Receiving Signal
Suppose kernel is returning from an exceptional handler and is ready to pass control to process p
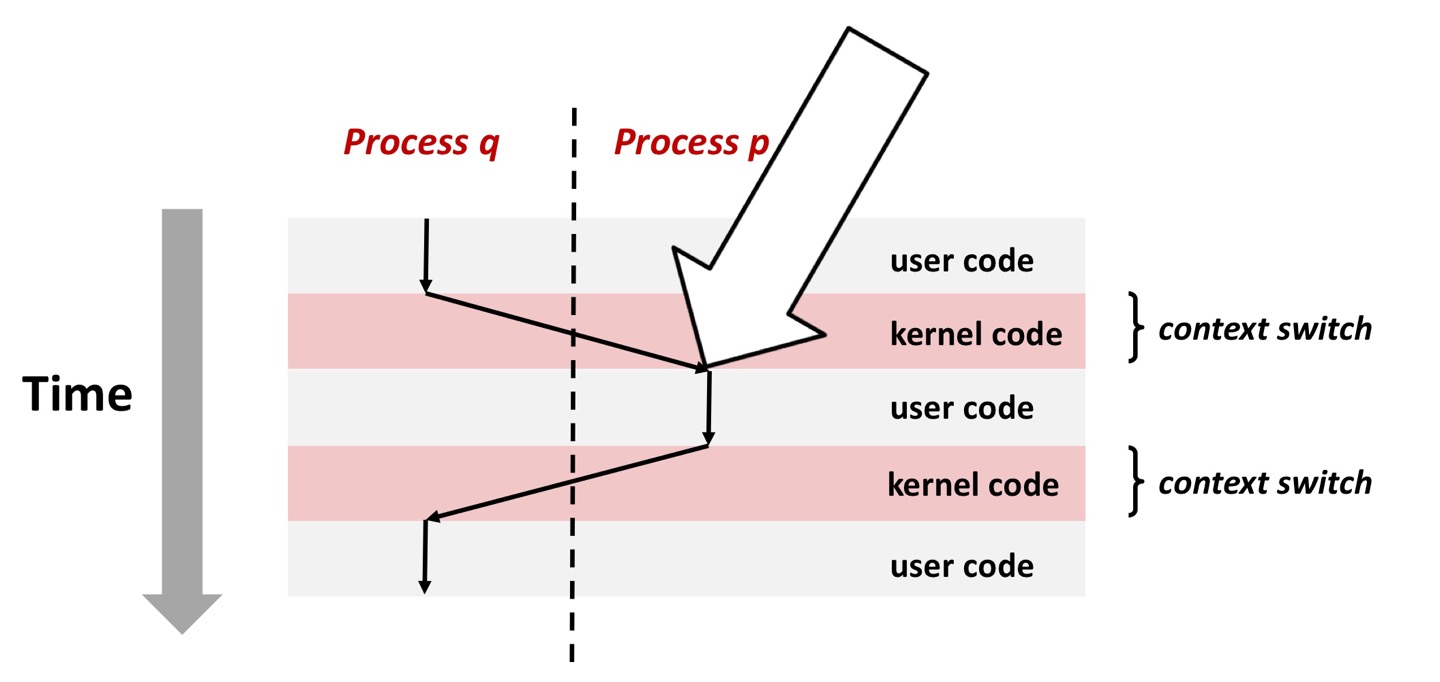
Kernel computes pnb = pending & ~blocked
->The set of pending nonblocked signals for process p
If (pnb == 0)
Pass control to next instruction in the logical flow for p
Else
-Choose least nonzero bit k in pnb and force process p to receive signal k
-The receipt of the signal triggers some action by p
-Repeat for all nonzero k in pnb
-Pass control to next instruction in logical flow for p
Default Actions
Each siganl type has a predefined default action, which is one of the followings:
- The process terminates
- The process stops until restarted by a SIGCONT signal
- The process ignores the signal
Installing Signal Handlers
The following functions modify the action associated with the receipt of siganl signum:
sighandler_t signal (int signum, sighandler_t hander);
int sigaction(int signum, const struct sigaction *act, struct sigaction *oldact);Possible values for the handler argument of siganl():
- SIG_IGN : ignore siganls of type signum
- SIG_DFL : revert to the default action for siganls of type signum
- Otherwhise, handler is the address of a user-level function
-Called when process receives signal of type signum
-Referred to as "installing" the handler
-Executing handler is called "catching" or "handling" the siganl
-When the handler returns, control passes back to the instruction in the process that was interrupted by the siganl
Signal Handling Example

sigint: 프로그램 실행 중에 ctrl-c를 누르면 프로그램 실행이 종료되고 쉘로 돌아온다. ctrl-c를 누를 때 발생하는 시그널이 sigint
sigint handler를 통해 ctrl-c로 프로그램을 종료시키는 걸 불가능하게 만들 수 있다.
