Calculus for Machine Learning and Data Science - Week 3
Optimization in Neural Networks
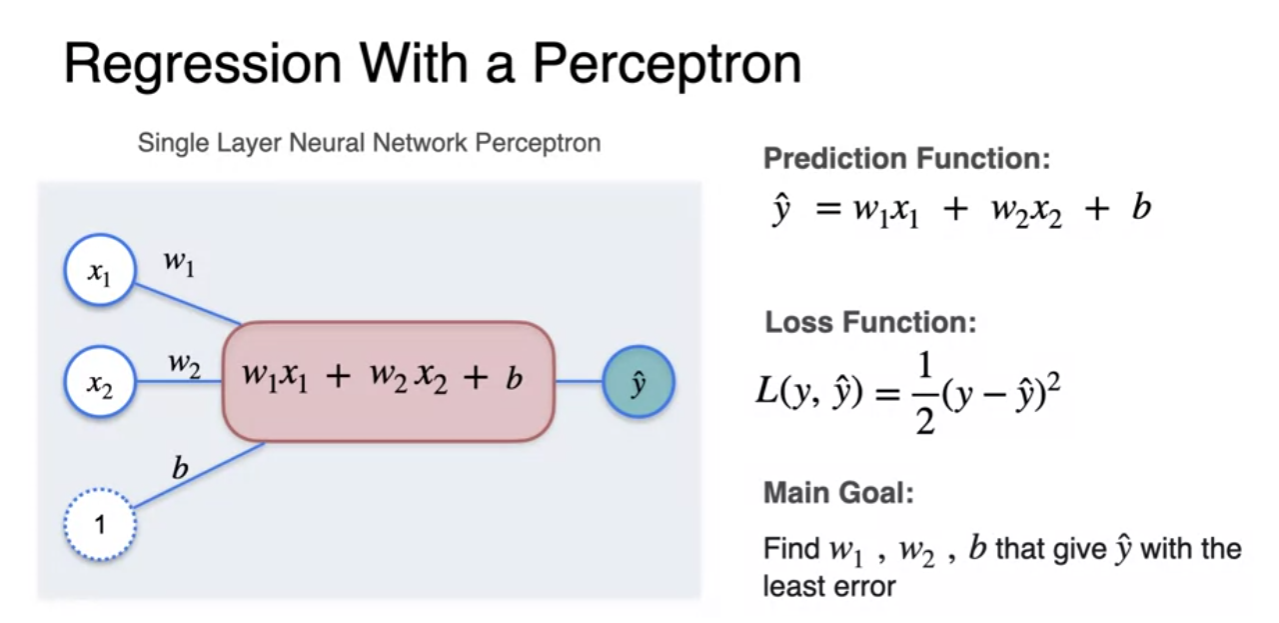
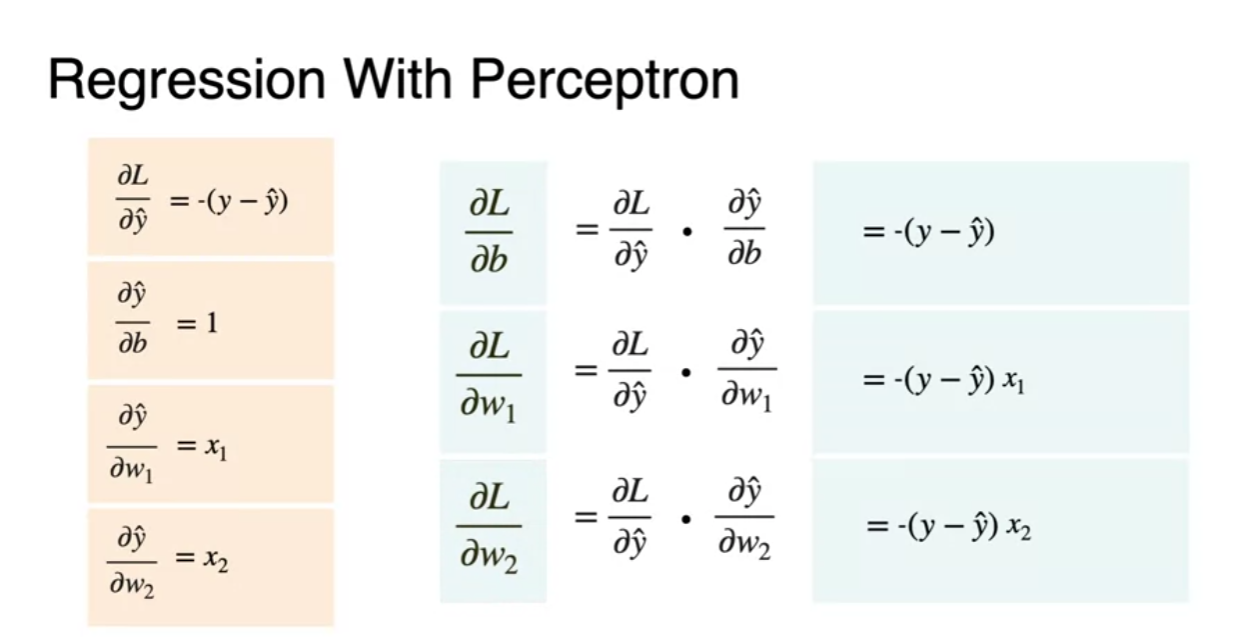
Regression with a perception
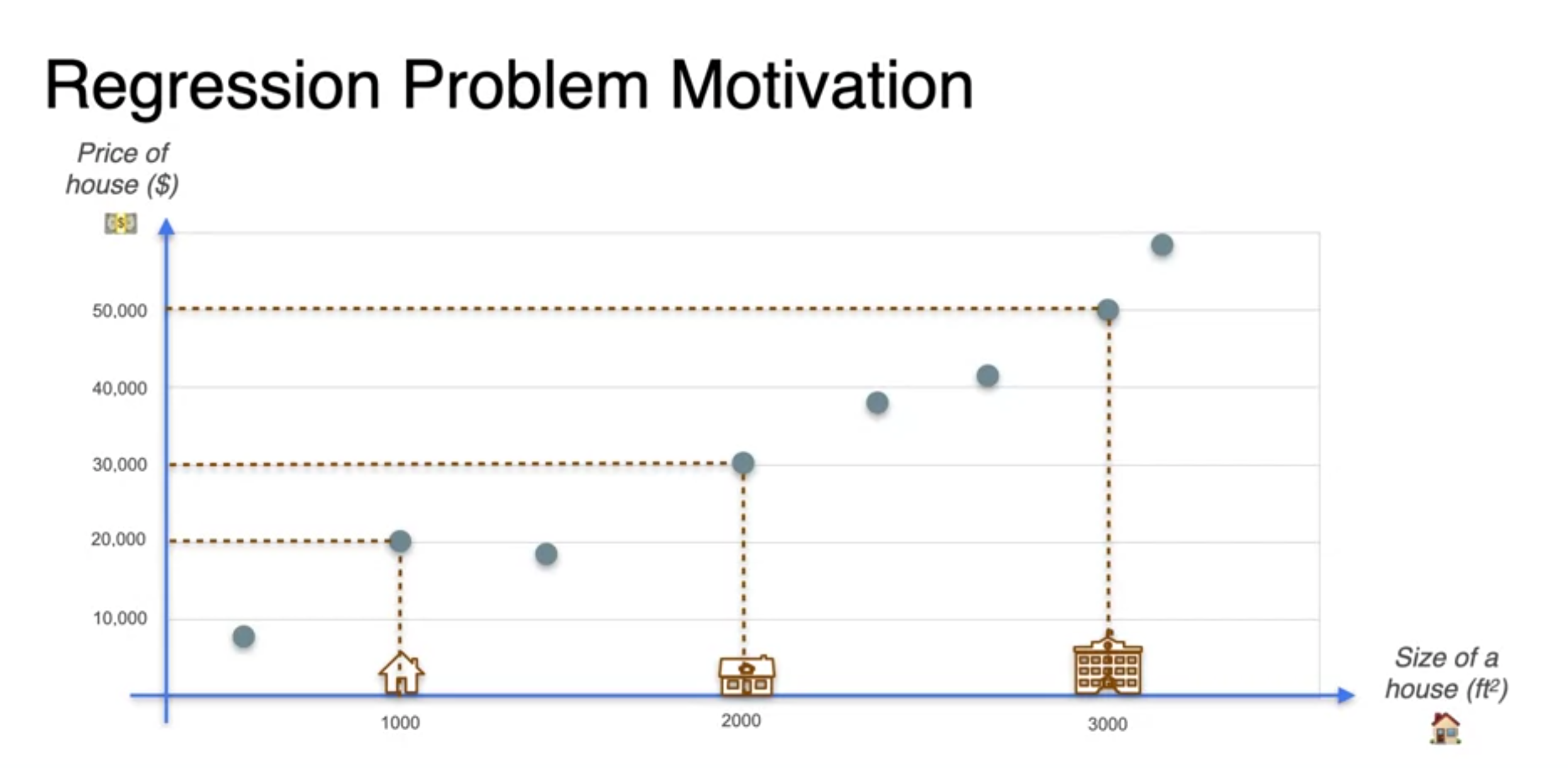
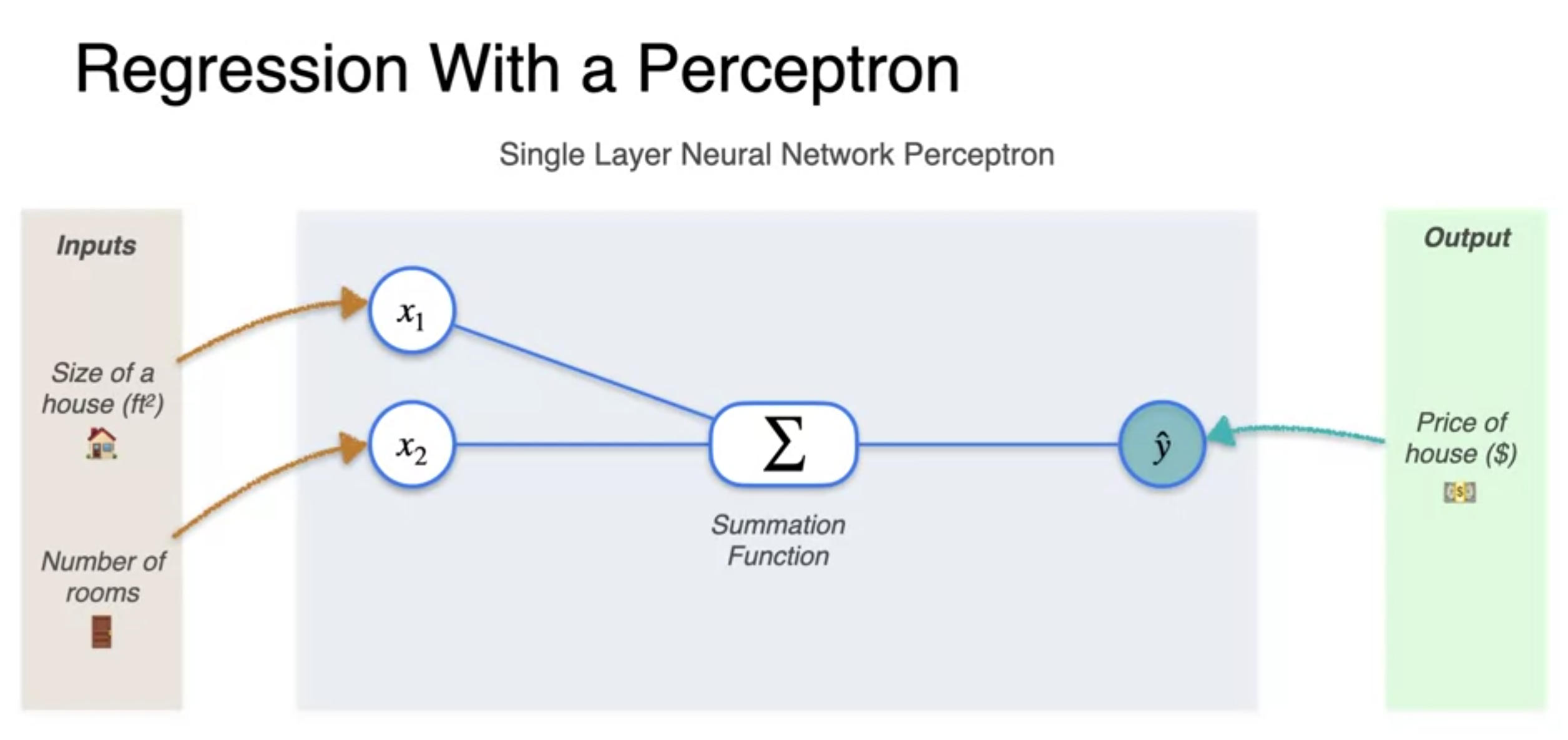
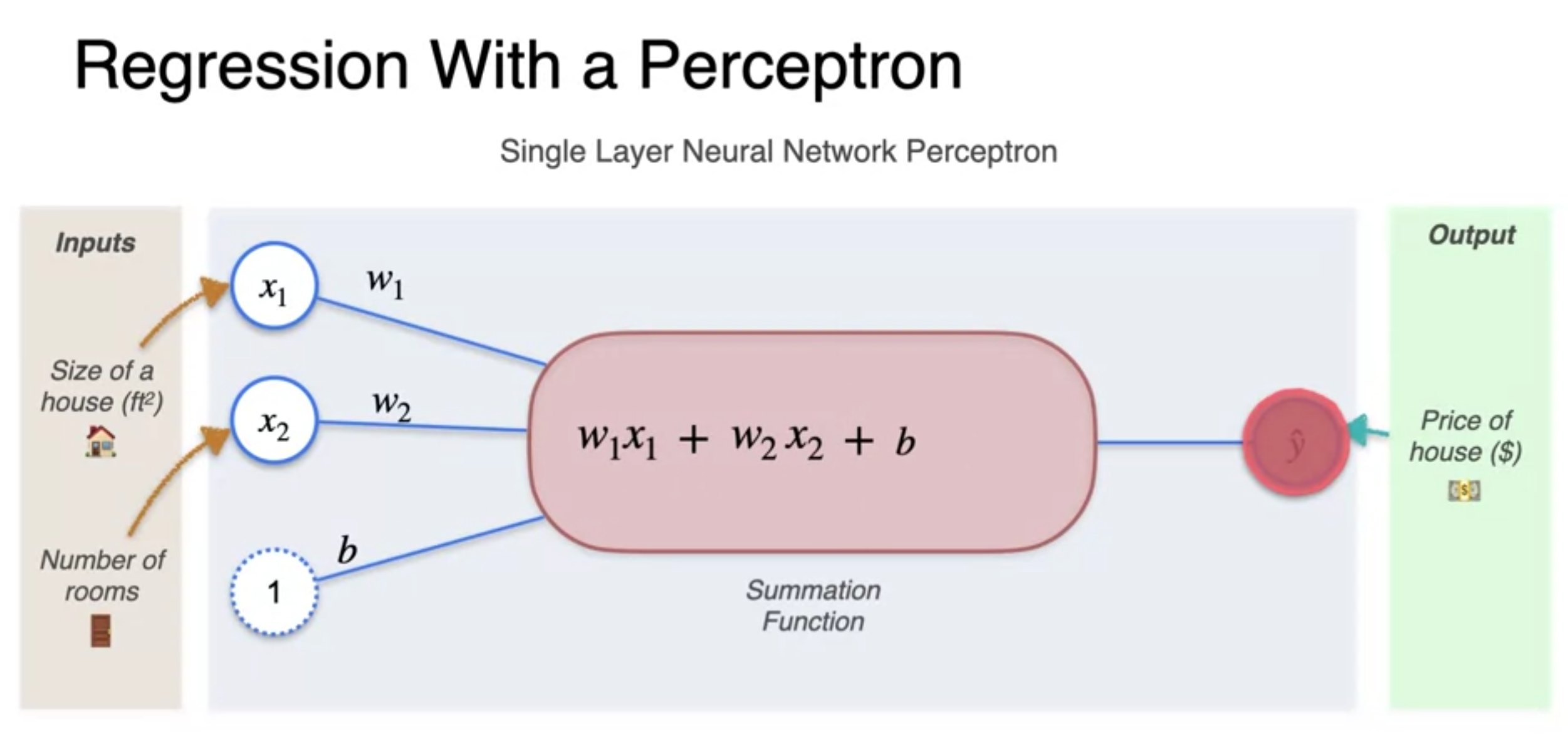
- 신경망(percetptron) : takes some inputs to output we want to predict
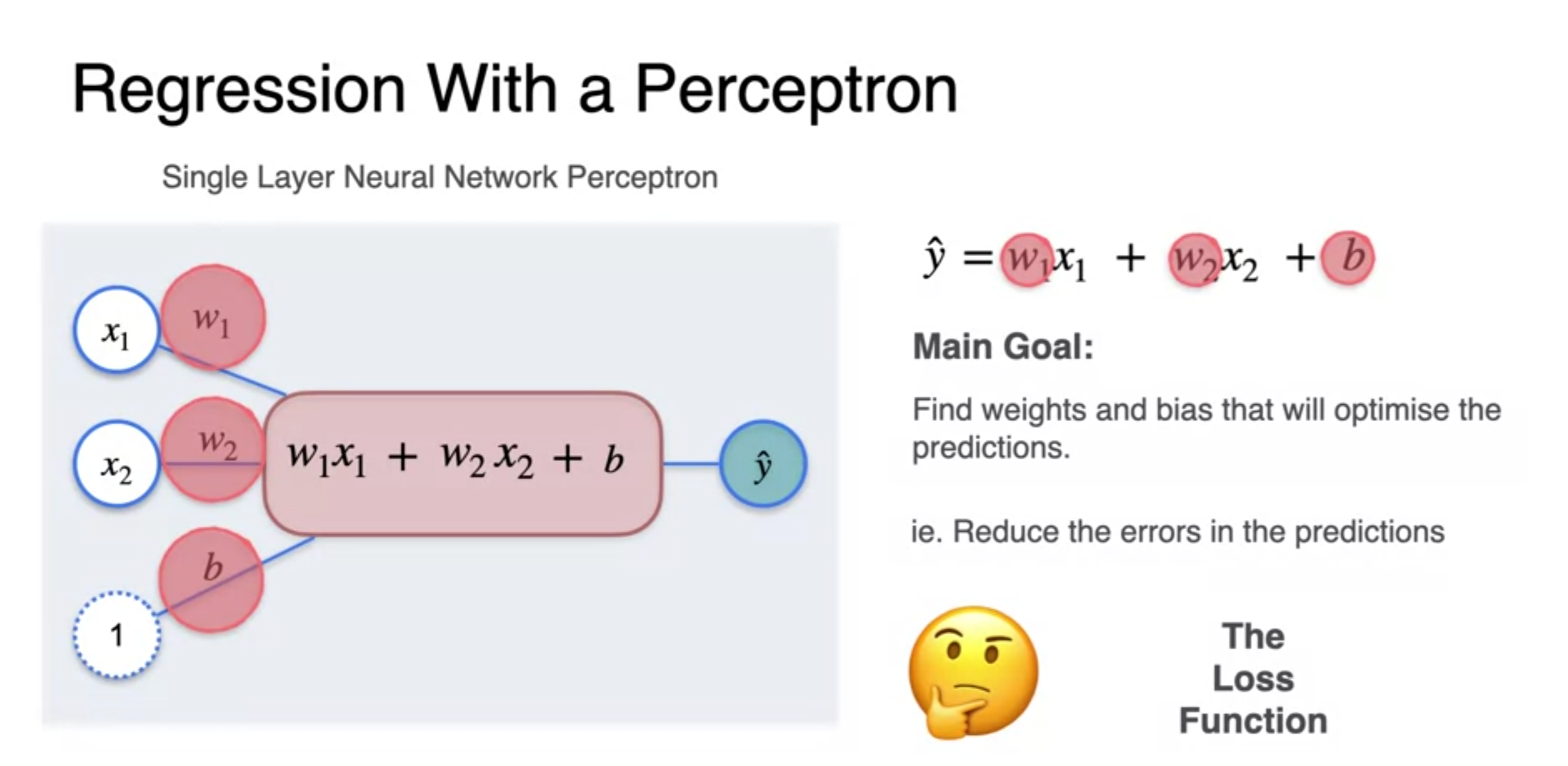
Regression with a perceptron - Loss function
