Natural Language Processing - Week 3
Lecture : Vector Space Models
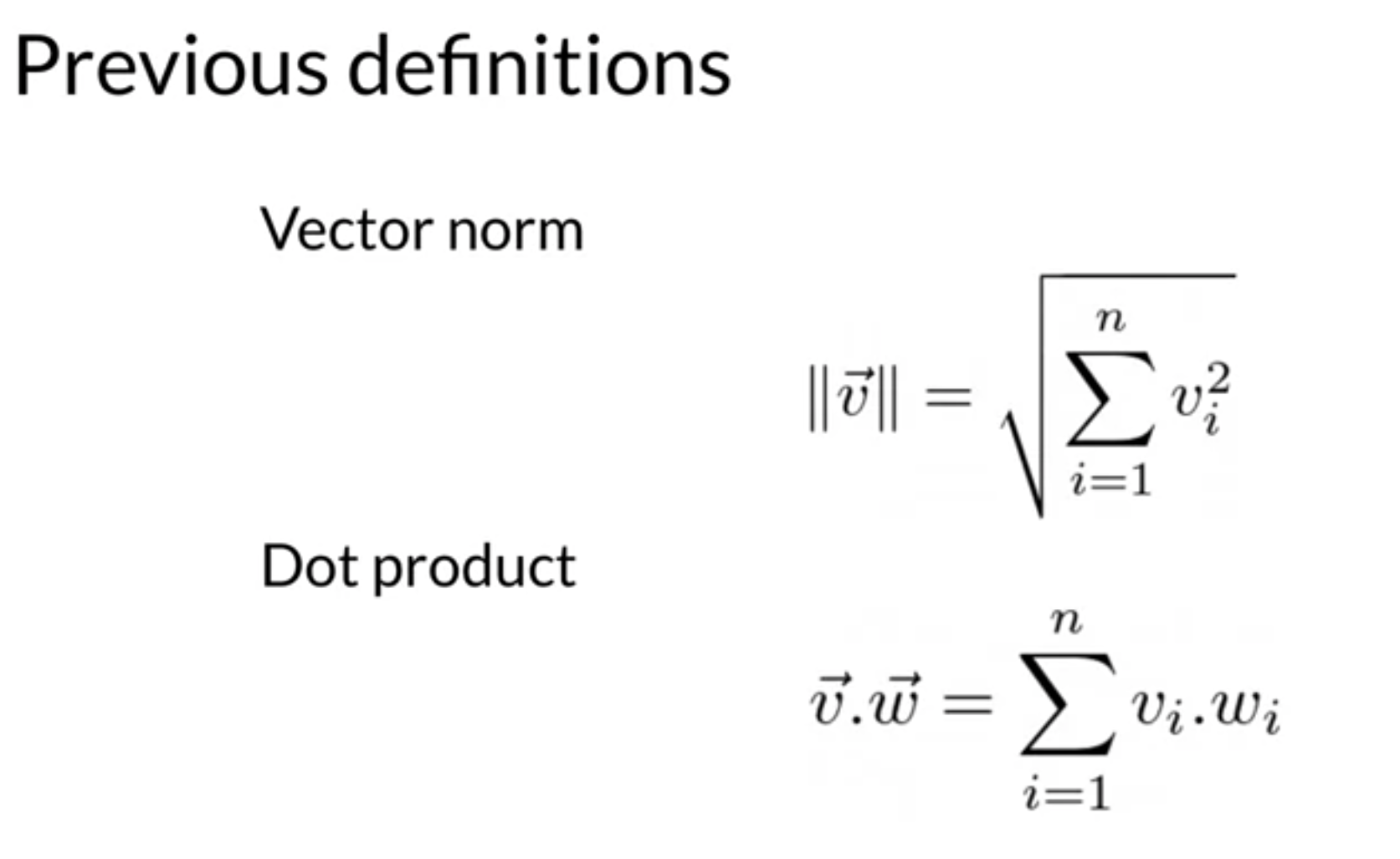
Vector Space Models

Summary
-
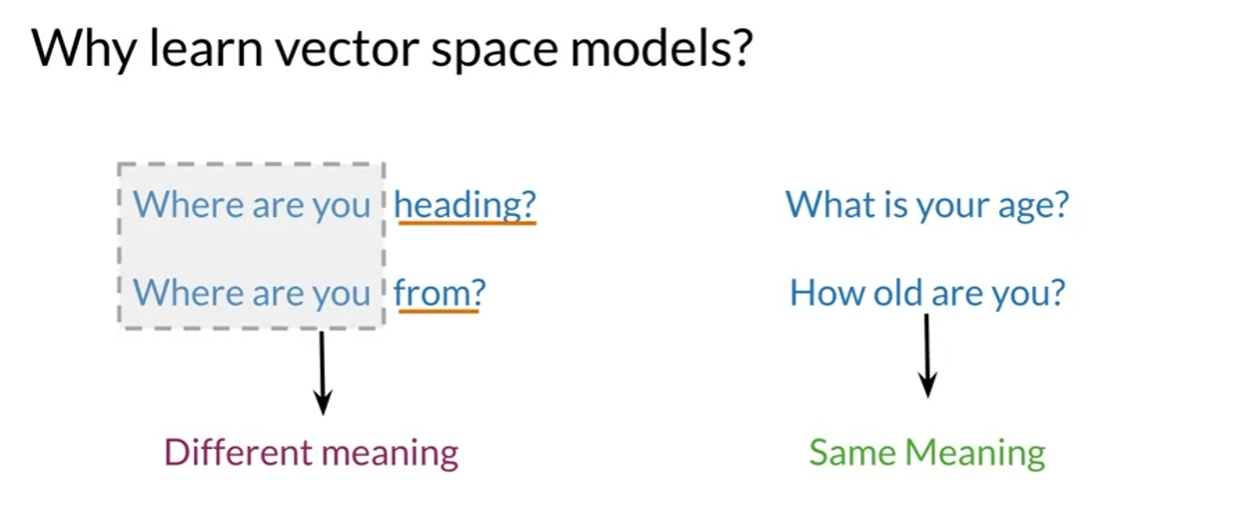
Represent words and documents as vectors
-
Representation that captures relative meaning
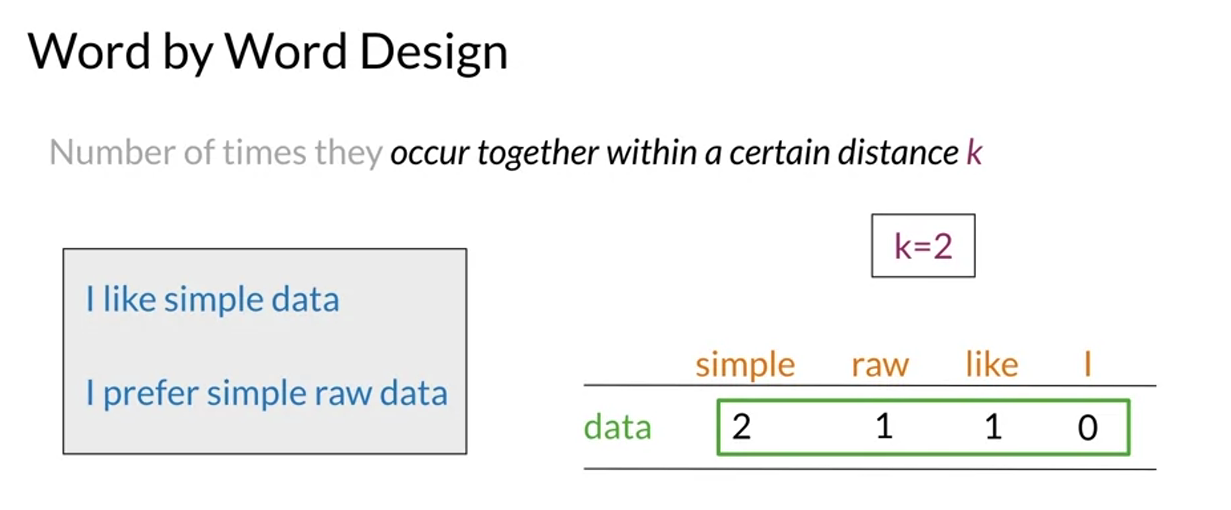
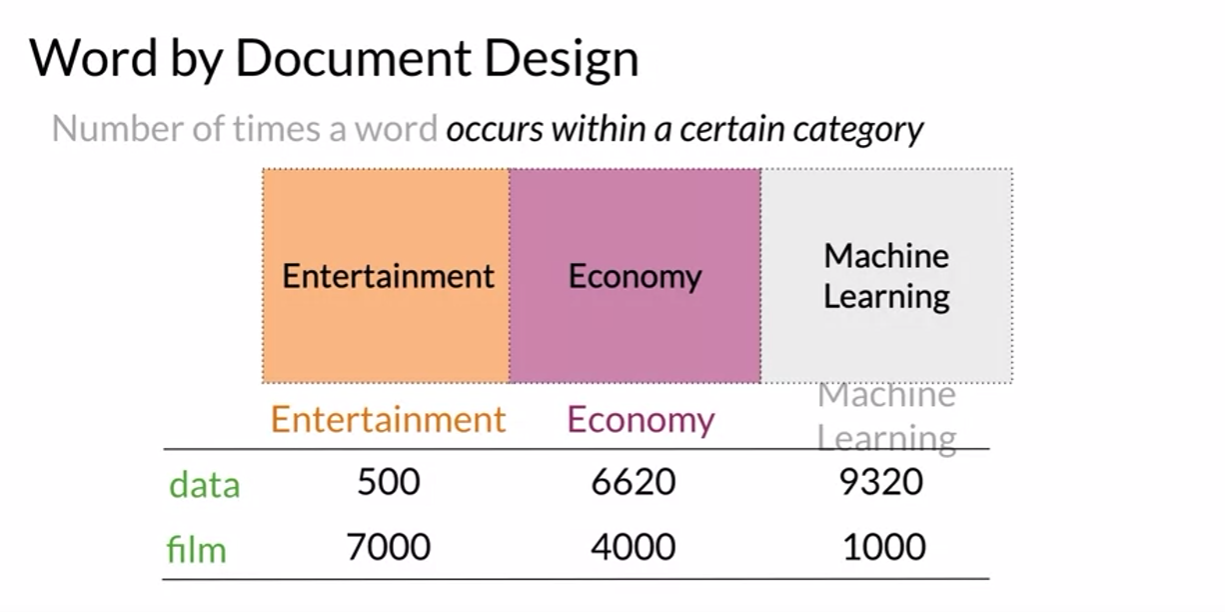
