Multiple Access Links and Protocols
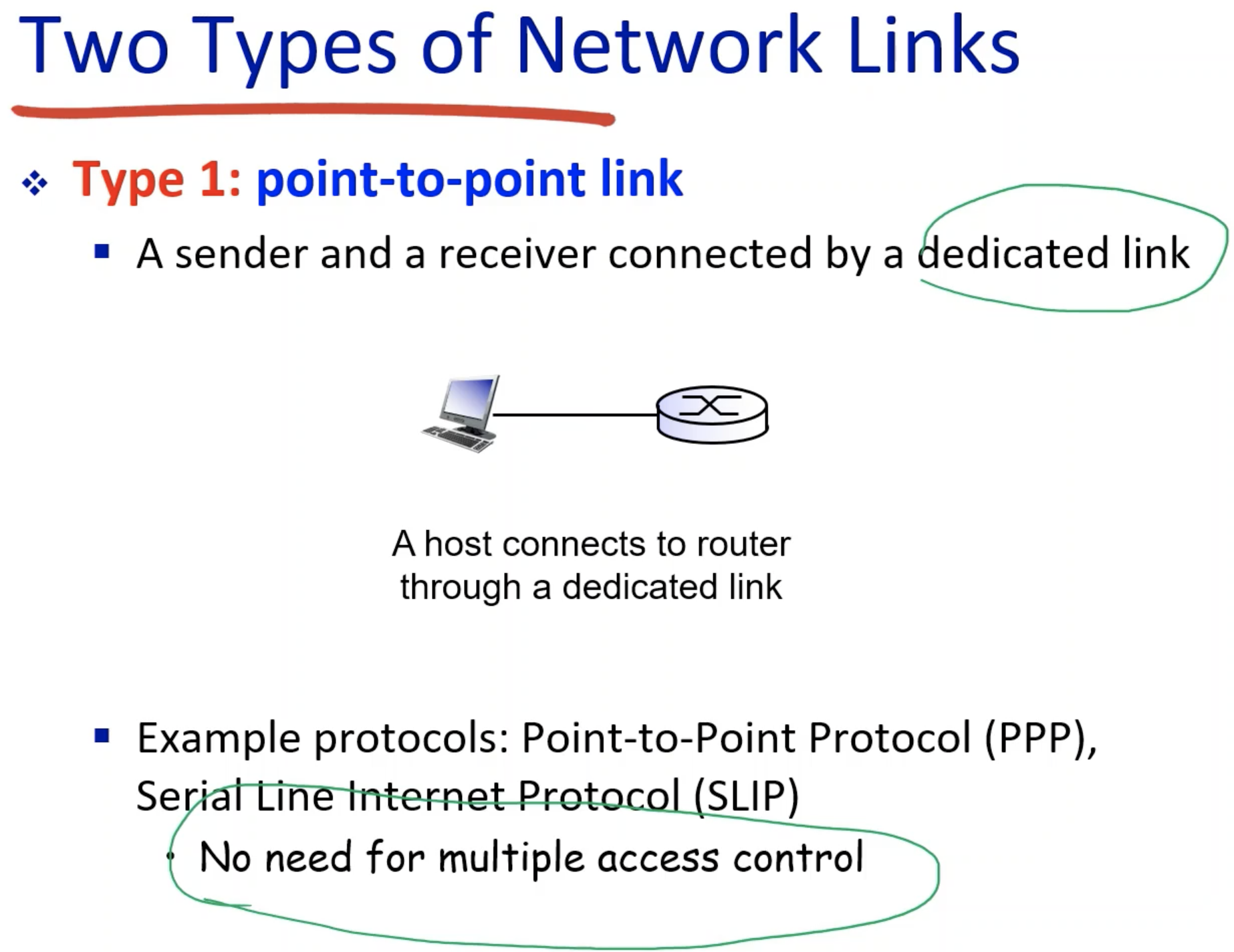
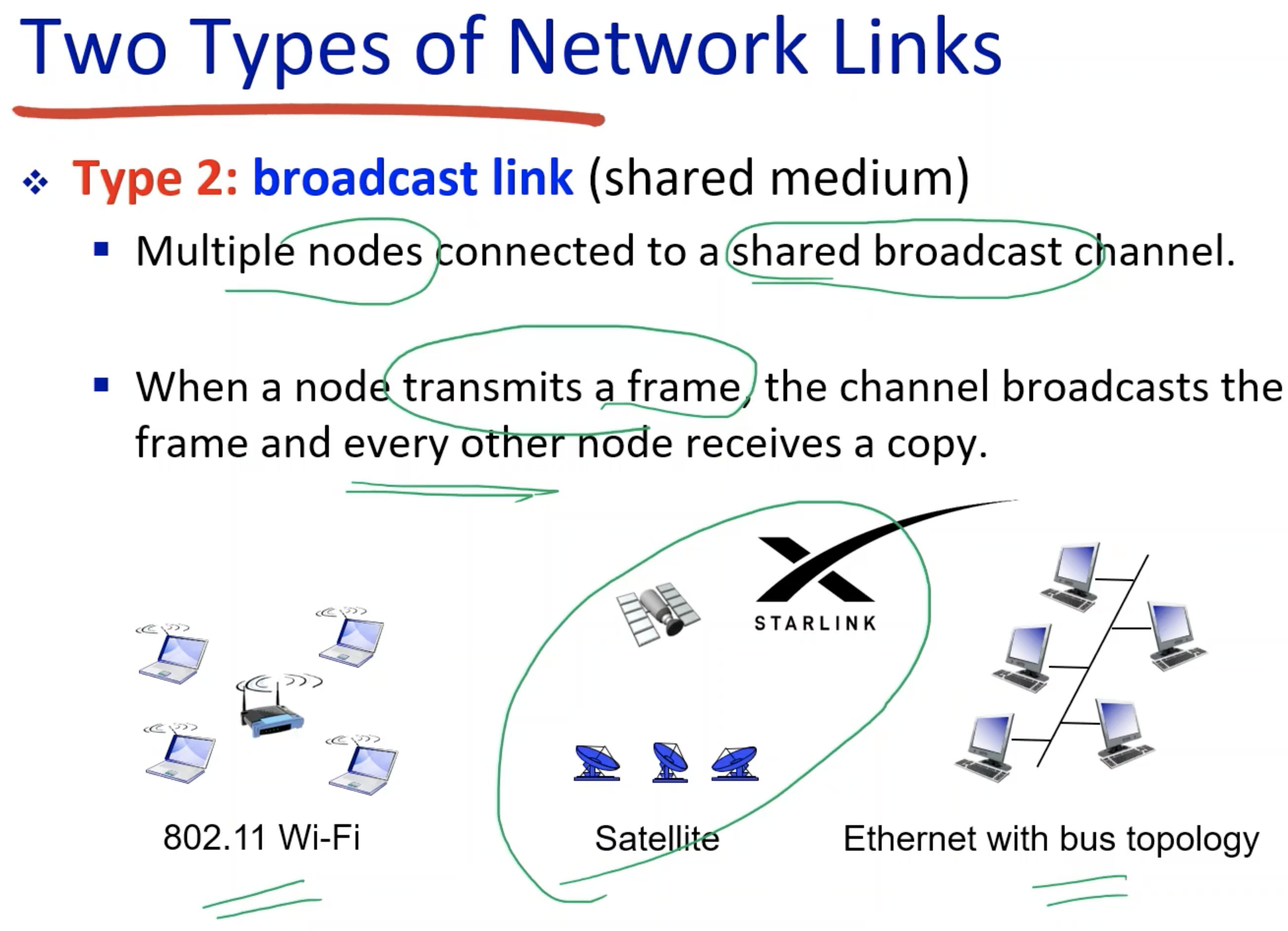
Two types of Network Links
Error?
