프림 알고리즘
최소 신장 트리 : 모든 정점을 연결하며 사이클이 없는 트리
- 하나의 정점에서 연결된 간선 중에 하나씩 선택하면서 최소 신장 트리를 만들어 가는 방식
- 임의 정점을 선택해서 시작
(크루스칼은 간선을 선택하면서 진행한다.)
※ 모든 정점을 선택할 것이기 때문에, 정점의 선택 순서는 중요하지 않다. - 선택한 정점과 인접하는 정점들 중에서 최소 비용의 간선이 존재하는 정점을 선택
- 모든 정점이 선택될 때까지 2번 과정을 반복
- 임의 정점을 선택해서 시작
- 서로소인 2개의 집합 정보를 유지 (boolean) 배열로 사용
자바 구현
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 프림01 { // 반복문을 이용하는 프림
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(input);
int V = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 번호 0번부터 시작
int E = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 수
int[][] arr = new int[V][V]; // 인접 행렬로 생성 예정
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int W = sc.nextInt();
arr[A][B] = arr[B][A] = W;
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
int[] p = new int[V]; // 부모 확인 배열, 사용하지 않는다면 작성하지 않아도 된다.
int[] dist = new int[V]; // 선택한 간선의 가중치
int result = 0;
// 프림 1 : 초기화
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
p[i] = -1;
dist[i] = INF;
}
Arrays.fill(dist, INF); // for 문을 사용하여 프림을 초기화 하는 것이 가능하다.
// 프림 2 : 시작 정점 선택
dist[0] = 0;
// 프림 3 : 가중치 배열을 돌면서 가장 값이 낮은 것을 골라서 방문 체크, 그 후 갱신
for(int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++) {
int min = INF;
int idx = -1;
// 방문하지 않았으면서, 가장 작은 값 탐색
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && dist[j] < min) {
min = dist[j];
idx = j;
}
} // 반복문이 종료가 되면, idx는 가장 작은 값이 된다.
visited[idx] = true;
// result를 여기서 더하려면, 반복문은 V 번 돌아야 한다.
// idx와 연결 처리가 되어잇고 방문하지 않았고, 갱신이 가능한 경우 갱신
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(!visited[j] && arr[idx][j] != 0 && dist[j] > arr[idx][j]) {
dist[j] = arr[idx][j];
p[j] = idx;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
result += dist[i];
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static String input = "7 11\r\n"
+ "0 1 32\r\n"
+ "0 2 31\r\n"
+ "0 5 60\r\n"
+ "0 6 51\r\n"
+ "1 2 21\r\n"
+ "2 4 46\r\n"
+ "2 6 25\r\n"
+ "3 4 34\r\n"
+ "3 5 18\r\n"
+ "4 5 40\r\n"
+ "4 6 51";
}자바 구현 2
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 프림02 { // 우선순위 큐를 사용 : 완전 이진트리로 heap 자료 구조가 된다
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int A, B, W;
public Edge(int a, int b, int w) {
super();
A = a;
B = b;
W = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(프림02.Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.W, o.W);
}
}
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(input);
int V = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 번호 0번부터 시작
int E = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 수
List<Edge>[] adjList = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int W = sc.nextInt();
adjList[A].add(new Edge(A, B, W));
adjList[B].add(new Edge(B, A, W)); // 무향이기 때문에 반대로 지정
