Messages
- Chat models use
messages, which capture different roles within a conversation
- LangChain supports various message types, including
HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage, and ToolMessage.
- These represent a message from the user, from chat model to instruct behavior, and from a tool call.
- Each message can be supplied with a few things;
content : content of the message.name : optionally, who is createing the message.repsponse_metadata: optionally, a dict of metadata that is often specific to each model provider.
from pprint import pprint
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage, SystemMessage
messages = [AIMessage(content=f"SO you said you werew researching ocean mammals?", name="Model")]
messages.extend([HumanMessage(content=f"Yes, that's right.", name="Lance")])
messages.extend([AIMessage(content=f"Great, what would you like to learn about.", name="Model")])
messages.extend([HumanMessage(content=f"I want to learn about the best place to see Orcas in the US.", name="Lance")])
for m in messages:
m.pretty_print()
- You can directly pass the messages to a chat model.
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4o')
result = llm.invoke(messages)
print(type(result), result)
- Tools are needed whenever you want a model to control parts of your code or call out to external APIs.
- Many LLM providers support tool calling.
- The tool calling interface in LangChain is simple.
- You can pass any Python function into
ChatModel.bind_tools()

def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a * b
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([multiply])
tool_call = llm_with_tools.invoke([HumanMessage(content=f"What is 2 multiplied by 3", name="Lance")])
print(tool_call)
print(tool_call.additional_kwargs['tool_calls'])
[{'name': 'multiply',
'args': {'a': 2, 'b': 3},
'id': 'call_lBBBNo5oYpHGRqwxNaNRbsiT',
'type': 'tool_call'}]
Using messages as state
- With these foundations in place, we can dnow use
messages in our graph state.
- Let's define our state
MessageState
- It's defined as a
TypedDict with a single key: messages.
messages is simply a list of type AnyMessage, meaning it's a list of messages.
from typing import TypedDict
from langchain_core.messages import AnyMessage
class MessagesState(TypedDict):
messages: list[AnyMessage]
Reducers
- As our graph runs, we want to append messages to the
messages state key.
- But, if no reducer function is explicitly specified, each node will override the prior state value.
- Reducer functions allow us to specify how state updates are performed.
- Since we want to append messages, we can use a pre-built
add_messages reducer!
- This ensures that state updates you send to the graph are appended to the existing list of messages.
- We annotate (via
Annotated) our key with a reducer function as metadata.
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_core.messages import AnyMessage
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class MessagesState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list[AnyMessage], add_messages]
- Since having a list of messages in the state is so common, LangGraph has a pre-built
MessagesState.
MessagesState is defined:
- with a pre-built single
messages key.
- which is a list of
AnyMessage objects and uses the add_messages reducer.
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
class State(MessagesState):
pass
- The
MessagesState and State both work equivalently.
- To go a bit deeper, we can see how the
add_messages reducer works in isolation.
initial_messages = [AIMessage(content="Hello! How can I assist you?", name="Model"),
HumanMessage(content="I'm looking for information on marine biology.", name="Lance")]
new_message = AIMessage(content="Sure, I can help with that. What specifically are you interested in?", name="Model")
add_messages(initial_message, new_message)
[AIMessage(content='Hello! How can I assist you?', name='Model', id='cd566566-0f42-46a4-b374-fe4d4770ffa7'),
HumanMessage(content="I'm looking for information on marine biology.", name='Lance', id='9b6c4ddb-9de3-4089-8d22-077f53e7e915'),
AIMessage(content='Sure, I can help with that. What specifically are you interested in?', name='Model', id='74a549aa-8b8b-48d4-bdf1-12e98404e44e')]
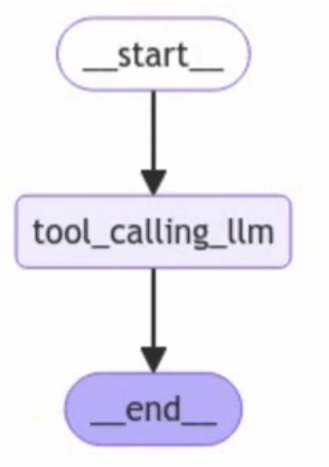
MessagesState with a Graph
from IPython.display import Image, display
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
class MessagesState(MessagesState):
pass
def tool_calling_llm(state: MessagesState):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node("tool_calling_llm", tool_calling_llm)
builder.add_edge(START, "tool_calling_llm")
builder.add_edge("tool_calling_llm", END)
graph = builder.compile()
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
- If we pass in
Hello!, the LLM responds without any tool calls.
messages = graph.invoke({"mesasges": HumanMessage(content="Hello!")})
print(messages)
= Human Message =
Hello!
= Ai Message =
Hi there! How can I assist you today?
messages = graph.invoke({"mesasges": HumanMessage(content="Multiply 2 and 3!")})
print(messages)
= Human Message =
Multiply 2 and 3!
= Ai Message =
Tool Calls:
multiply (call_Er4gChFoSGzU7lsuaGzfSGTQ)
Call ID: call_Er4gChFoSGzU7lsuaGzfSGTQ
Args:
a: 2
b: 3




Drain cleaning experts use advanced equipment like hydro-jetting to eliminate blockages. Kitchen sinks, bathrooms, and drain repair in mississauga basement drains are common problem areas. Persistent clogs can lead to foul odors and backups. Regular maintenance prevents damage and ensures free-flowing pipes. Experienced professionals handle all types of drainage systems with care.