- Node has no method of distinguishing data -> collision
- Who, when, and for how long does a person talk at a cocktail party?

- Channel partitioning could be breaking down into time / subjects.

- The more rules there are, the easier it is to manage - the complexity increases as there are less rules, because there is higher chance of collisions.
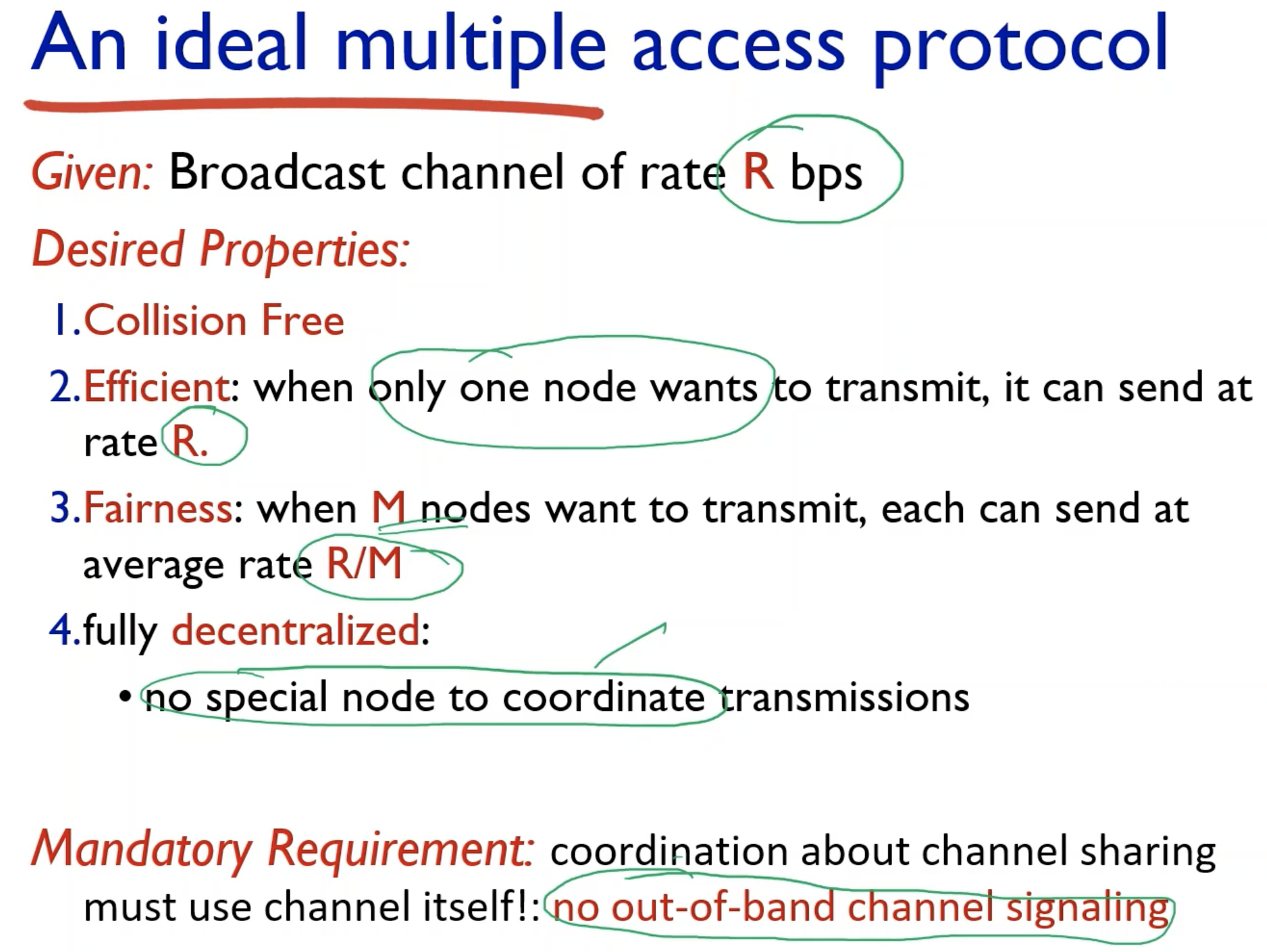
- The channel we are using to transmit must be the same channel we are using to coordinate.
- Decentralized means there is no single point of failure.
1. Channel Partitioning Protocols
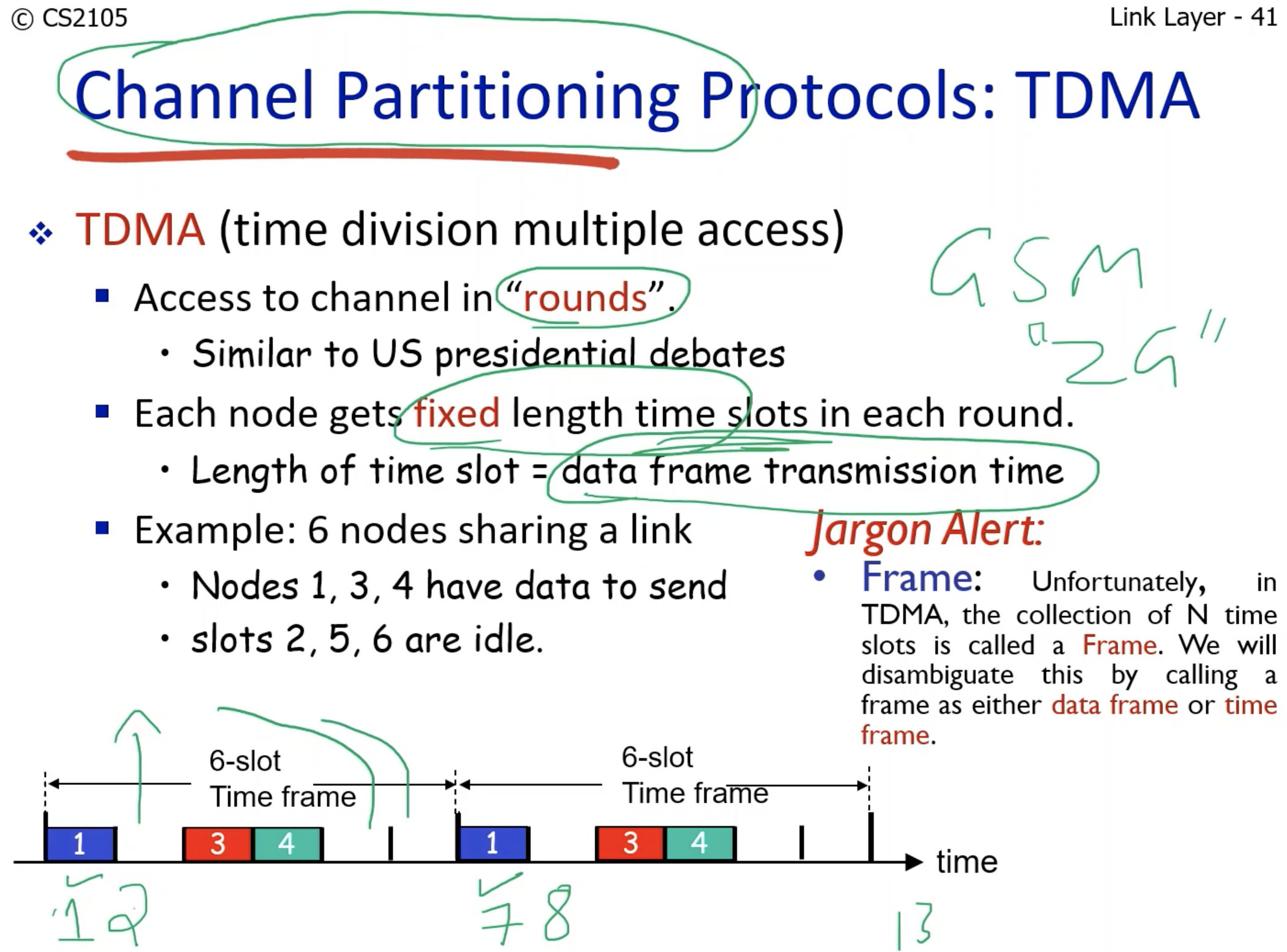
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA):
Kinda like Round-Robin - not exactly the same because there could be empty time slots.
