What is Machine Learning?
- Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
(Arthur Samuel, 1959)
- Machine learning algorithms:
- Supervised Learning
- Supervised Learning is used most in real-world applications.
- Unsupervised Learning
- Recommender systems
- Reinforcement learning
Supervised Learning
What is it?
- X -> Y, input to output mappings.
- Give examples to learn from.
- Learns from being given "right answers"
- Later only given X input and tries to predict outputs.
- Example:
- input -> output
- email -> spam? = spam filtering,
- ad, user info -> click? = online advertising.
- image, radar info -> position of other cars = self-driving car
- image of phone -> defect? = visual inspection (manufacture)
- Types of supervised learning algorithms are regression and classification.
Regression Algorithm
- predicting a number from infinitely many possible numbers.
- Example: Housing price prediction
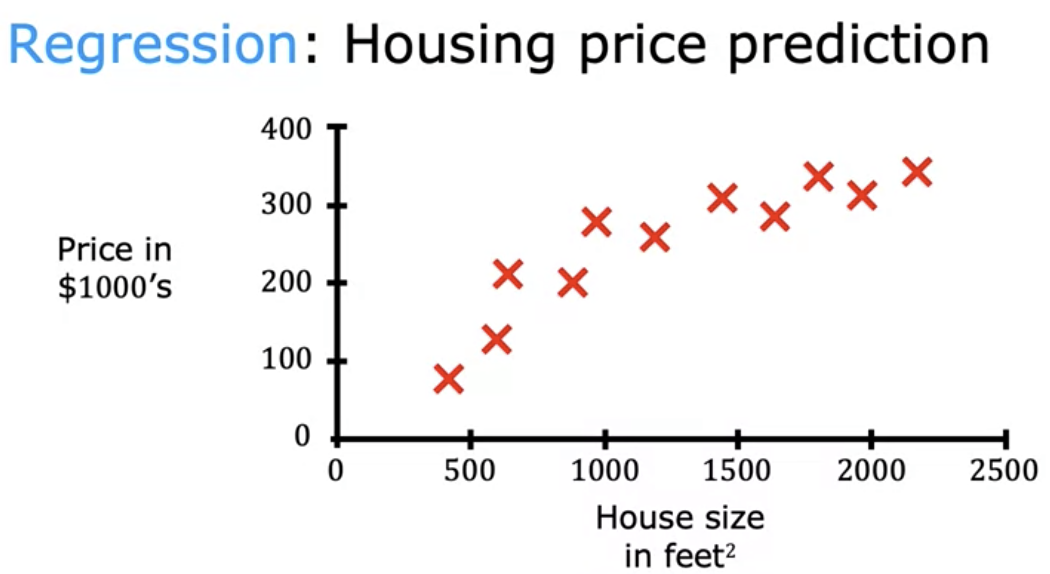
- What is the price of 750 feet^2?
- draw a straight line (regression) that fits the data and pinpoint for 750 feet^2 what the price would be.
- or even better draw a curve.
- The data set (right answers) are given, and the learning algorithm is asked to predict a house price.
Classification
- Predict categories that can be non-numeric or numeric (cat or dog, benign or malignant, (0, 1, or 2)).
- Only a limited number of outputs (category/class), as compared to infinitely many outputs from Regression.
- Example: Breast cancer detection
- Trying to devise a diagnostic tool for detecting malignant vs benign tumors.
- Only a limited number of outputs: 0 for benign, 1 for malignant.