Word by Word and Word by Doc.
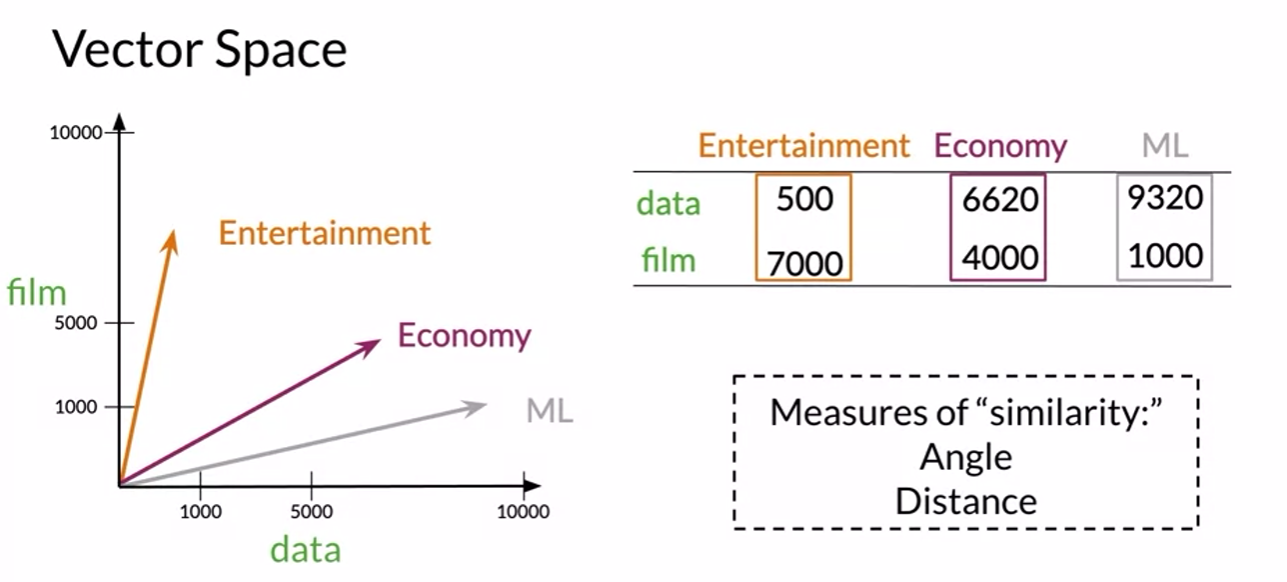
Summary
-
W/W and W/D, counts of occurrence
-
Vector Spaces -> Similarity between words/documents
Gonna learn about Euclidean distance and Cosin similarity
Euclidean Distance
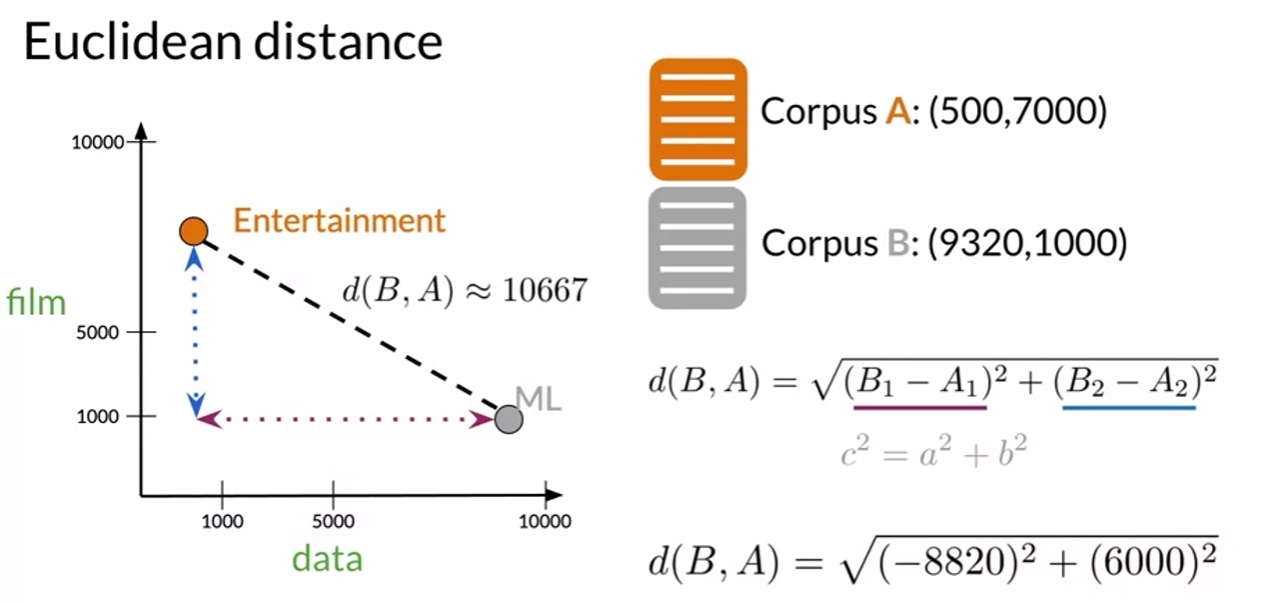
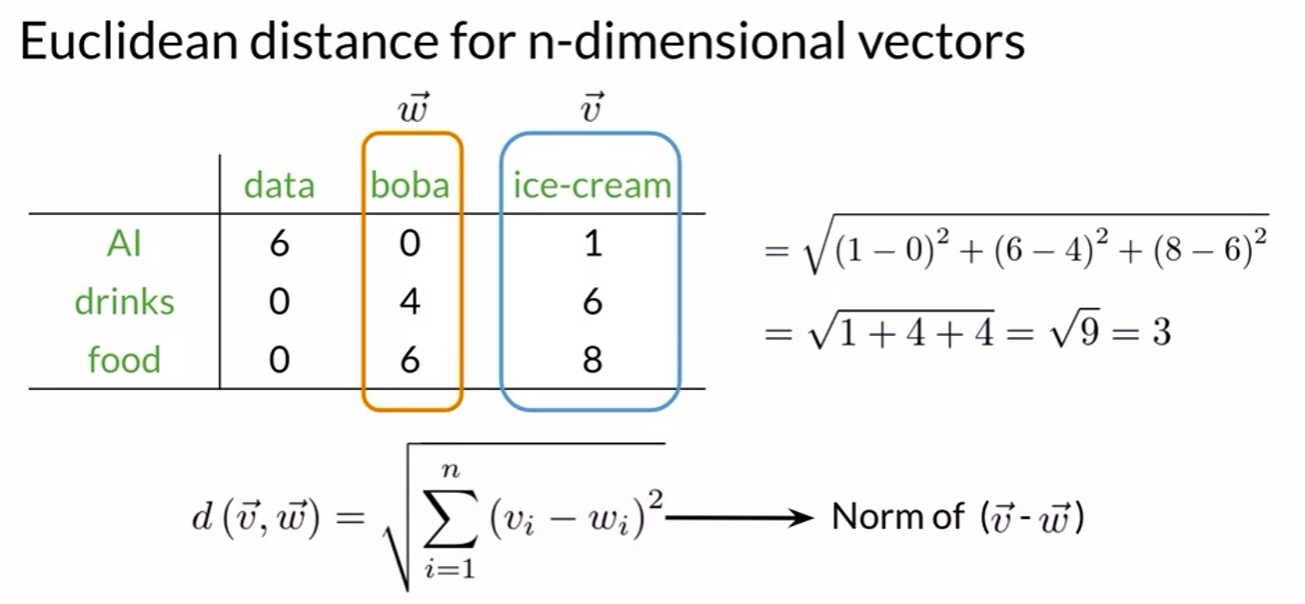

Summary