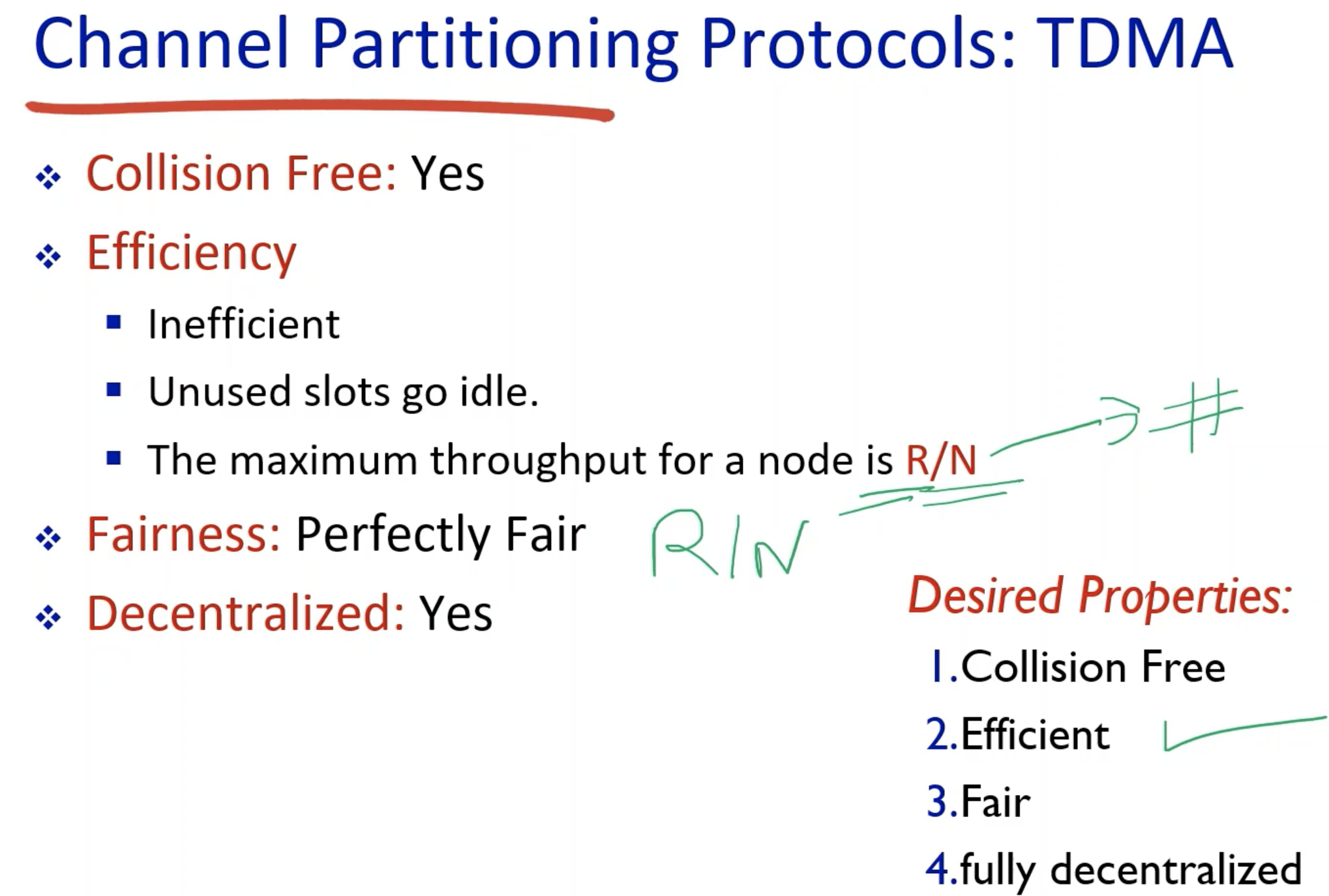
- The R/N is both the upper bound and the lower bound.
- This is because if the 6 nodes are active within a second, each node will split the second into 1/6 second. - Each node is using its internal clock to synchronize (coordinate) the data trasmission.
FDMA:
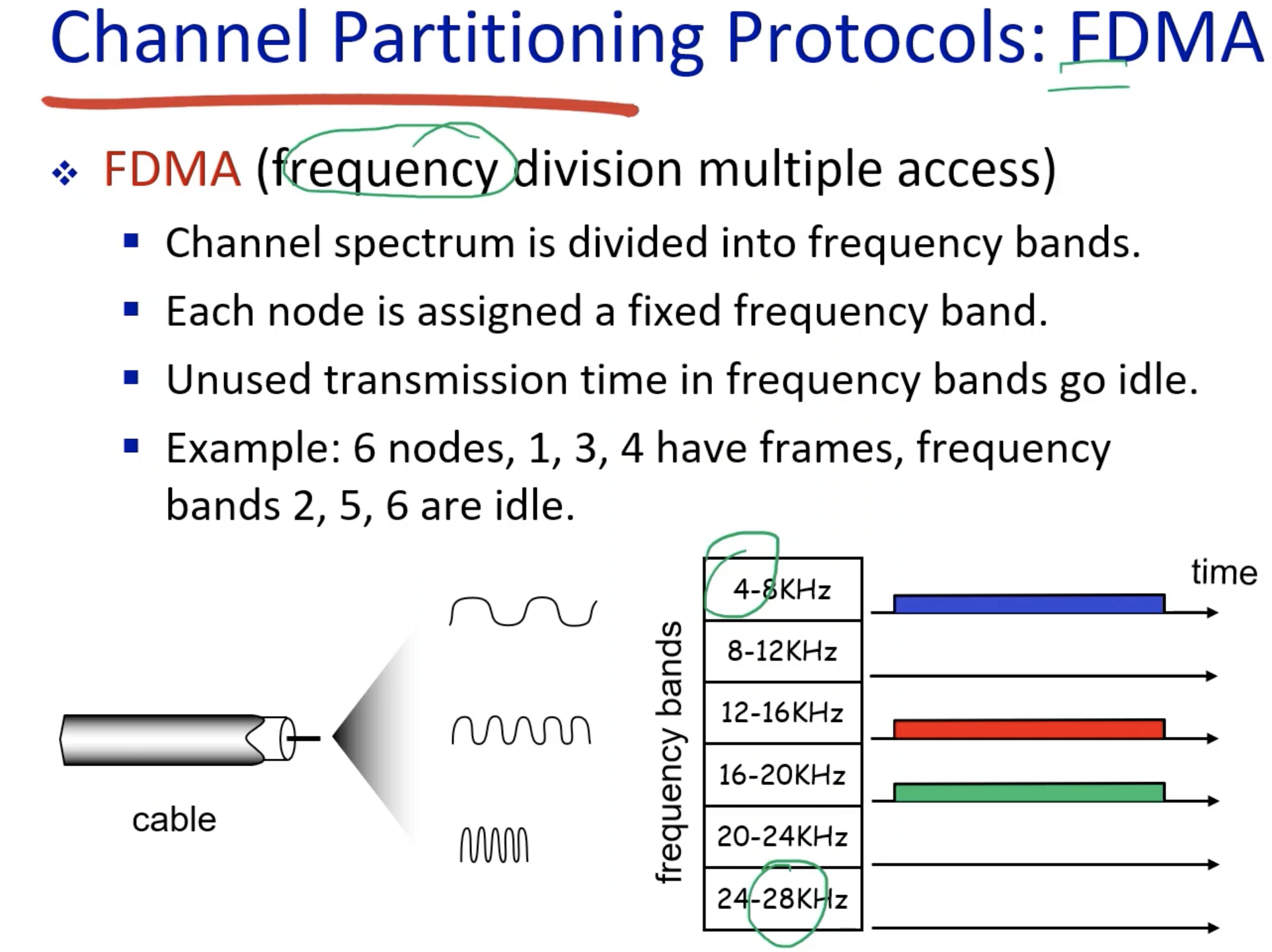
- The properties are the same as TDMA.