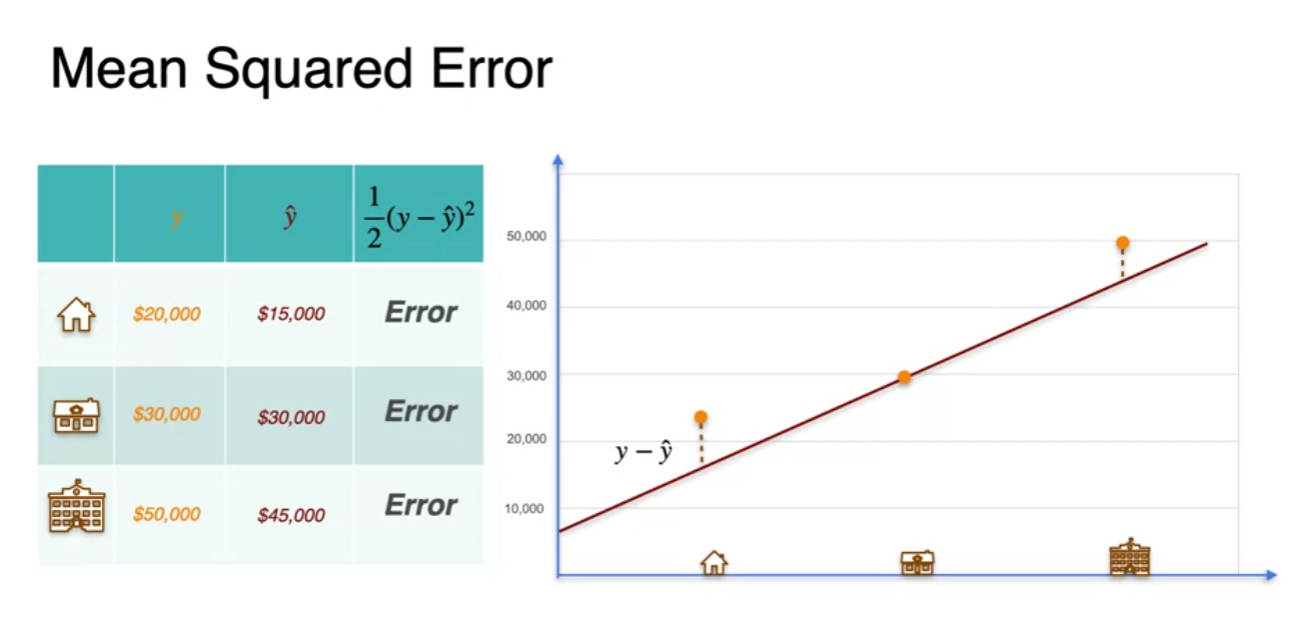
- For handle positive error and negative one same we square the error
- multiplying by half : cosmetic reason(y-y')^2 derivative get a lingering two
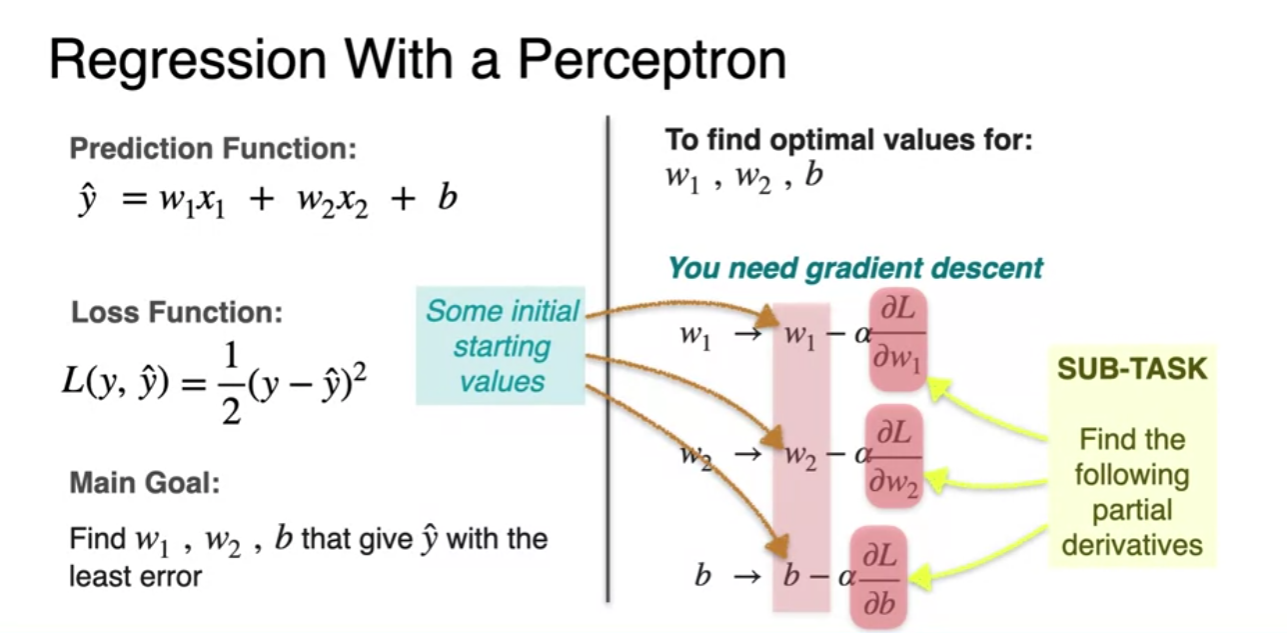
Regression with a perceptron - Gradient Descent
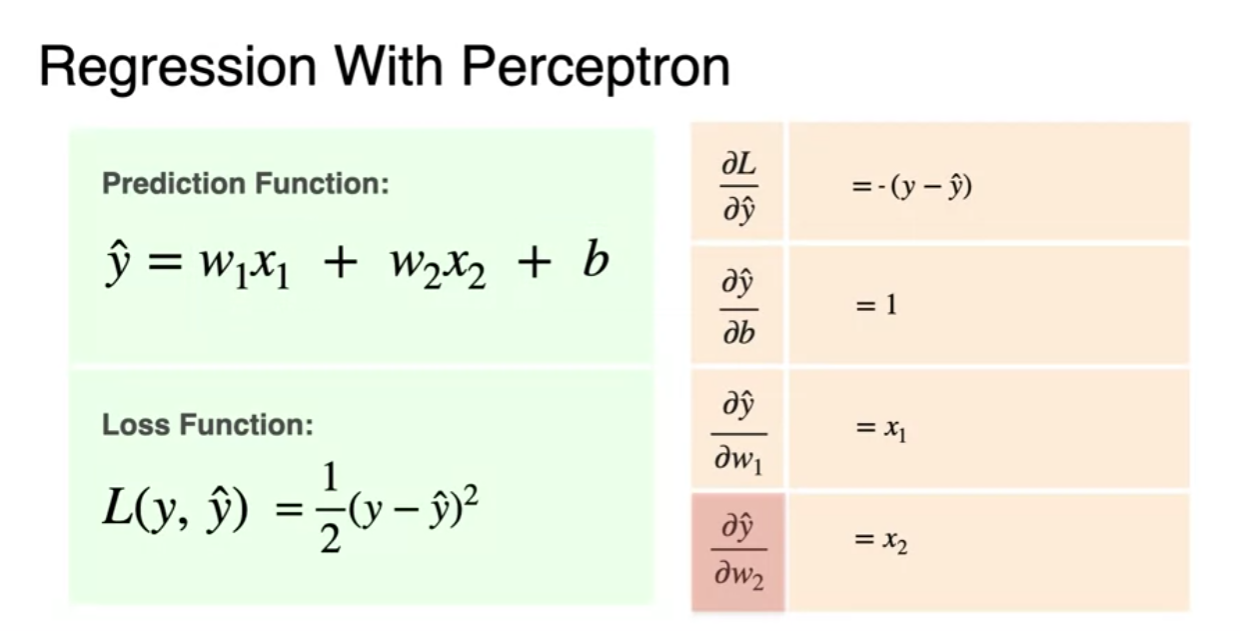

Classification with Perceptron
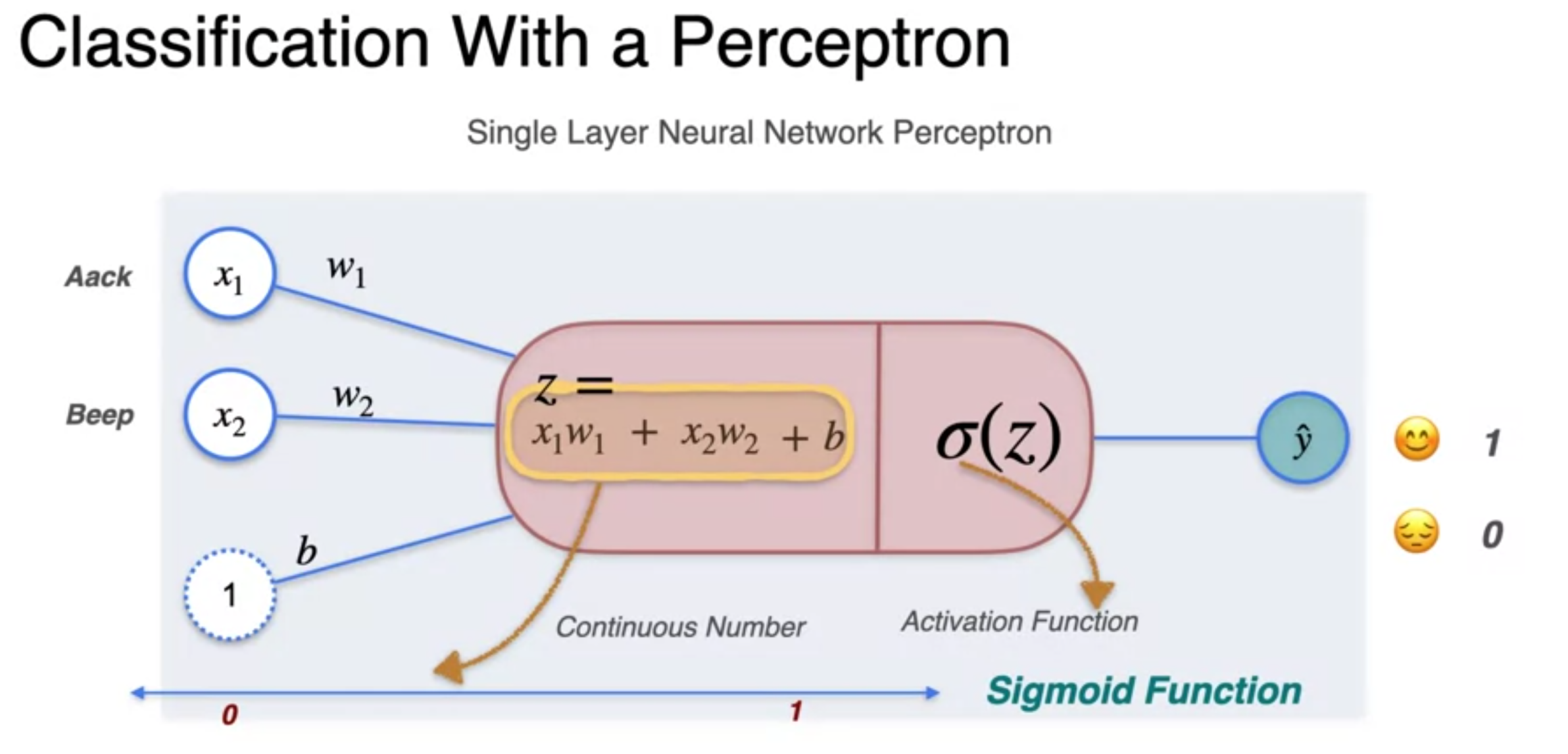
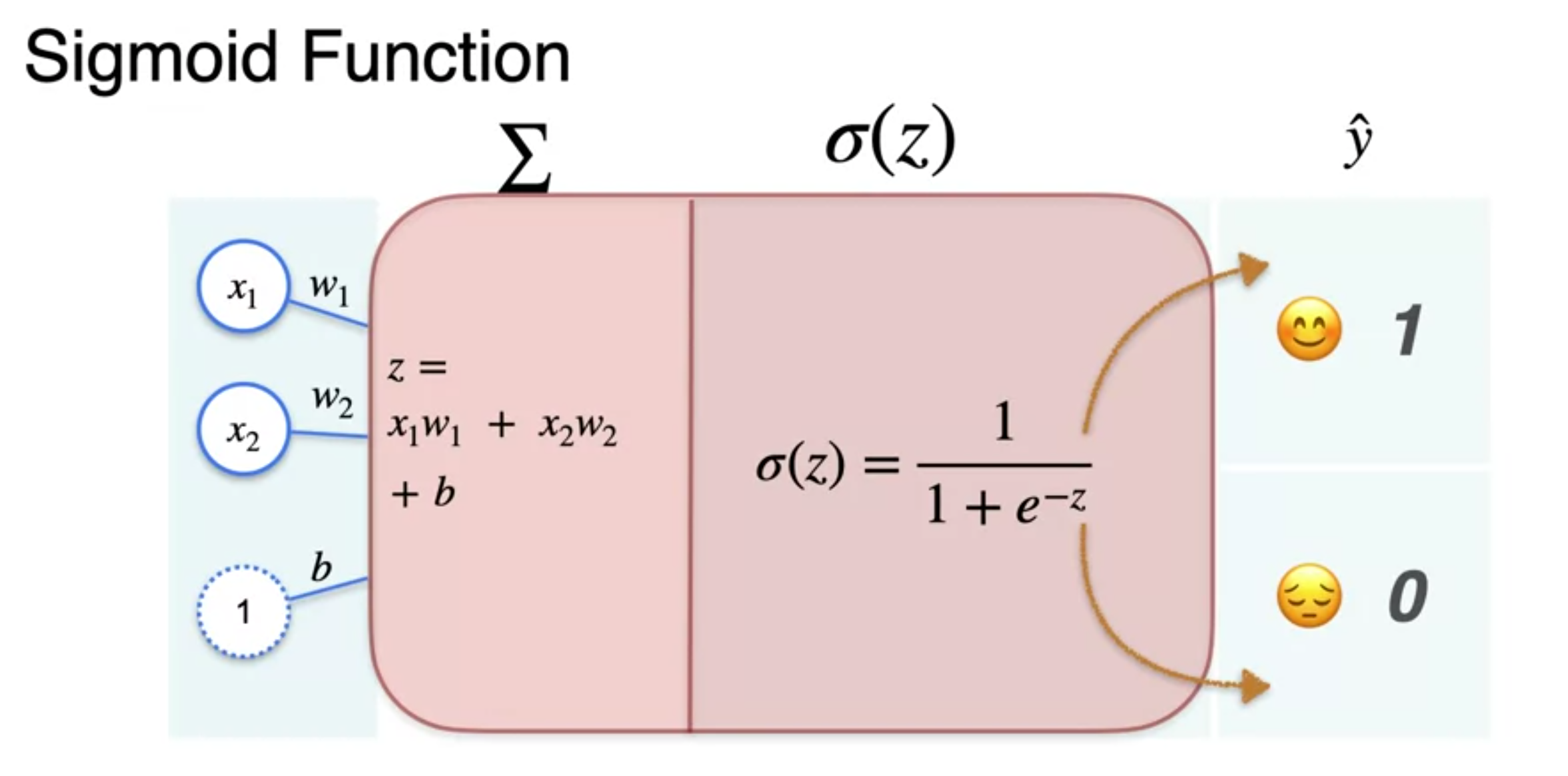
- Activation function : crunch the number interval 1 and 0
