시스템 프로그래밍
1.[시스템 프로그래밍] Exception

Processors do only one thing: CPU simply reads and executes(interprets) a sequence of instructions, one at a time.This sequence is CPU's control flow.
2.[시스템 프로그래밍] Process
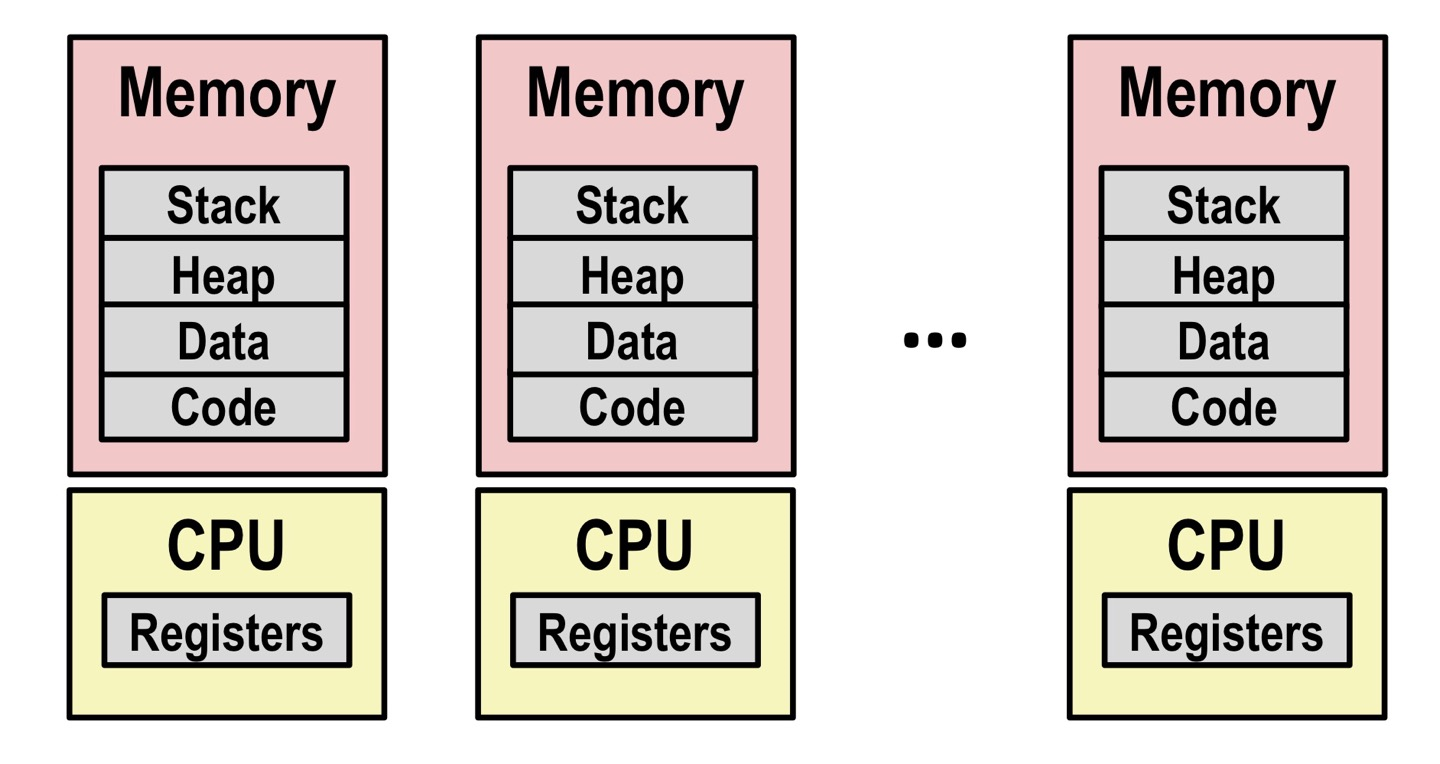
Definition: An instance of a running programProcess has a context (state: 각 레지스터는 어떻게 세팅되어 있으며 메모리에는 뭐가 저장되어 있는지 등) for the program executionProcess p
3.[시스템 프로그래밍] Process Control
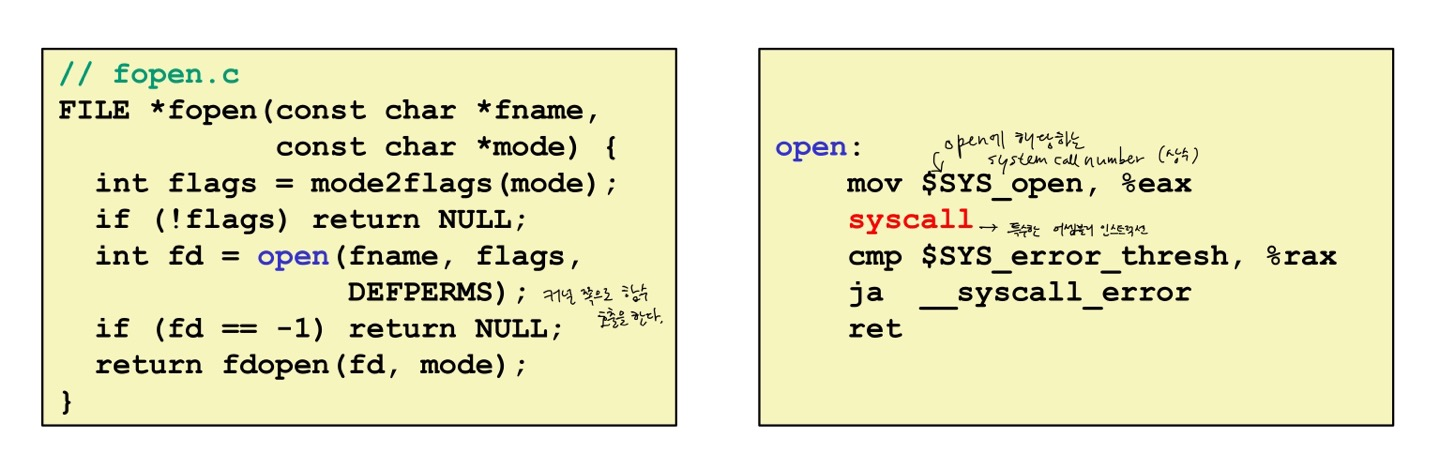