만약 ctrl-c를 연달아 5번 누르면 어떻게 될까?
시그널이 두 번 실행된다. 시그널이 누적돼서 저장되지 않고 panding된 게 있으면 discard되기 때문에. 첫 번째 signal을 받아서 sleep하고 나서 panding되어 있던 시그널을 꺼내서 한 번 더 실행한다.
Signal Handlers as Concurrent Flows
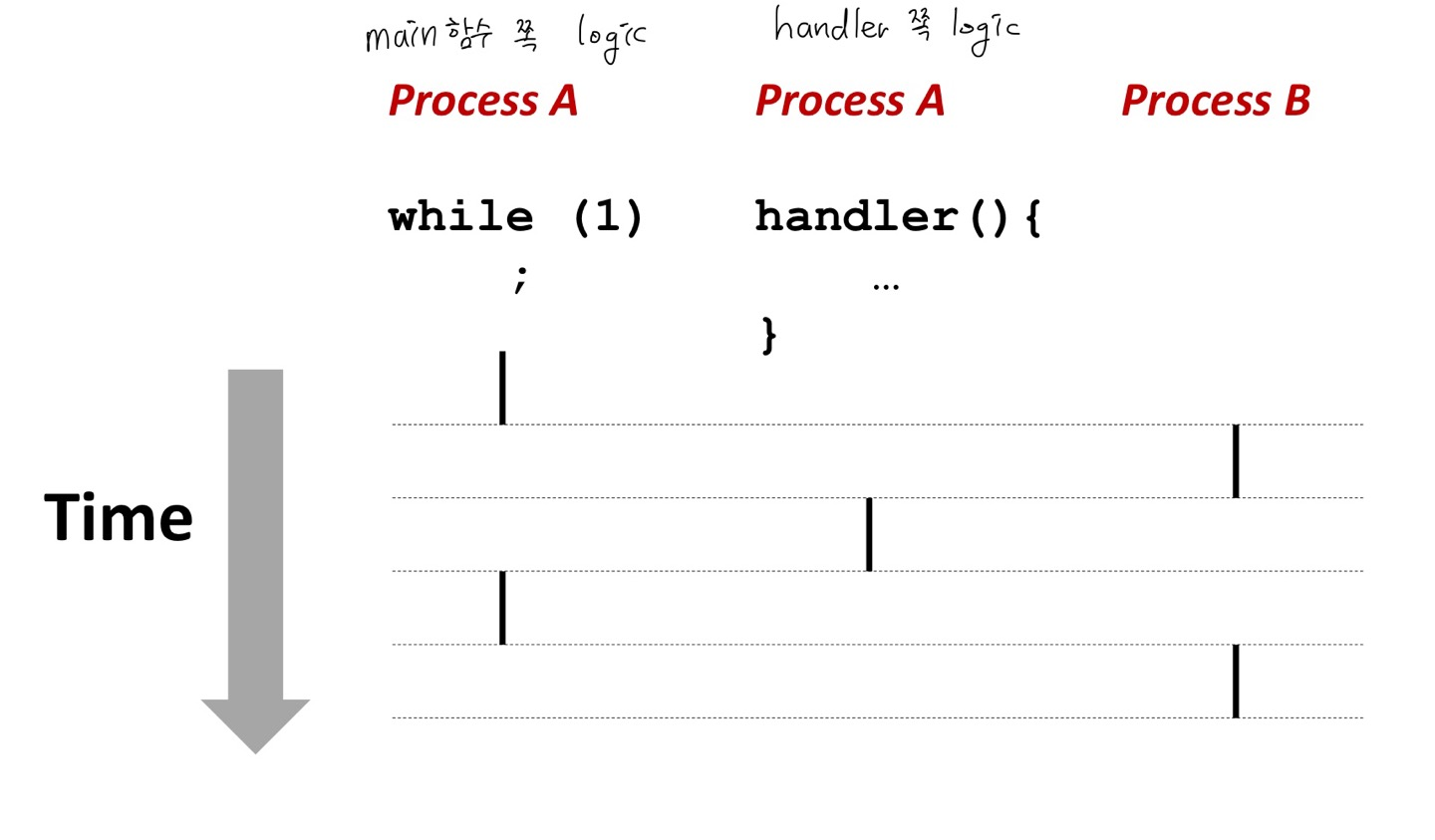
A signal handler is a seperate logical flow (not process) that runs concurrently with the main program