- Sigmoid function :
Classification with Perceptron - The sigmoid function
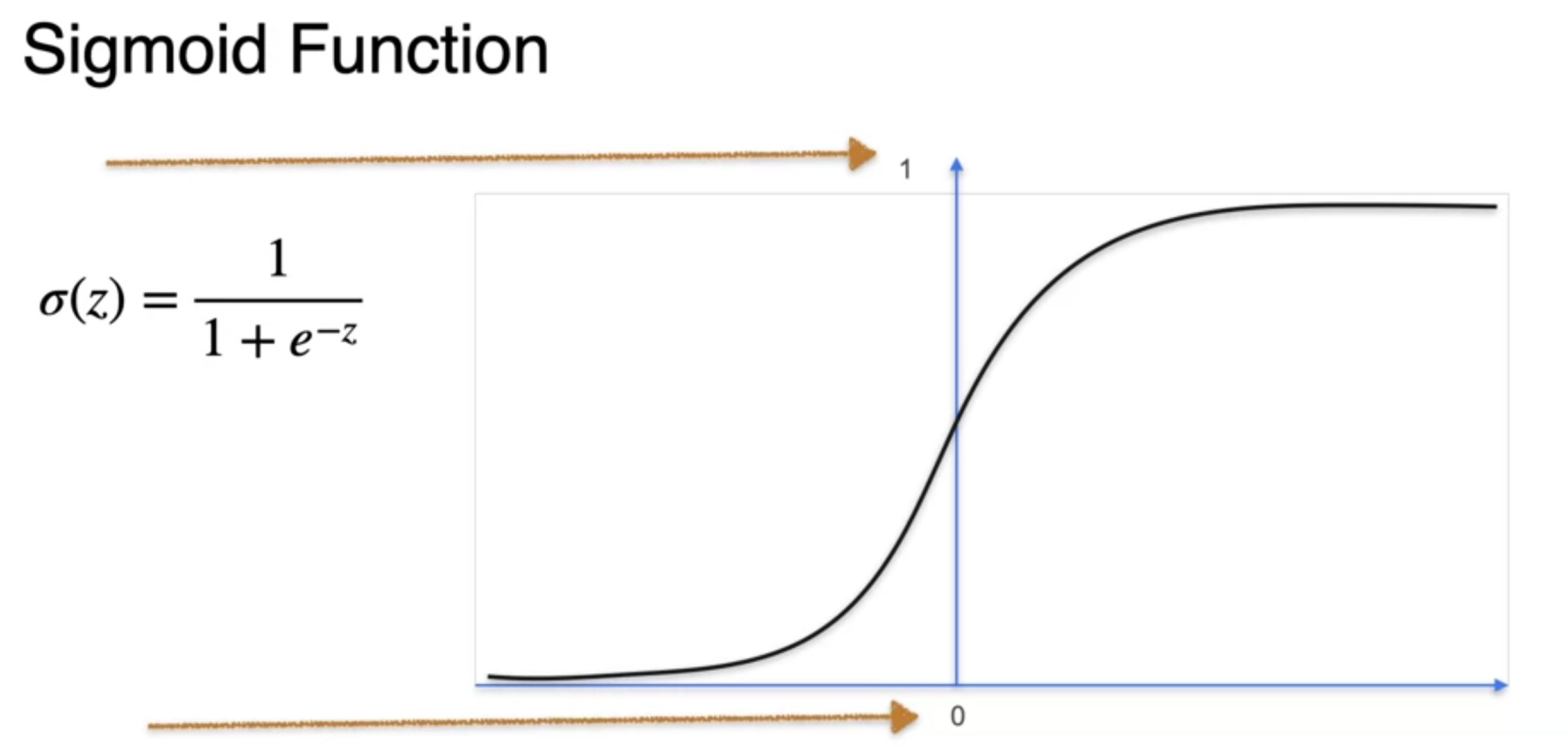
Q. why sigmoid is useful?
A. Its derivatives is really nice
- chain rule 가
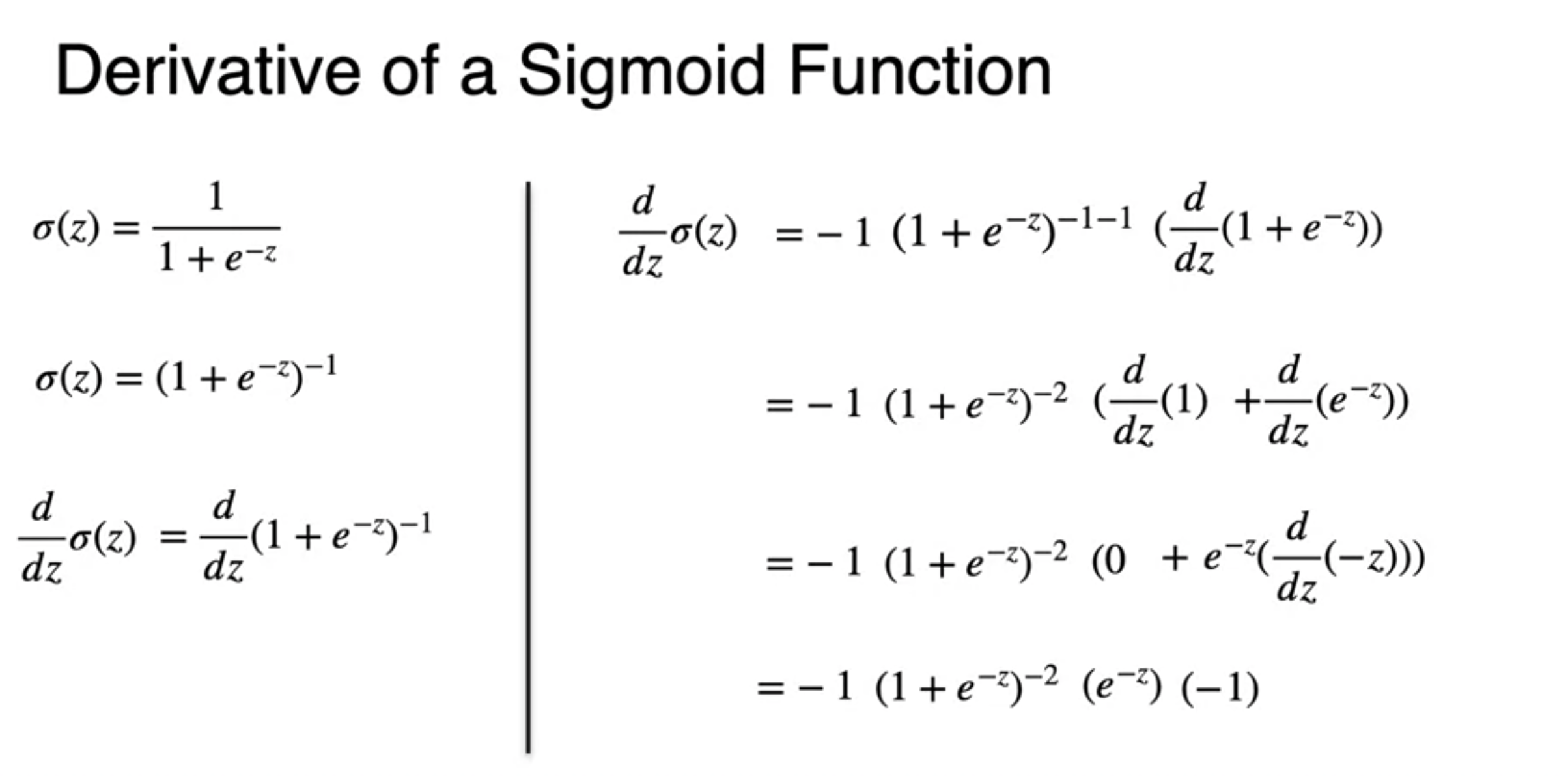
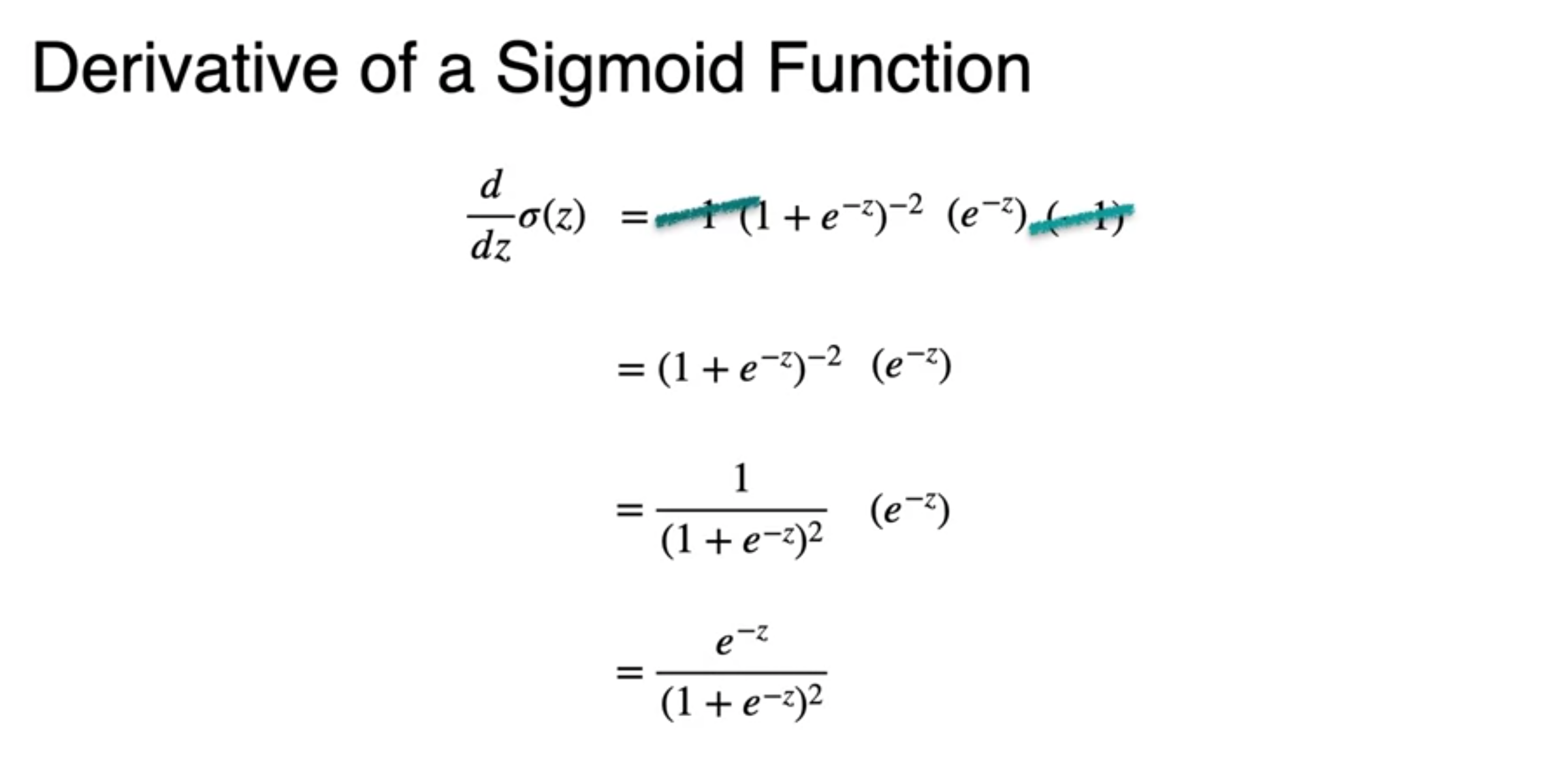
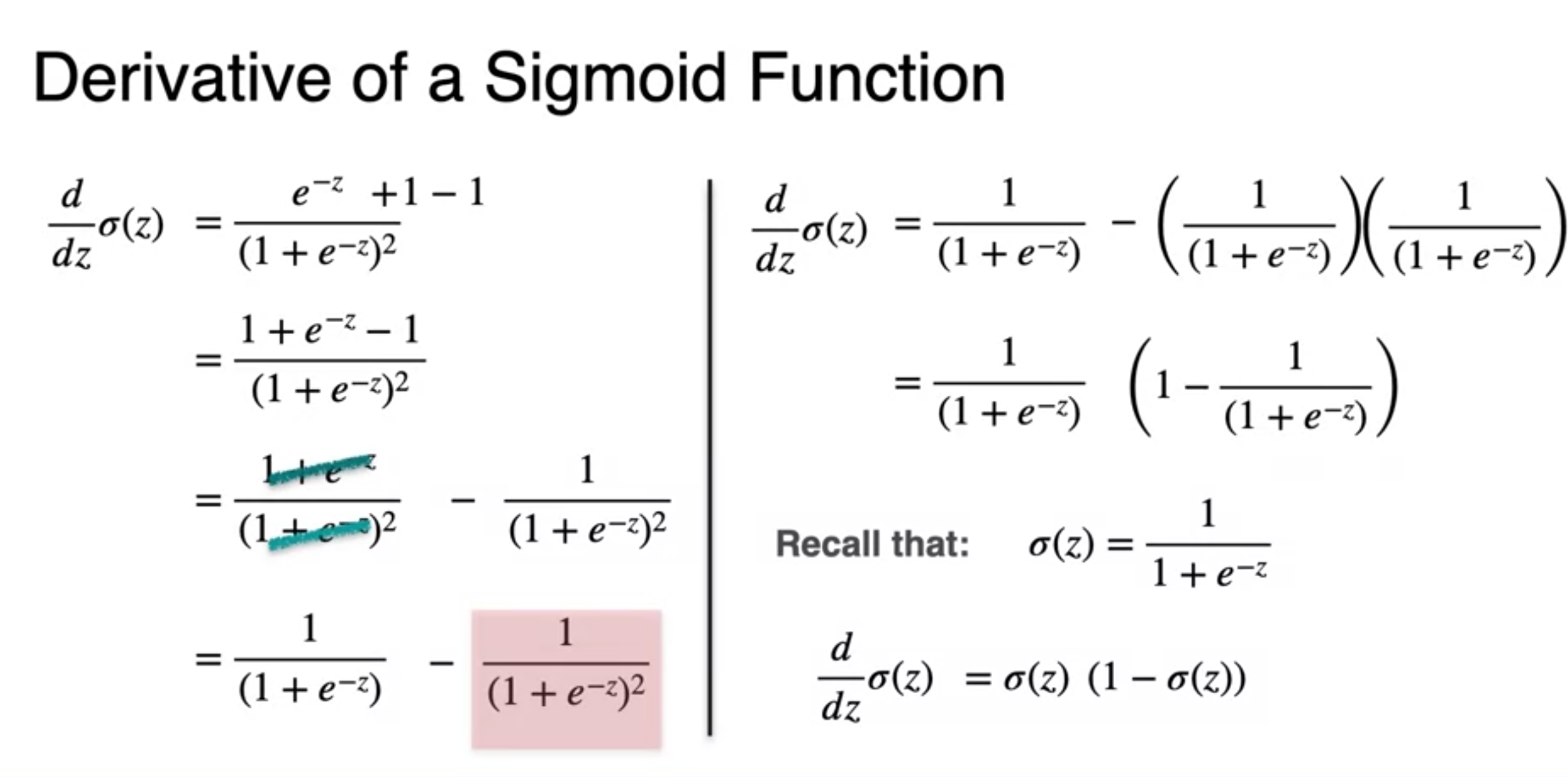
- at the end the derivatives of sigmoid is
- It looks beautiful
Classification with Perceptron - Gradient Descent
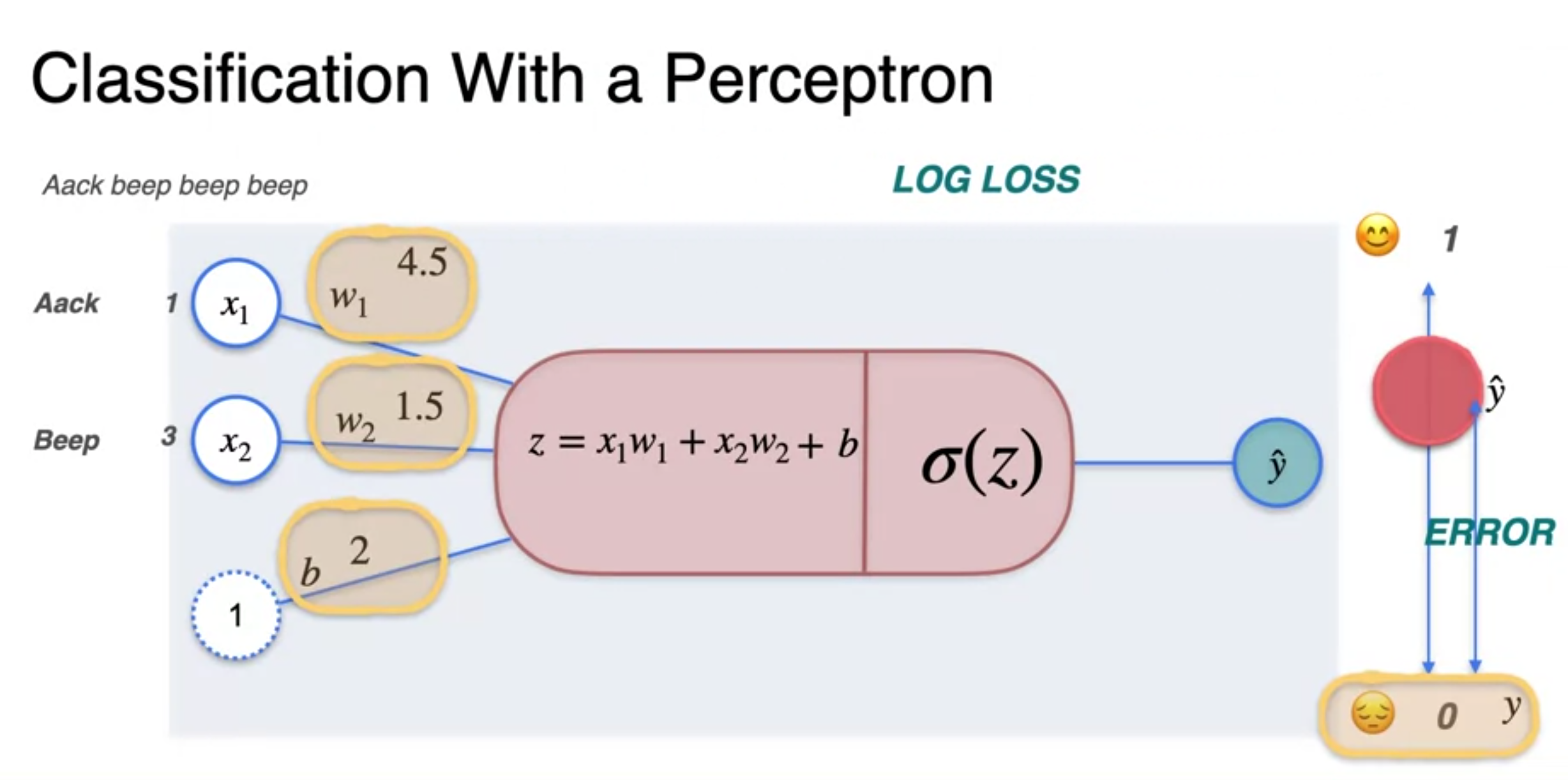
