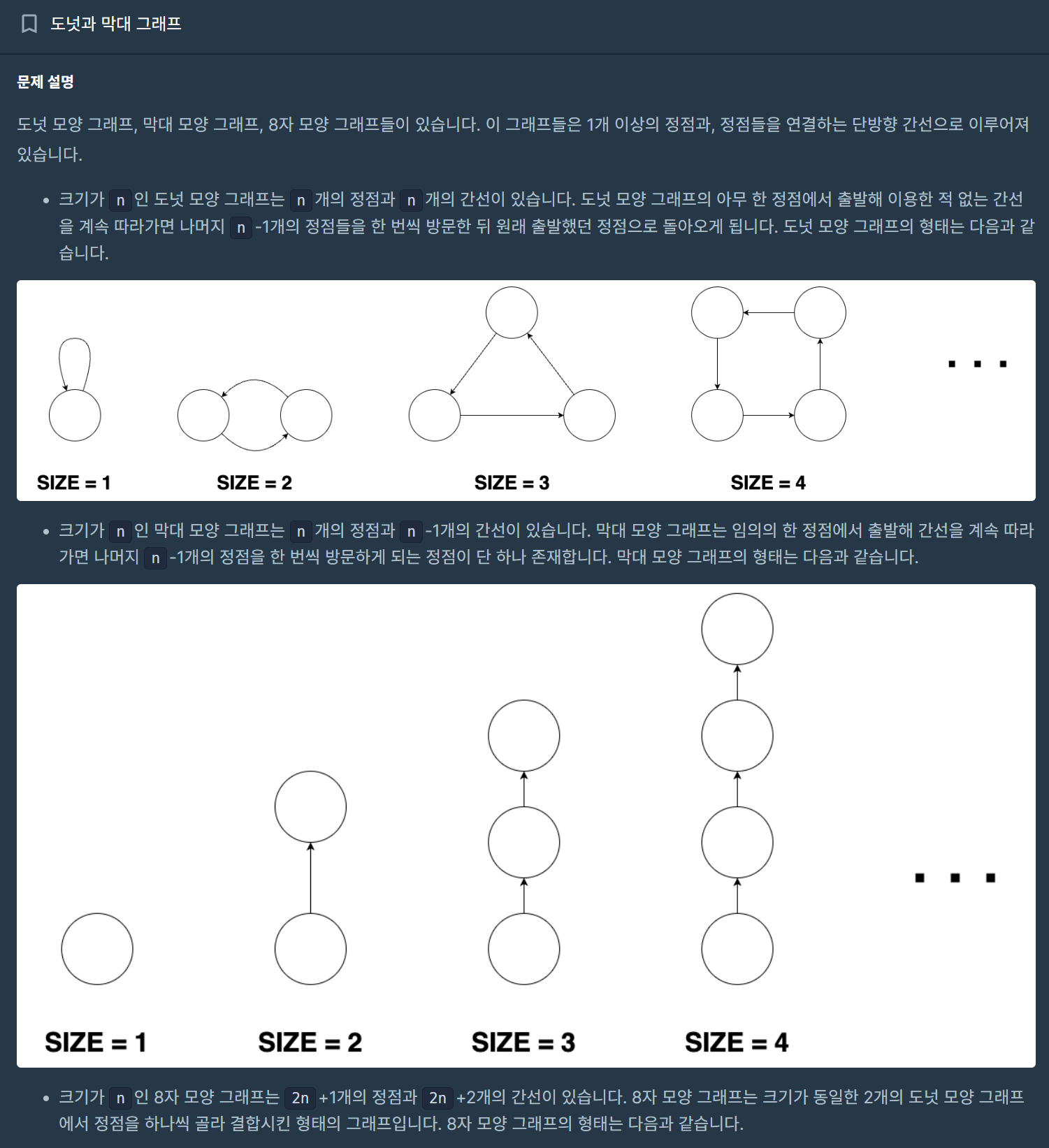
카카오 코딩 테스트에서 나온 문제다. 실제로 문제 풀 당시에는 많이 어렵게 느껴졌고... 좀 도전하다가 포기했던 기억이 난다.
보통 이런 그래프류의 문제에서는 탐색이 무조건 필요할거라고 생각 했는데 사실 이 문제는 단순한 구현 문제다.
그리고 이 구현 문제에서 필요한 건 나가는 라인과 들어오는 라인..이게 전부다.
문제 풀 당시에는 그래프를 연결해주는 접점을 어떻게 찾지? 에 되게 의문을 많이 두었는데 그냥 들어오는 라인이 없고 나가는 라인이 하나 이상이면 되는 조건이다.
도넛 그래프가 좀 헷갈렸는데 이 부분은 들어오는 라인이 자기 자신이었는지만 확인해주면 되는 부분이었다.
첫번째는 탐색을 이용한 풀이고, 두번째는 탐색 없이 그냥 라인 정보만 가지고 푸는 방식이다. 시간은 두번째가 훨~씬 빠르다.
그래프 문제에서의 구현 정말 조심해야겠다.
V1
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool visited[1000001];
bool flag = false;
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int& inward, int& outward, int& nodeNum, int& node, int& start){
nodeNum++;
visited[node] = true;
for(int& n : adj[node]){
if(!visited[n]){
outward++;
dfs(adj,inward,outward,nodeNum,n,start);
} else if(visited[n]){
inward++;
if(n == start) flag = true;
//if(n == node) outward++;
}
}
}
vector<int> solution(vector<vector<int>> edges) {
vector<int> answer(4,0);
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
map<int,pair<int,int>> inoutMap; //first = out, second = in
vector<vector<int>> adj(1000001);
for(vector<int>& e : edges){
int from = e[0];
int to = e[1];
adj[from].push_back(to);
inoutMap[from].first++;
inoutMap[to].second++;
}
int connectNode = 0;
for(auto& it : inoutMap){
if(it.second.first > 1 && it.second.second == 0) connectNode = it.first;
}
for(auto& it : adj[connectNode]){
inoutMap[it].second--;
}
visited[connectNode] = true;
answer[0] = connectNode;
for(auto& it : inoutMap){
if(!visited[it.first] && it.second.first > 0){
int inward = 0, outward = 0, nodeNum = 0, node = it.first;
dfs(adj,inward,outward,nodeNum, node,node);
//cout << node << ' ' << inward << ' ' << outward << ' '<< nodeNum << endl;
if(inward == 0 && nodeNum-1 == outward){
answer[2]++;
} else if(inward >= 2 && outward >= 2){
answer[3]++;
} else if(flag){
answer[1]++;
}
flag = false;
}
}
for(auto& it : inoutMap){
if(!visited[it.first]) answer[2]++;
}
return answer;
}V2
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> solution(vector<vector<int>> edges) {
vector<int> answer(4,0);
map<int, pair<int,int>> inoutMap; //first = out, second = in
int maxNode = -1;
for(vector<int>& v : edges){
int from = v[0], to = v[1];
inoutMap[from].first++;
inoutMap[to].second++;
maxNode = max(maxNode,max(from,to));
}
for(int node = 1; node <= maxNode; node++){
if(inoutMap[node].first >= 2 && inoutMap[node].second == 0){
answer[0] = node;
}
else if(inoutMap[node].first == 0){
answer[2]++;
}
else if(inoutMap[node].first >= 2 && inoutMap[node].second >= 2){
answer[3]++;
}
}
answer[1] = inoutMap[answer[0]].first - (answer[2] + answer[3]);
return answer;
}