonnegative integers if (b==0) : gcd(a,b) = a # stopping condition else gcd(a,b) = gcd(b, a%b) # recursive step- 예시
a = 54, b = 30.
gcd(54, 30) = gcd(30, 54%30) = gcd(30, 24)
gcd(30, 24) = gcd(24, 30%24) = gcd(24, 6)
gcd(24, 6) = gcd(6, 24%6) = gcd(6,0)
gcd(6,0) = 6
==> GCD는 6이다!
-
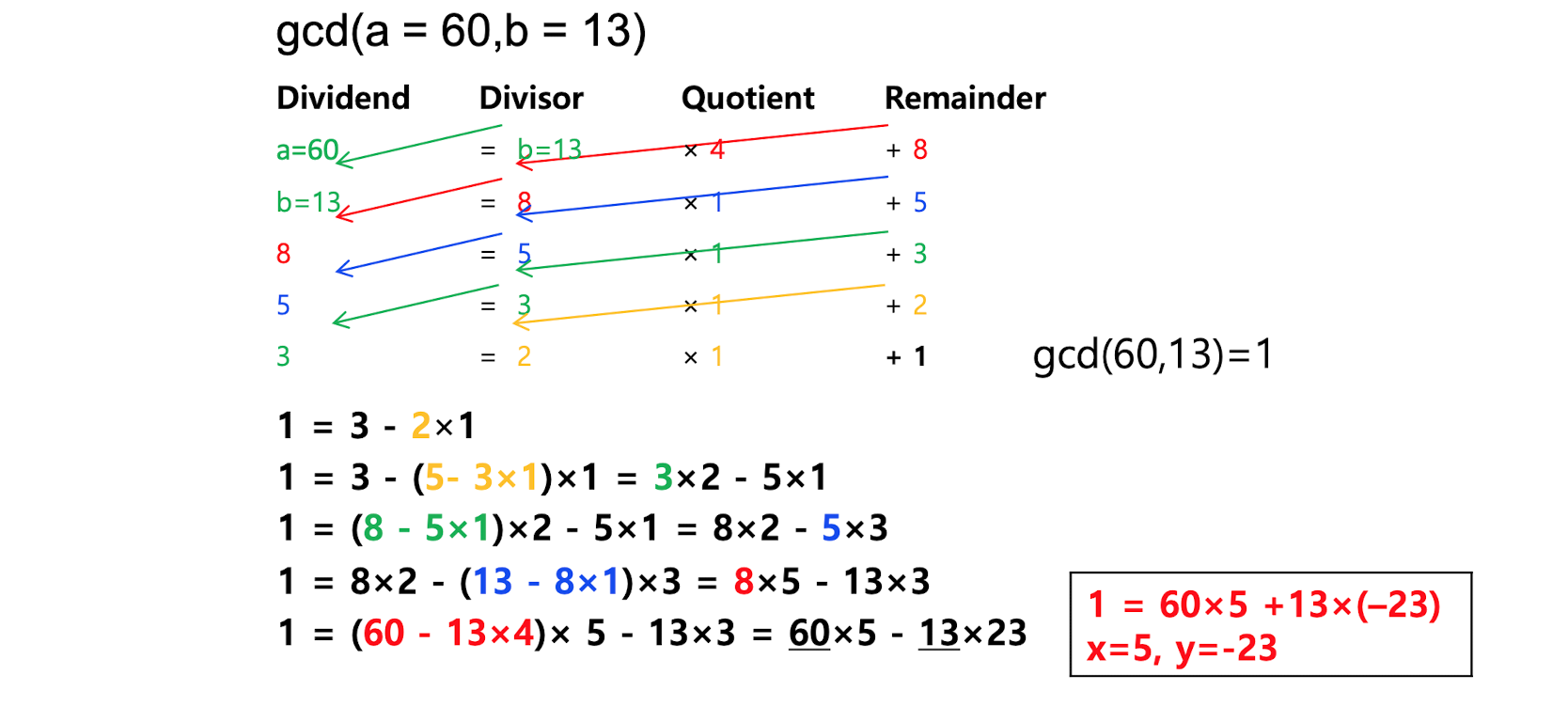
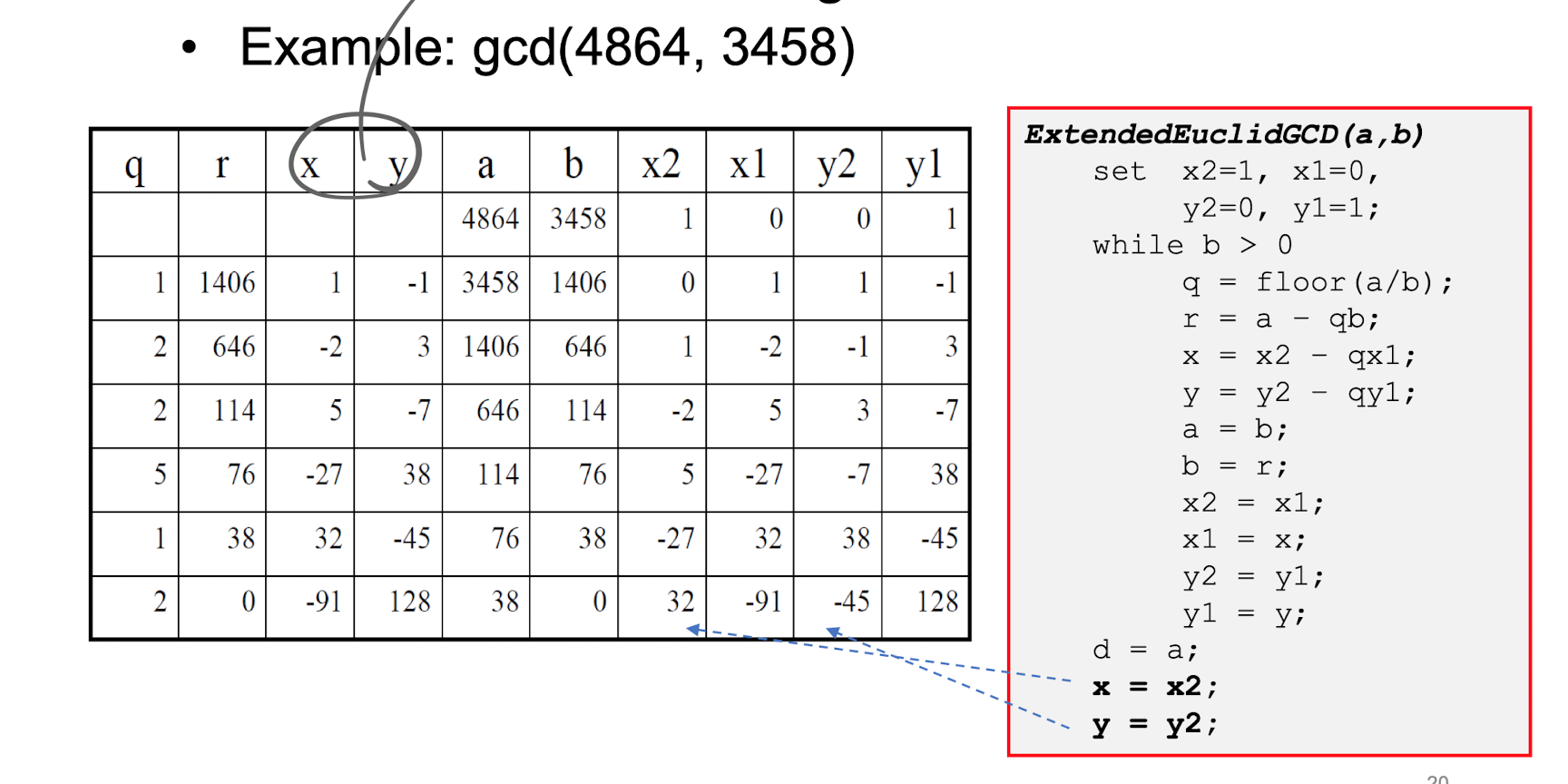
Extended Euclidean Algorithm
정수 a,b가 주어질때, 중간과정의 x와 y도 알 수 있다!-
예시1
-
예시 2
-
Modular Arithmetic
나머지 연산
-
용어정리
- congruence
modular 연산후 같은 remainder 가질때
ex) 100 mod 11 = 34 mod 11 = 1 - Residue
a mod n = b 혹은 a = qn + b 일때 b
보통 가장 작은 정수를 고름
- congruence
-
⚠️Properties⚠️