- In the diagram, each frequency bands are 4KHz. Equally allocated, and thus fair.
- Just like TDMA, idle nodes will make the allocated resources unused.
2. Taking-Turns Protocols
Very much like round-robin.
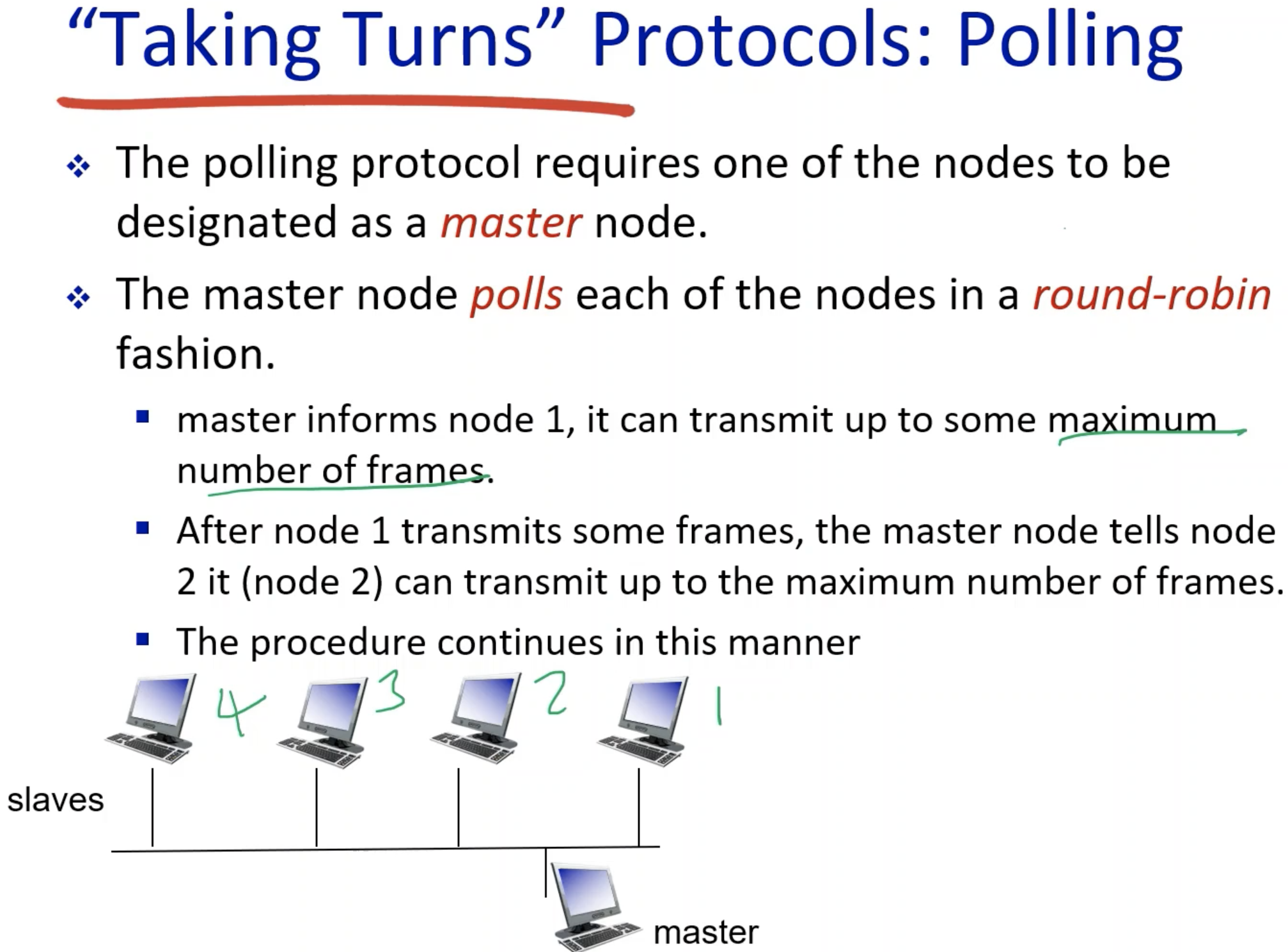

- Overhead?: there is no way to actually acheive the maximum bandwidth of R, because of the polling process.