- Straight line between points
- Norm of the difference between vectors
Cosine Similarity: Intuition
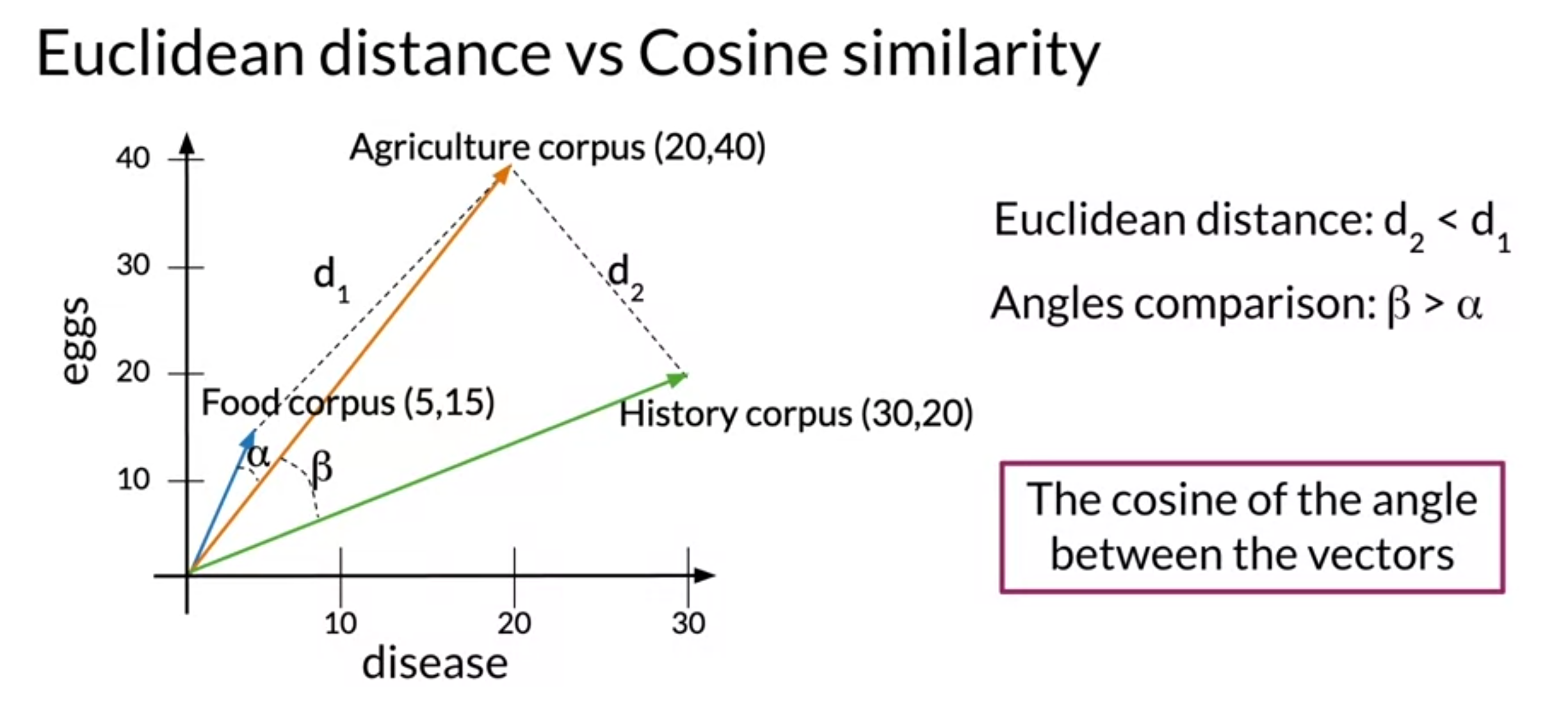
- Cosine similarity might overcome the problem of Euclidean distance
- It isn't biased by the size differences
Summary
- cosine similarity when corpora are different sizes
Cosine Similarity
