[인공지능사관학교: 자연어분석A반] 학습 내용 보충 - nn.Linear
nn.Linear
KEYWORD: pytorch / Linear / Dot Product
- pytorch 는 Neural Network 상에서 Linear Layer 를 구성할 수 있도록 관련 모듈을 제공
- torch.nn 모듈 내부의 Linear 클래스가 존재 → 통상적으로
nn.Linear와 같은 형식으로 사용
- torch.nn 모듈 내부의 Linear 클래스가 존재 → 통상적으로
- nn.Linear 모듈
- Input Tensor 와 nn.Linear 의 weight 를 Dot Product 한 결과를 출력
- nn.Linear 는 곧 Dot Product 를 수행하는 수학적인 함수라고 생각해도 무방
- nn.Linear Layer 는 Dot Product 를 수행하는 Neural Net 의 Layer!
- Input Tensor 와 nn.Linear 의 Weight Tensor 의 내적으로 Output Tensor 가 출력
# Dot Product 와 Linear Transformation 을 적용한 결과
import numpy as np
A_matrix = [
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0]
]
B_matrix = [
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[2.0, 2.0, 2.0],
[3.0, 3.0, 3.0],
[4.0, 4.0, 4.0]
]
print(f"numpy Dot Product : {np.dot(A_matrix, B_matrix)}")
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
B = nn.Linear(4, 3, bias=False)
B.weight.data = torch.tensor(B_matrix).T
A = torch.tensor(A_matrix)
print(f"A Linear Layer Weight {B.weight}")
print(f"torch Linear Output : {B(A)}")numpy Dot Product : [[10. 10. 10.]
[20. 20. 20.]]
A Linear Layer Weight Parameter containing:
tensor([[1., 2., 3., 4.],
[1., 2., 3., 4.],
[1., 2., 3., 4.]], requires_grad=True)
torch Linear Output : tensor([[10., 10., 10.],
[20., 20., 20.]], grad_fn=<MmBackward0>)사용법
- torch.nn 모듈 내의 Linear 클래스를 통해서 nn.Linear Layer 객체를 생성
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
linear = nn.Linear(in_features=4, out_features=3, bias=False)- nn.Linear 클래스는 in_features 인자와 out_features 인자를 가짐
- nn.Linear의 동작 방식은 행렬의 내적과 동일
- 따라서 dimension 의 길이가 4인 Input Tensor 만이 nn.Linear 의 입력으로 사용될 수 있음
# input_tensor 는 1x4 인 Tensor 이고, nn.Linear 은 4x3 인 Layer
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
linear = nn.Linear(in_features=4, out_features=3, bias=False)