아예 별개의 process가 아니기 때문에 서로 영향을 미치므로 문제가 생길 수 있다. 전역변수 같은 게 꼬일 수 있다.
Nested Signal Handlers
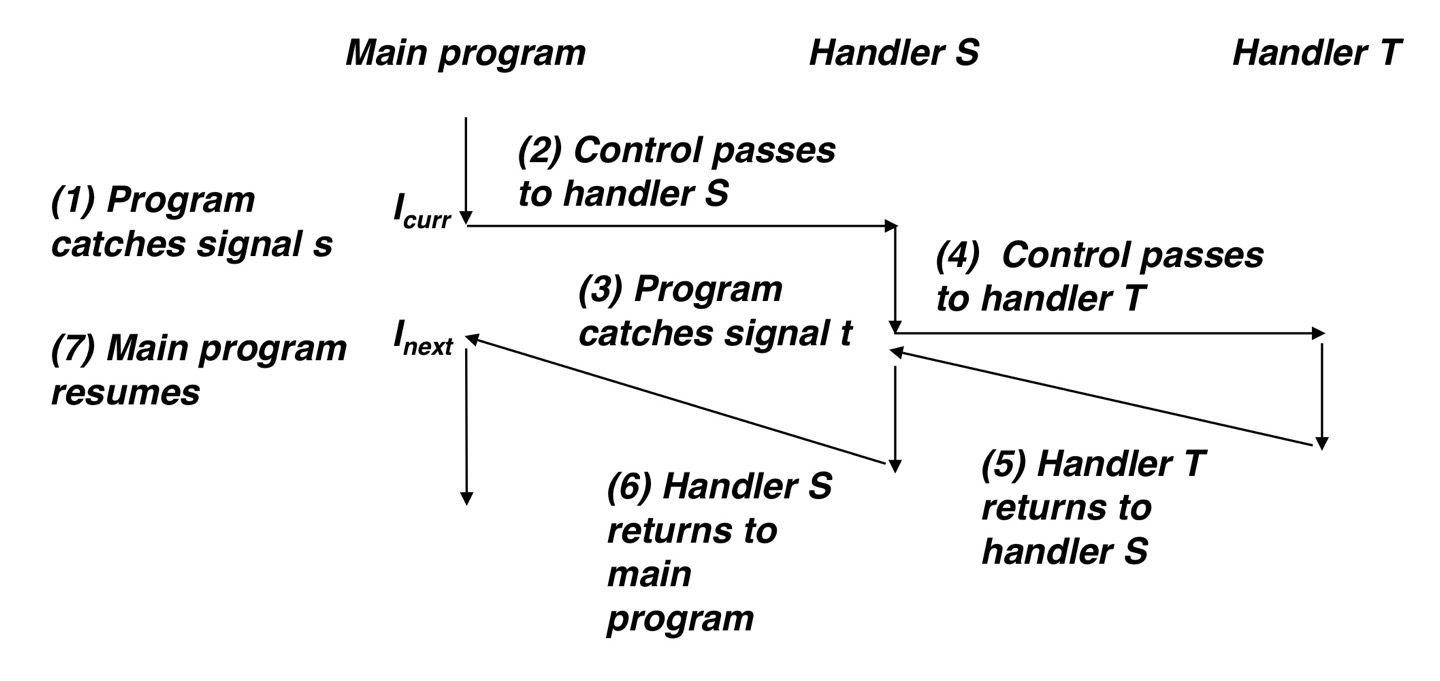
Blocking and Unblocking Signals
Implicit blocking mechanism
Kernel blocks any pending signals of type currently being handled. SIGINT handler can't be interrupted by another SIGINT.