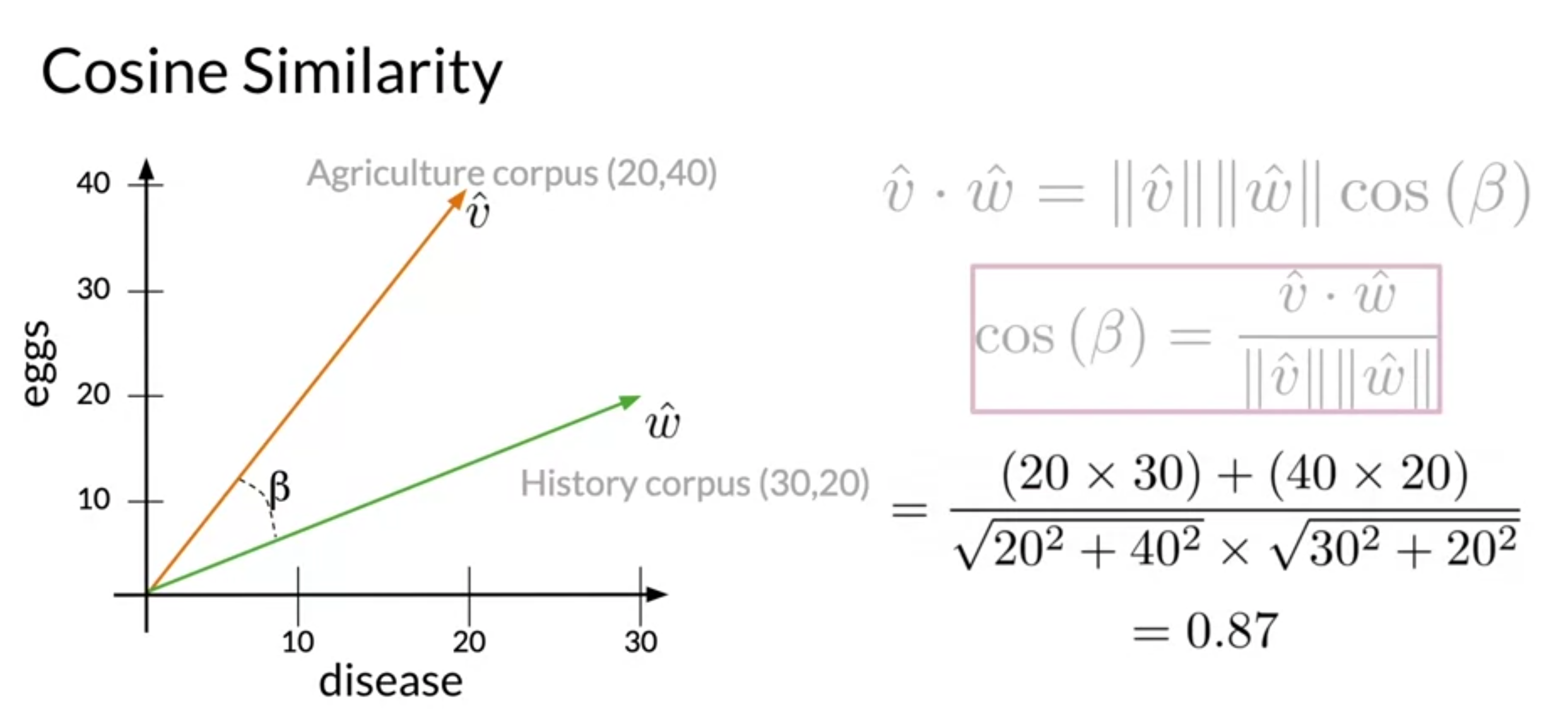
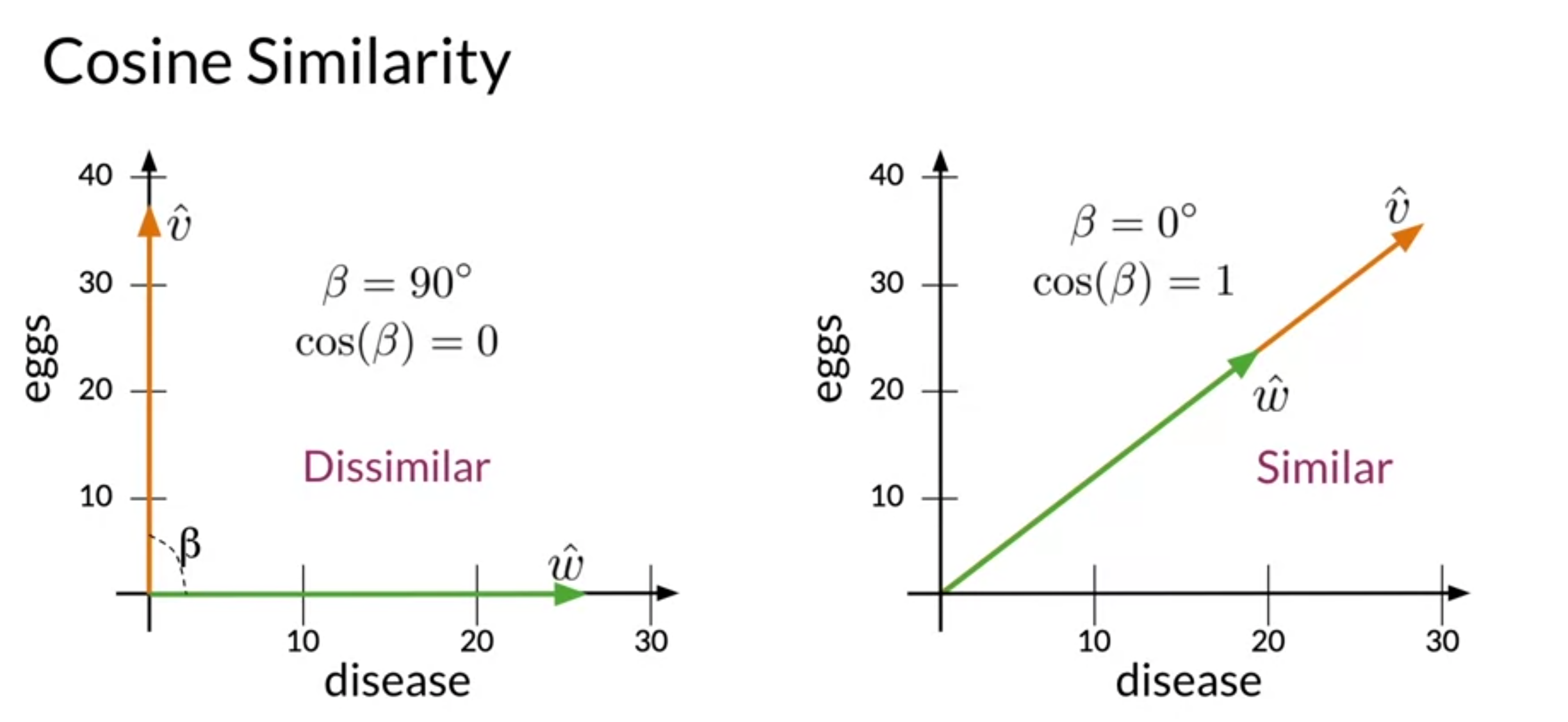
Summary
- Cosine Similarity
- Cosine Similarity gives values between 0 and 1
Manipulating Words in Vector Spaces

Summary
- Use known relationships to make predictions
Visualization and PCA
- use principal component analysis to visualize vector
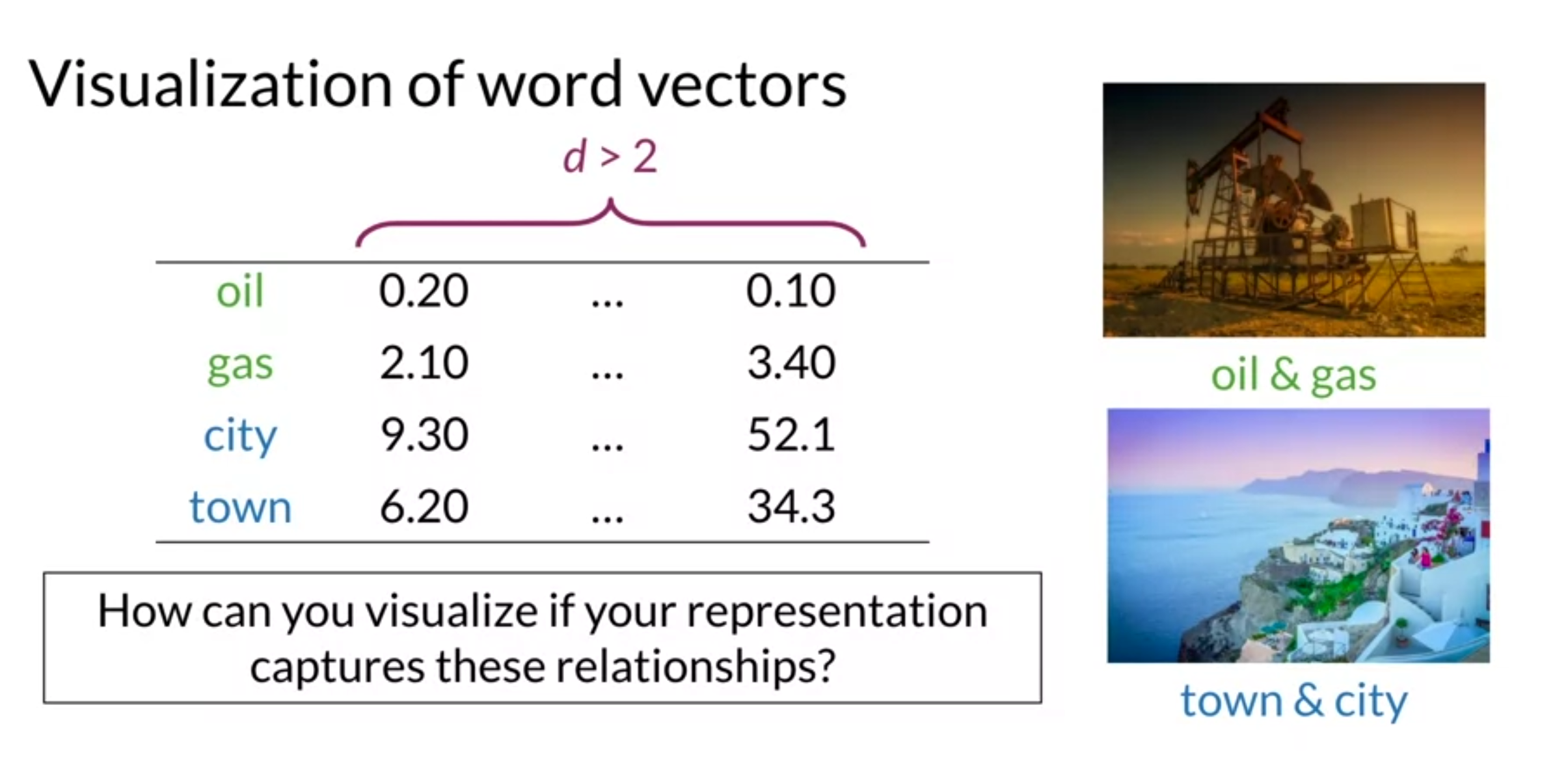