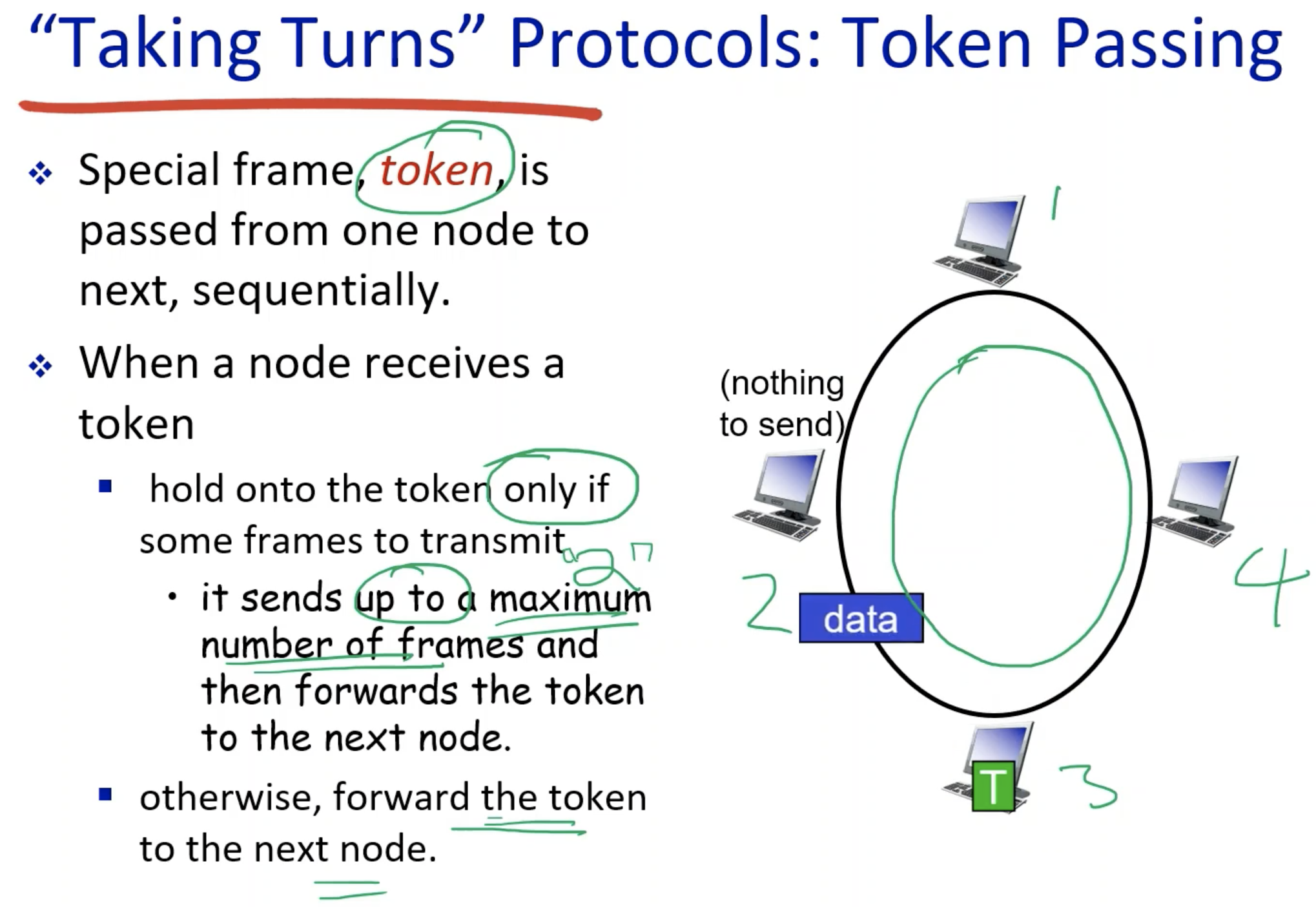
- Token passing is an example of "taking-turns" protocols.
- The node holds onto the token only if it has frames to be sent.
- The node passes the token if it does not have.
- When the node has the token, the node can only send the frame upto the maximum number of frames.
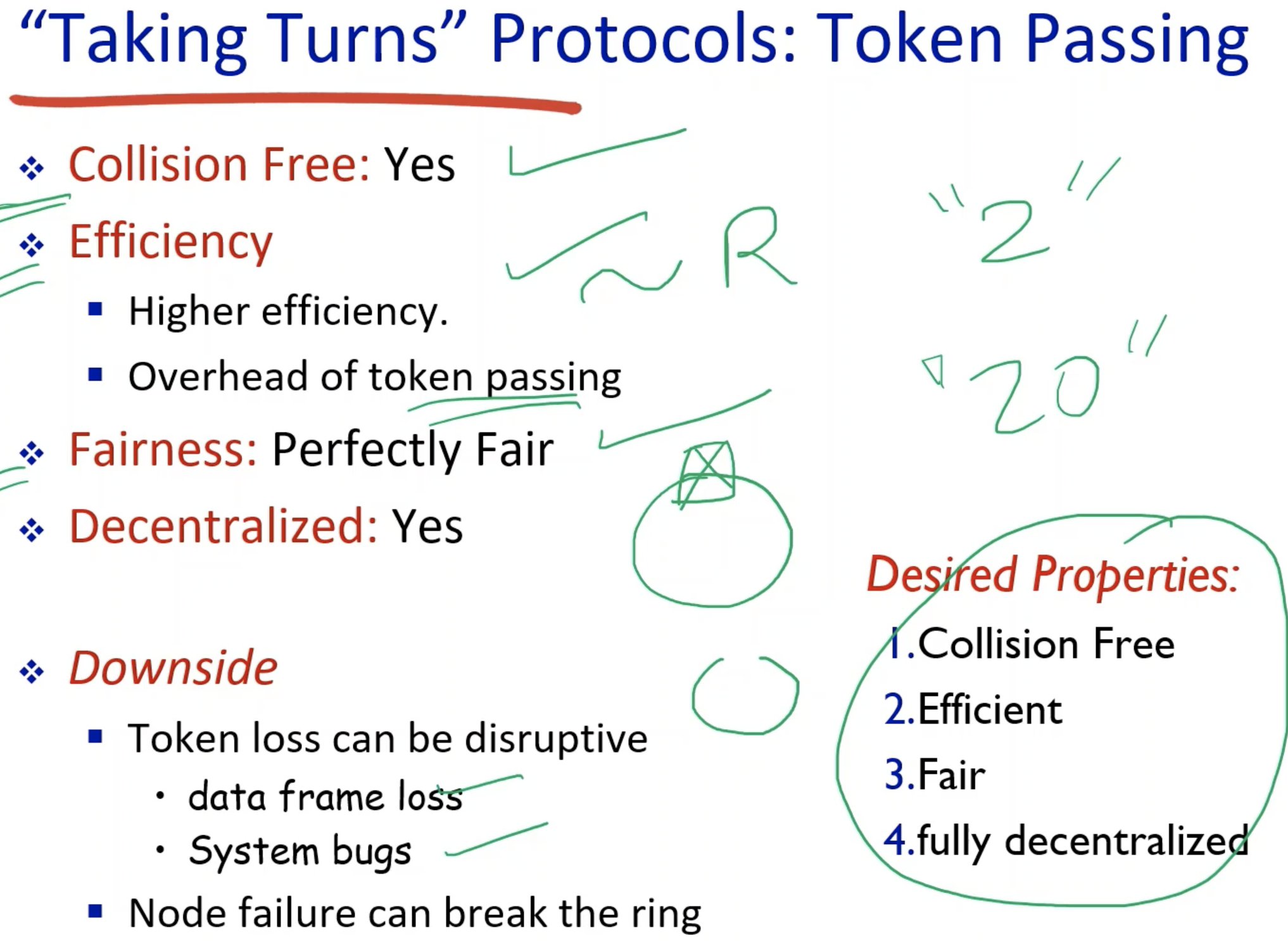
- Loss of token can be disastrous.