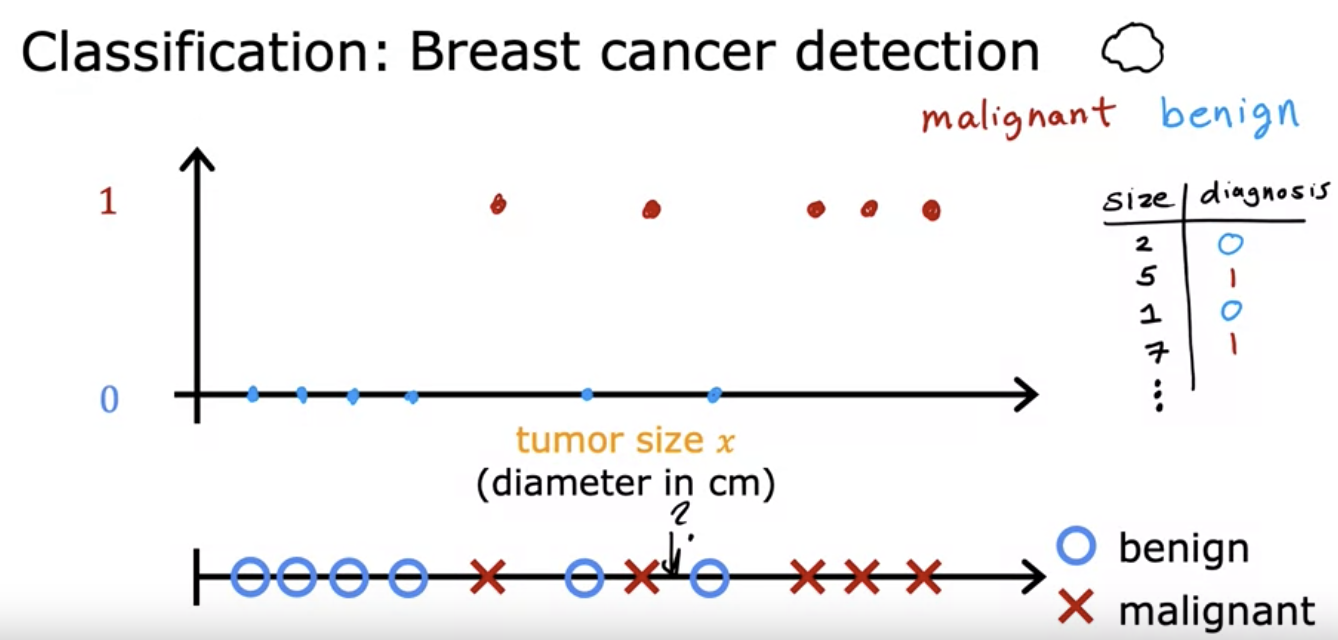
- Can be drawn with 2 axes, or just one.
- attempts to guess malignant vs benign with tumor size.
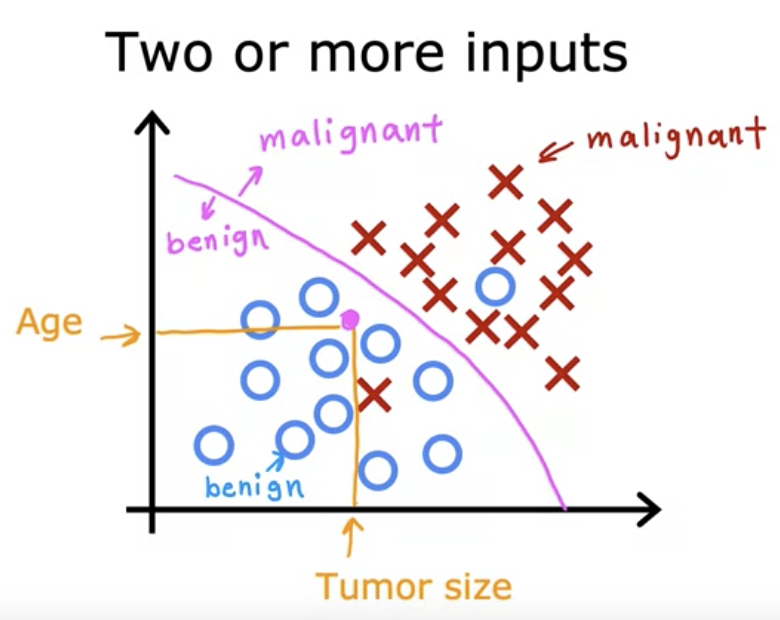
- More than one input can be used for classification.
- Attempts to draw the boundary line that separates malignant and benign and tries predicting the result.
Unsupervised Learning
- Finding something intersting in unlabeled data. (All by yourself hehe)
- Data only comes with inputs x, but not output labels y.
- Algorithm has to find structure in the data.