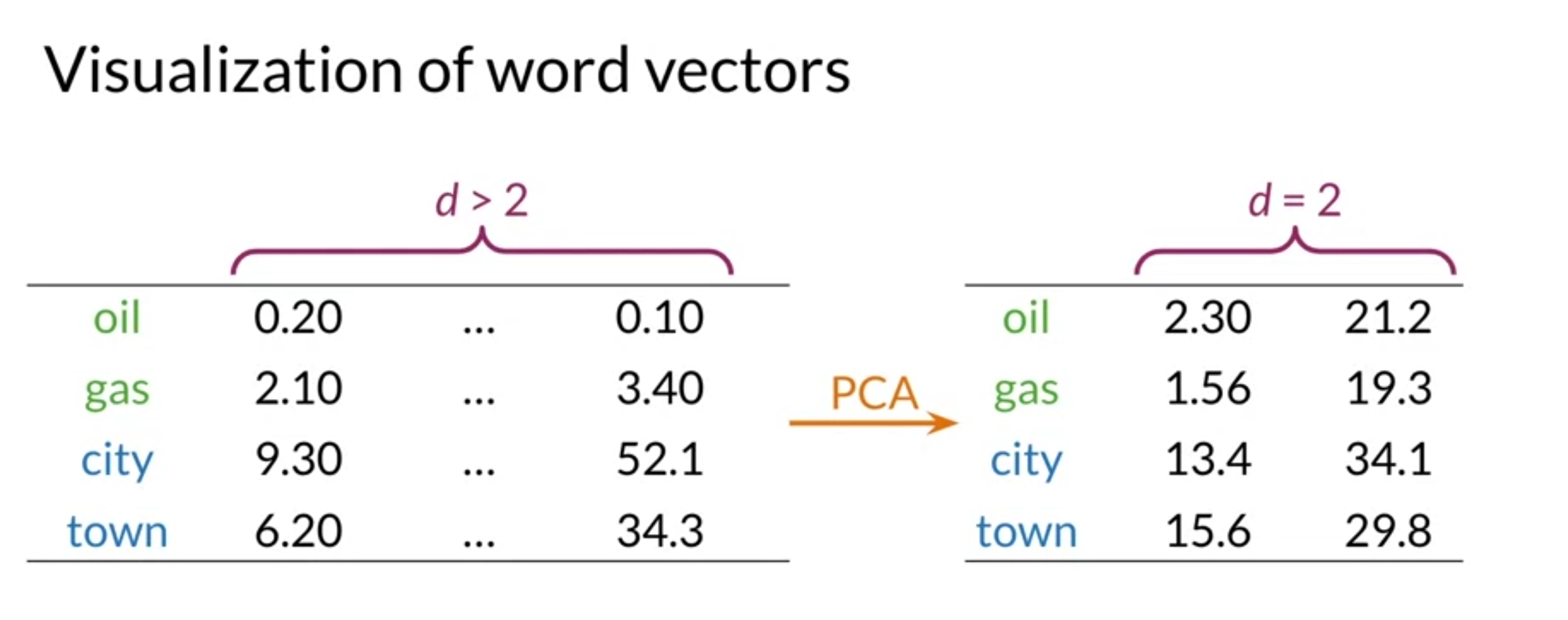
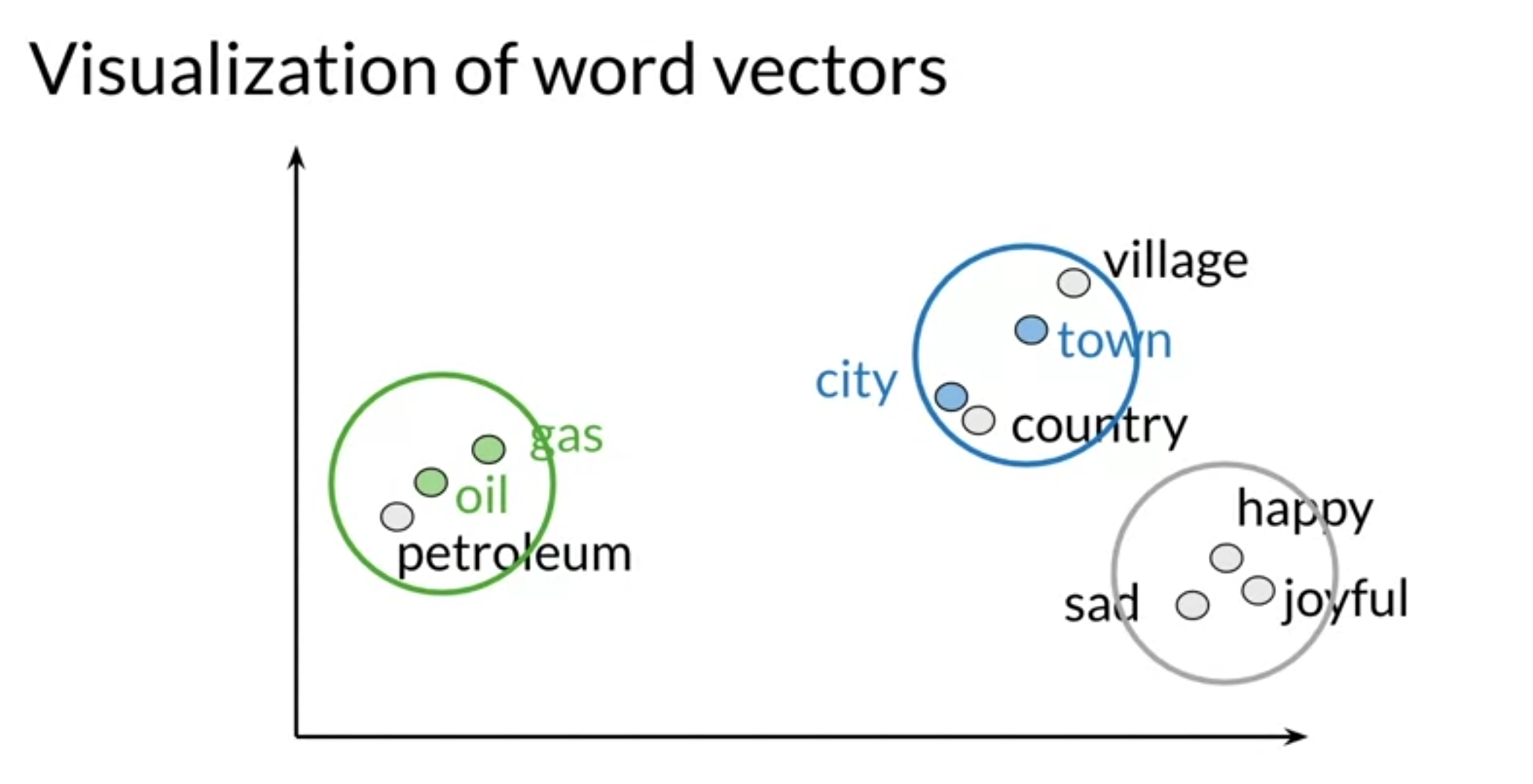
Summary
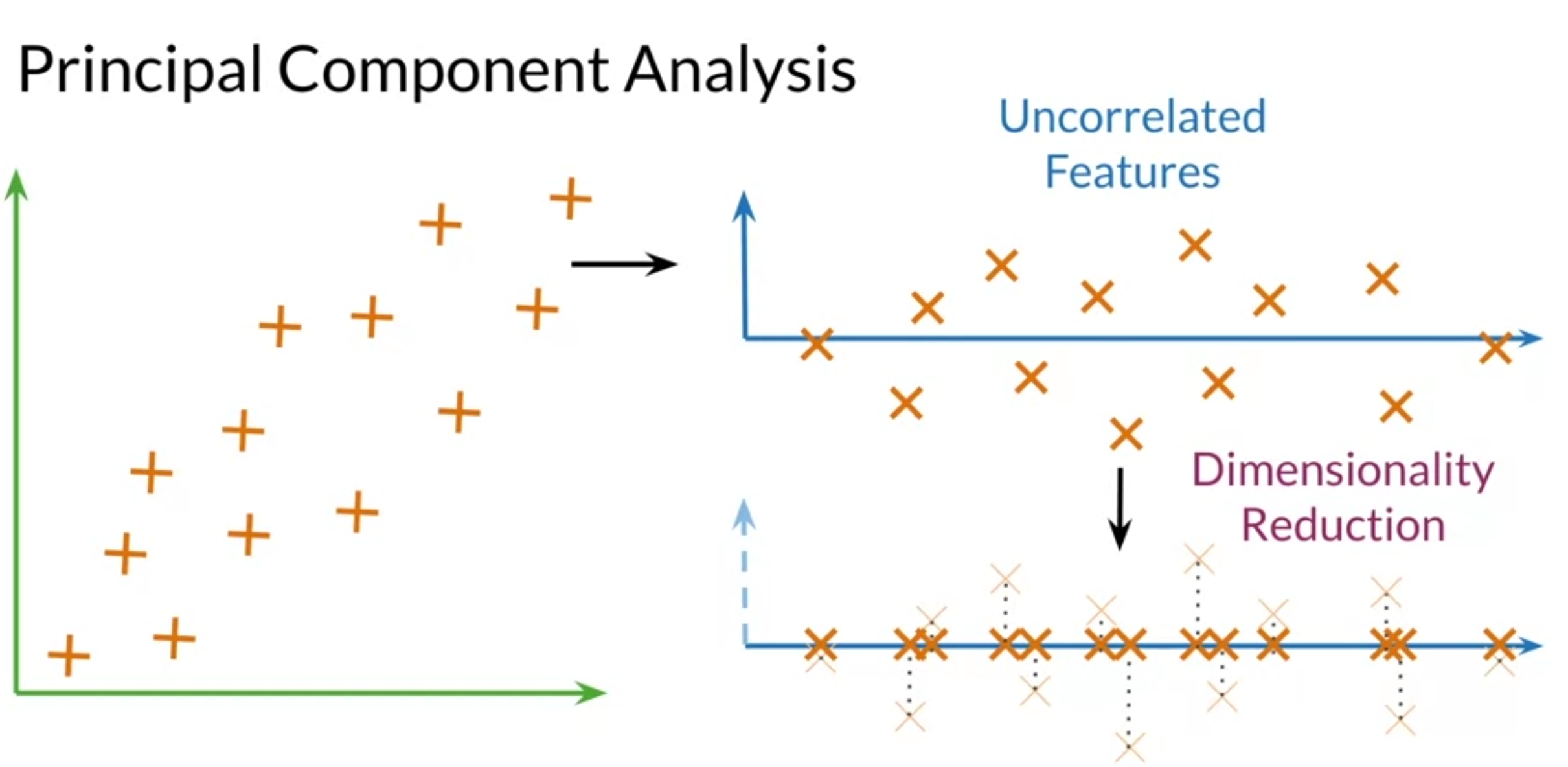
- PCA : algorithm used for dimensionality reduction that can find uncorrelated features for data
PCA Algorithm

- Eigenvectors give directions of uncorrelated features and t he Eigenvalues are