Explicit blocking and unblocking mechanism
sigmask function
Signal Blocking/Unblocking Example
signal mask는 어떤 signal을 block하고 있는지 나타내는 비트 벡터.
sigset_t mask, prev_mask;
sigemptyset(&mask); //mask는 다 0으로 세팅. 아무 시그널도 specify하지 않는 비트 벡터.
sigaddset(&mask, SIGINT); //mask는 SIGINT만을 원소로 갖는 집합이 된다.
/*Block SIGINT and save previous blocked set*/
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &mask, &prev_mask);
//sigprocmask는 siganl mask를 변화시키는 요청.
//변화시키기 전 현재 상태를 저장하는 인자가 prev_mask.
//SIG_BLOCK은 macro로 define되어 있는 상수값.
.
. /*Code region that will not interrupted by SIGINT*/
.
/*Restore previous blocked set, unblocking SIGINT*/
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &prev_mask, NULL);
Guidelines for Writing Safe Handlers
G0: Keep your handler as simple as possible
- e.g., set a global flag and return
- signal handler에서 모든 동작을 다 하려고 하지 말고 global flag의 세팅값을 보고 main에 돌아와서 필요한 조치 취하기.
G1: Call only async-signal-safe functions in your handlers
- Function is async-signal-safe if either reentrant(e.g., all variables stored on stack frame) or non-interruptible by signals
- Popular functions that are safe: _exit, write, wait, waitpid, sleep, kill
- Popular functions that are not sate: exit, printf, sprintf, malloc
- e.g., main에서 printf 함수 호출. 실행되는 도중 signal handler가 도착하고 실행됨. printf는 signal에 의해 interrupt될 수 있음. printf 함수가 signal handler와 concurrent하게 실행될 수 있다. printf가 내부적으로는 버퍼를 관리하기 위한 global state, global variable을 사용하고 있다. printf는 global state가 A라고 생각하고 작동하는데 signal handler를 실행하고 왔더니 global state가 B가 되어 있을 수도 있다.
- 안전한 함수만 쓰는 건 비현실적이다. 권고사항 정도로 생각하면 된다.
G2: Save and restore errno on entry and exit
- So that your handler does not affect errno value observed in main
- signal handler가 실행된 후 errno가 update될 수 있다. 예를 들어 시스템콜이 실패했을 때. signal handler 실행 후 main으로 돌아왔을 때 main이 모르는 새에 errno가 update되어 있을 수 있다. 그래서 signal handler 실행 시작될 때 errno값을 백업해뒀다가 끝낼 때 errno 복구하는 게 권장된다.
G3: Protect accesses to shared data structures by temporarily blocking all signals
- To prevent possible corruption
- How can we accomplish this?
- By calling sigprocmask in the handler (may be unstable)
- When using sigaction, you can specify which signals should be additionally blocked when your handler is executing
G4: Declare global variables as volatile
- To prevent compiler from storing them in a register
- If a variable is stored in a register, an update to this variable may not be visible to the reader
- 컴파일러가 최적화하는 과정에서 변수를 메모리에서 읽어오지 않고, 레지스터에 저장해 뒀다가 레지스터에서 읽어오는 방식으로 machine code를 짠다.
signal hander가 메모리의 global variable을 update했더라도 main은 update 전 값을 레지스터에 저장해 두고 그 값을 읽어오는 문제가 생길 수 있다.
volatile 키워드를 제시하면 변수 값을 메모리에서 읽어온다.