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
int result = 0;
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
visited[0] = true;
int pick = 1; // 0번 정점에서 시작하고, 이것은 1개를 뽑은 것이라는 뜻
for(int i = 0; i < adjList[0].size(); i++) {
pq.add(adjList[0].get(i));
}
// pq.addAll(adjList[0]); 동일한 내용이다
while(pick != V) {
Edge e = pq.poll();
if(visited[e.B]) continue;
result += e.W;
visited[e.B] = true;
pick++;
pq.addAll(adjList[e.B]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static String input = "7 11\r\n"
+ "0 1 32\r\n"
+ "0 2 31\r\n"
+ "0 5 60\r\n"
+ "0 6 51\r\n"
+ "1 2 21\r\n"
+ "2 4 46\r\n"
+ "2 6 25\r\n"
+ "3 4 34\r\n"
+ "3 5 18\r\n"
+ "4 5 40\r\n"
+ "4 6 51";
}
최단 경로
가중치가 있는 그래프에서 두 정점 사이의 경로들 중, 간선의 가중치의 합이 최소인 경로
- 하나의 시작 정점에서 끝 정점까지의 최단 경로
- 다익스트라 알고리즘 (음의 가중치 허용 X)
- 벨만포드 알고리즘 (음의 가중치 허용 O)
- 모든 정점들에 대한 최단 경로 : 플로이드-워셜 알고리즘 (경우지-출발지-도착지 순서로 for문 작성)
다익스트라 알고리즘
- 시작 정점에서 거리가 최소인 정점을 선택해 나감녀서, 최단 경로를 구하는 방식
- 탐욕 알고리즘 중 하나이고, 프림 알고리즘과 유사
- A에서 B까지의 최단 경로
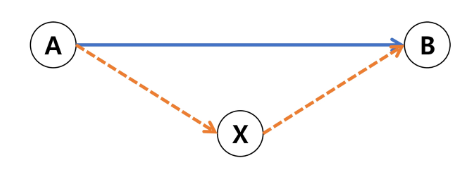
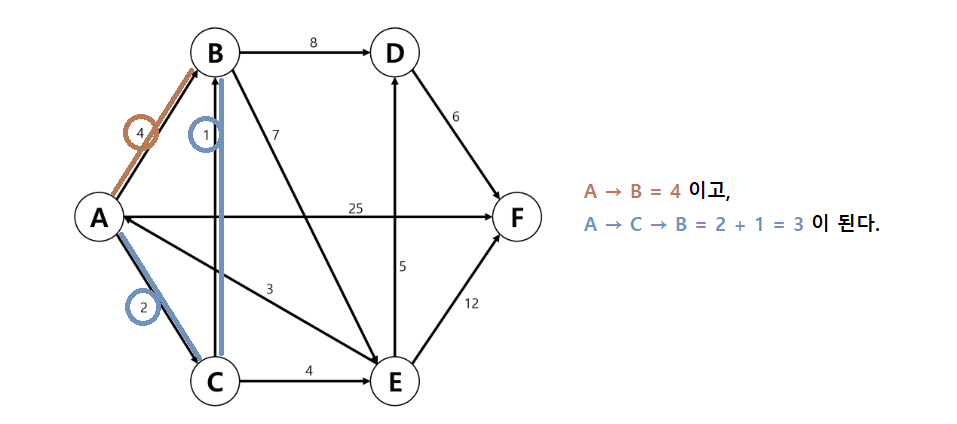
- 동작 과정
- 시작 정점 입력
- 거리 저장 배열을 최대 값으로 초기화
- 시작 점에서 갈 수 있는 곳의 값을 갱신
- 아직 방문하지 않은 점들이 갖고 있는 거리 값과, 현재 정점에서 방문하지 않은 정점까지의 가중치의 합이 작다면 갱신
- 모든 정점을 방문할 때까지 반복
자바구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 다익스트라_반복문 {
static class Node{
// 시작 정점은 사용하지 않는다, 인덱스를 사용하면 되므로
int V, W;
public Node(int v, int w) {
super();
V = v;
W = w;
}
}
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static int V, E;
static List<Node>[] adjList;
static int[] dist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(input);
V = sc.nextInt();
E = sc.nextInt();
adjList = new ArrayList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
dist = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
adjList[sc.nextInt()].add(new Node(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt()));
}
dis(0);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dist));
}
private static void dis(int st) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
dist[st] = 0; // 시작 노드의 경우, 거리 0으로 초기화
// i 의 범위는 문제를 보고 결정
// 도착지가 정해져있다면, 거기까지만 돌리면 된다.
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
int min = INF;
int idx = -1;
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(!visited[j] && min > dist[j]) {
min = dist[j];
idx = j;
}
}
if(idx == -1) break;
visited[idx] = true;
for(Node node : adjList[idx]) {
if (!visited[node.V] && dist[node.V] > dist[idx] + node.W) {
dist[node.V] = dist[idx] + node.W;
}
}
}
}
static String input = "6 11\r\n"
+ "0 1 4\r\n"
+ "0 2 2\r\n"
+ "0 5 25\r\n"
+ "1 3 8\r\n"
+ "1 4 7\r\n"
+ "2 1 1 \r\n"
+ "2 4 4\r\n"
+ "3 0 3\r\n"
+ "3 5 6\r\n"
+ "4 3 5\r\n"
+ "4 5 12";
}