the variants of your data sets in each of those new features.
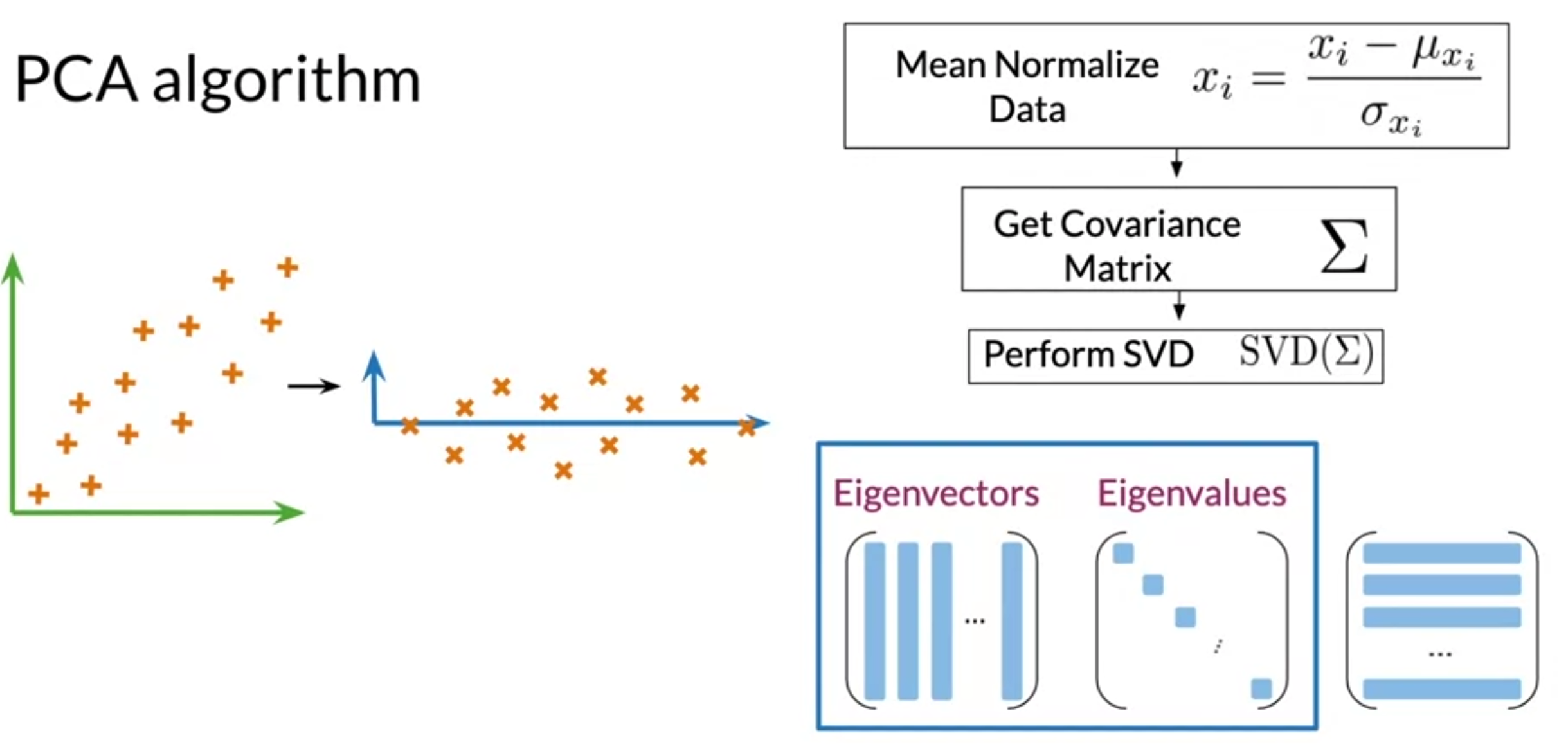
- get a set of uncorrelated features
- mean normalize data
- get covariance matrix
- perform singular value decomposition
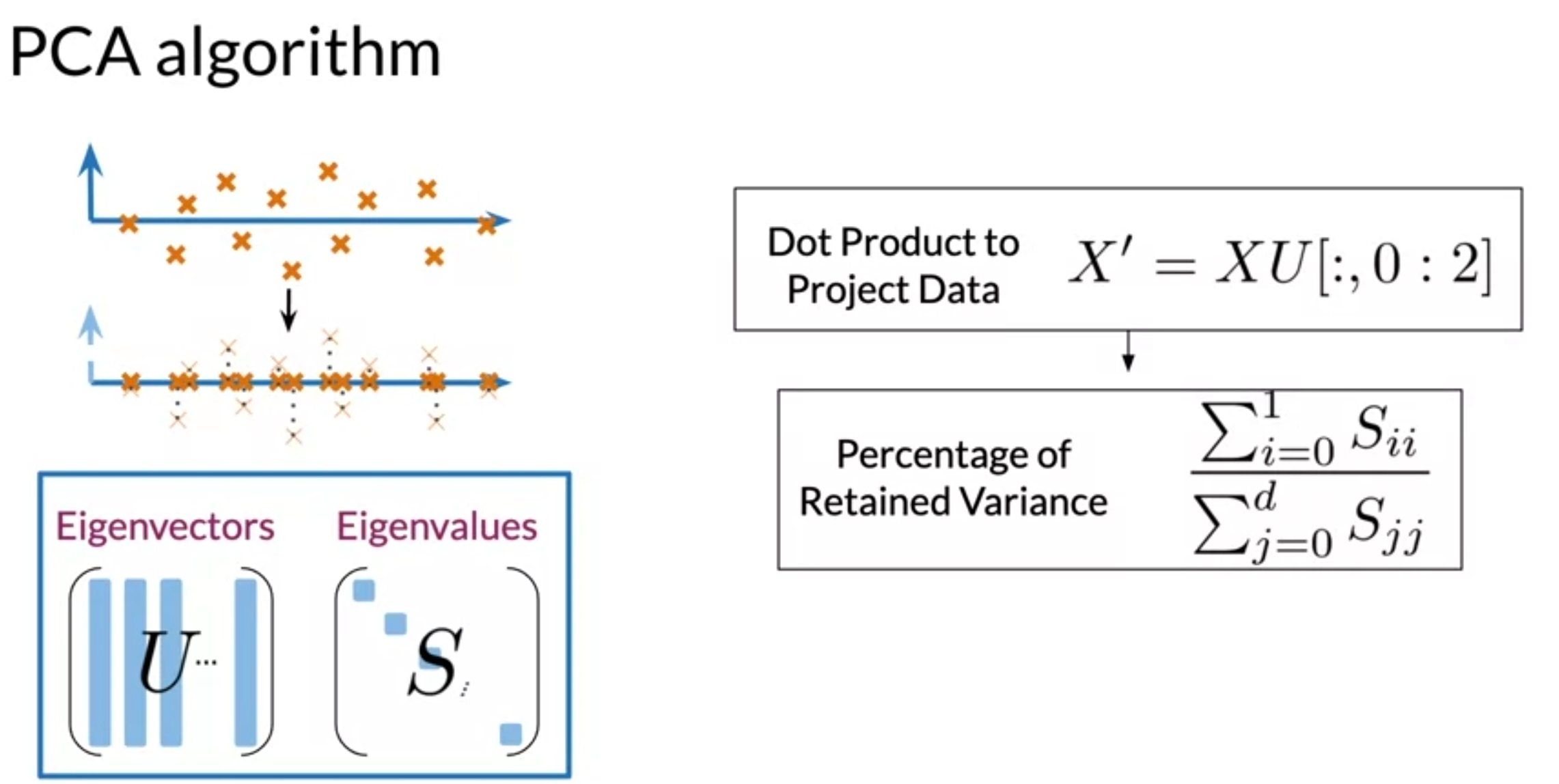
- project data to a new sets of features