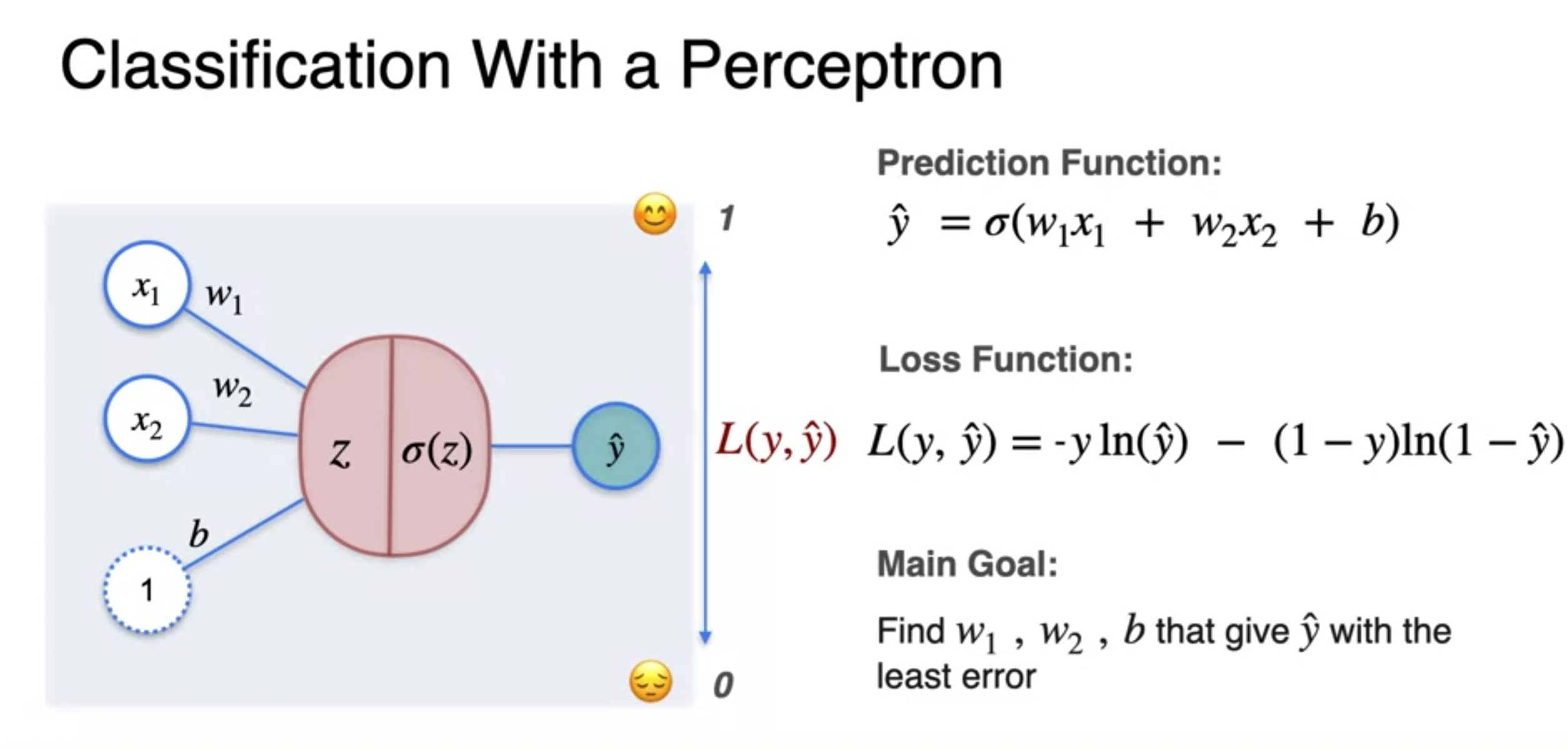
- To get the least log loss(y, y-hat) error
- Gradient descent
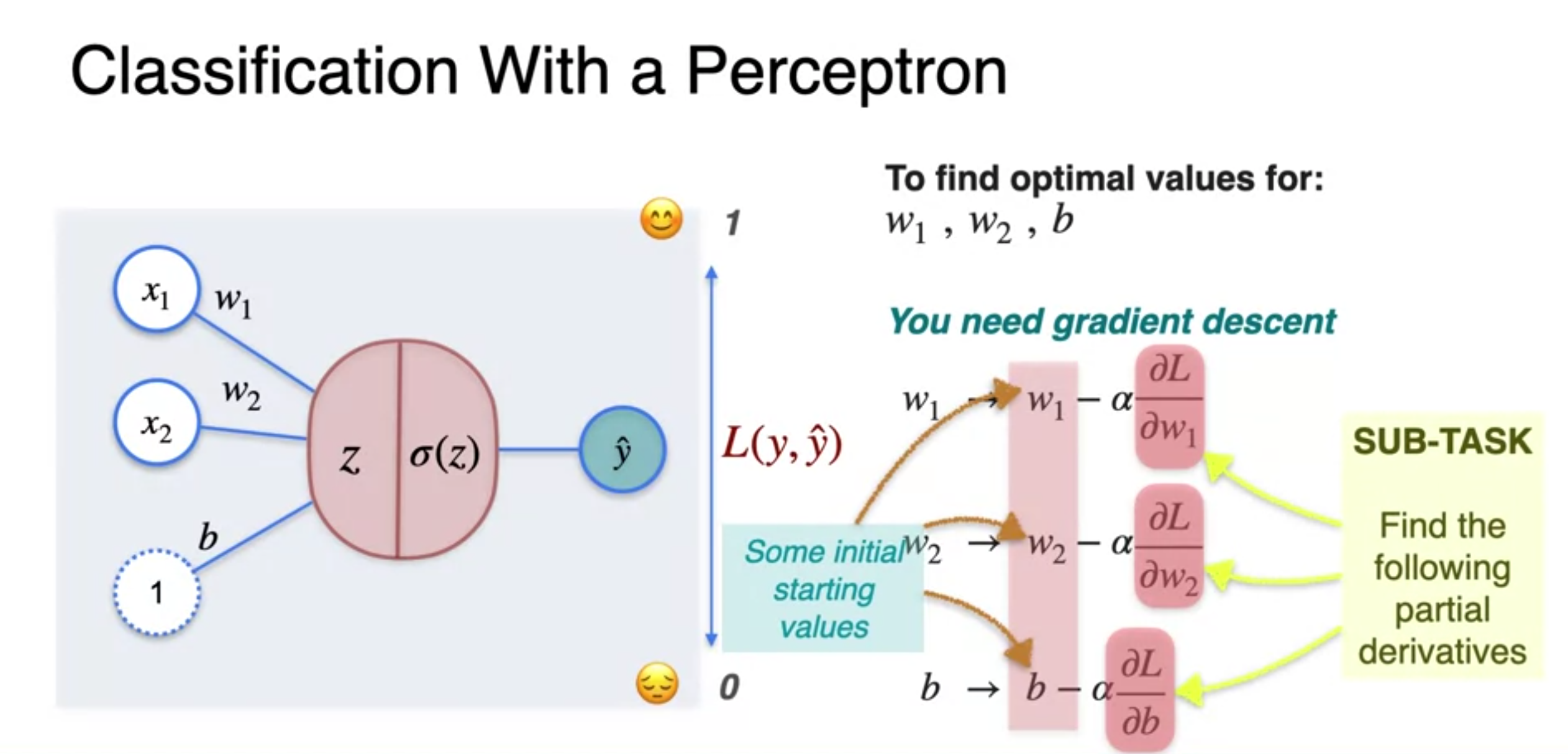
- Starts with arbitrary(random) values for weights and biases
Classification with a Neural Network
- Neural network : a bunch of perceptrons organized in layers
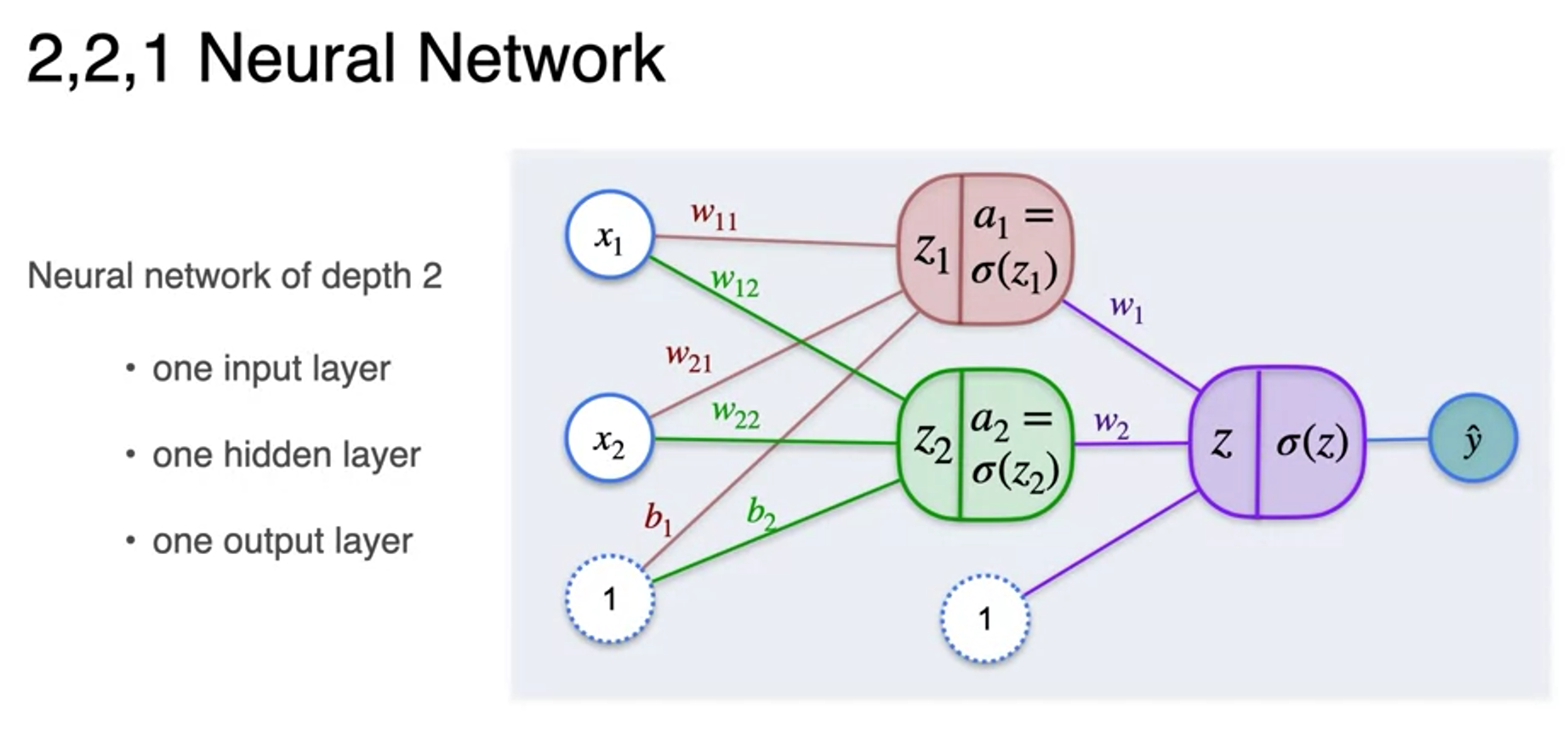
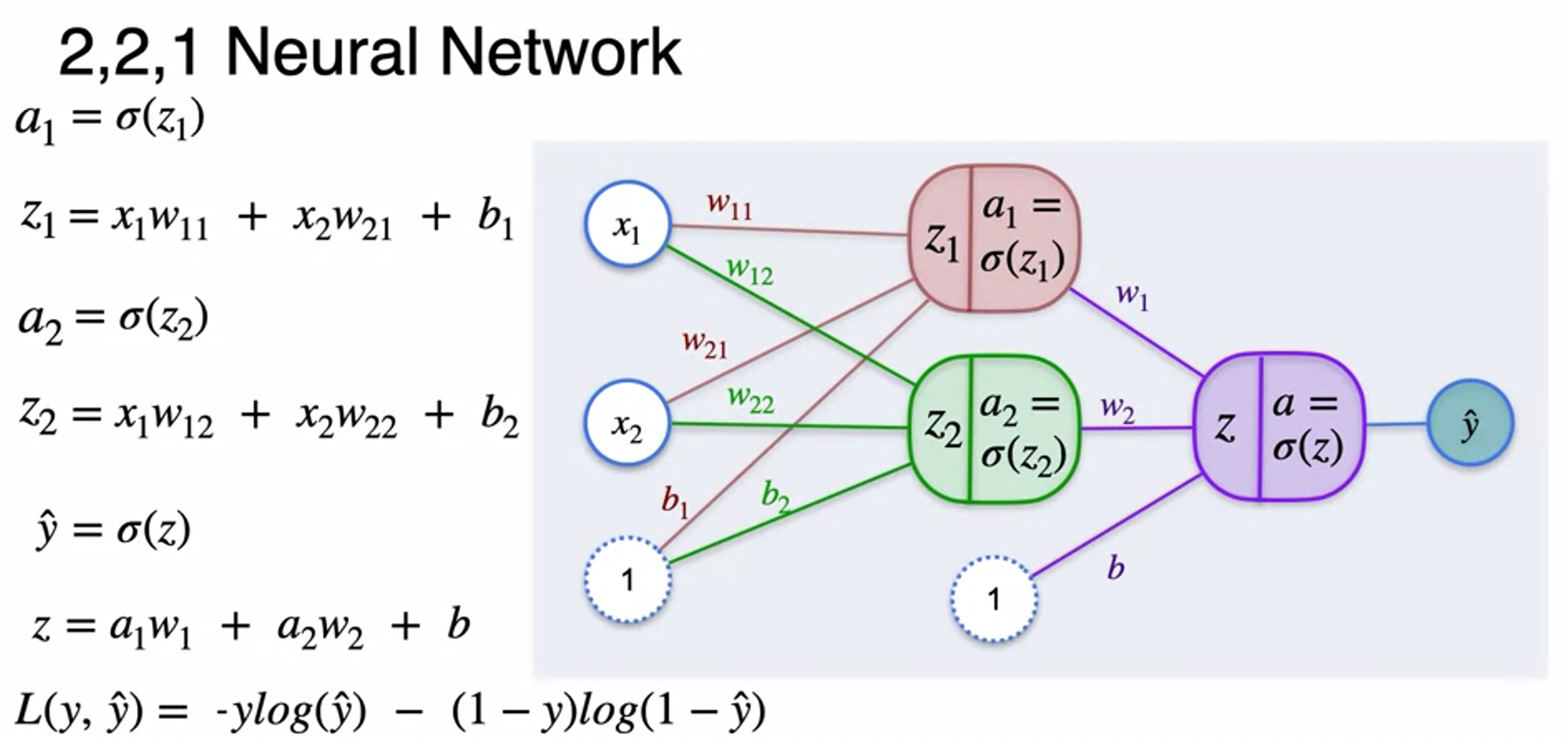
- How neural network calculated
Classification with a Neural Network - Minimizing log-loss
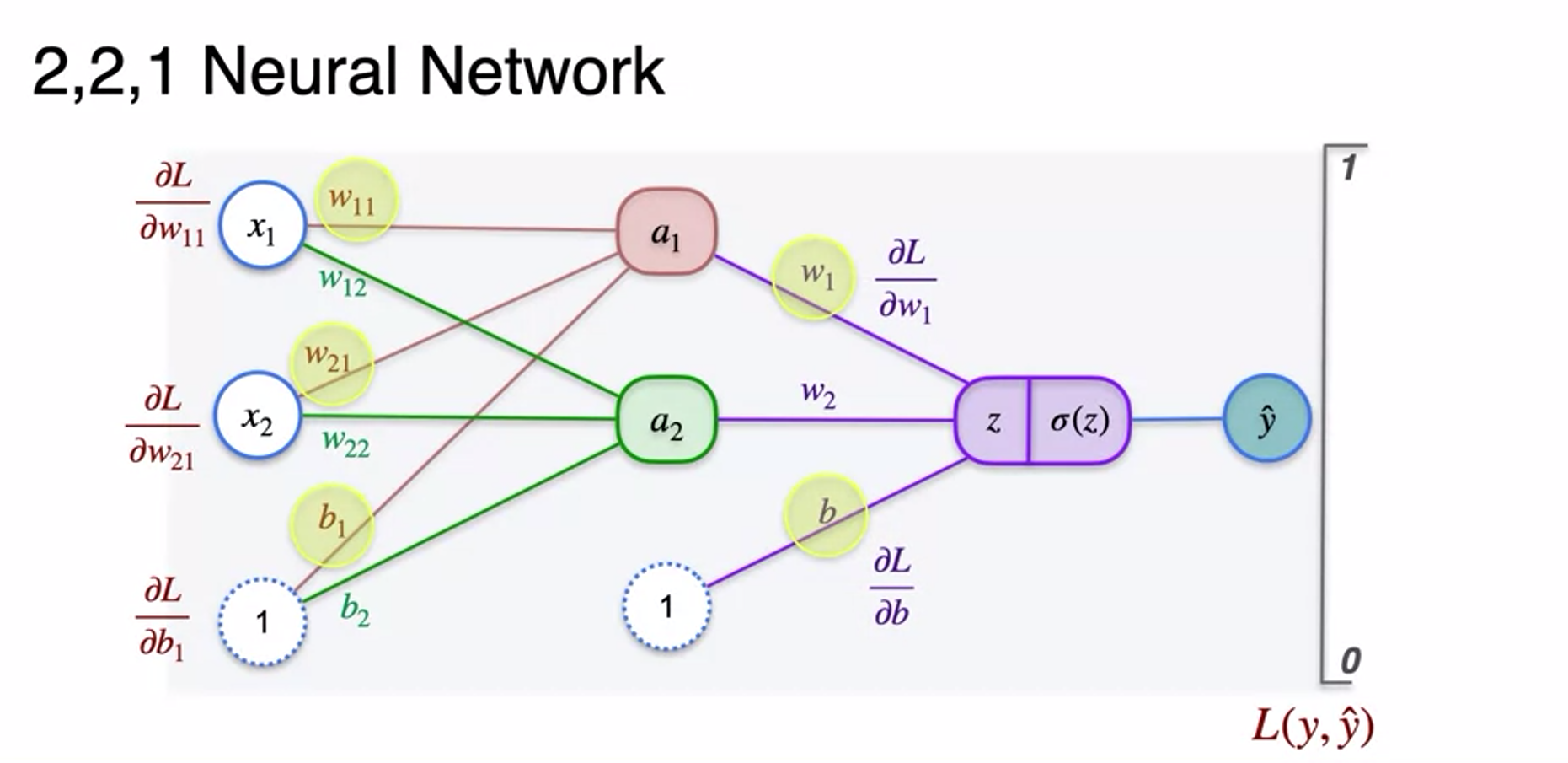
