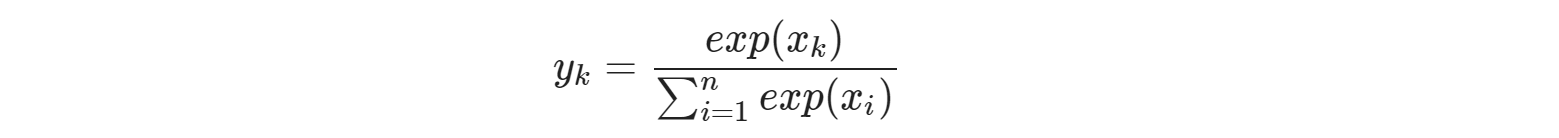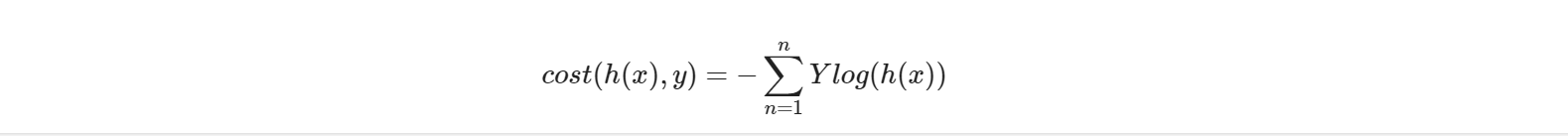import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tf.__version__
Softmax classification
- 임의의 Dataset 준비
- 3개의 클래스로 분류할 데이터 준비
x_data = [[1., 2., 1., 1.],
[2., 1., 3., 2.],
[3., 1., 3., 4.],
[4., 1., 5., 5.],
[1., 7., 5., 5.],
[1., 2., 5., 6.],
[1., 6., 6., 6.],
[1., 7., 7., 7.]]
y_data = [[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 0.]]
x_test = [[1., 1., 1., 1.]]
y_test = [[0., 0., 1.]]
임의의 Data를 이용해서 3개의 클래스를 가지는 데이터셋 생성
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_data, y_data))
dataset = dataset.repeat(1).batch(8)
nb_classes = 3
print(tf.Variable(x_data))
print(tf.Variable(y_data))
W = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([4, nb_classes]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([nb_classes]), name='bias')
variables = [W, b]
tf.print(W,b)
가설 설정
- 가설에서 예측한 값들을 이용해 예측값들을 확률로 표현한다.
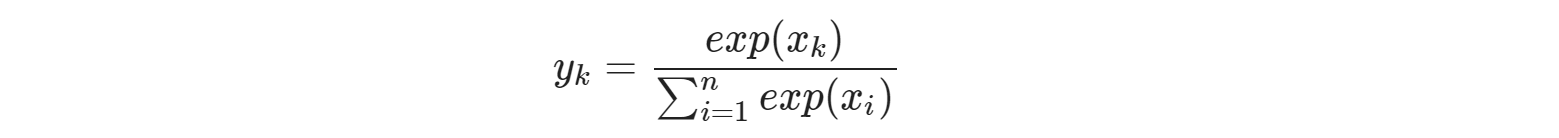
def hypothesis_softmax(X):
return tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X, W) + b)
tf.print(hypothesis_softmax(tf.Variable(x_data)))
가설을 검증할 Cross Entropy 함수를 정의합니다
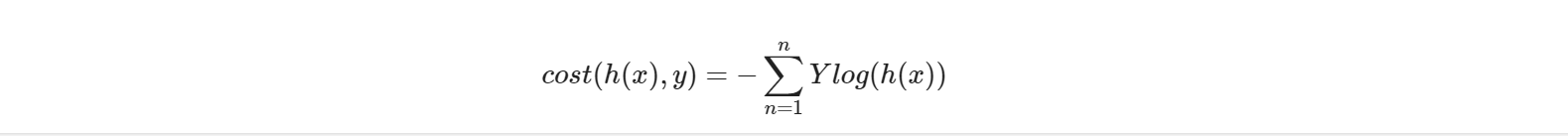
def loss_fn(hypothesis, labels):
loss = tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(labels, hypothesis)
return loss
optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01)
학습 진행
epochs = 5000
for step in range(epochs):
for features, labels in dataset:
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss_value = loss_fn(hypothesis_softmax(features),labels)
grads = tape.gradient(loss_value, [W,b])
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads,[W,b]))
if step % 100 == 0:
print("Iter: {}, Loss: {:.4f}".format(step, tf.reduce_mean(loss_value.numpy()).numpy()))
Iter: 0, Loss: 8.2729
Iter: 100, Loss: 4.2904
Iter: 200, Loss: 4.2179
Iter: 300, Loss: 4.1823
Iter: 400, Loss: 4.1599
Iter: 500, Loss: 4.1439
Iter: 600, Loss: 4.1317
Iter: 700, Loss: 4.1219
Iter: 800, Loss: 4.1139
Iter: 900, Loss: 4.1072
Iter: 1000, Loss: 4.1014
Iter: 1100, Loss: 4.0964
Iter: 1200, Loss: 4.0921
Iter: 1300, Loss: 4.0882
Iter: 1400, Loss: 4.0848
Iter: 1500, Loss: 4.0818
Iter: 1600, Loss: 4.0790
Iter: 1700, Loss: 4.0765
Iter: 1800, Loss: 4.0743
Iter: 1900, Loss: 4.0722
Iter: 2000, Loss: 4.0704
Iter: 2100, Loss: 4.0686
Iter: 2200, Loss: 4.0670
Iter: 2300, Loss: 4.0656
Iter: 2400, Loss: 4.0642
Iter: 2500, Loss: 4.0629
Iter: 2600, Loss: 4.0617
Iter: 2700, Loss: 4.0606
Iter: 2800, Loss: 4.0596
Iter: 2900, Loss: 4.0586
Iter: 3000, Loss: 4.0577
Iter: 3100, Loss: 4.0569
Iter: 3200, Loss: 4.0561
Iter: 3300, Loss: 4.0553
Iter: 3400, Loss: 4.0546
Iter: 3500, Loss: 4.0539
Iter: 3600, Loss: 4.0532
Iter: 3700, Loss: 4.0526
Iter: 3800, Loss: 4.0520
Iter: 3900, Loss: 4.0515
Iter: 4000, Loss: 4.0510
Iter: 4100, Loss: 4.0504
Iter: 4200, Loss: 4.0500
Iter: 4300, Loss: 4.0495
Iter: 4400, Loss: 4.0491
Iter: 4500, Loss: 4.0486
Iter: 4600, Loss: 4.0482
Iter: 4700, Loss: 4.0478
Iter: 4800, Loss: 4.0475
Iter: 4900, Loss: 4.0471
Sample 데이터를 넣고 테스트해봅시다.
sample_data = [[2,1,3,2]]
sample_data = np.asarray(sample_data, dtype=np.float32)
a = hypothesis_softmax(sample_data)
print(a)
print(tf.argmax(a, 1))
데이터를 이용해서 예측
b = hypothesis_softmax(x_test)
print(b)
print(tf.argmax(b, 1))
print(tf.argmax(y_test, 1))
def accuracy_fn(hypothesis, labels):
hypothesis = tf.argmax(hypothesis)
hypothesis = tf.cast(hypothesis, dtype=tf.float32)
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
labels = tf.argmax(labels)
labels = tf.cast(labels, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, labels), dtype=tf.float32))
return accuracy
test_acc = accuracy_fn(hypothesis_softmax(x_test),y_test)
print("Testset Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(test_acc))