Whenever a program wants to cuase an effect outside its own process, it must ask the kernel for help.Example: read/write filesfopen internally calls o
4.[시스템 프로그래밍] Signal

ProblemShell must be designed to run indefinitely and should not accumulate unneeded resources (memory, child processes, ...)Example shell correctly w
5.[시스템 프로그래밍] Signal Handling
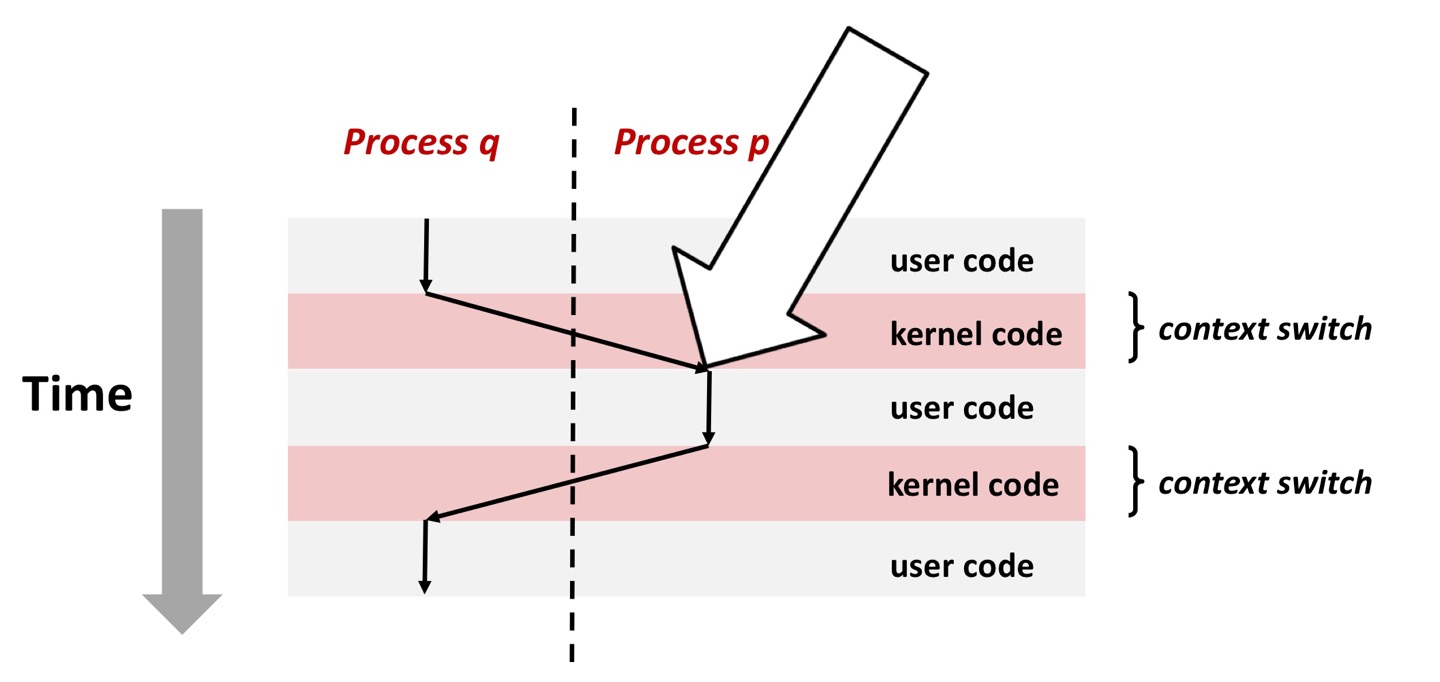
Suppose kernel is returning from an exceptional handler and is ready to pass control to process pKernel computes pnb = pending & ~blocked\->The set of