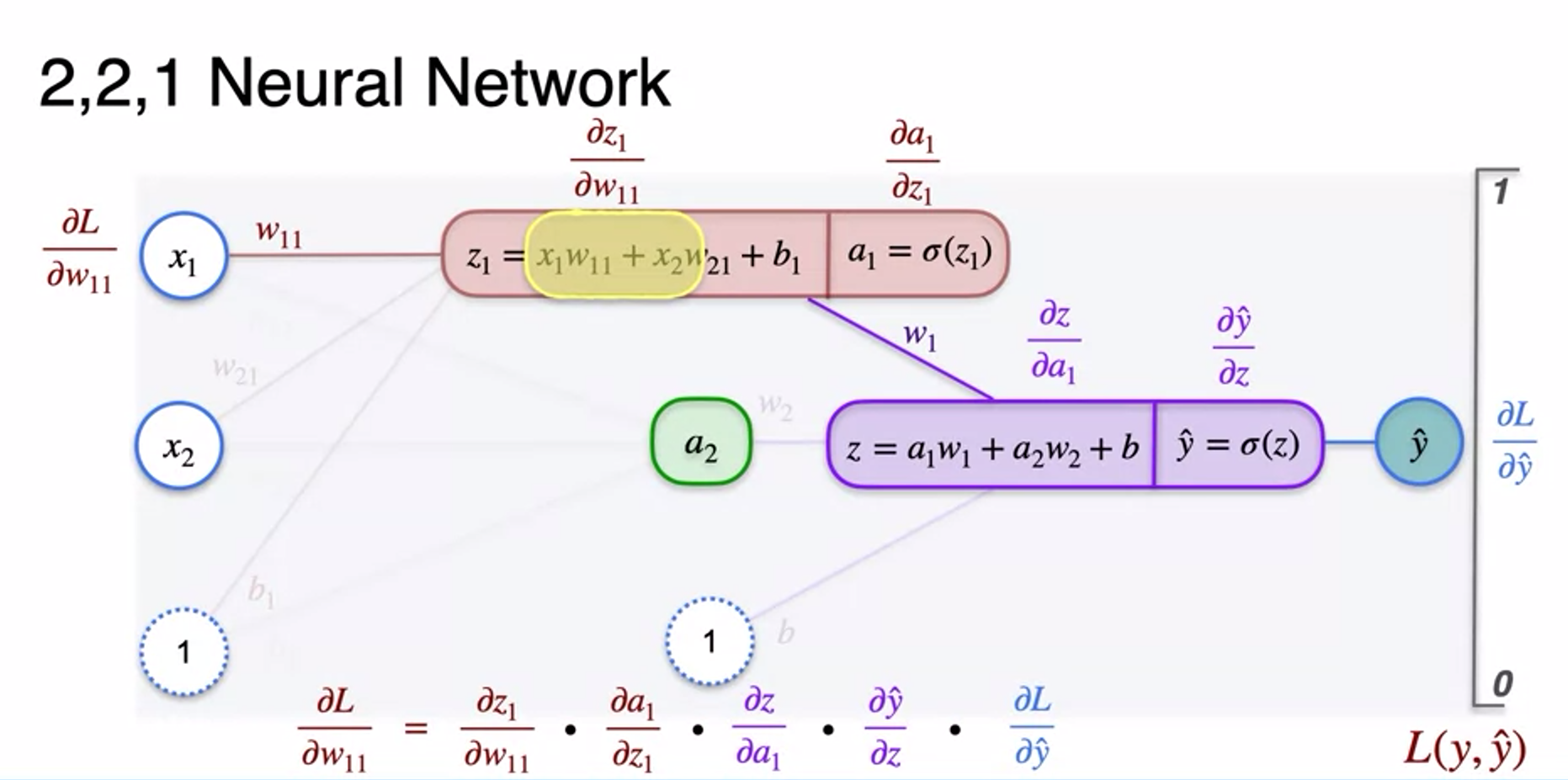
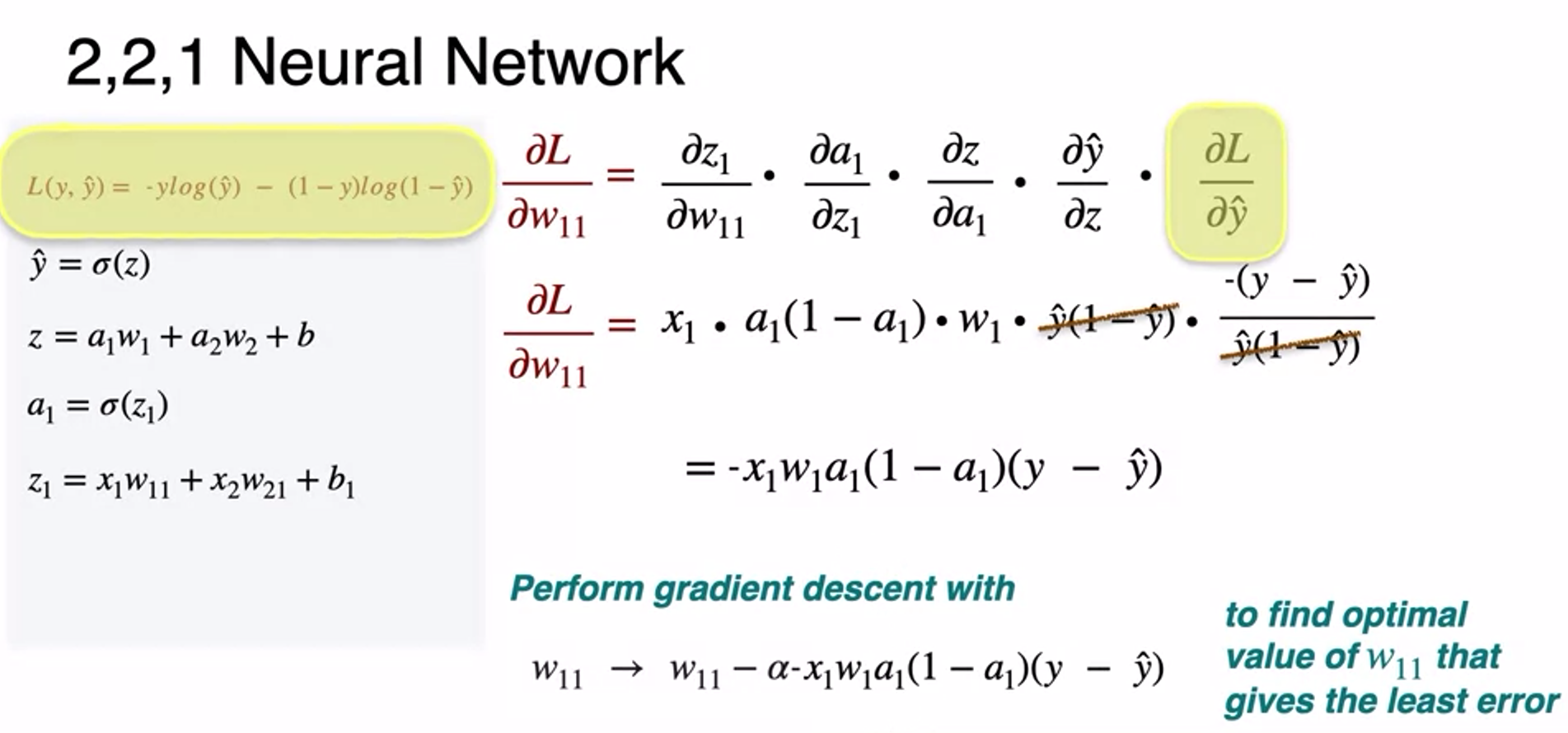
- how to update hidden weight to minimize log-logss
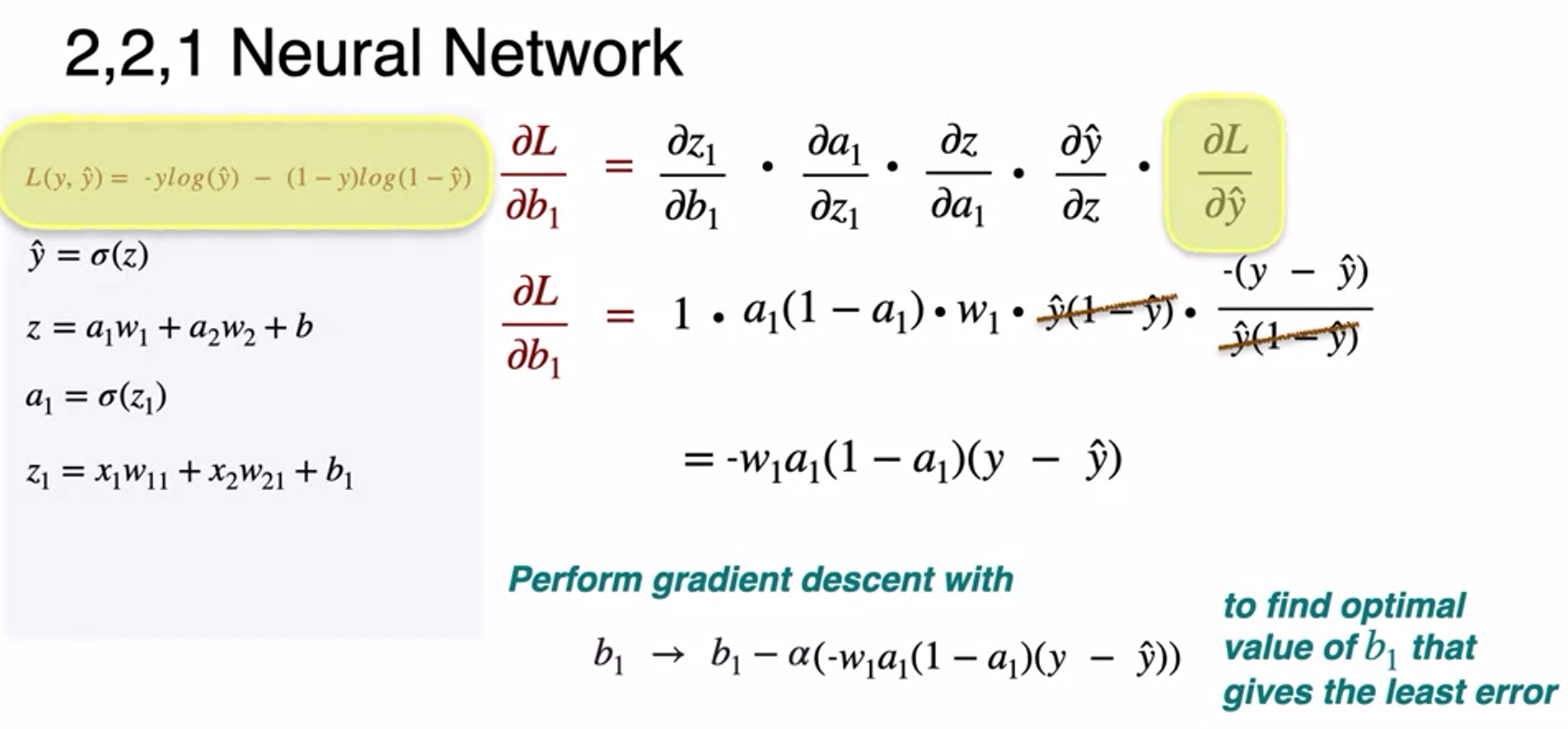
- so as bias
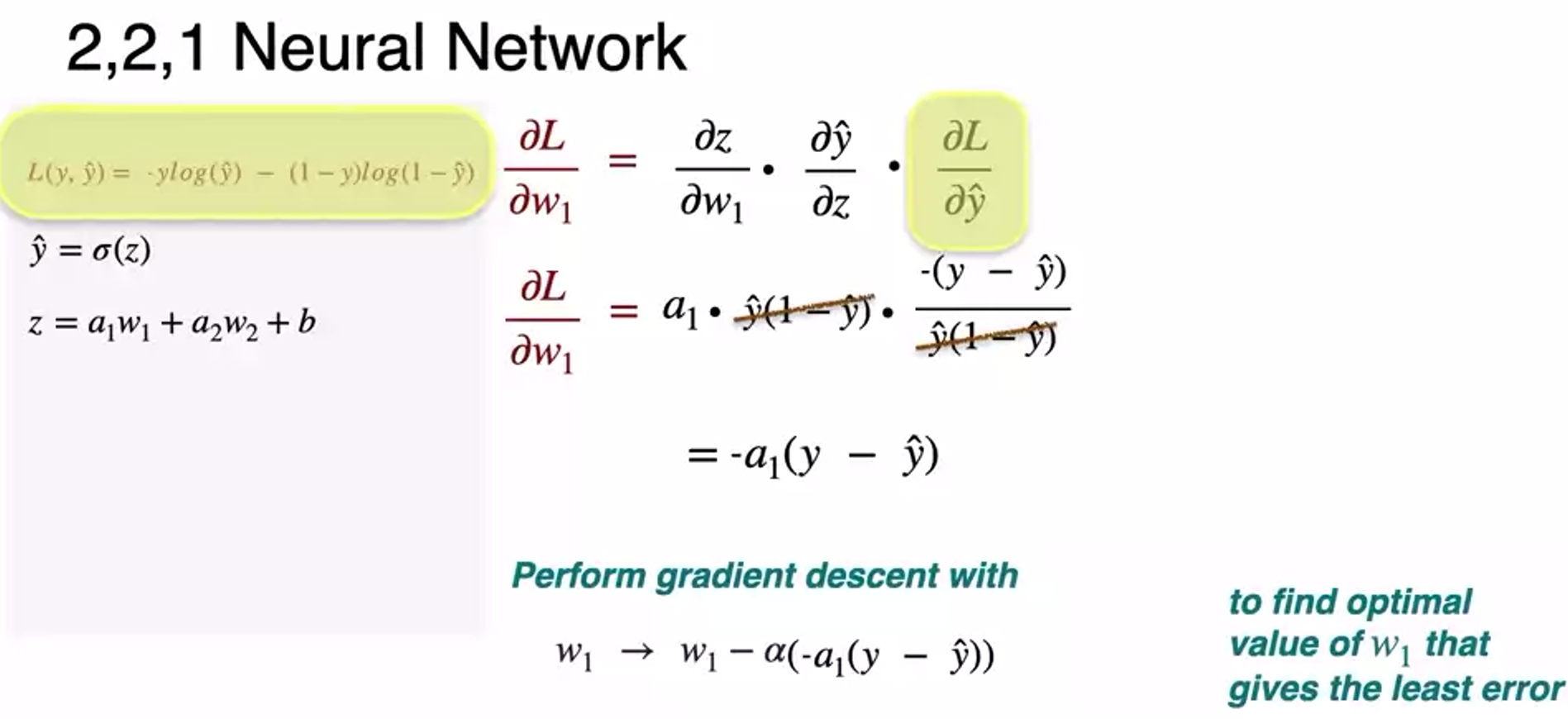
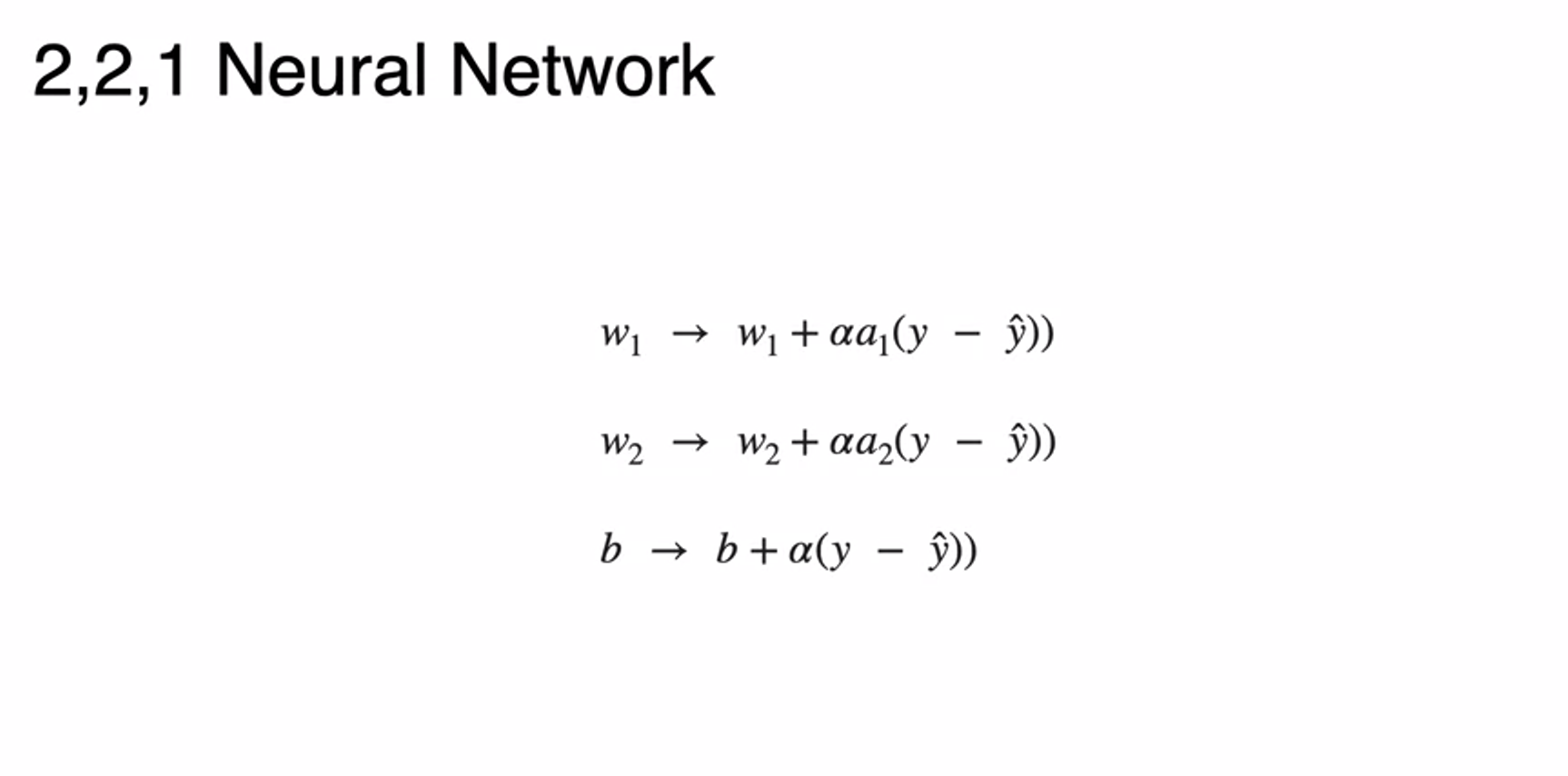
- so as weight
Gradient Descent and Backpropagation
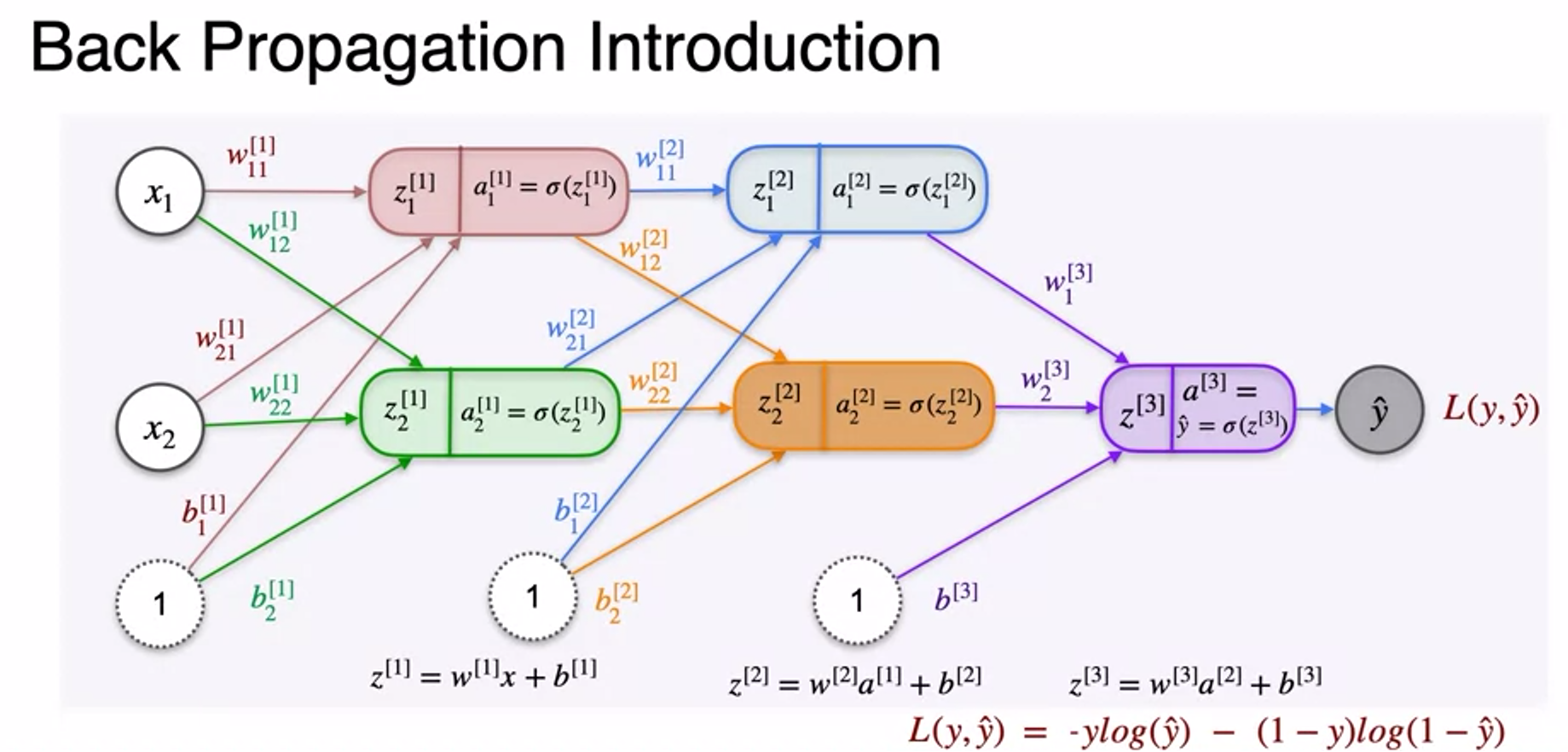
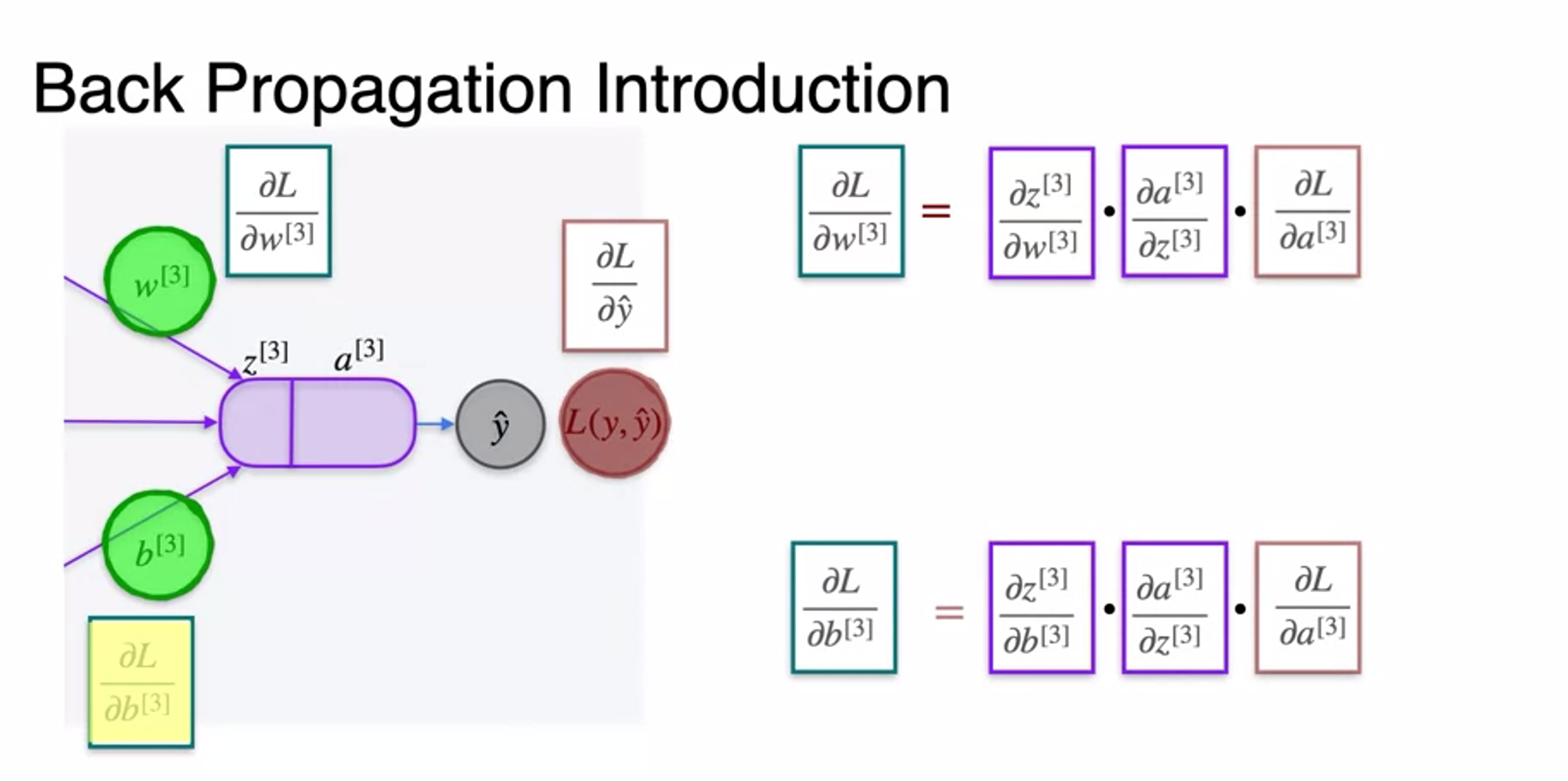
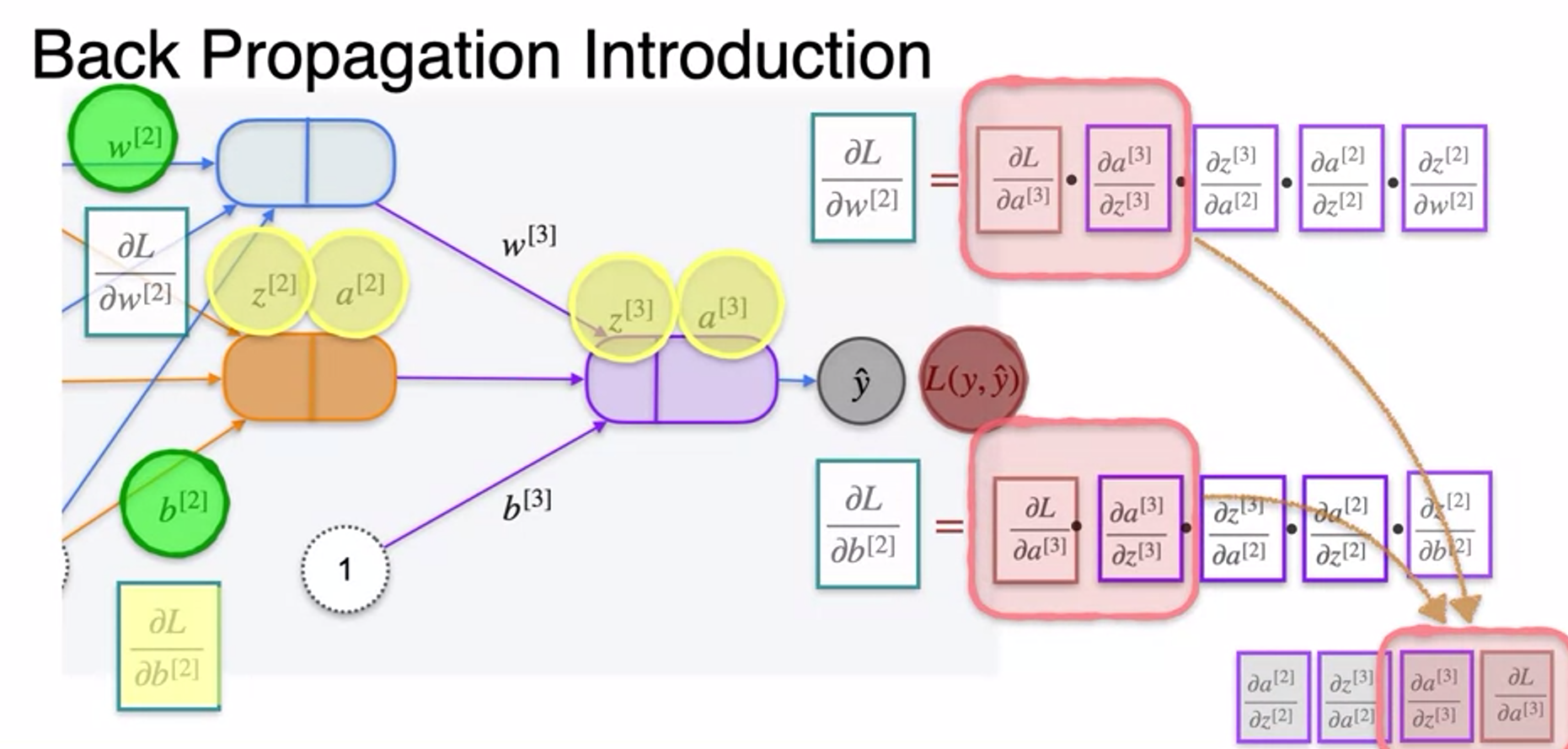
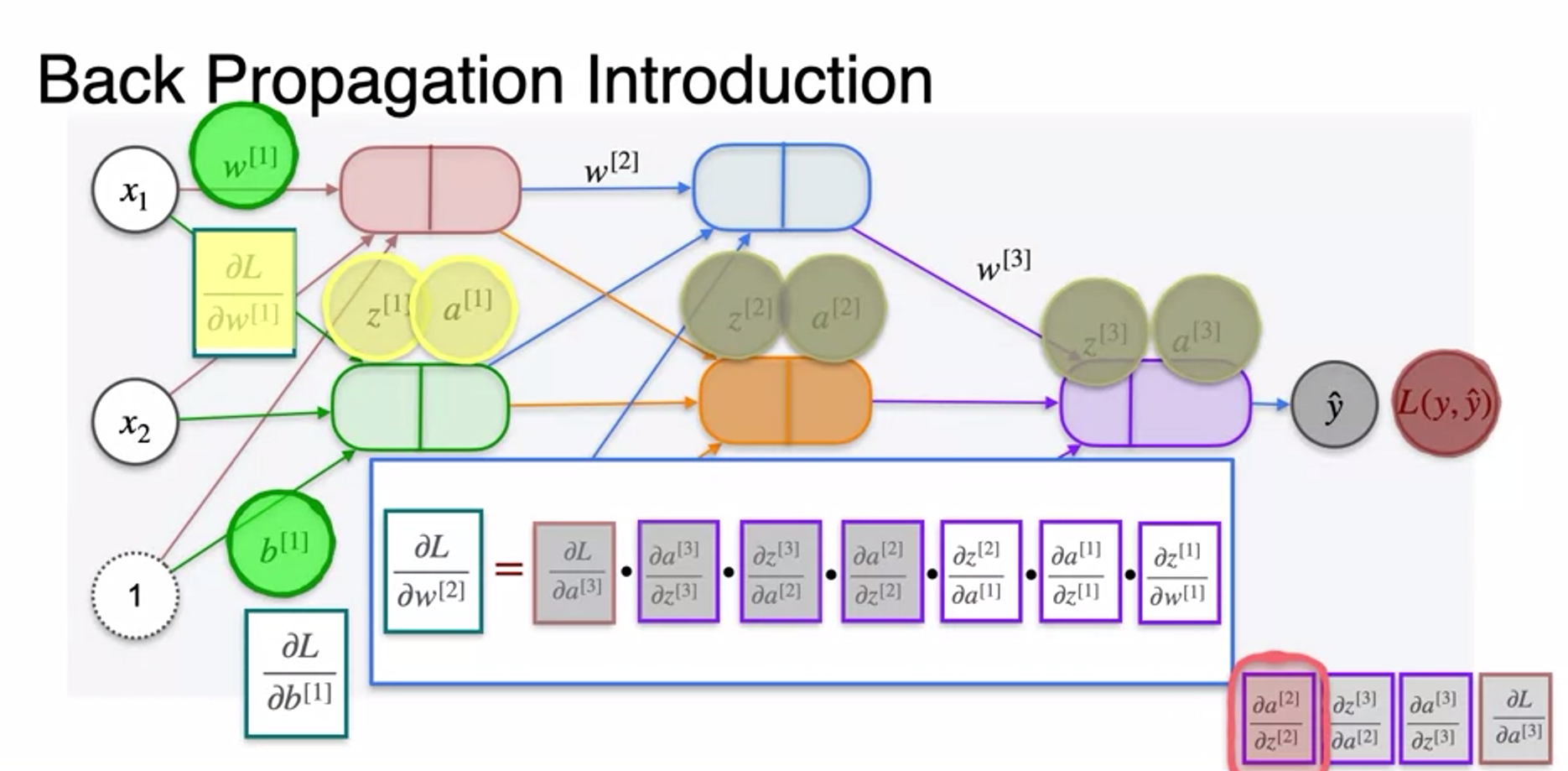