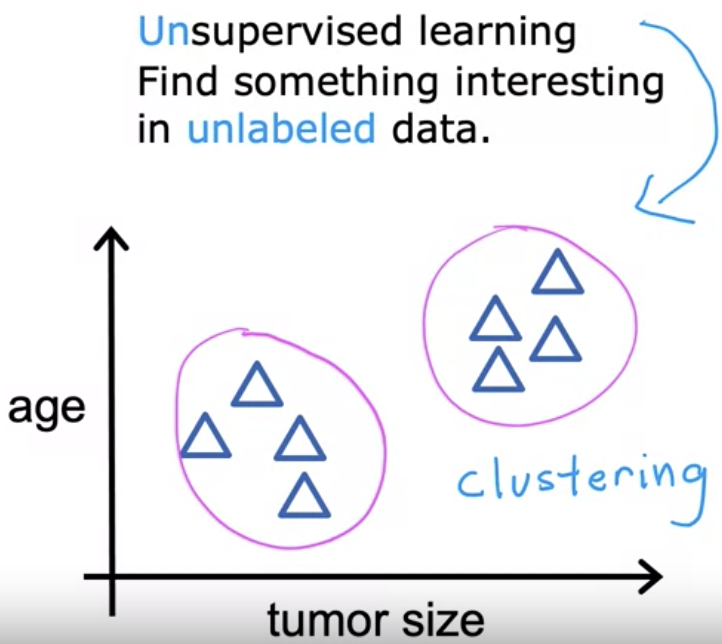
- In the same breast cancer example, the algorithm should be able to find that there are clusters in the data set.
- This is a particular type of unsupervised learning called clustering algorithm.
- Clustering - Google news: Grouping articles related with pandas & twins & zoo together.
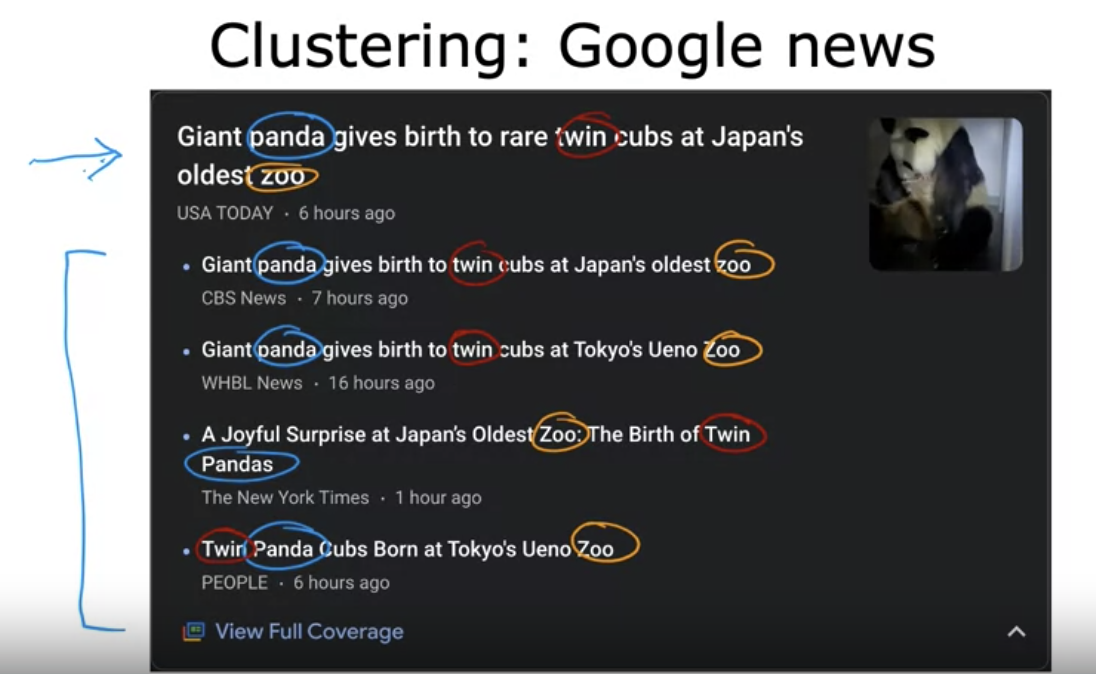
- The algorithm looks for the clusters by itself: in other words, the algorithm figures out that there are some articles with panda & twins & zoos together.
- Anomaly detection algorithm:
- find unusual data points.
- Dimensionality reduction algorithm
- compress data using fewer numbers.
Optional Lab: Brief python and Jupyter Notebooks
variable = "something"
print(f"f strings allow you to embed variables {varaible}")