- perform the dot products between the matrixd containing word embeddings and the first n columns of the U matrix
Summary
-
Eigenvectors give the direction of uncorrelated features
-
Eigenvalues are the variance of the new features
-
Dot product gives the projection on uncorrelated features
Background
-
Cov(x,y) =
-
대각선 기준으로 sematric
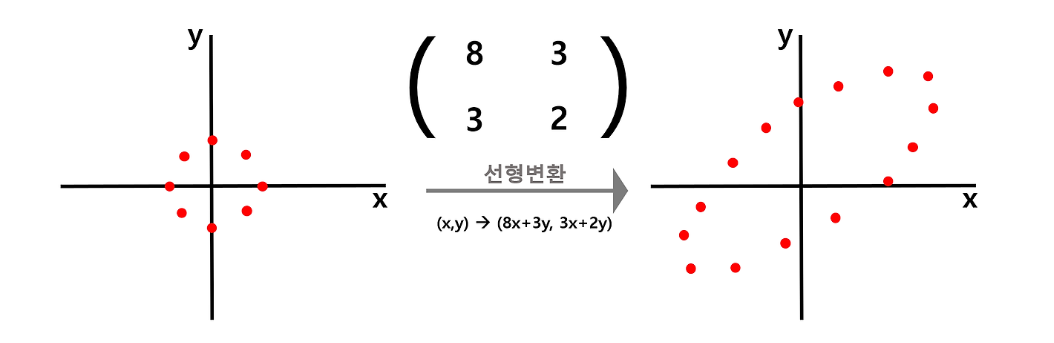
-