- very long chain rule
Newton's Method
Newton's Method
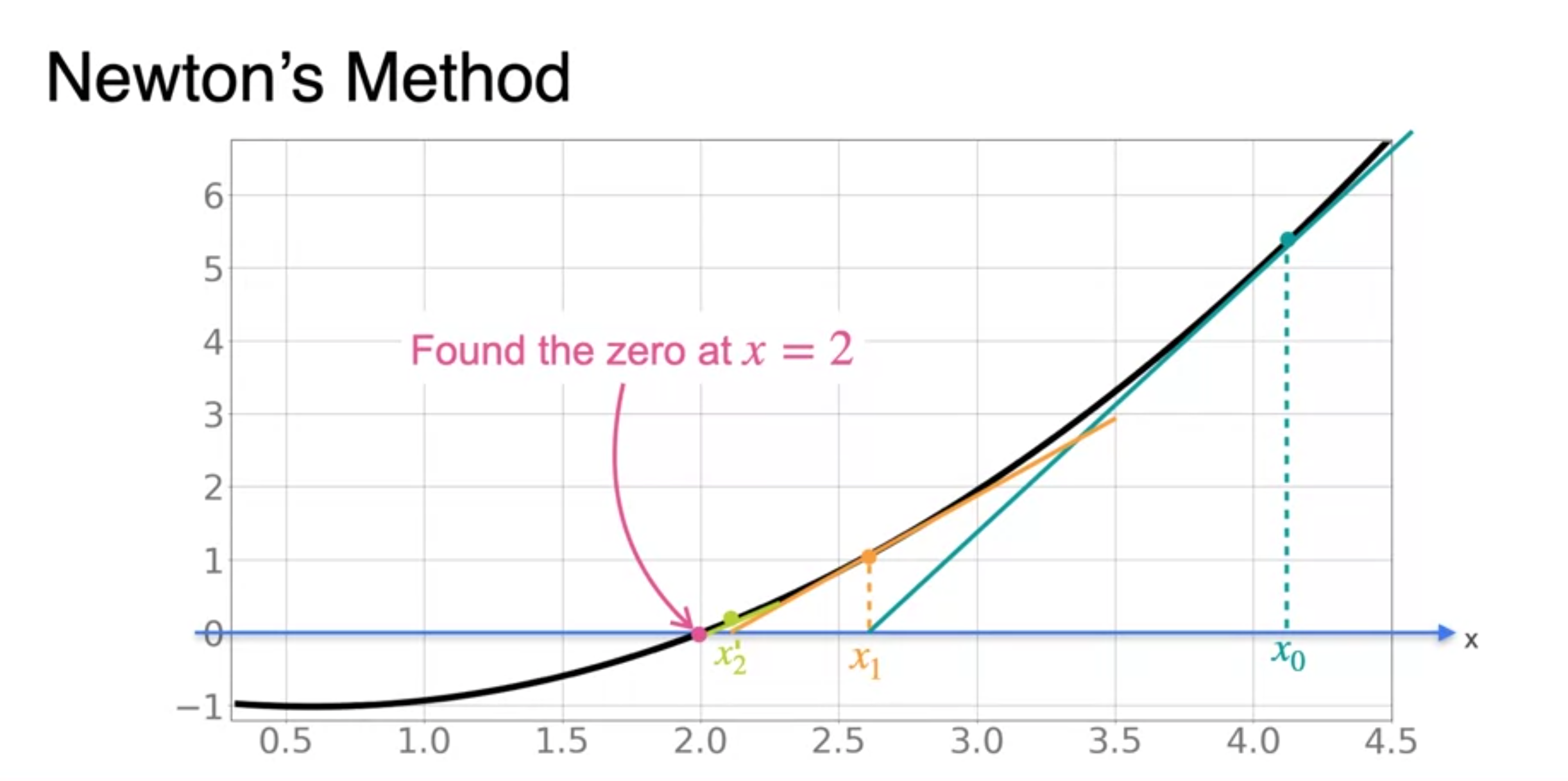
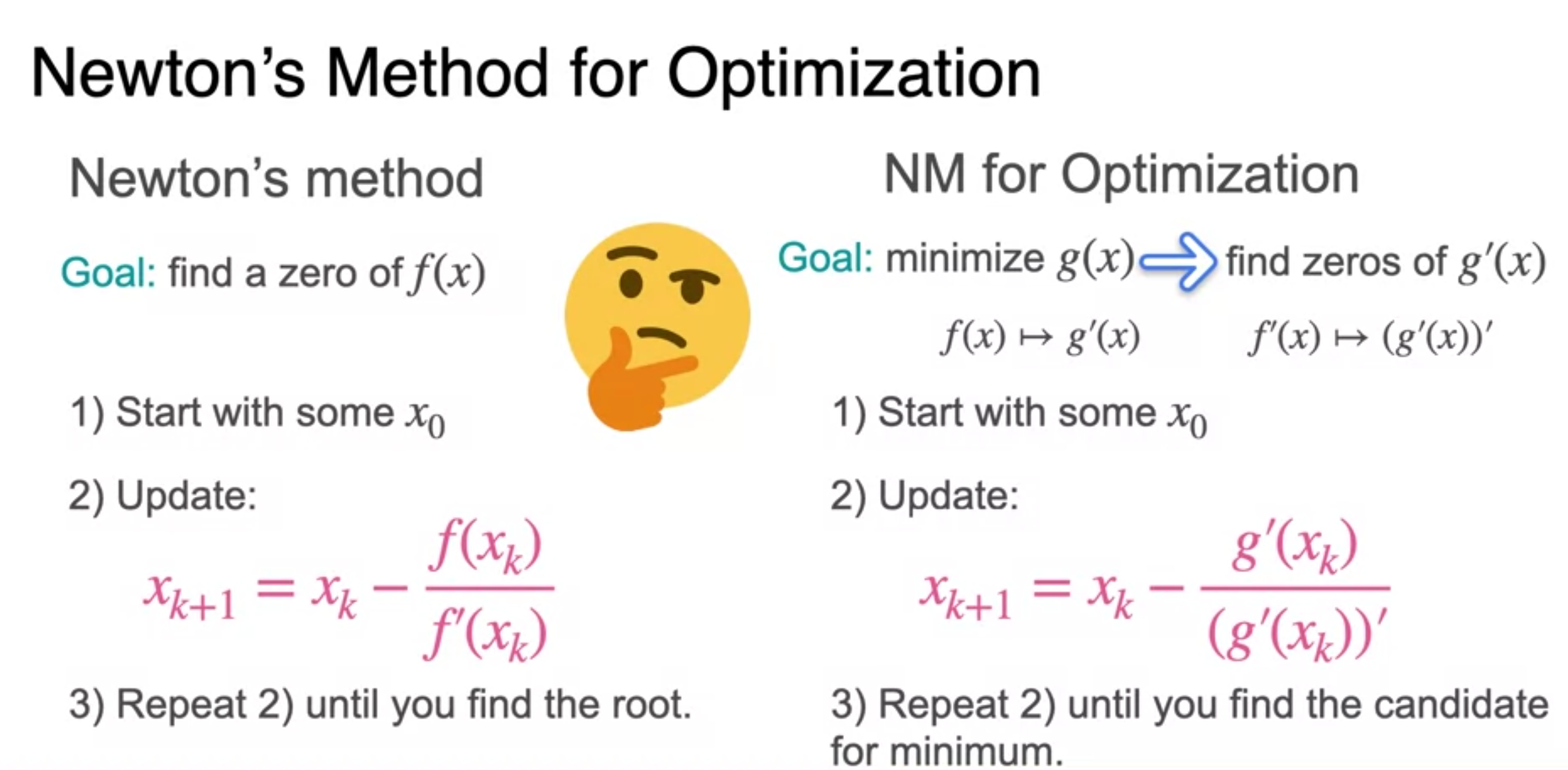
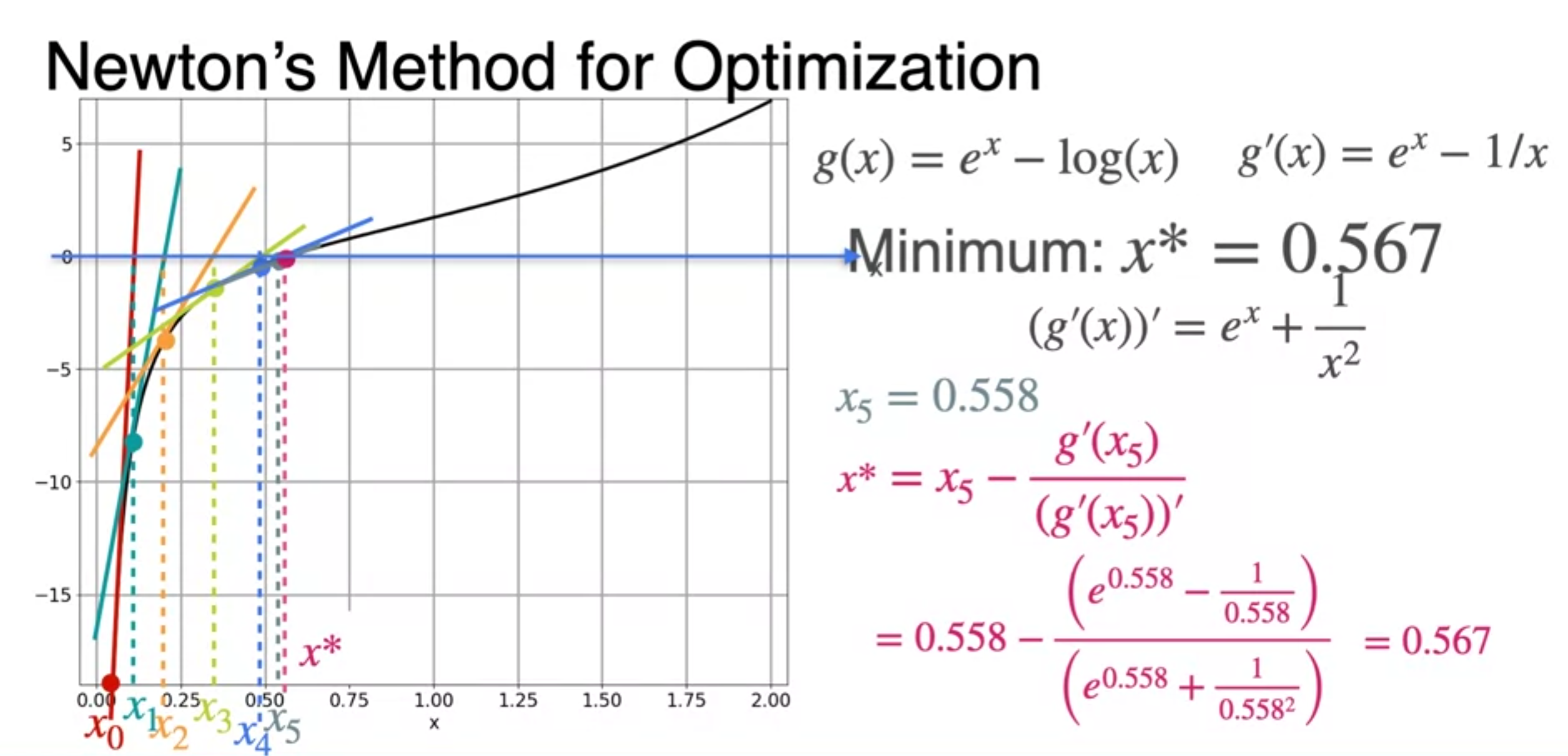
Newton's Method: An example
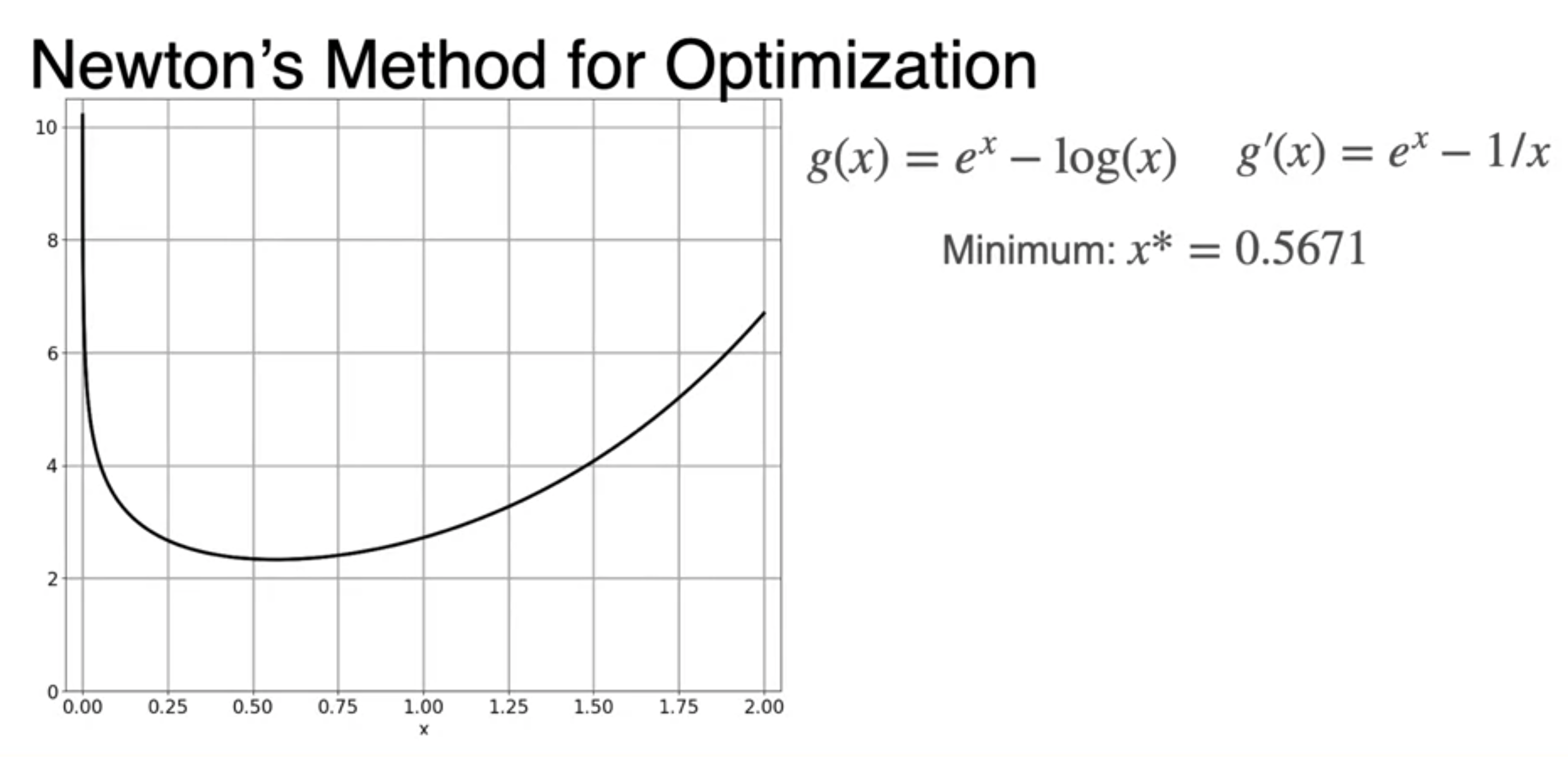
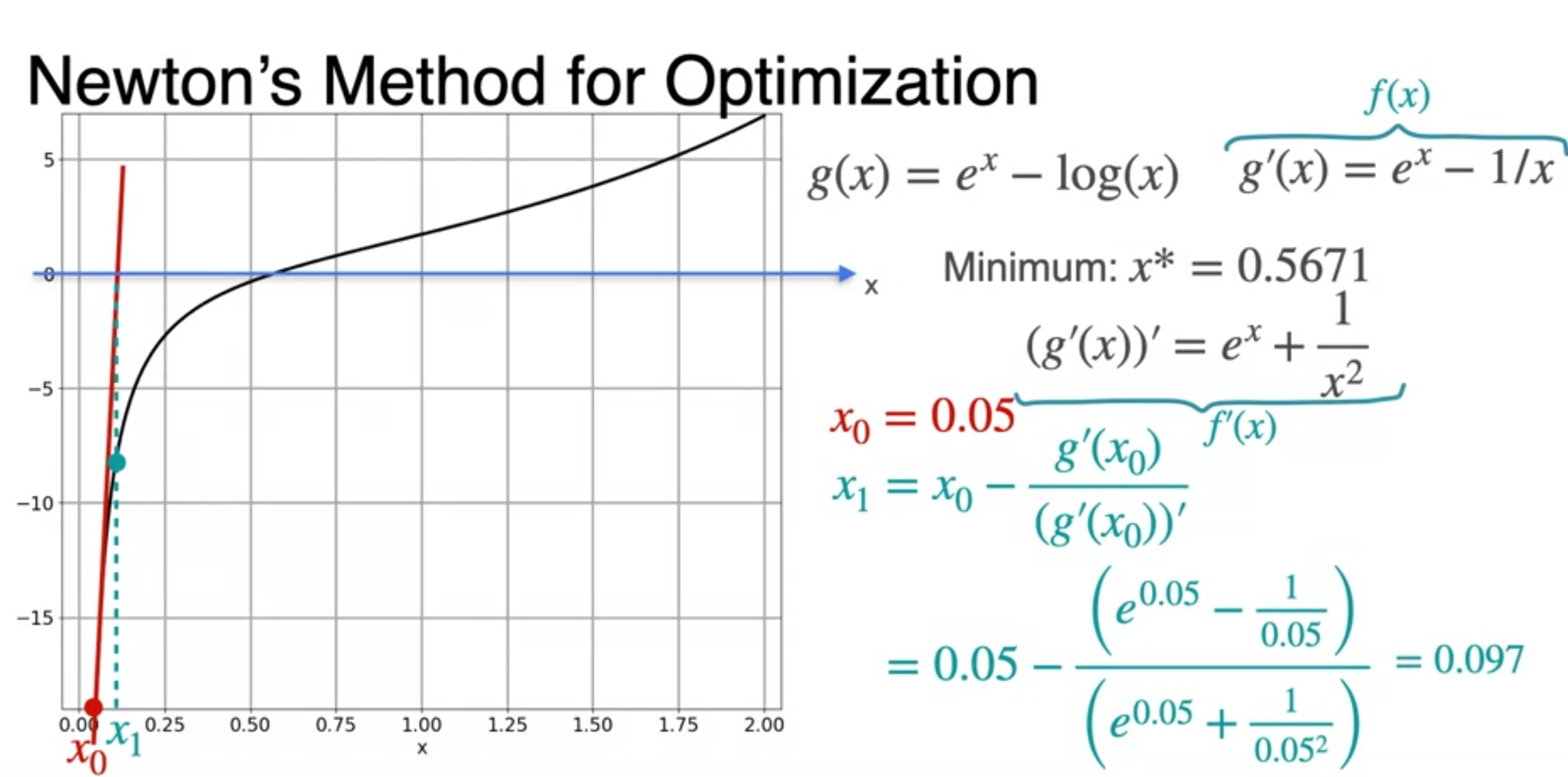
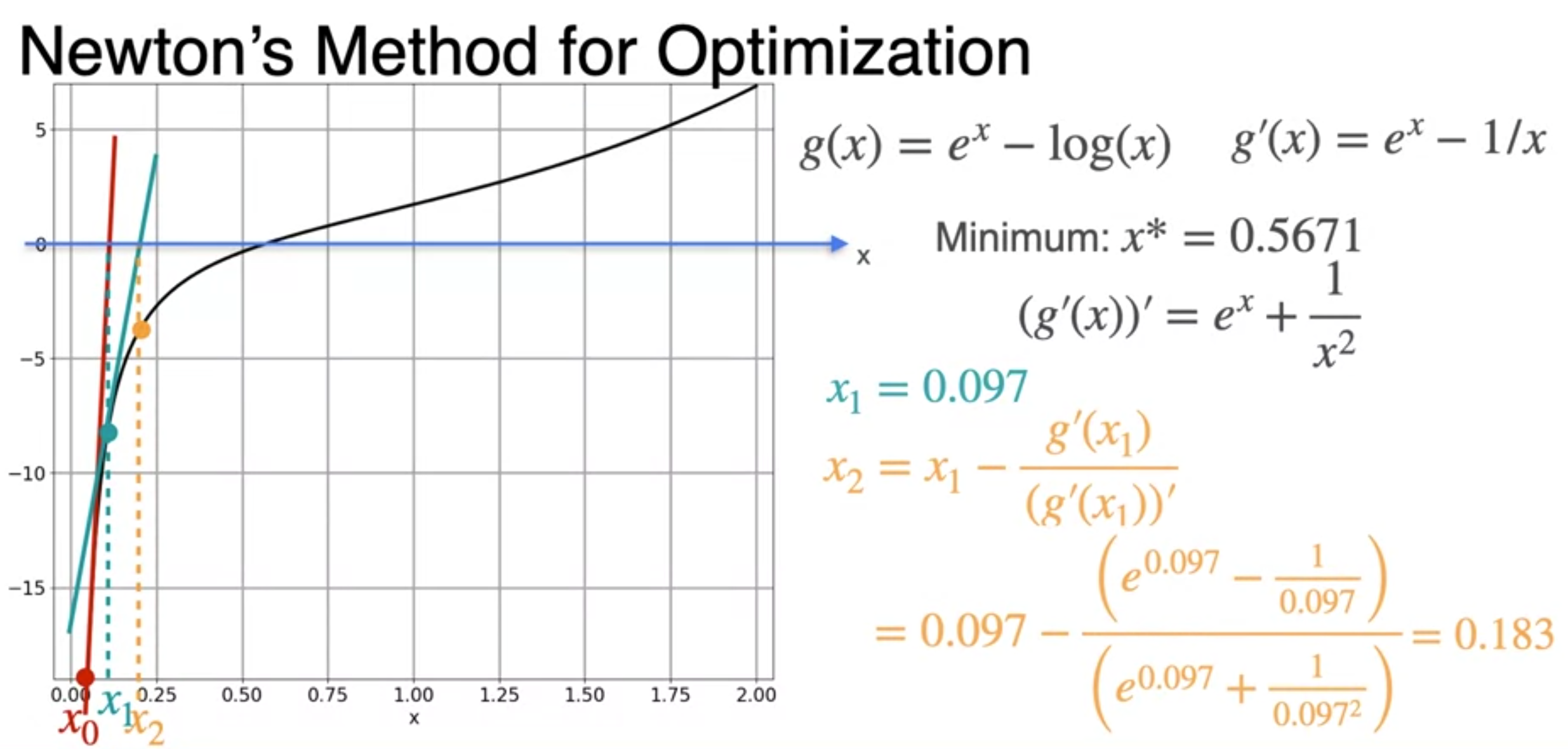
- repeat to the minimum
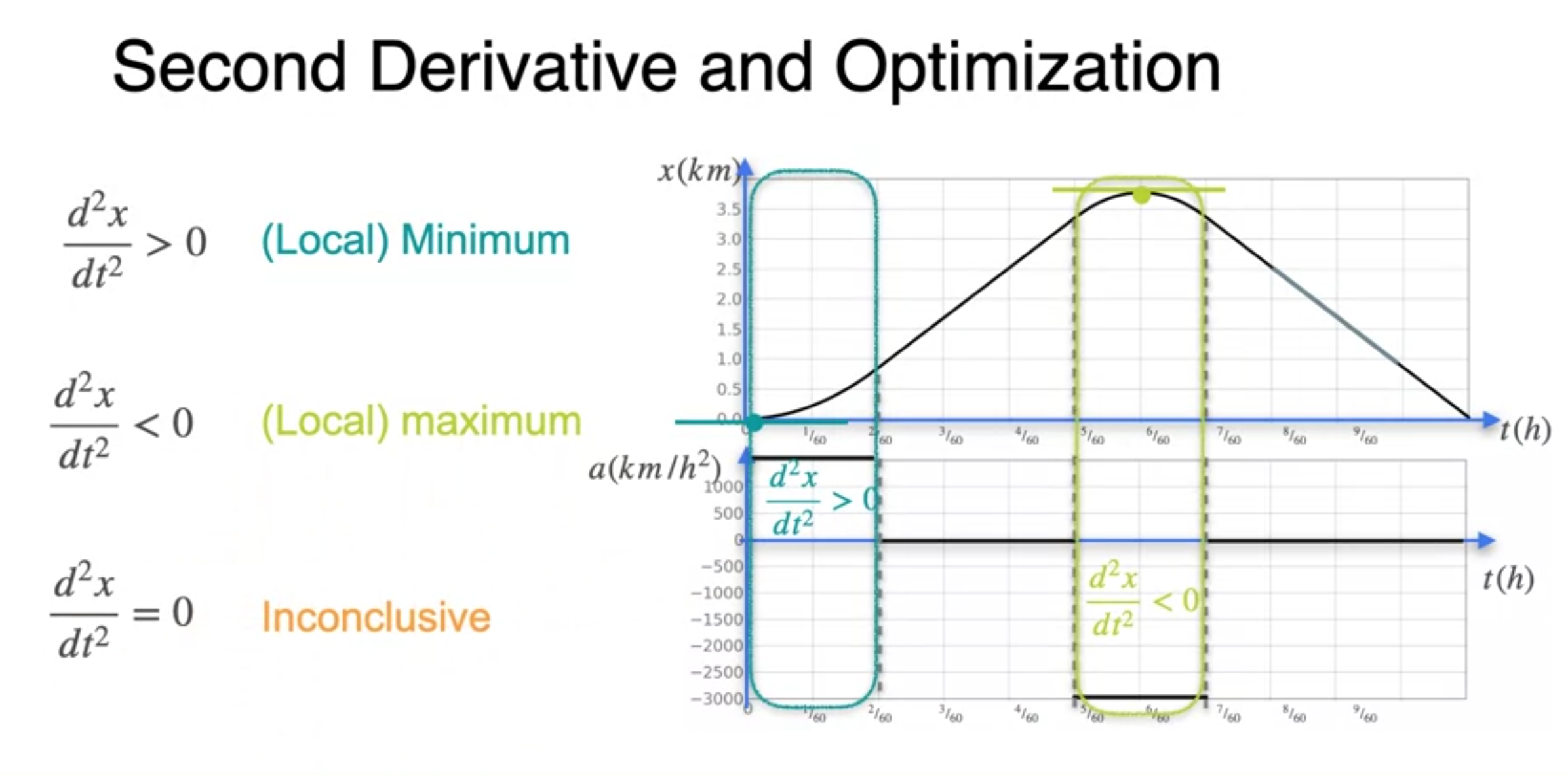
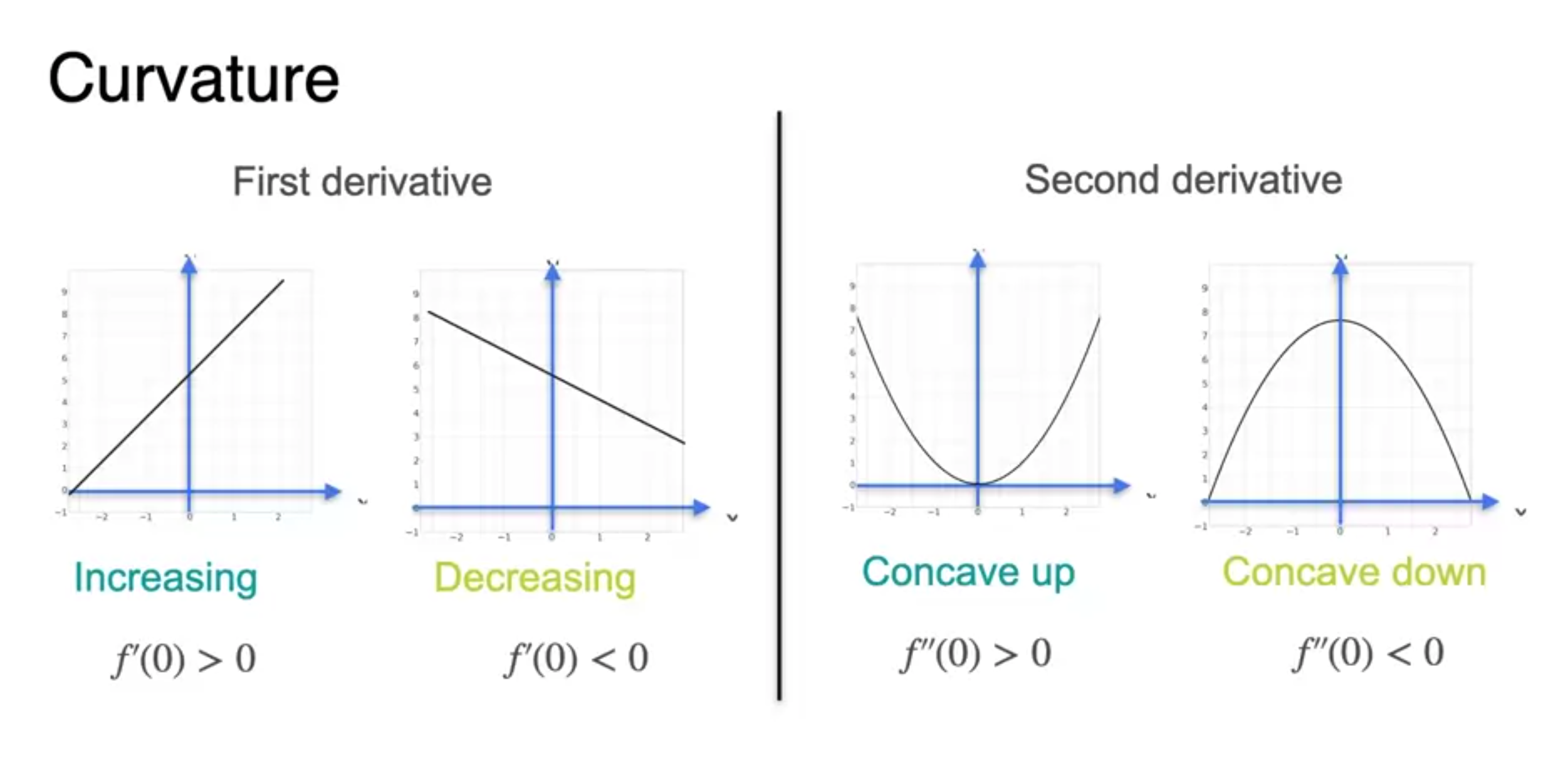
The second derivative
