1. 문제 소개
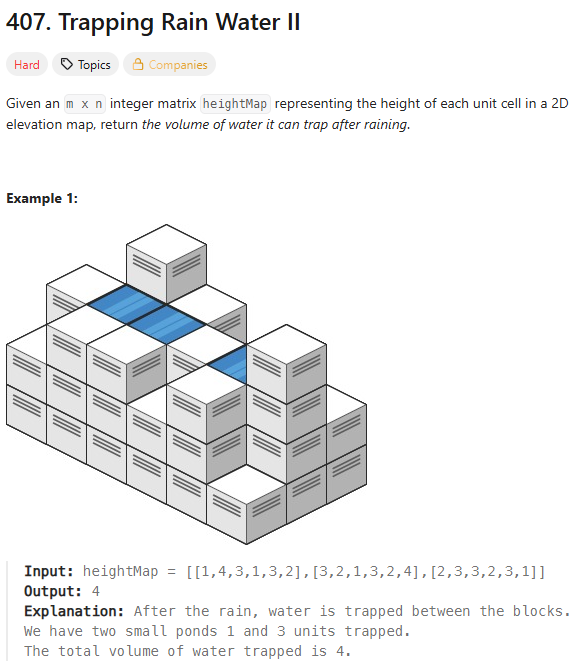
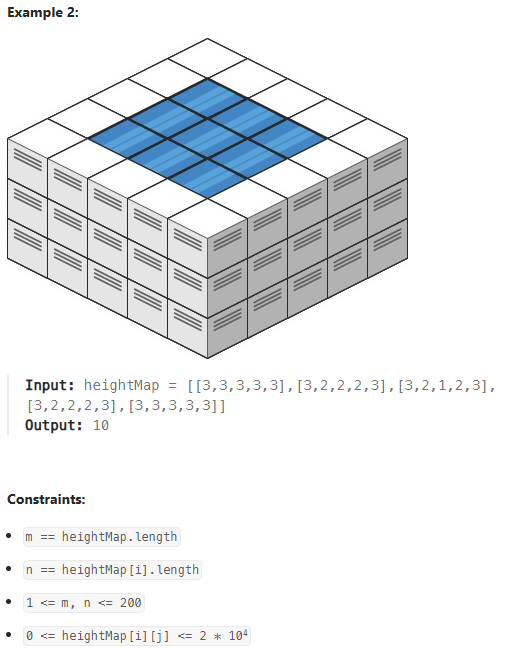
2. 나의 풀이법
길이 의 리스트로 풀었을 때에는 투포인터 방식으로 풀었기에, 이것도 비슷한 것인 줄 알았는데, BFS와 Heap으로 푸는 것이라고 한다.
감이 잘 안잡혀서 조금 찾아보며 풀었다.
import heapq as hq
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(heightMap), len(heightMap[0])
if m < 3 or n < 3:
return 0
boundary = []
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
boundary.append((heightMap[i][0], i, 0))
boundary.append((heightMap[i][-1], i, n-1))
visited[i][0] = True
visited[i][-1] = True
for j in range(1, n-1):
boundary.append((heightMap[0][j], 0, j))
boundary.append((heightMap[-1][j], m-1, j))
visited[0][j] = True
visited[-1][j] = True
hq.heapify(boundary)
answer = 0
dirs = [(1,0), (-1,0), (0,1), (0,-1)]
while boundary:
h, x, y = hq.heappop(boundary)
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if nx < 0 or nx >= m or ny < 0 or ny >= n or visited[nx][ny]:
continue
nh = heightMap[nx][ny]
level = max(h, nh)
if nh < h:
answer += h - nh
visited[nx][ny] = True
hq.heappush(boundary, (level, nx, ny))
return answer
3. 다른 풀이법
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, height: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dir = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
m, n = len(height), len(height[0])
if m <= 2 or n <= 2:
return 0
boundary = []
for i in range(m):
boundary.append((height[i][0], i, 0))
boundary.append((height[i][-1], i, n - 1))
height[i][0] = height[i][-1] = -1
for j in range(1, n - 1):
boundary.append((height[0][j], 0, j))
boundary.append((height[-1][j], m - 1, j))
height[0][j] = height[-1][j] = -1
heapify(boundary)
ans, water_level = 0, 0
while boundary:
h, i, j = heappop(boundary)
water_level = max(water_level, h)
for a in range(4):
i0, j0 = i + dir[a], j + dir[a + 1]
if i0 < 0 or i0 >= m or j0 < 0 or j0 >= n or height[i0][j0] == -1:
continue
currH = height[i0][j0]
if currH < water_level:
ans += water_level - currH
height[i0][j0] = -1
heappush(boundary, (currH, i0, j0))
return ans
다른 풀이법과 나의 풀이법은 거의 똑같다.
이미 존재하는 풀이에 visited블럭만 추가한 것이기 때문이다.
따라서 두 경우 모두 의 시간복잡도를 가지며, 거의 비슷하다.
4. 결론
heap을 사용해서 최소 높이의 경계부터 시작해 차근차근 물을 채워나간다는 생각을 통해 풀 수 있는 문제였다. 두고두고 복습을 해야할 문제다.