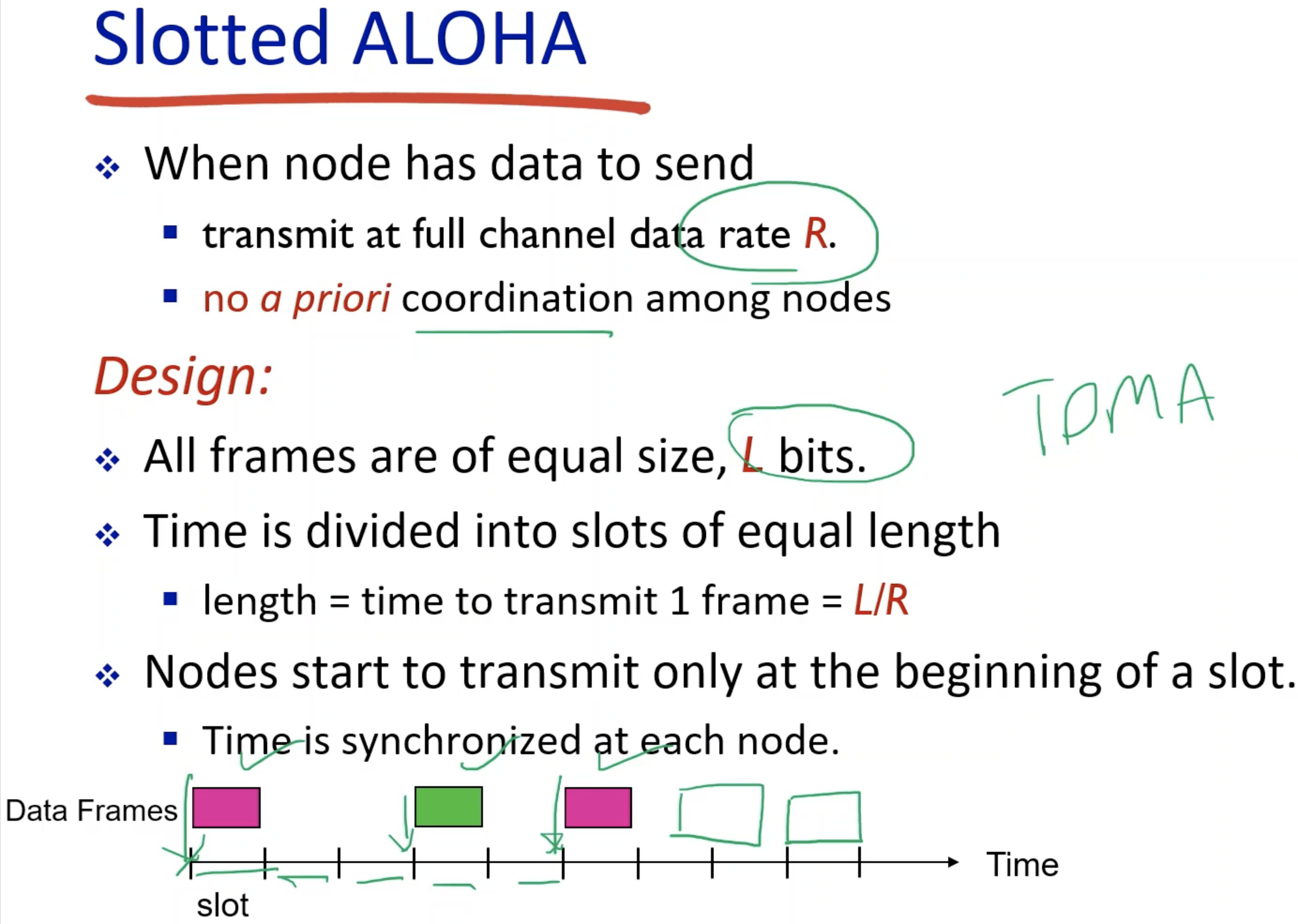
3. Random Access Protocols

- partition: wasted resources due to idle nodes
- Taking turns: needed master node or complicated protocol.
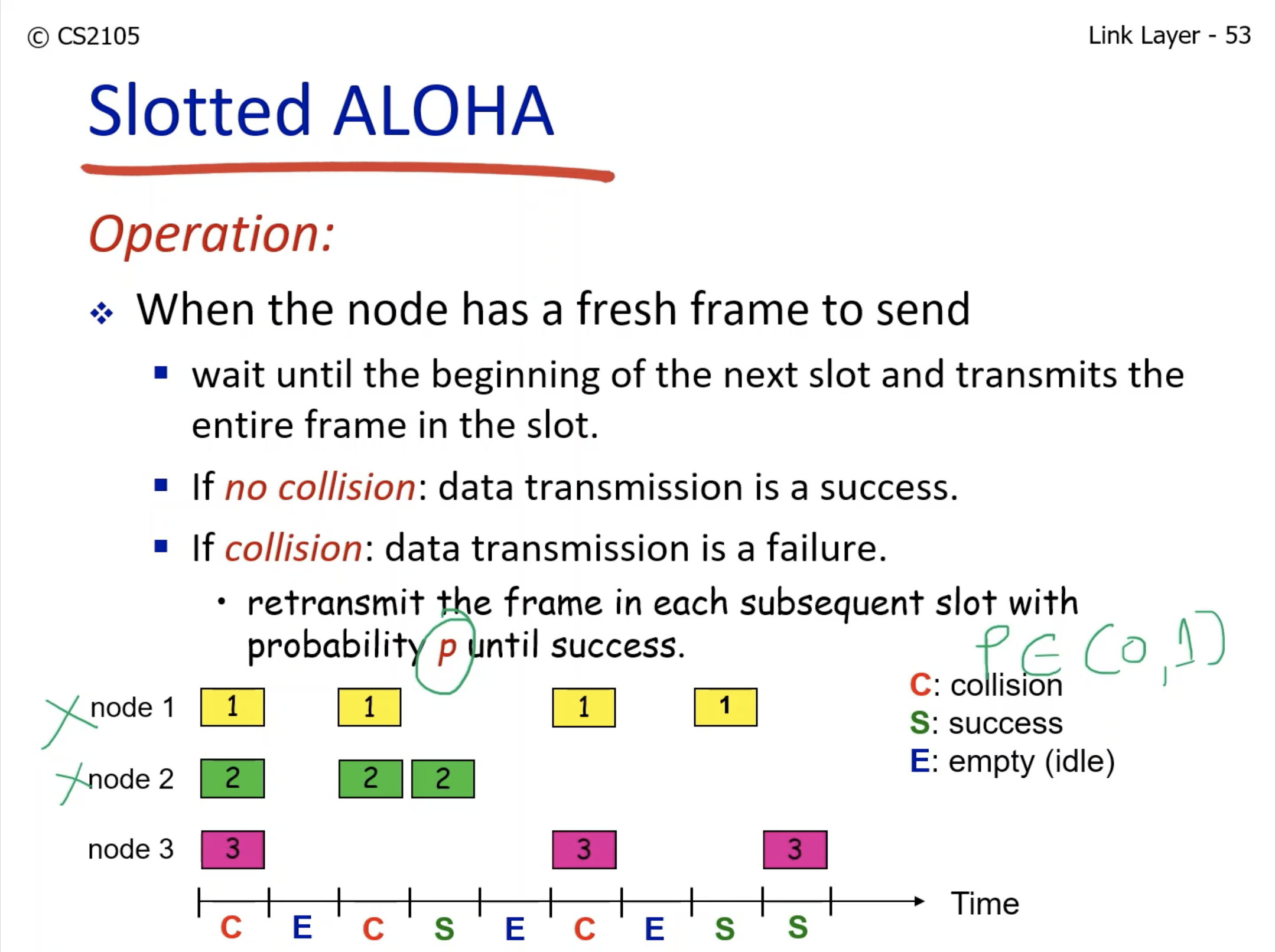
- If the two or more nodes win the chance to transmit the frame then there is a conflict.
- If none of the nodes get the chance to transmit, then it is empty (idle).
- It is like flipping a coin to decide which node gets to transmit.