shearing : covariance matrix를 normal distributed data에 곱하는 것을 선형변환 관점에서 보기도 한다
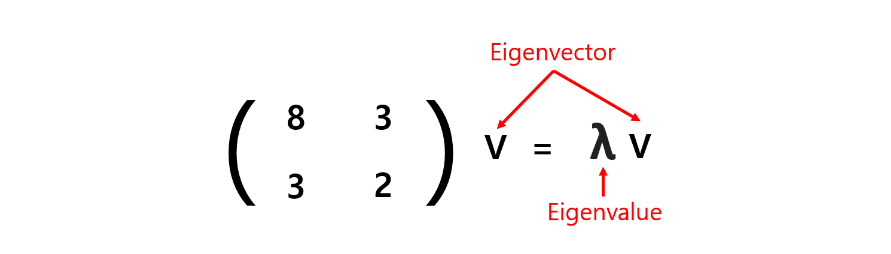
- Linear transform 후에 방향이 같은 vector가 Eigenvector, 길이 변화 비율이 Eigenvalue
- why PCA? : 다중 공신성(multi colinearity)을 해결
- 데이터의 여러 attributes 중 몇 개가 높은 상관 관계를 가졌을때 그대로 Linear Regression을 하면 그 결과값인 종속변수에 대한 독립변수의 영향력을 신뢰할 수 없어진다.