input_tensor = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]])
print(f"torch Linear Output : {linear(input_tensor)}")torch Linear Output : tensor([[-0.6756, 0.7807, -0.7505]], grad_fn=<MmBackward0>)- Input Tensor 의 사이즈와 nn.Linear Layer 의 in_features 가 맞지 않다면, 아래와 같은 유형의 에러가 발생
RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied (1x5 and 4x3)
in_features 인자
- Input Tensor 의 마지막 dimension 의 개수를 의미
- 가장 안쪽 배열의 길이가 in_features와 동일해야 함
# torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 4])
input_tensor = torch.tensor([
[
[
[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
]
]
])
print(input_tensor.shape)
print(f"torch Linear Output : {linear(input_tensor)}")torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 4])
torch Linear Output : tensor([[[[ 2.3263, -2.5094, 1.5137]]]], grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward0>)nput_tensor = torch.tensor([
[
[
[
[
[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
]
]
]
]
])
print(input_tensor.shape)
print(f"torch Linear Output : {linear(input_tensor)}")torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4])
torch Linear Output : tensor([[[[[[ 2.3263, -2.5094, 1.5137]]]]]], grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward0>)out_features 인자
- nn.Linear Layer 로부터 출력되는 Tensor 의 feature의 개수
- 일반적으로 Regression 문제의 경우 out_features를 1로 설정
- Classification 문제의 경우 결과의 범주 개수만큼 out_features 설정(이진분류 제외)
구현 예시: Linear Regression
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
X = torch.tensor(list(range(10)), dtype=torch.float32).reshape(-1, 1)
y = X * 10 + 5
class my_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(my_model, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(1, 1, bias=True)
# self.relu = nn.relu()
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