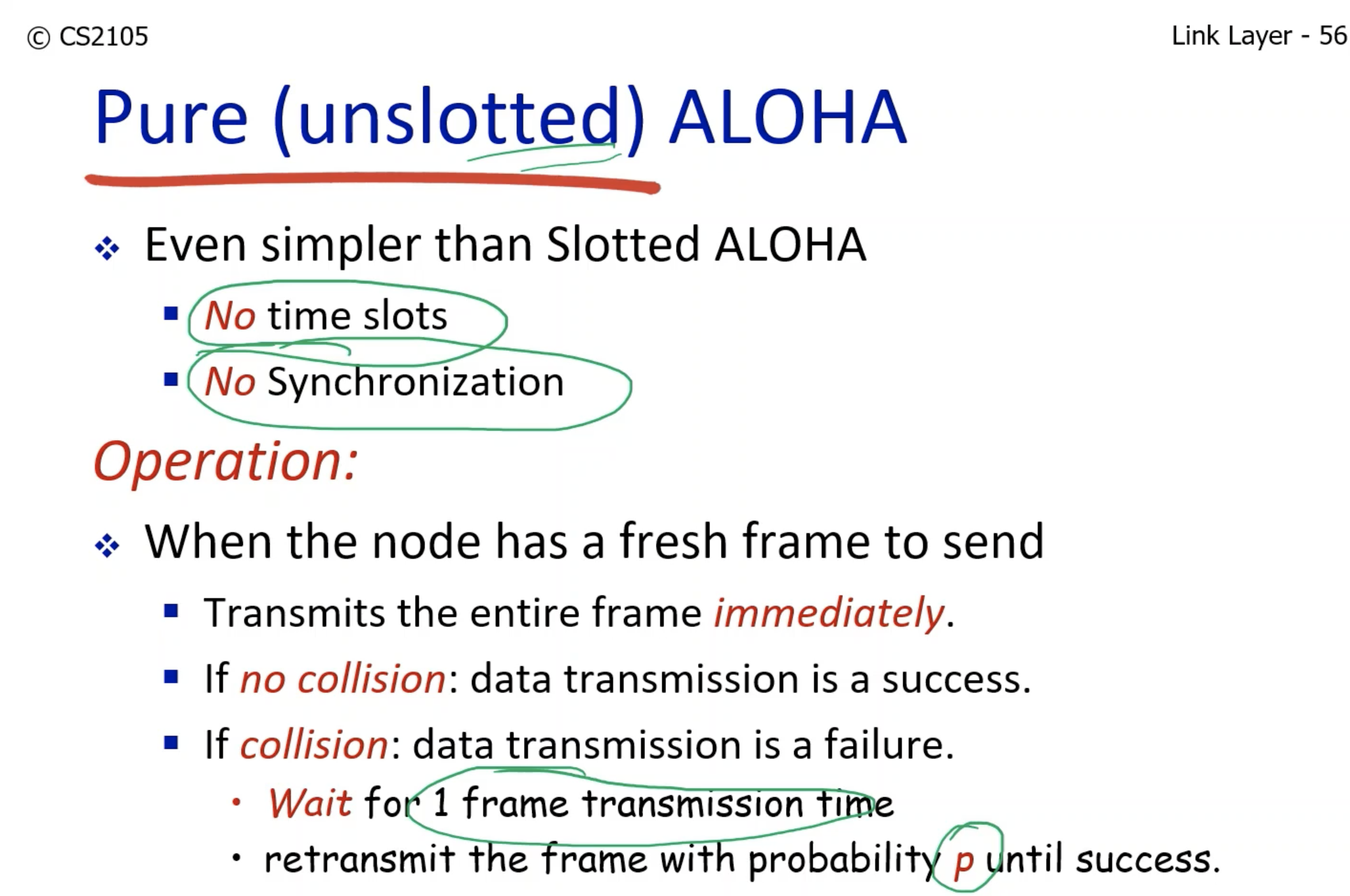


- The efficiency is halved, because the chance of colliding is almost doubled due to the overlap in transmission.
Design Flaws in RAP
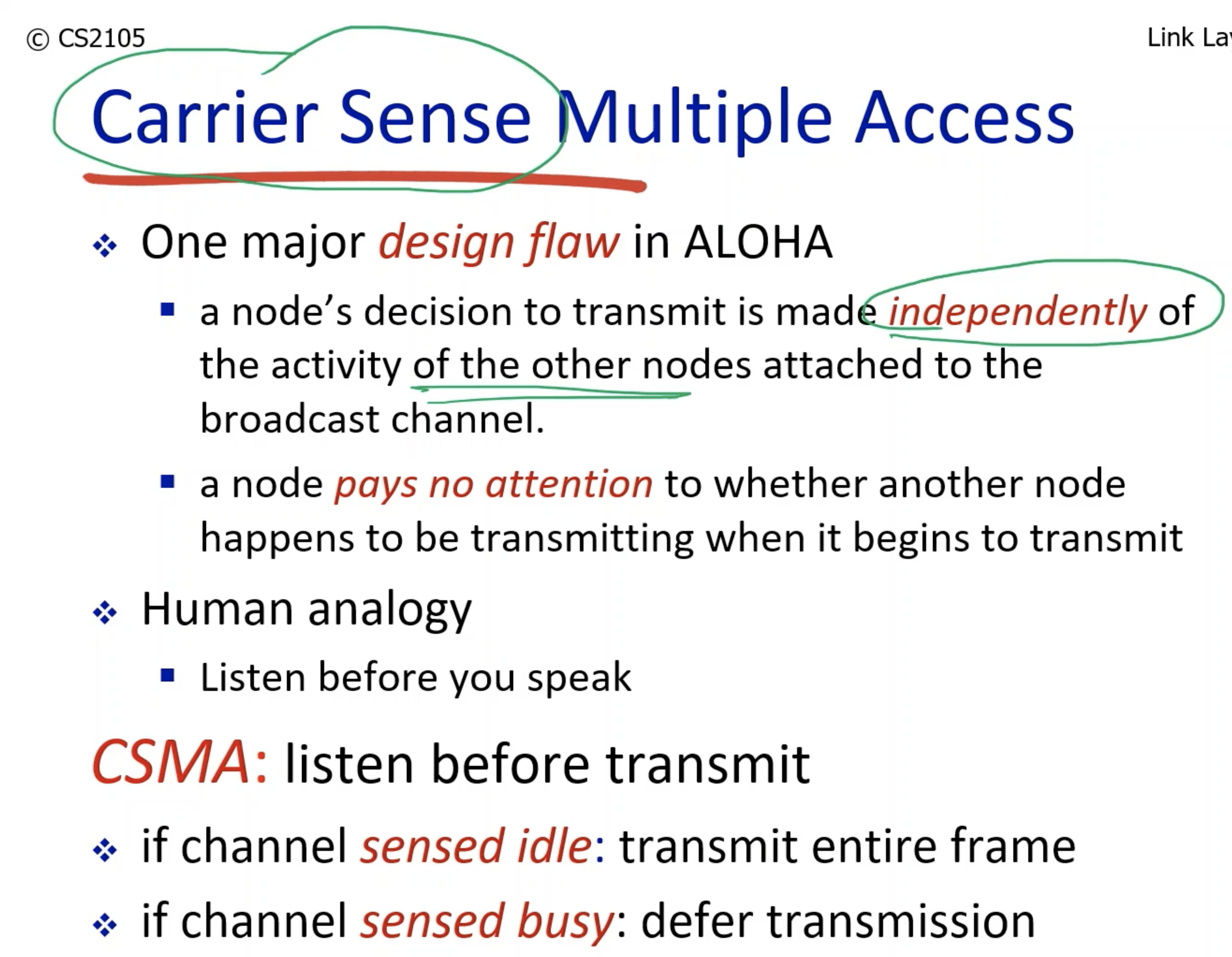
- Senses the channel. If the channel is busy, the transmission is deferred; otherwise if it is idle, the frame is transmitted.