a = b (mod n) and c = d (mod n) 일때,- a + c = b + d (mod n)
- ac = bd (mod n)
- a = b(mod n) (mod n)
- a + kn = b(mod n)
-
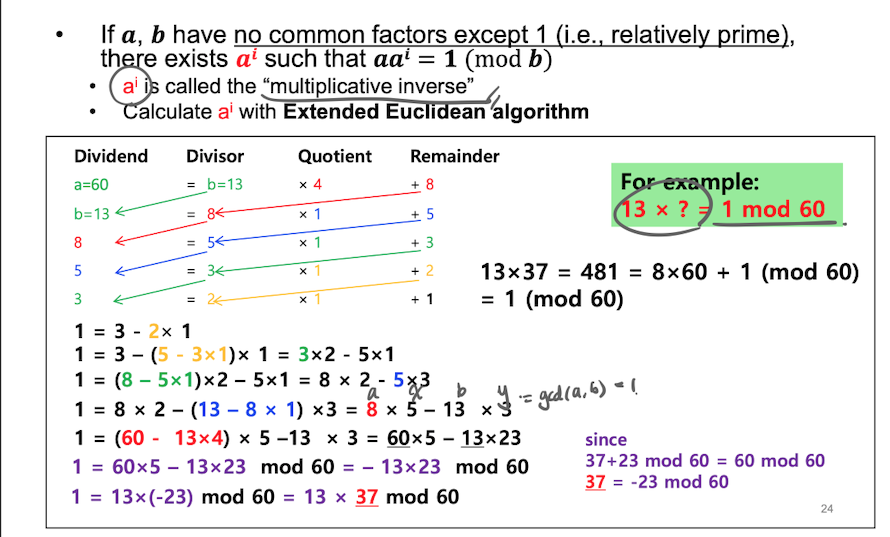
relatively prime한 두 수 a, b가 있을때
인 가 존재한다.- 는 Extended Euclidean algorithm으로 계산가능
Euler Totient Fucntion
-
residues
- complete residue : 모든 residue
- reduced residue : n과 relative prime인 residue
- ex) n = 10일때
complete set of residues = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,7, 8, 9}
reduced set of residues = {1, 3, 7, 9}
- ex) n = 10일때
-
Euler Totient Function
reduced set of residues의 원소 갯수
ex) (1, 3, 7, 9)
-> n=pq이고, p,q는 prime일때, n보다 작은 n에 대해 relatively prime인 양수의 갯수를 구할 수 있다.
p가 prime ->
p,q가 prime->- ex) = 37-1 = 36
= 11-1 = 10
= (3-1)*(7-1)=2*6=12
= (2-1)*(5-1)=1*4=4
- ex) = 37-1 = 36
-
Fermat's Little Theorem
(mod )
where is prime and gcd(a, p) = 1
(p는 Prime이고, a,p는 relatively prime일때)-
ex
mod 7 = 1
mod 23 = 1Fermat's Little Theorem 응용
매우 큰 수 p에 대해, (mod ) 이까
- mod
- mod = a -
ex
mod 7 = mod 7 = 4 mod 7 = 4
mod 23 = mod 23 = 19
mod 101 = 89 mod 101 = 89
-
-
Euler's Theorem
이 Euler's Totient function 이고,
gcd(a,n) = 1 이면
(mod ) 이다.- ex
mod 143 = mod 11 X 13 = 1
mod 77 = mod 7 X 11 = 1
- ex
-
Euler's Theorem 응용
mod n = 1 이니까- mod n = a
- mod n = a
- ex
mod 143 = mod 11 X 13 = 25
mod 77 = mod 7 X 11 = 19