model = my_model()
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
for epoch in range(1000):
outputs = model(X)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = criterion(outputs, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.linear.weight, model.linear.bias(Parameter containing:
tensor([[10.0017]], requires_grad=True),
Parameter containing:
tensor([4.9891], requires_grad=True))→ weight 는 10.0017 그리고 bias 는 4.9891 로 y = X * 10 + 5 인 Train Dataset 과 유사한 결과
bias 인자
- bias 는 Input Tensor 와 nn.Linear Weight 의 Dot Product 의 결과와 더해짐
- 즉, Output Tensor 에 부가적인 영향력을 제공
- out_features 의 값에 해당하는 크기만큼 bias Tensor 가 생성됨
- out_features 의 값이 5 로 설정된다면, bias Tensor 의 크기는 5
- bias 의 값이 False 로 설정된다면, bias Tensor 는 None
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
linear = nn.Linear(in_features=10, out_features=1, bias=True)
print(linear.weight)
print(linear.bias)Parameter containing:
tensor([[-0.0365, 0.1214, -0.2508, -0.2174, -0.1147, -0.0663, -0.2425, -0.2478,
0.2966, -0.2276]], requires_grad=True)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0.0310], requires_grad=True)활용 예시
3x3 Tensor → 3x6 Tensor
- Feature 길이가 3인 Tensor 가 존재한다고 가정
- DataLoader 의 batch_size 가 3이라면, DataLoader 에 의해서 Iteration 마다 출력되는 Tensor 는 3x3 의 Tensor 가 됨
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
], dtype=torch.float32)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=3, shuffle=False)
tensor = next(iter(loader))
# tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
# [4., 5., 6.],
# [7., 8., 9.]])- 3 → 6 으로 Linear Transformation 이 수행되는 nn.Linear Transformation 을 거치면, 3x6 인 Tensor 로 변환
linear = nn.Linear(3, 6)
linear(tensor)
