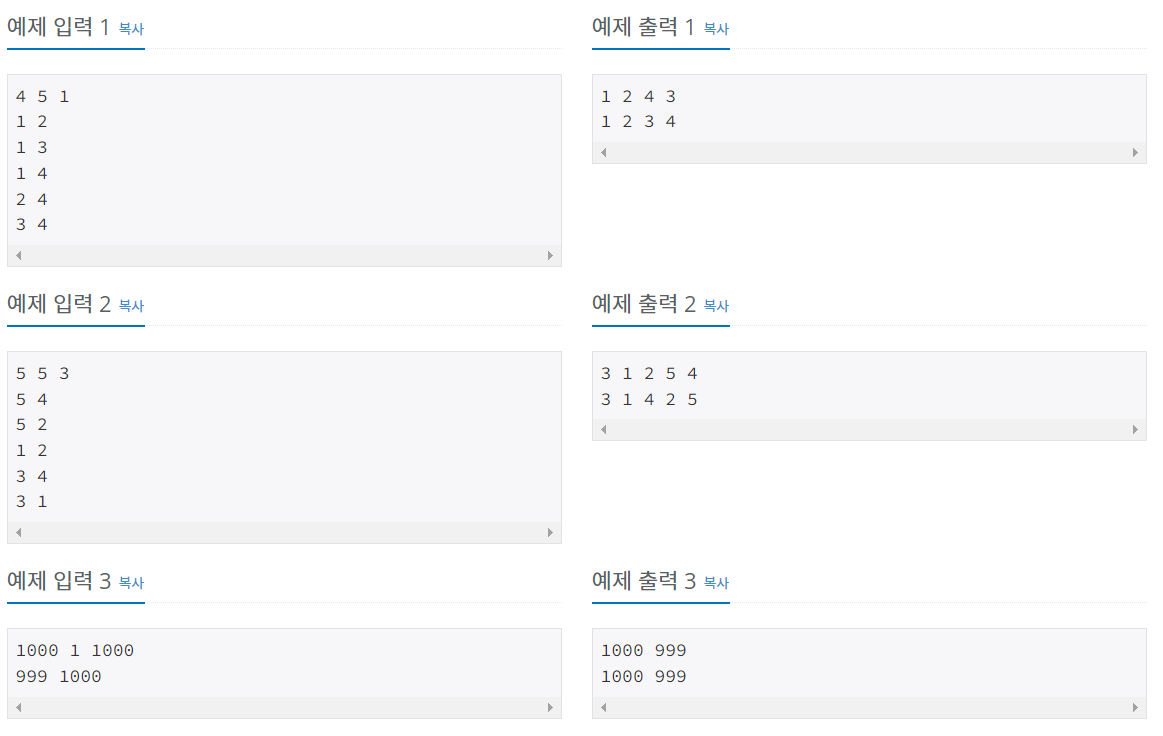
백준 1260번
DFS와 BFS
문제
그래프를 DFS로 탐색한 결과와 BFS로 탐색한 결과를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 단, 방문할 수 있는 정점이 여러 개인 경우에는 정점 번호가 작은 것을 먼저 방문하고, 더 이상 방문할 수 있는 점이 없는 경우 종료한다. 정점 번호는 1번부터 N번까지이다.
입력
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사이에 여러 개의 간선이 있을 수 있다. 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 DFS를 수행한 결과를, 그 다음 줄에는 BFS를 수행한 결과를 출력한다. V부터 방문된 점을 순서대로 출력하면 된다.
예제
알고리즘 분류
- DFS, BFS
코드
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int[][] DFSGraph = new int[1001][1001];
static int[][] BFSGraph = new int[1001][1001];
static boolean[] DFSVisit = new boolean[10001];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int u = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 간선은 양방향
DFSGraph[u][v] = DFSGraph[v][u] = 1;
BFSGraph[u][v] = BFSGraph[v][u] = 1;
}
DFS(V);
System.out.println();
BFS(V);
}
public static void DFS(int node) {
DFSVisit[node] = true;
System.out.print(node + " ");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
if(!DFSVisit[i] && DFSGraph[node][i] == 1)
DFS(i);
}
}
public static void BFS(int node) {
boolean BFSVisit[] = new boolean[10001];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
BFSVisit[node] = true;
queue.offer(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int P = queue.poll();
System.out.print(P + " ");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
if(!BFSVisit[i] && BFSGraph[P][i] == 1) {
BFSVisit[i] = true;
queue.offer(i);
}
}
}
}
}
풀이
DFS와 BFS를 구분하여 푸는 문제이다.
DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색으로,
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 4
3 4
가 들어왔을 때,
1 2 그 다음 2 4 그 다음 4와 이어지는게 없으므로 1 3으로 가는 방식이다.
BFS는 넓이 우선 탐색으로
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 4
순서이다.
그 차이를 DFS는 재귀로, BFS는 Queue를 활용하여 보인다. (DFS에서 Stack을 활용하는 방법도 있다.)