6.[시스템 프로그래밍] Virtual Memory
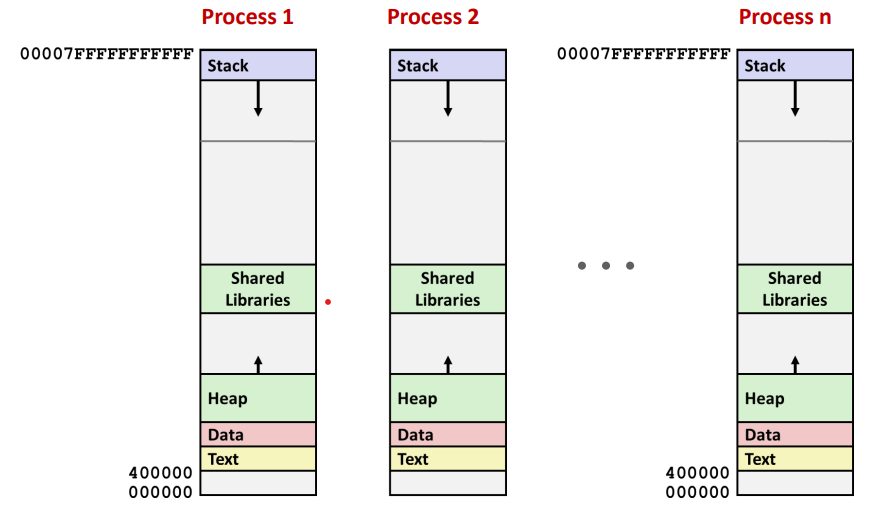
A process is an instance of a running program.Not the same as "program" or "processor"A process has a context (state) for the program executionProcess
7.[시스템 프로그래밍] System Levle I/O
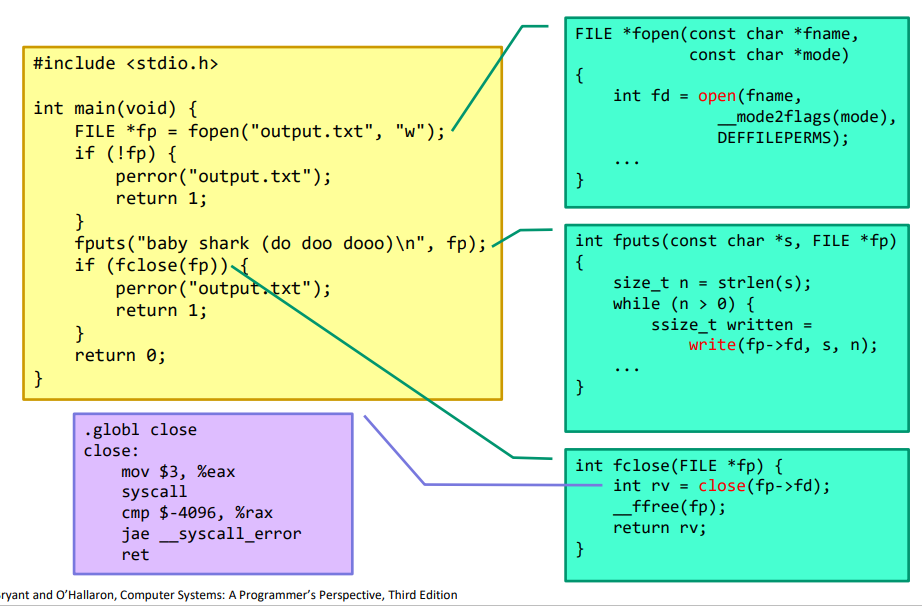
fopen도 open이라는 시스템콜로 redirect된다. fopen은 c library에서 제공하는 api 함수이고 open은 unix 계열의 로우 레벨 시스템콜로 구현된다. 이런 시스템콜은 함수를 호출하는 것처럼 부를 수 있다. 커널과 직접적으로 맞닿아있는 함수라고