# tensor([[-0.5625, -1.7144, -0.0318, 0.9240, 1.7183, -0.2757],
# [-1.1148, -4.9342, 0.2390, 2.6098, 5.4051, -1.6341],
# [-1.6672, -8.1539, 0.5098, 4.2956, 9.0919, -2.9925]],
# grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)3x28x28 Tensor → 3x10x10 Tensor
- MNIST 의 digits 이미지는 28x28 사이즈의 이미지들로 구성
- 조회한 Tensor 는 1x28x28 의 크기를 가짐
- 이는 1개의 Channel 과 width, height 가 각각 28 픽셀로 구성되었다는 의미
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
trainset = datasets.MNIST(
root="/tmp/mnist",
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
# trainset 의 첫번째 Tensor
trainset[0][0].shape
# torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
# 첫번째 데이터의 1번 값은 Label 에 해당함.
trainset[0][1]
# 3- batch_size 가 3 인 DataLoader 를 사용하게 되면, 각 Iteration 마다 3x1x28x28 인 Tensor 를 얻음
loader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=3, shuffle=False)
train, label = next(iter(loader))
train.shape
# torch.Size([3, 1, 28, 28])- 이후 8 → 100 으로 Linear Transform 을 수행하는 nn.Linear 를 적용시키게 되면, Tensor 의 차원이 변형됨
linear = torch.nn.Linear(28, 100)
linear(train).shape
# torch.Size([3, 1, 28, 100])Linear Layer (선형 계층)
- 심층 신경망(deep neural networks)의 가장 기본적인 요소
- single layer 즉, 한 층으로 구성된 신경망과 동일
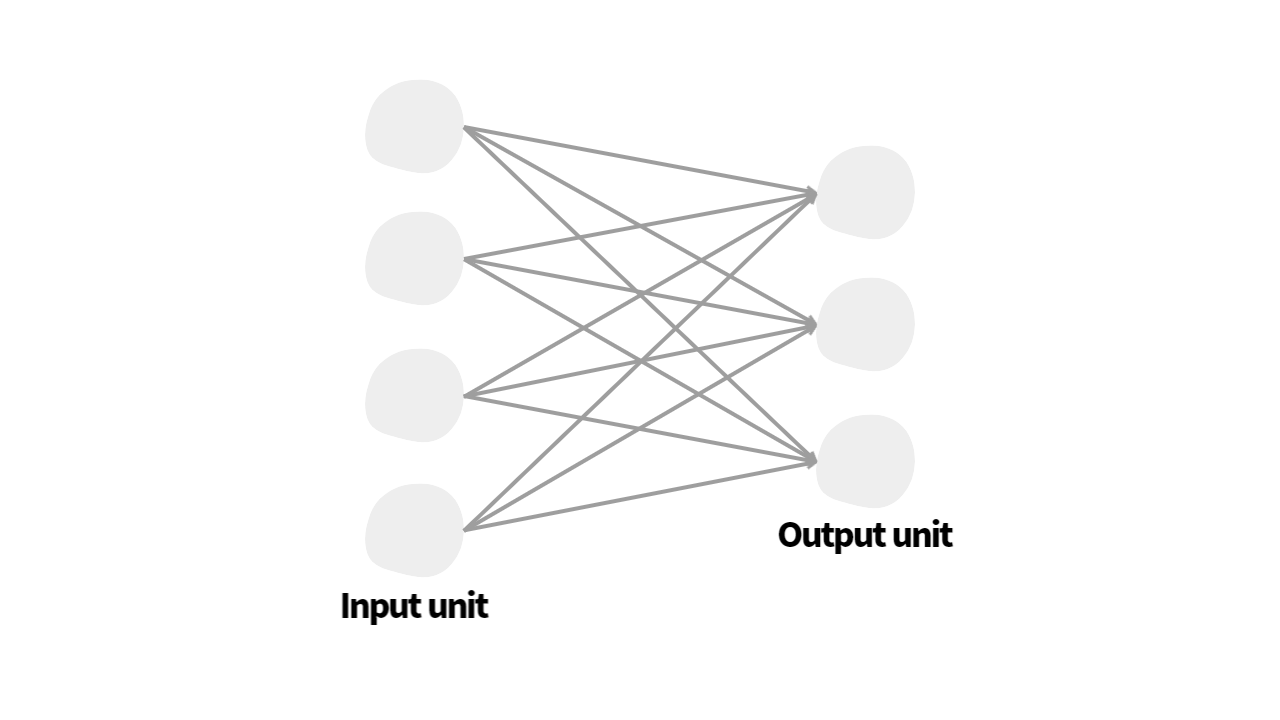
- 출력 노드(output node)
- 입력 노드(input node)로부터 들어온 값에 weight parameter()를 곱한 후 bias term()를 더한 값
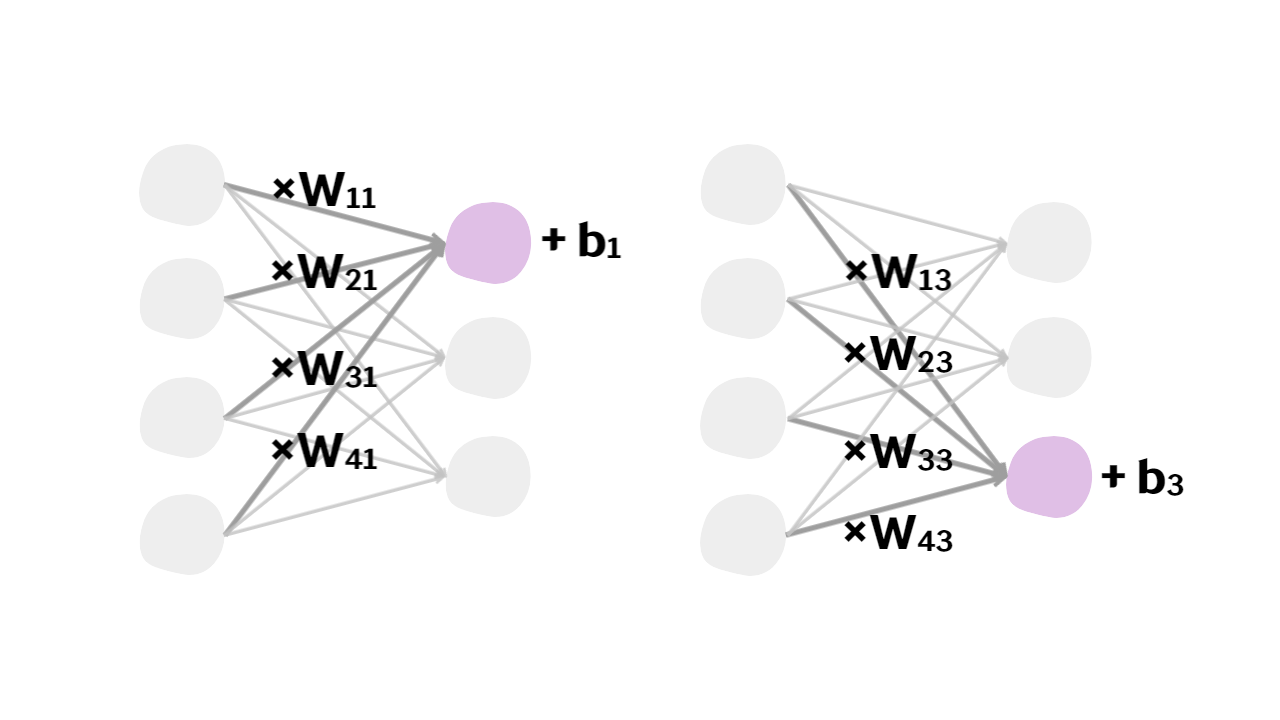
- 입력 노드(input node)로부터 들어온 값에 weight parameter()를 곱한 후 bias term()를 더한 값
- 예시: 총 12개의 weight parameter와 3개의 bias term을 행렬 및 벡터로 표현
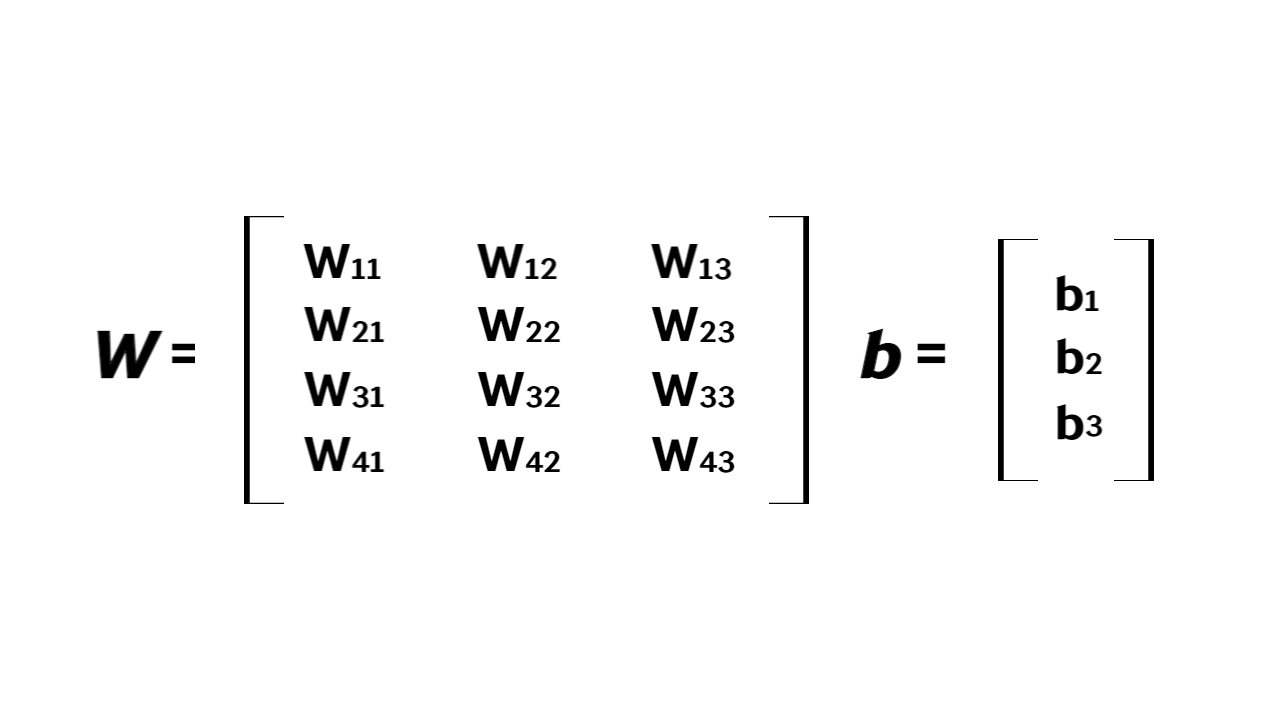
- nxm의 크기를 가진 행렬 W에 의해 n차원의 실수 벡터인 입력 벡터 x가 m차원의 실수 벡터인 출력 벡터 y로 변환
- 선형 계층은 행렬의 곱셈과 덧셈으로 이루어져 있음 → 선형 변환
- 따라서 선형 계층의 구조를 가진 모델을 설계하여 선형 데이터에 대한 관계를 분석하거나 선형 함수를 근사 계산할 수 있음
PyTorch에서 model 구현하기
직접 만들기
- torch.nn.Module 상속 받기
nn.Module(소스코드)- PyTorch의 모든 Neural Network의 Base Class
- 우리가 만들고자 하는 Model은 nn.Model이 subclass가 됨 → 즉, Deep Learning Model 생성을 위해서는 mm.Model을 상속 받는 class를 만들어야 함!