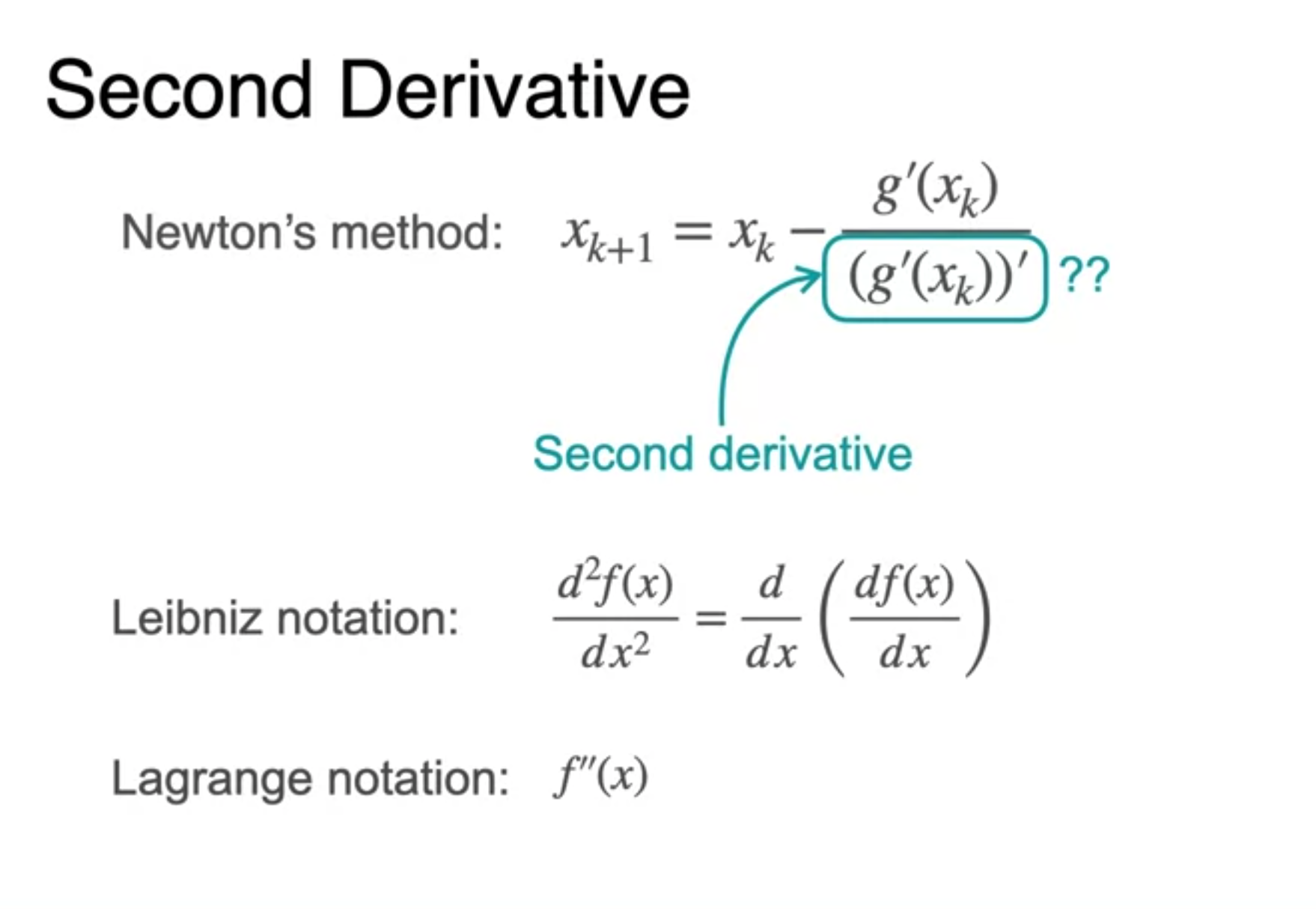
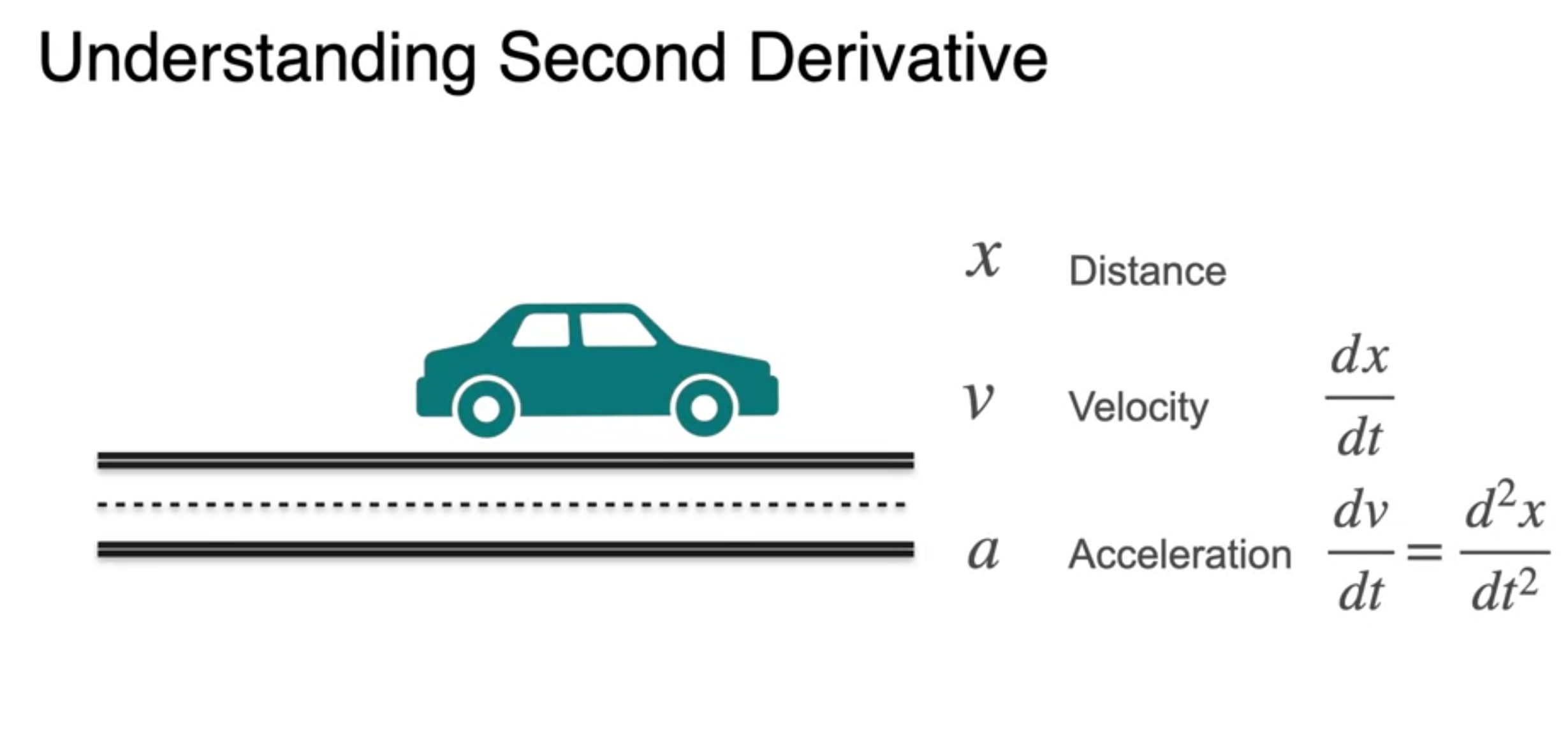
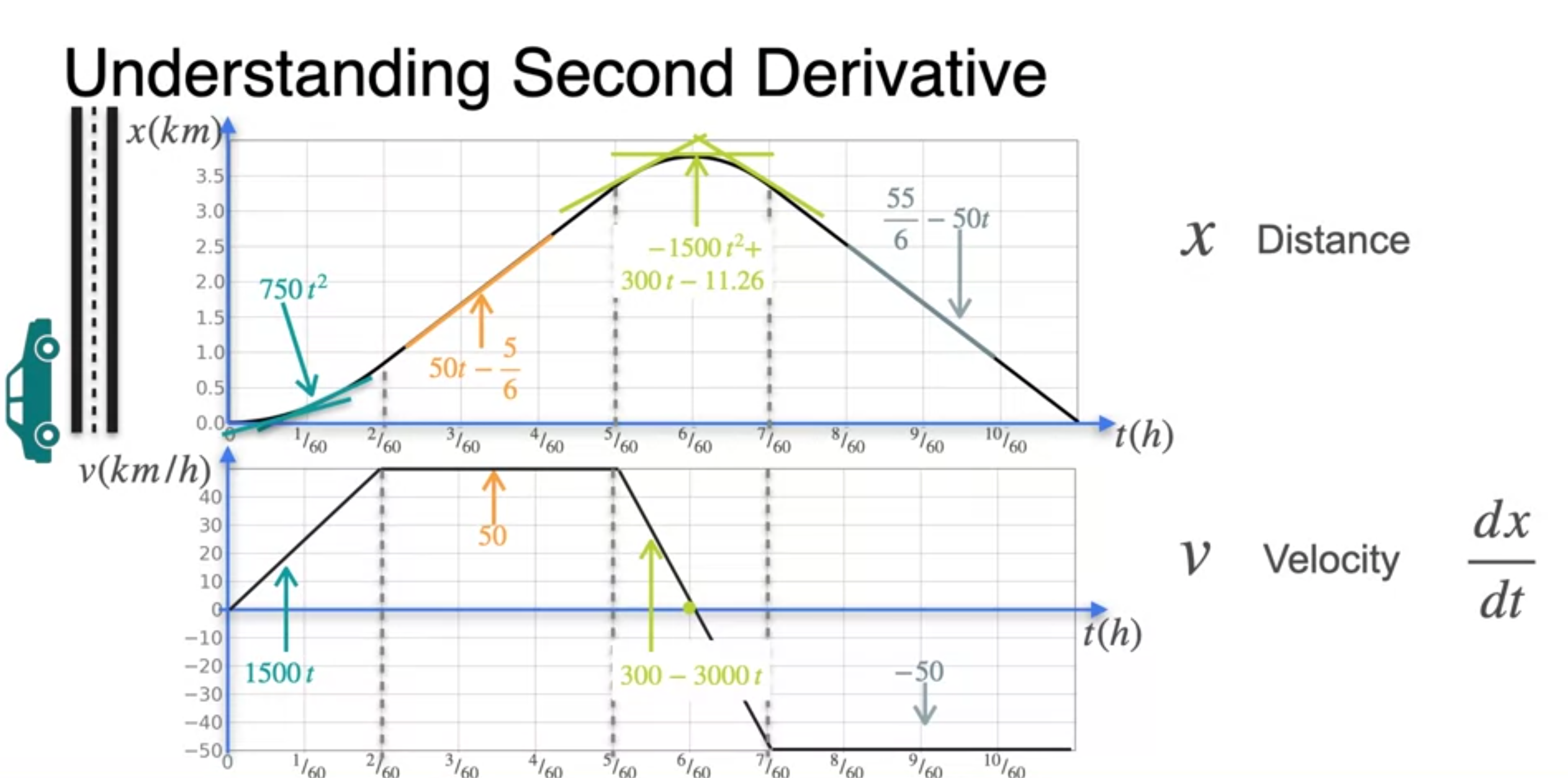
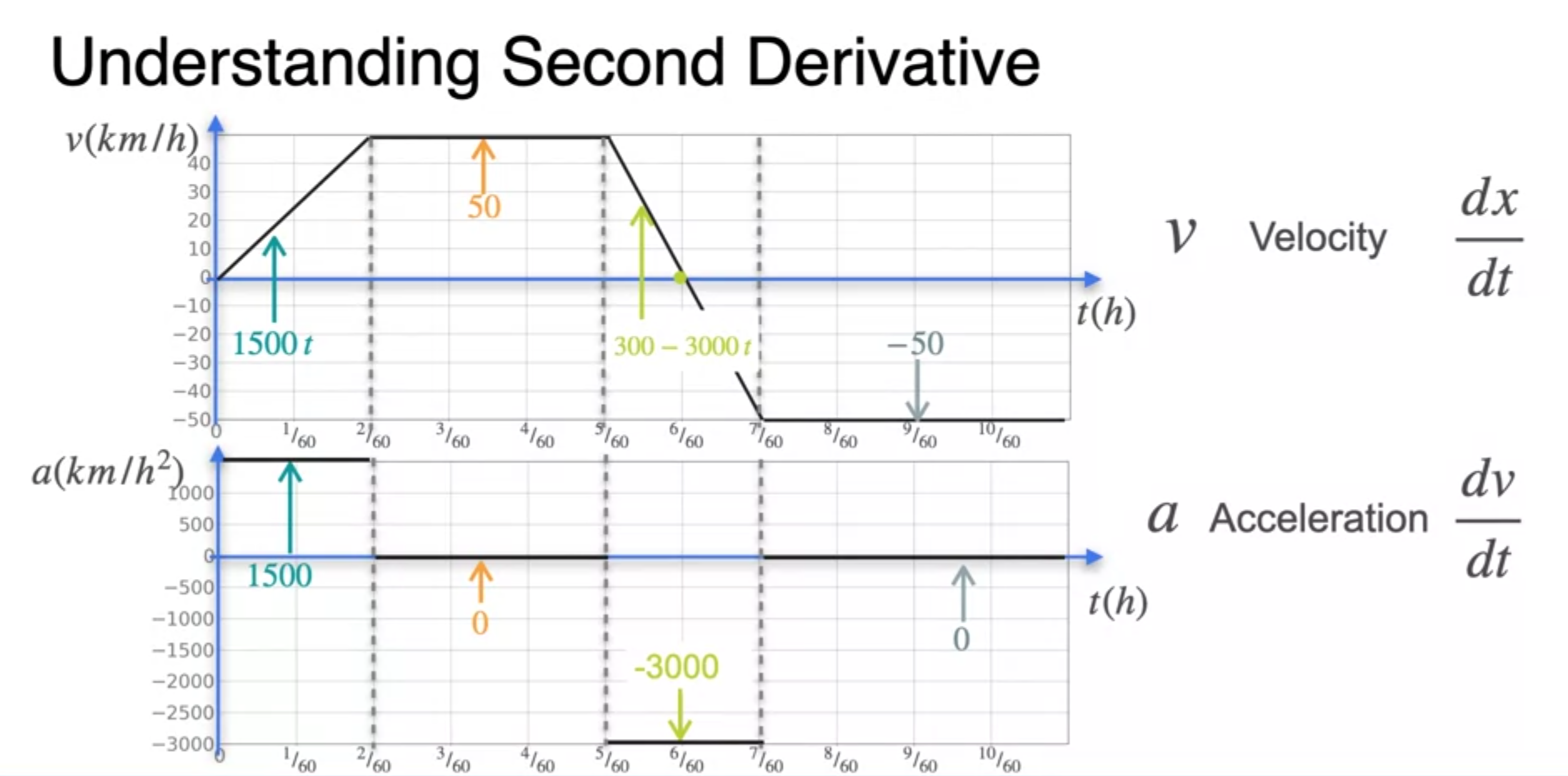
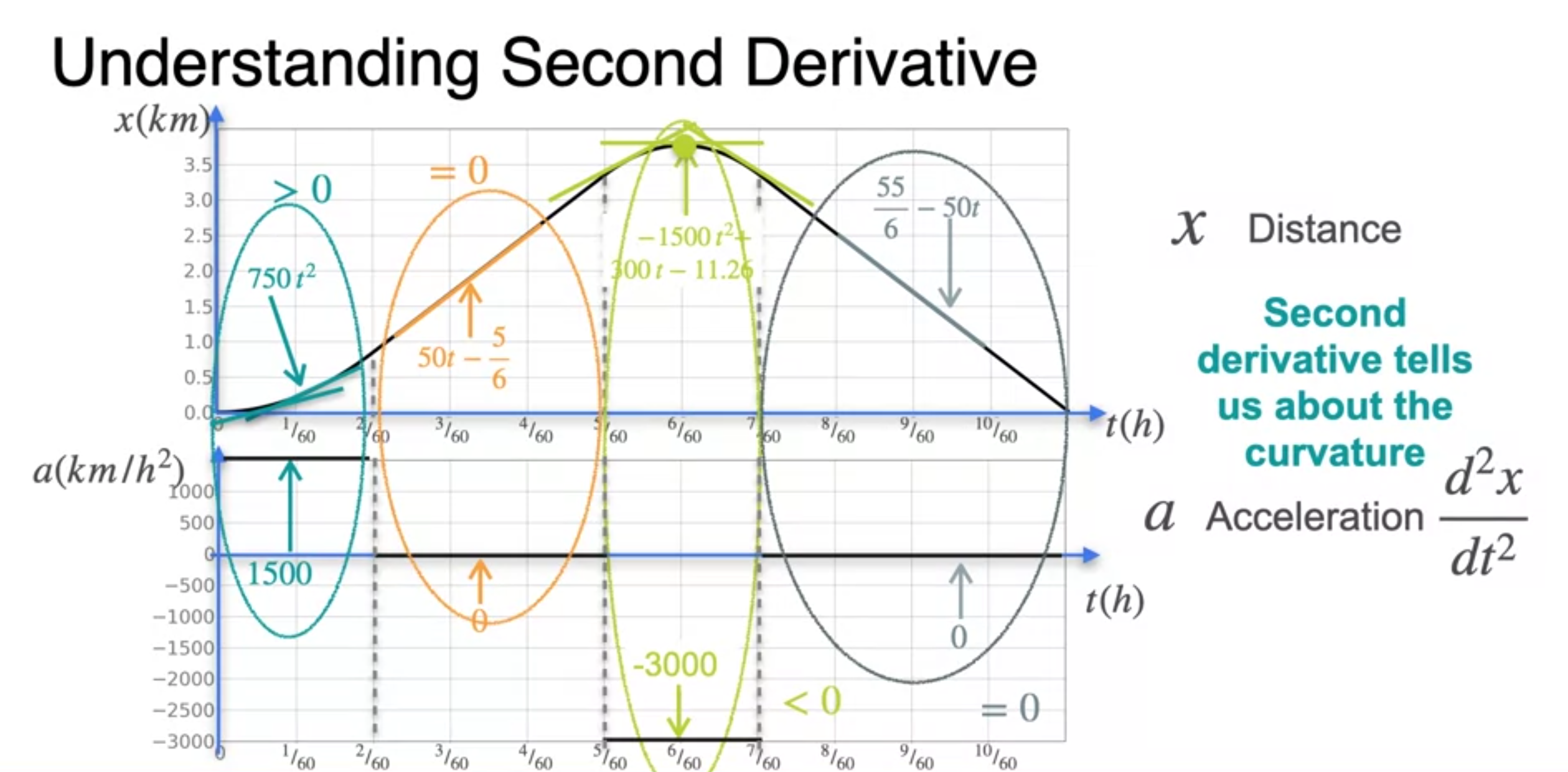
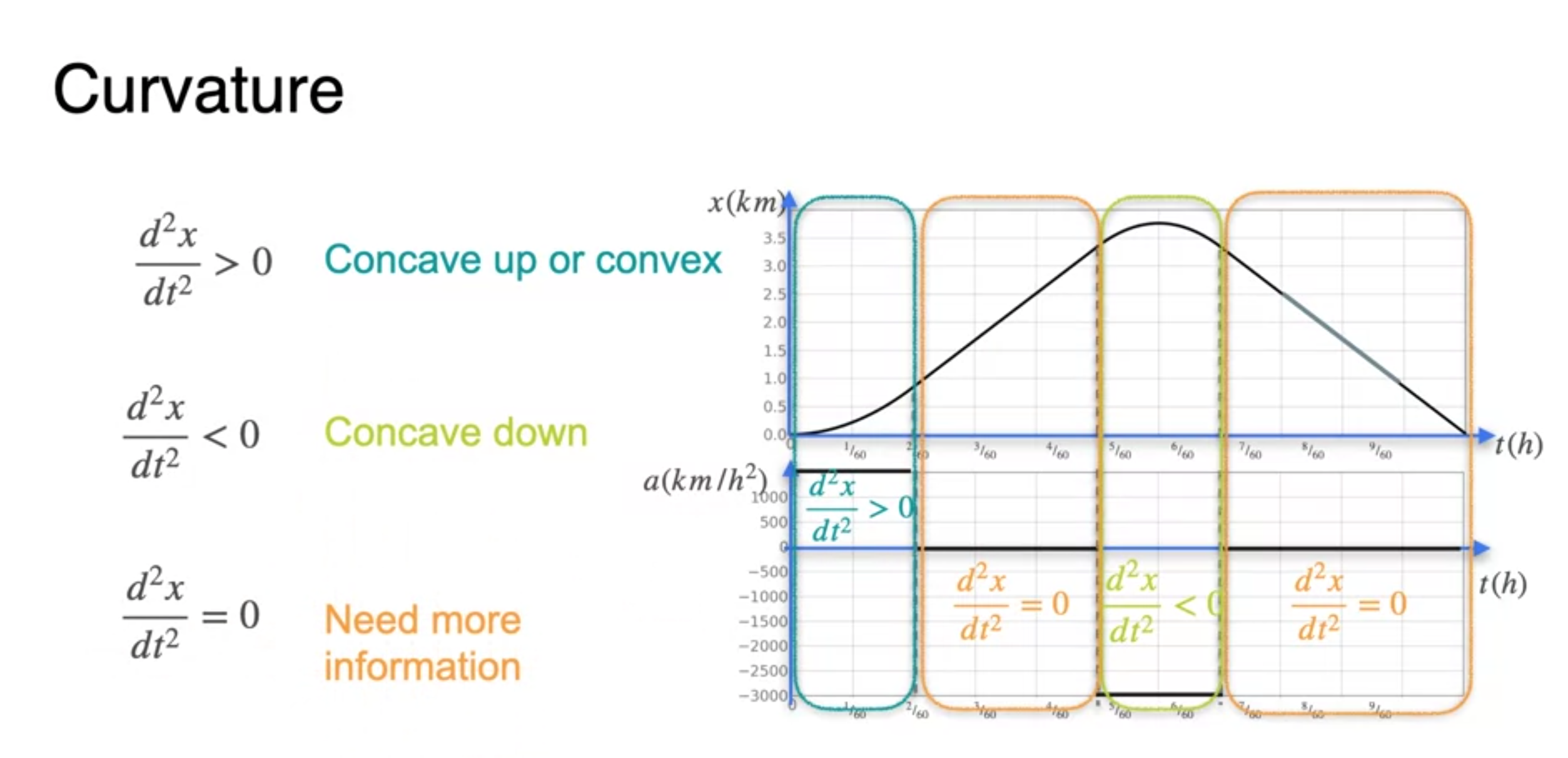
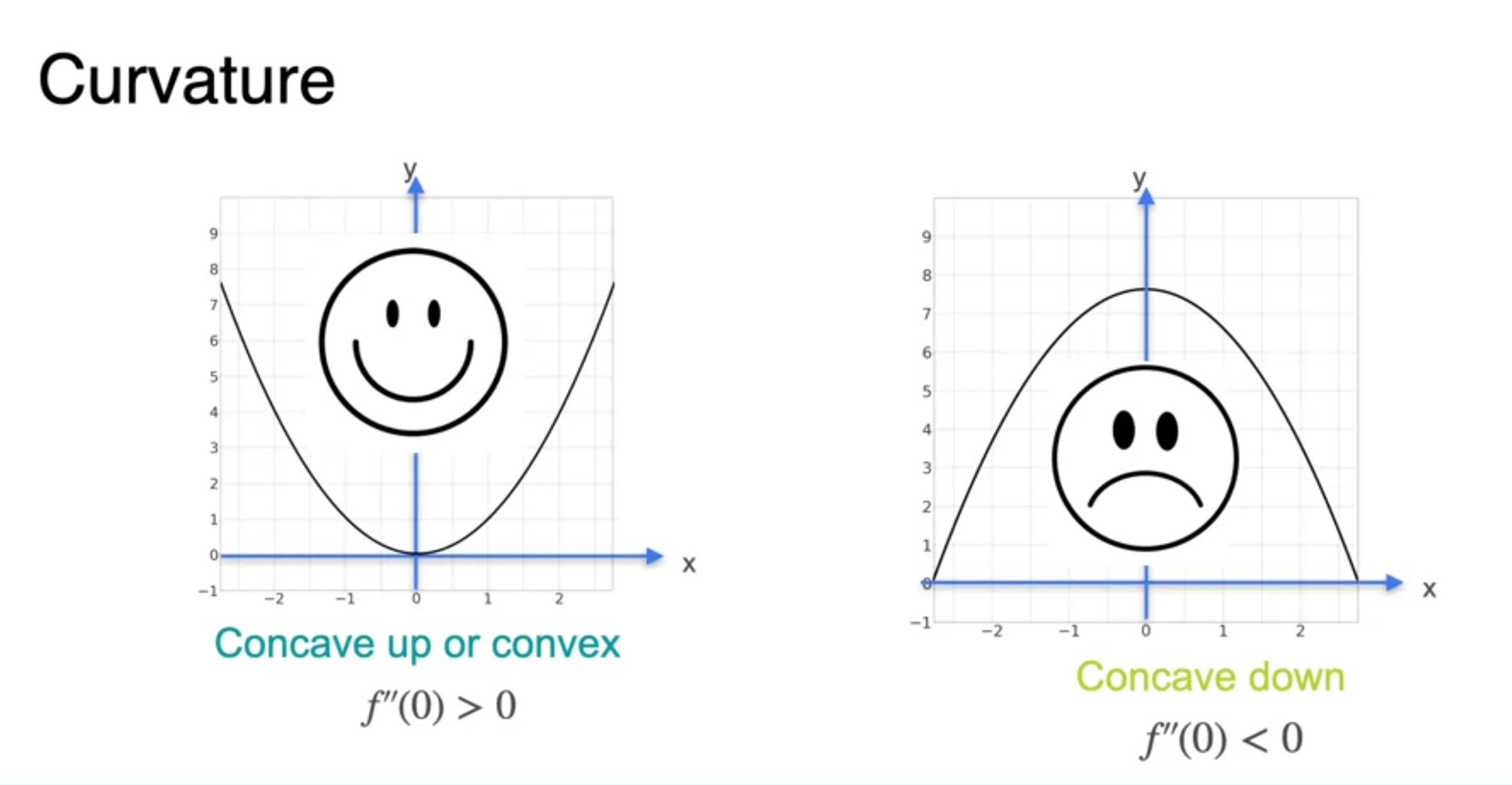
- Curvature(곡률)에 대한 이해
The Hessian

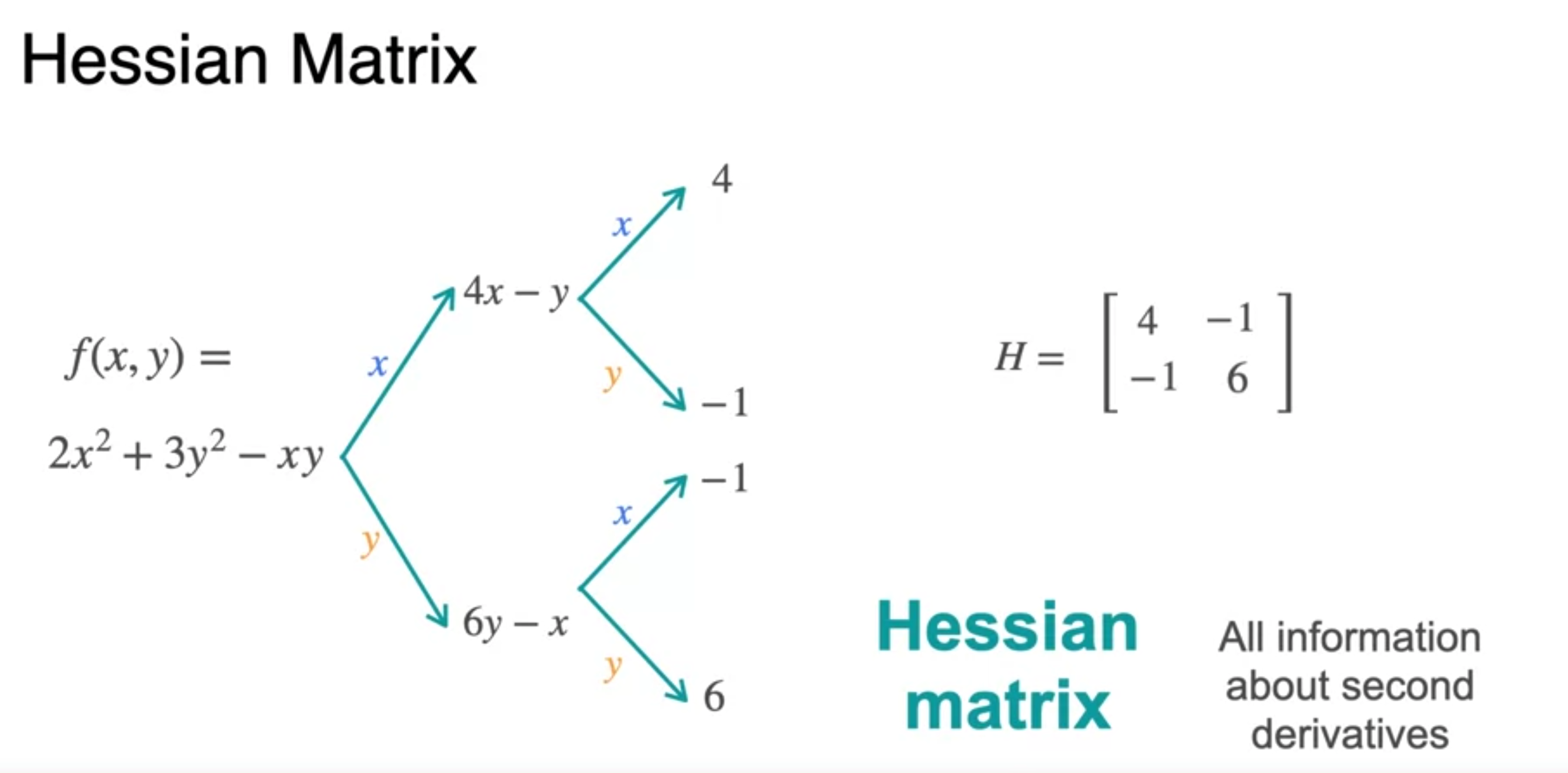
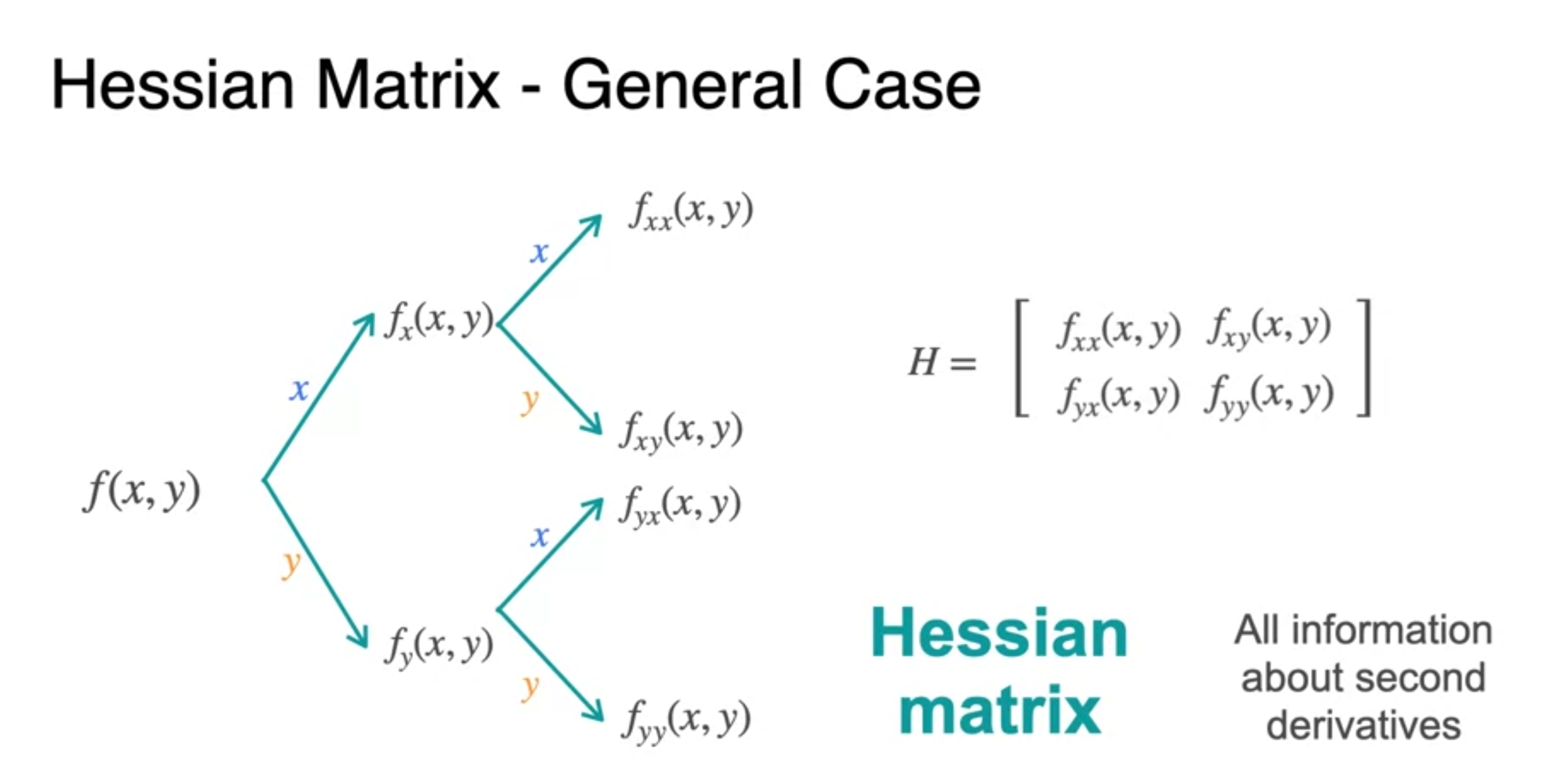
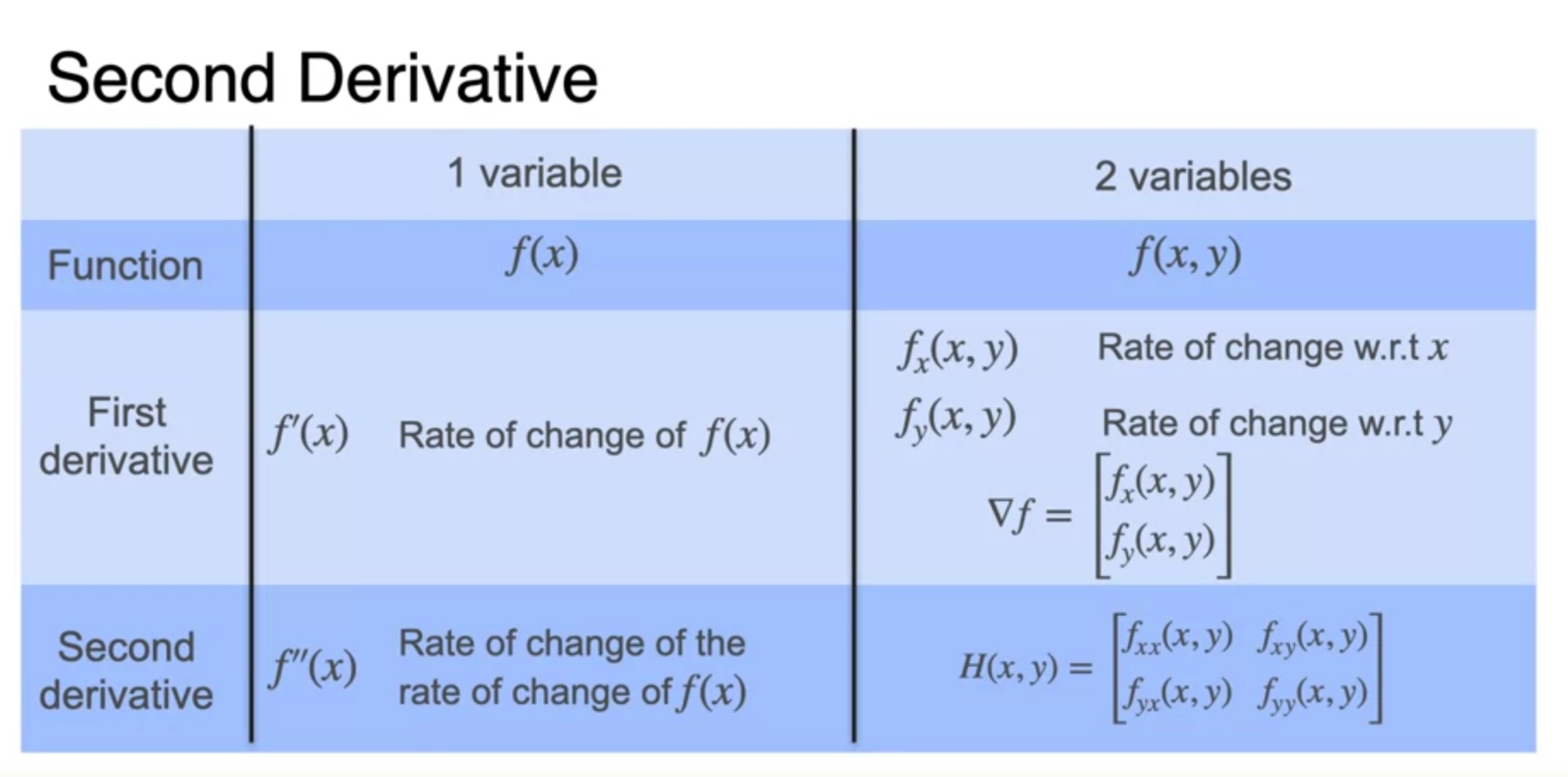
- Hessian은 symmetric하다
Hessians and concavity