__init__()과forward()를 overriding__init__()method에서super().__init__()을 입력해 주어야 함super(class_name, self).__init__():super().__init__()와 기능의 차이는 없으며, 단지 파생클래스를 명시함
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
x = torch.FloatTensor(4, 3)
class MyLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim=3, output_dim=2):
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.outpu_dim = output_dim
super().__init__()
self.W = torch.FloatTensor(input_dim, output_dim)
self.b = torch.FloatTensor(output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
y = torch.matmul(x, self.W)+self.b
return y
linear = MyLinear(3, 2)
y = linear(x)- 중요한 점
nn.Module을 상속받은 객체는__call__함수가forward함수와 mapping 되어 있어foward를 따로 호출할 필요가 없음__call__과 mapping 되어 있지 않아서 따로 호출해야 할 경우:y = linear.forward(x)
- 이렇게 nn.Module을 상속받아 선형 계층(linear layer)를 구현여 계산을 수행할 수 있지만 W(weight)와 b(bias)가 학습이 가능한 parameter로 설정되어 있지 않기 때문에 이 방법으로는 학습 진행 X
- nn.Parmater을 활용하여 학습이 가능한 parameter로 인식시켜 줄 수 있음
class MyLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim=3, output_dim=2):
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.outpu_dim = output_dim
super().__init__()
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(input_dim, output_dim))
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(output_dim))
def forward(self, x):
y = torch.matmul(x, self.W)+self.b
return y
선형 회귀 모델 nn.Linear 활용
- torch.nn에 이미 정의된 linear layer인 nn.Linear을 이용하여 모델을 구현
torch.nn.Linear(in_features,out_features,bias = True, device = None,dtype = None)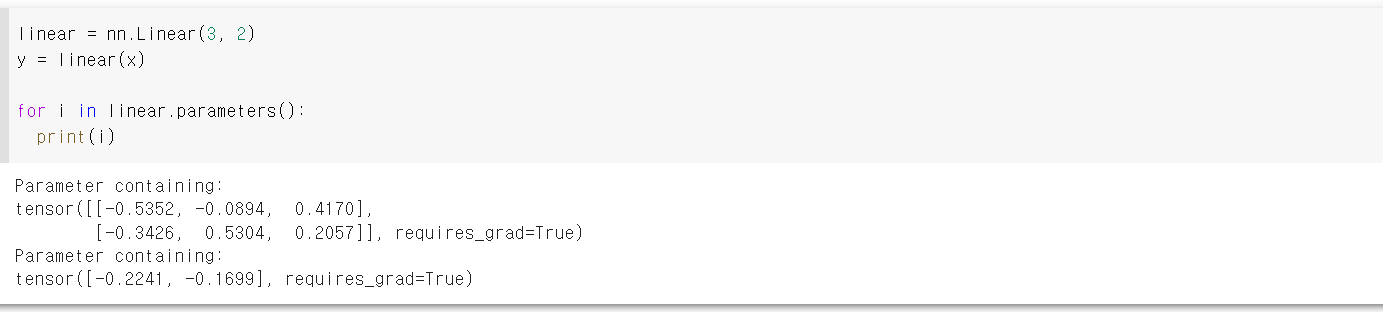
- nn.Module을 상속받는 class 내부에서 nn.Linear을 이용하는 방법도 가능
class MyLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim=3, output_dim=2):
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.outpu_dim = output_dim
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.linear(x)
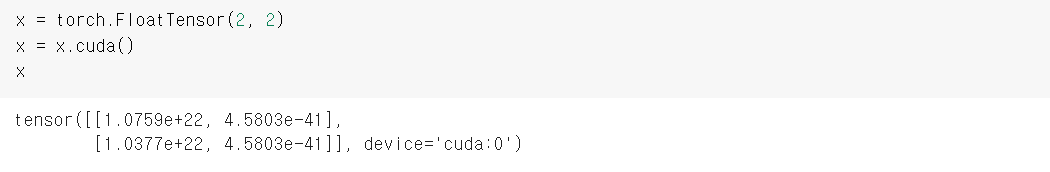
return yGPU 사용하기
- PyTorch에서는 CUDA를 통한 GPU 연산을 지원 → 구현한 코드들이 GPU에서 동작하도록 해보기
cuda() 함수
- tensor에 적용
- cuda() 함수는 tensor 뿐만 아니라 nn.Module의 하위 클래스 객체에도 적용할 수 있음

- device='cuda:0' 에서 cuda: 뒤에 오는 숫자는 GPU device의 index를 의미
- 즉, 0은 첫 번째 device인 0번 GPU
- cuda() 함수의 인자에 GPU 장치의 인덱스를 입력하여 원하는 device에 복사 또는 이동 가능
x = x.cuda(device=1)과 같이 tensor를 원하는 device에 복사- nn.Module 하위 클래스 객체의 경우에는 복사가 아닌 이동 수행
- 단, 두 번째 GPU device를 가지고 있지 않는다면 오류가 발생
- Tensor와 nn.Module의 하위 클래스 객체끼리는 서로 같은 device에 있을 때만 연산 가능
- device=0과 device=1 사이의 연산도 불가능
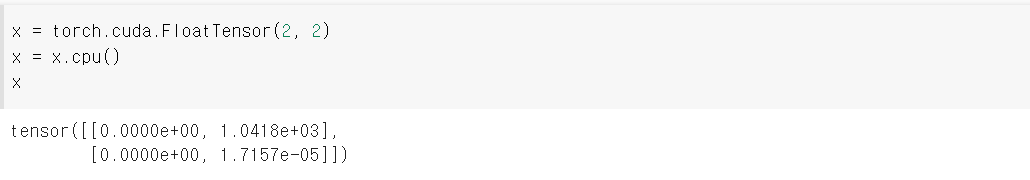
cpu() 함수
- GPU 메모리 상에 있는 tensor는 cpu() 함수를 이용하여 CPU 메모리로 복사 가능
to() 함수
- Pytorch에서 제공하는 to() 함수: device의 정보를 담은 객체를 인자로 받아 함수 자신을 호출한 객체를 해당 디바이스로 복사 또는 이동 (device 정보를 담은 객체는 torch.device를 통해 생성 가능)
cpu = torch.device('cpu')
gpu = torch.device('cuda:0')
x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(2, 2)
print(x)
x = x.to(gpu)
print(x)
x = x.to(cpu)
print(x)tensor([[0.0000e+00, 1.0418e+03],
[0.0000e+00, 1.7157e-05]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([[0.0000e+00, 1.0418e+03],
[0.0000e+00, 1.7157e-05]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([[0.0000e+00, 1.0418e+03],
[0.0000e+00, 1.7157e-05]])device 속성
- Tensor는 device 속성을 가지고 있어 해당 tensor가 위치한 device를 확인할 수 있음
x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(2, 2)
x.devicedevice(type='cuda', index=0)- nn.Module의 하위 클래스 객체는 device 속성을 가지고 있지 않아 아래와 같은 방법을 이용
- 이 경우 model 내부의 모든 parameter가 같은 device에 위치해야 함
layer = nn.Linear(2, 2)
next(layer.parameters()).devicedevice(type='cpu')