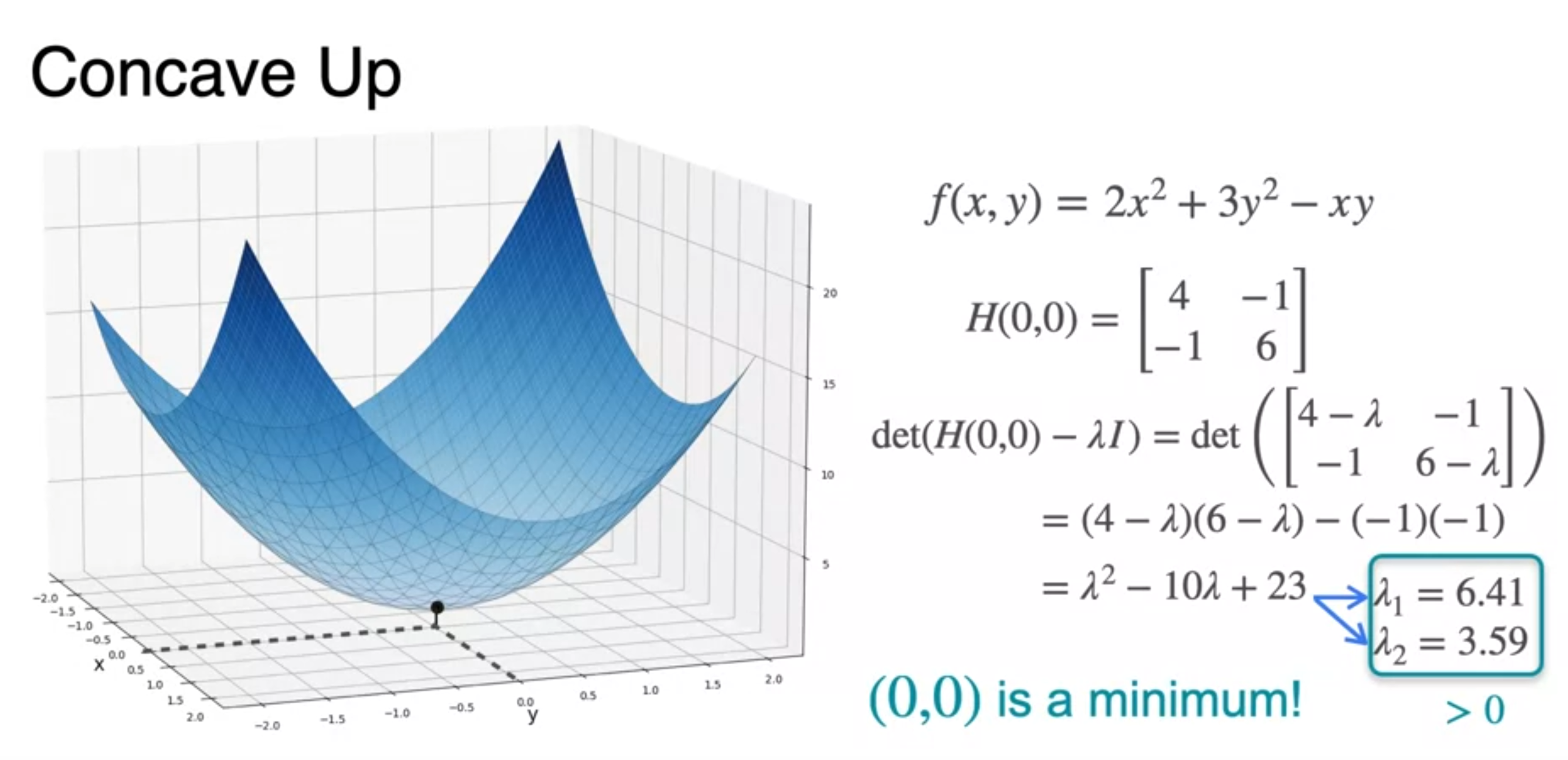
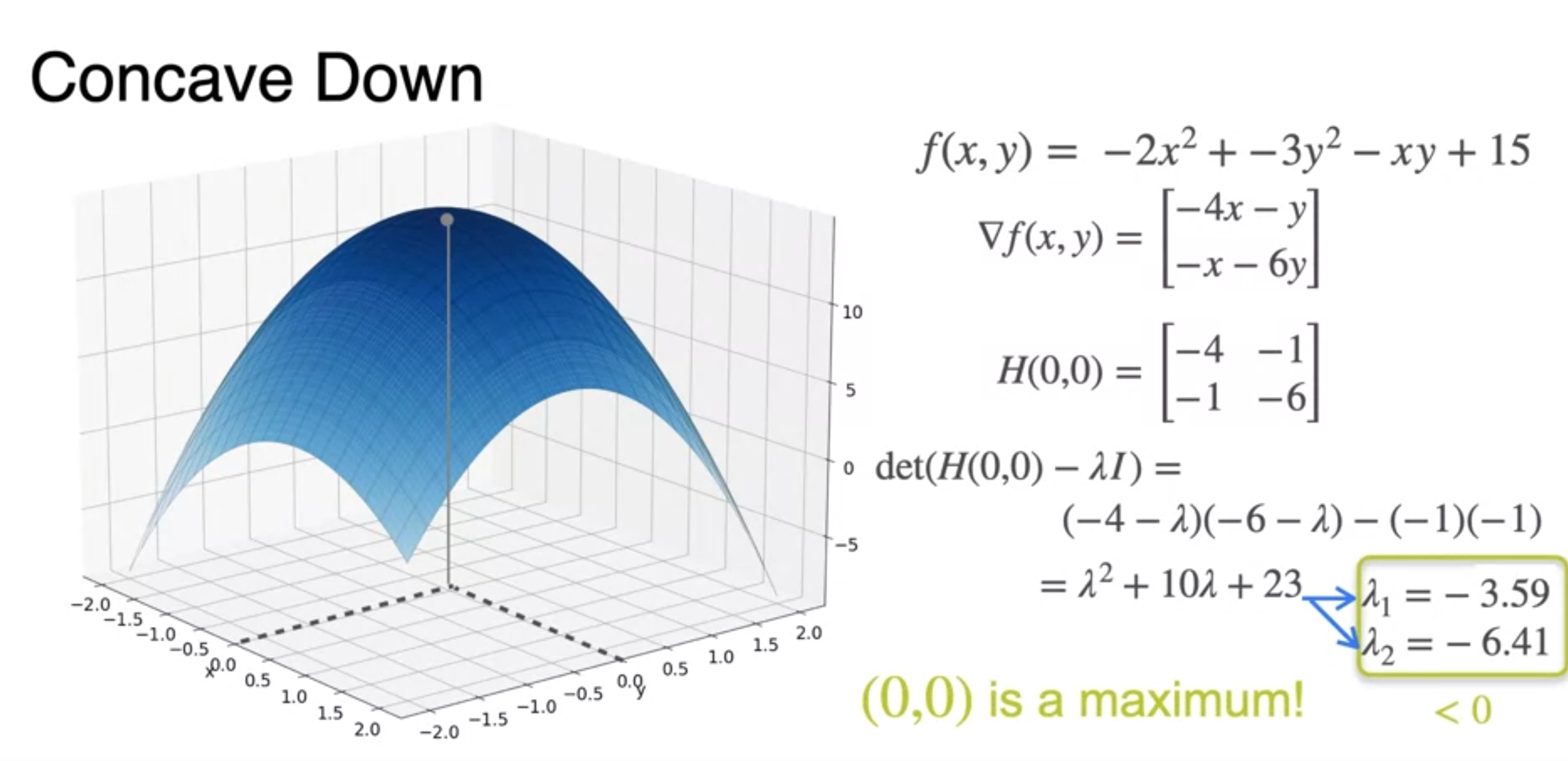
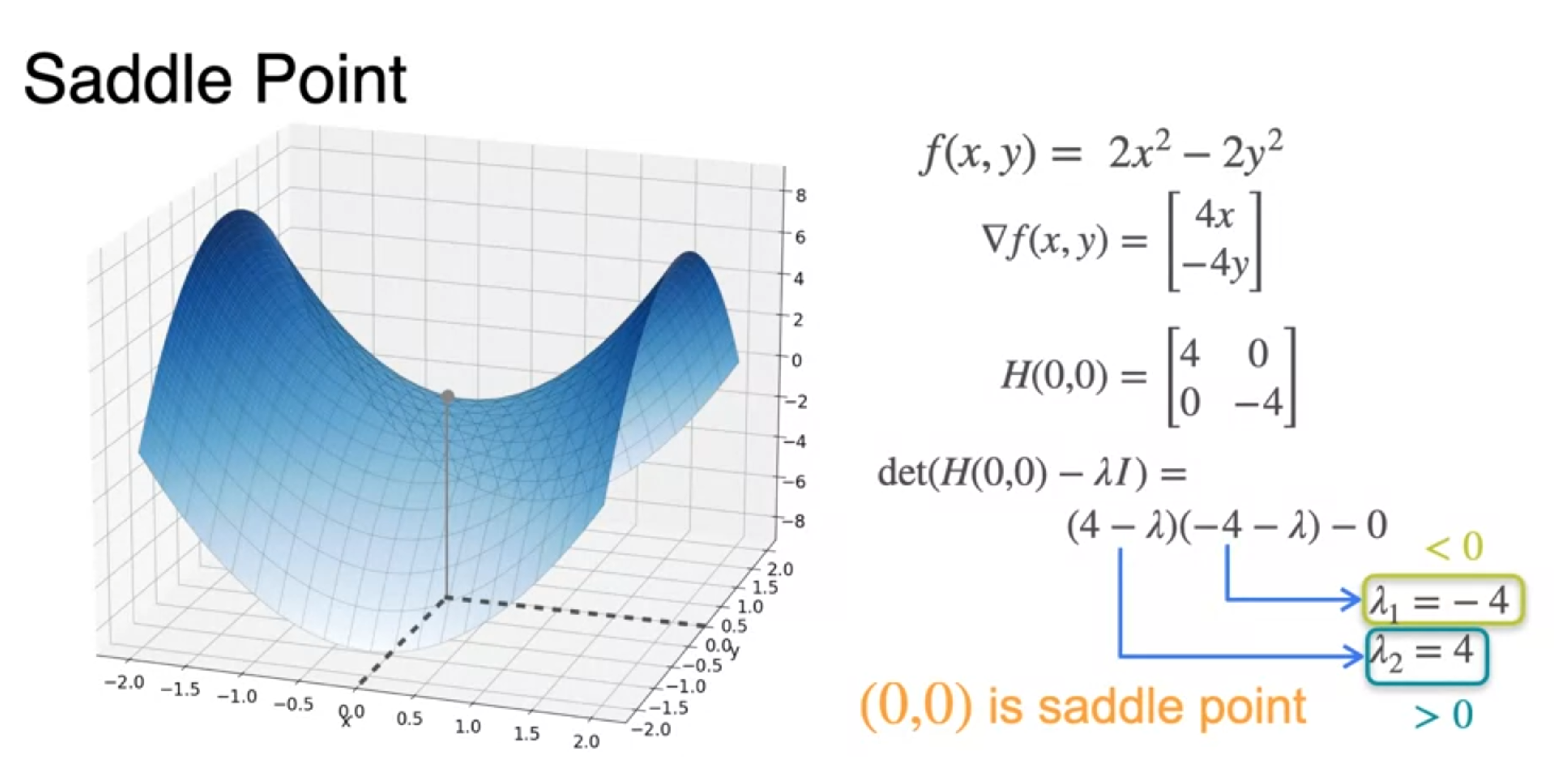
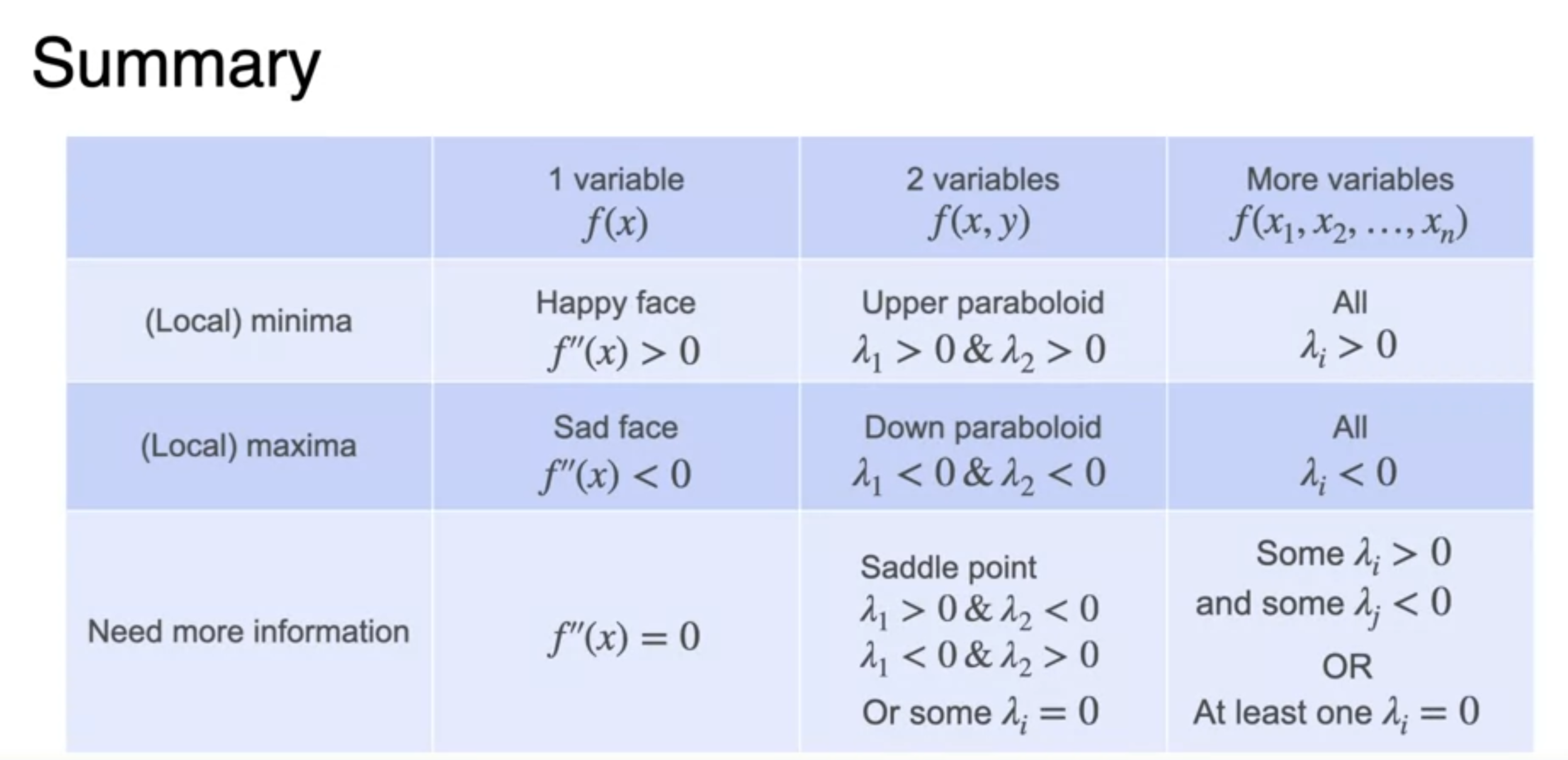
Newton's Method for two variables
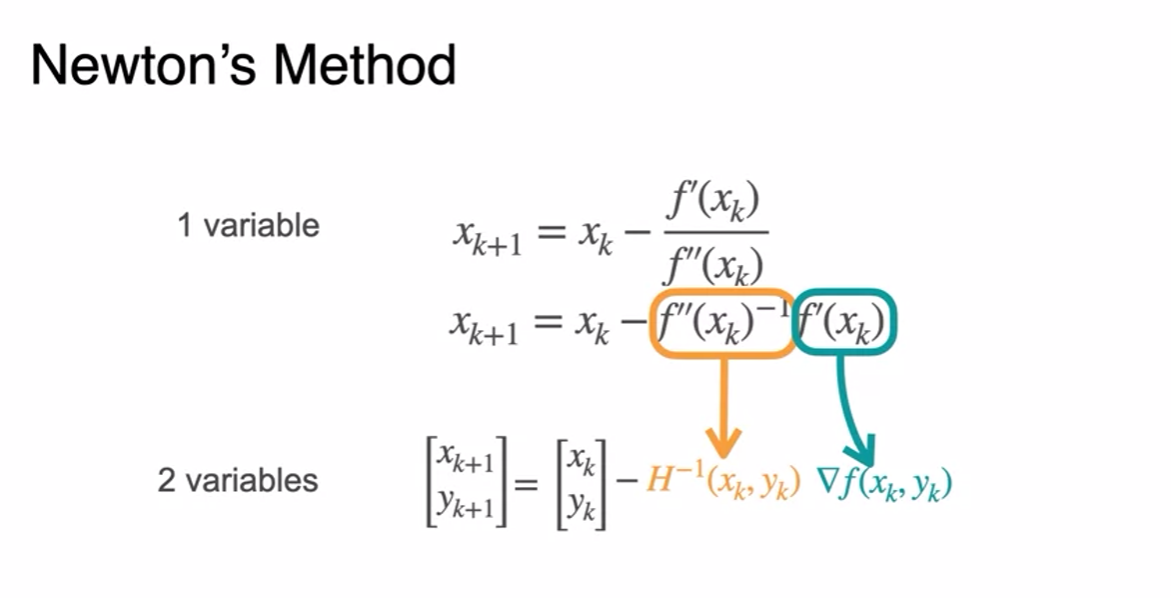
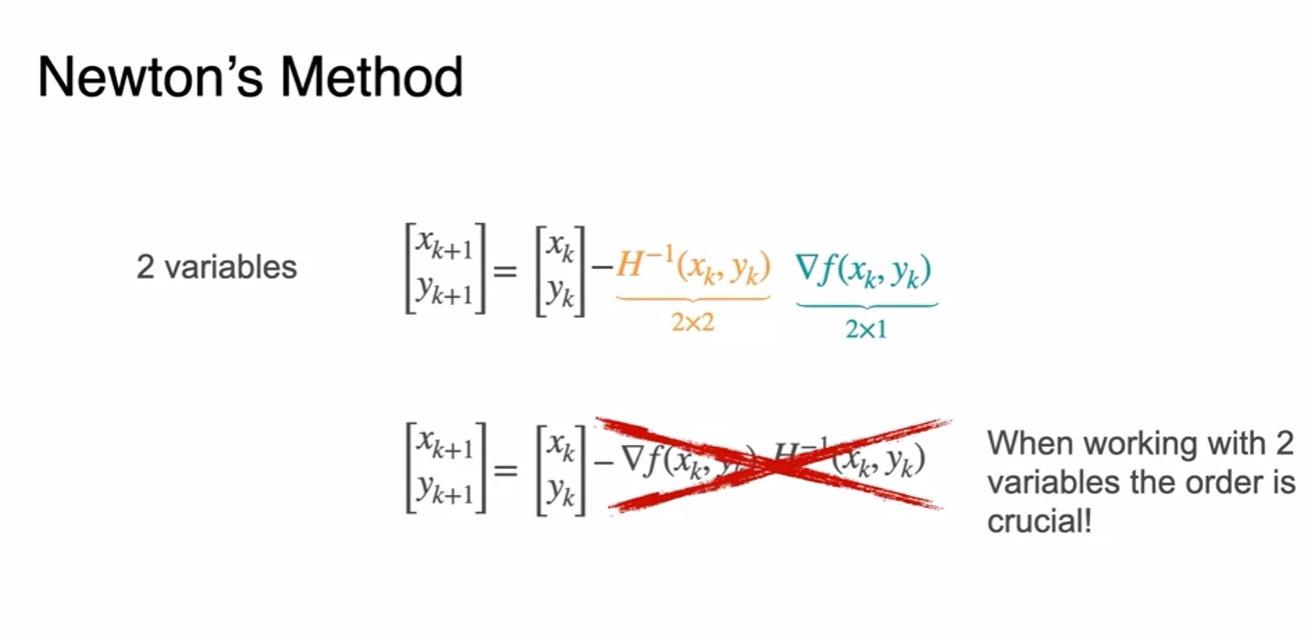
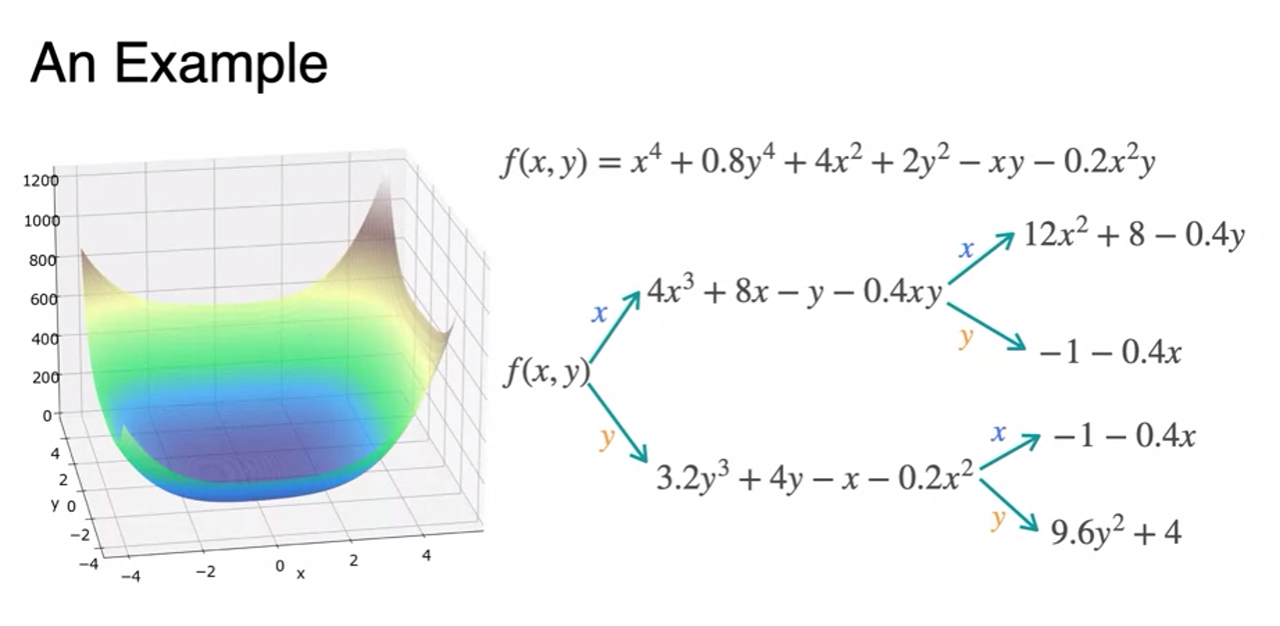
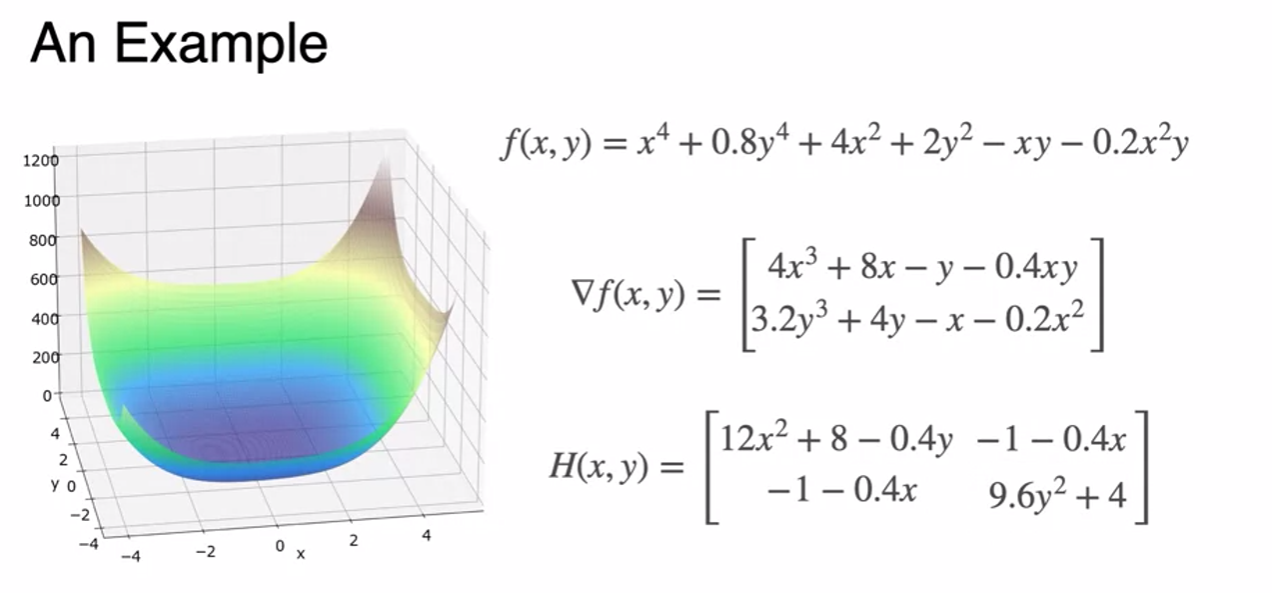
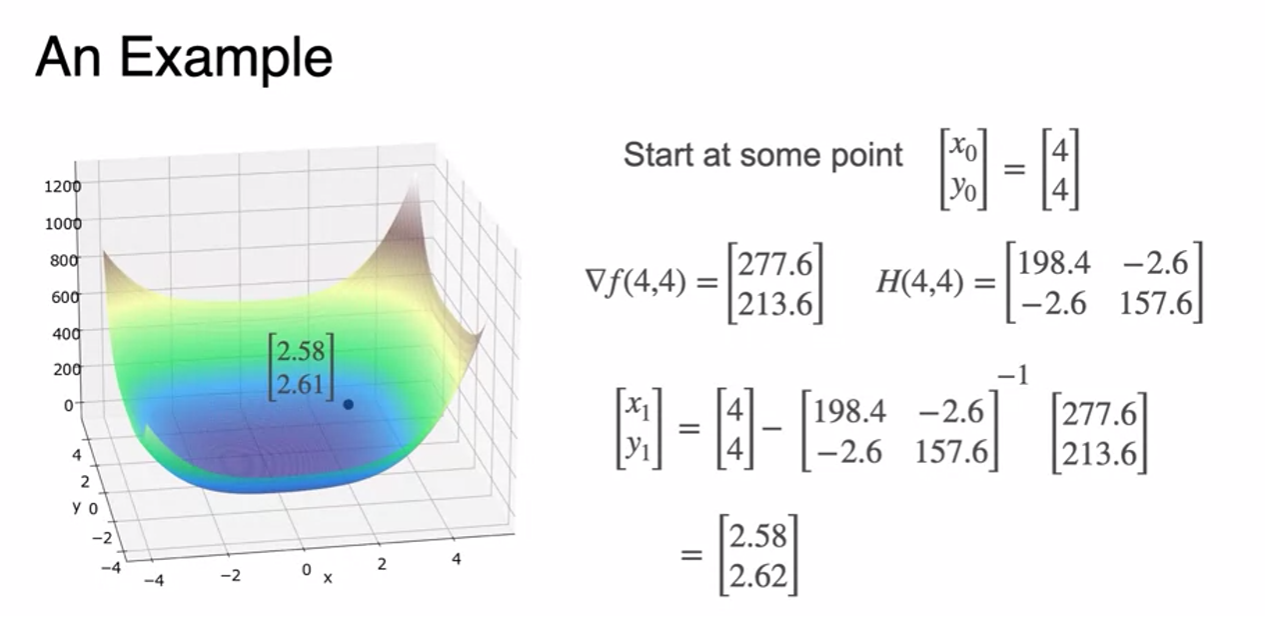
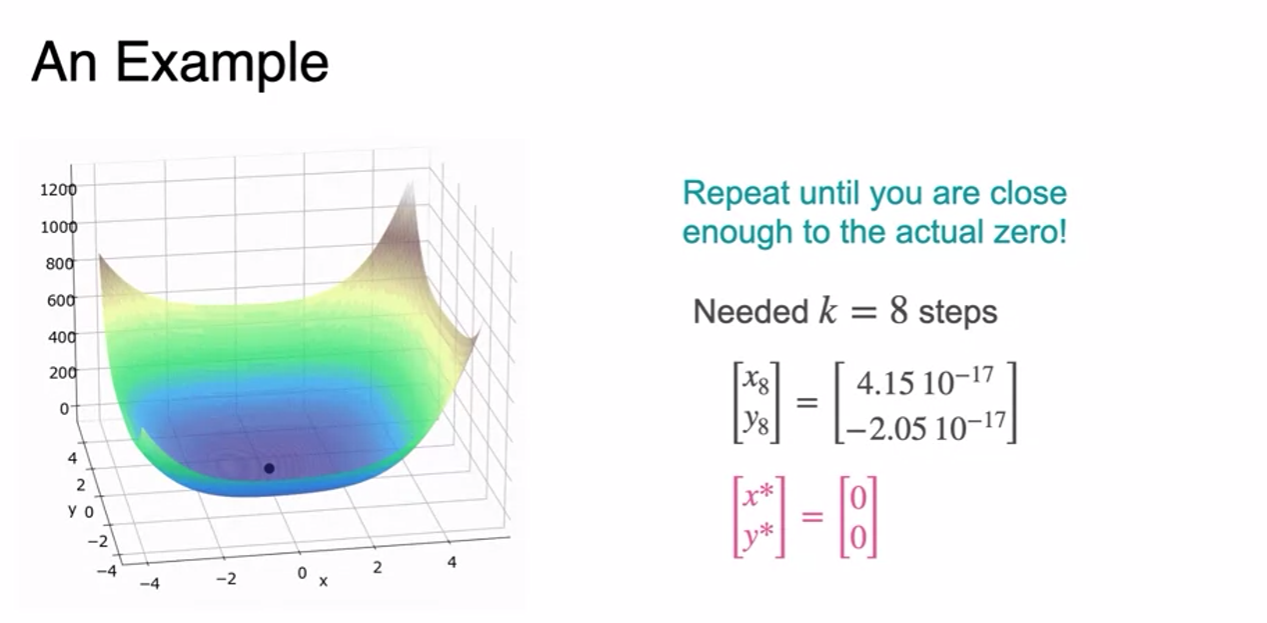
- Only 8 steps to obtain minimum - Fast!