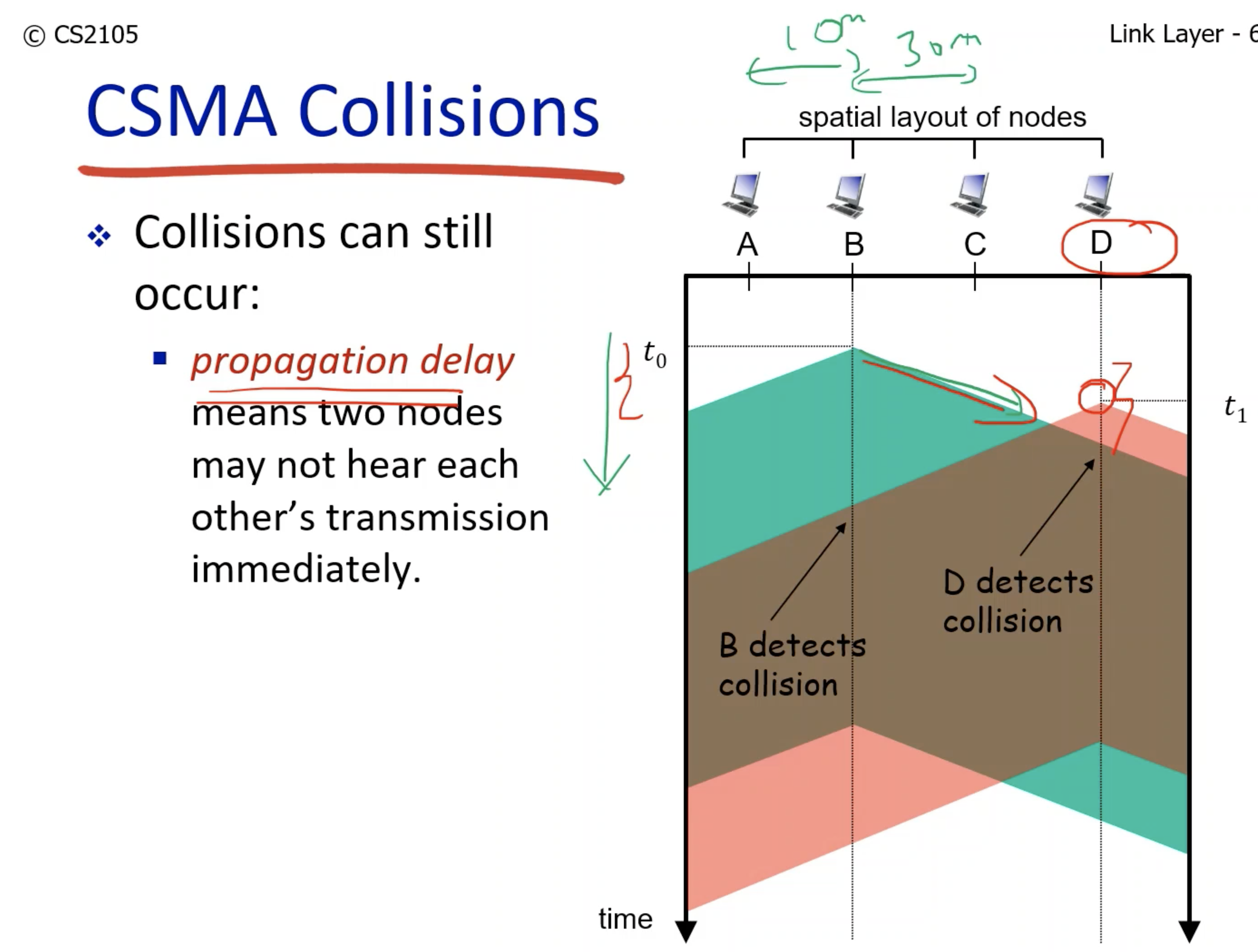
- Node B starts transmitting packets at time t0.
- However, when t1, D node listens to the channel and sees it is not busy because the packets are not fully transmitted yet due to the propagation delay.
- Therefore node D starts transmitting as well, resulting in collision.
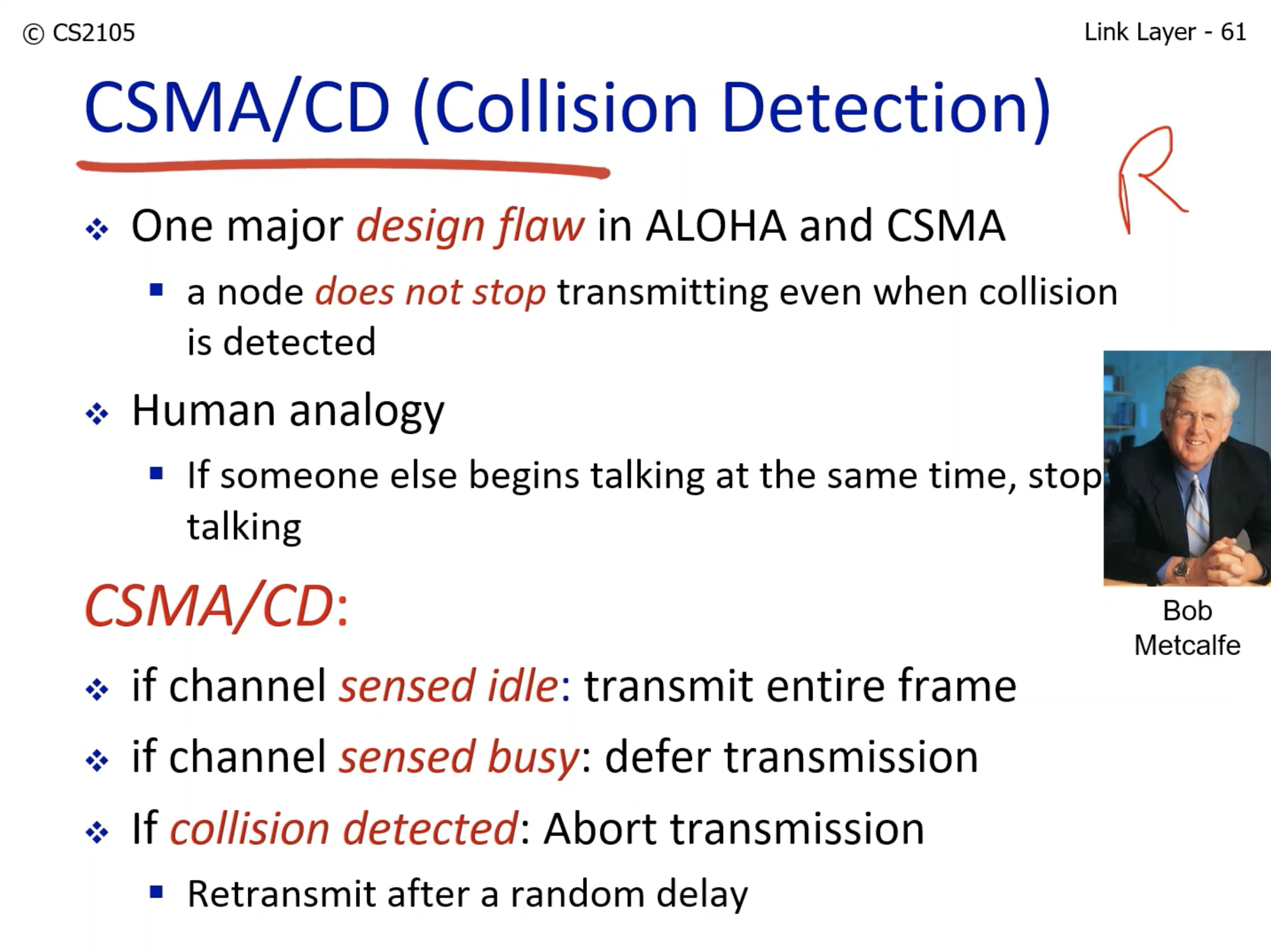
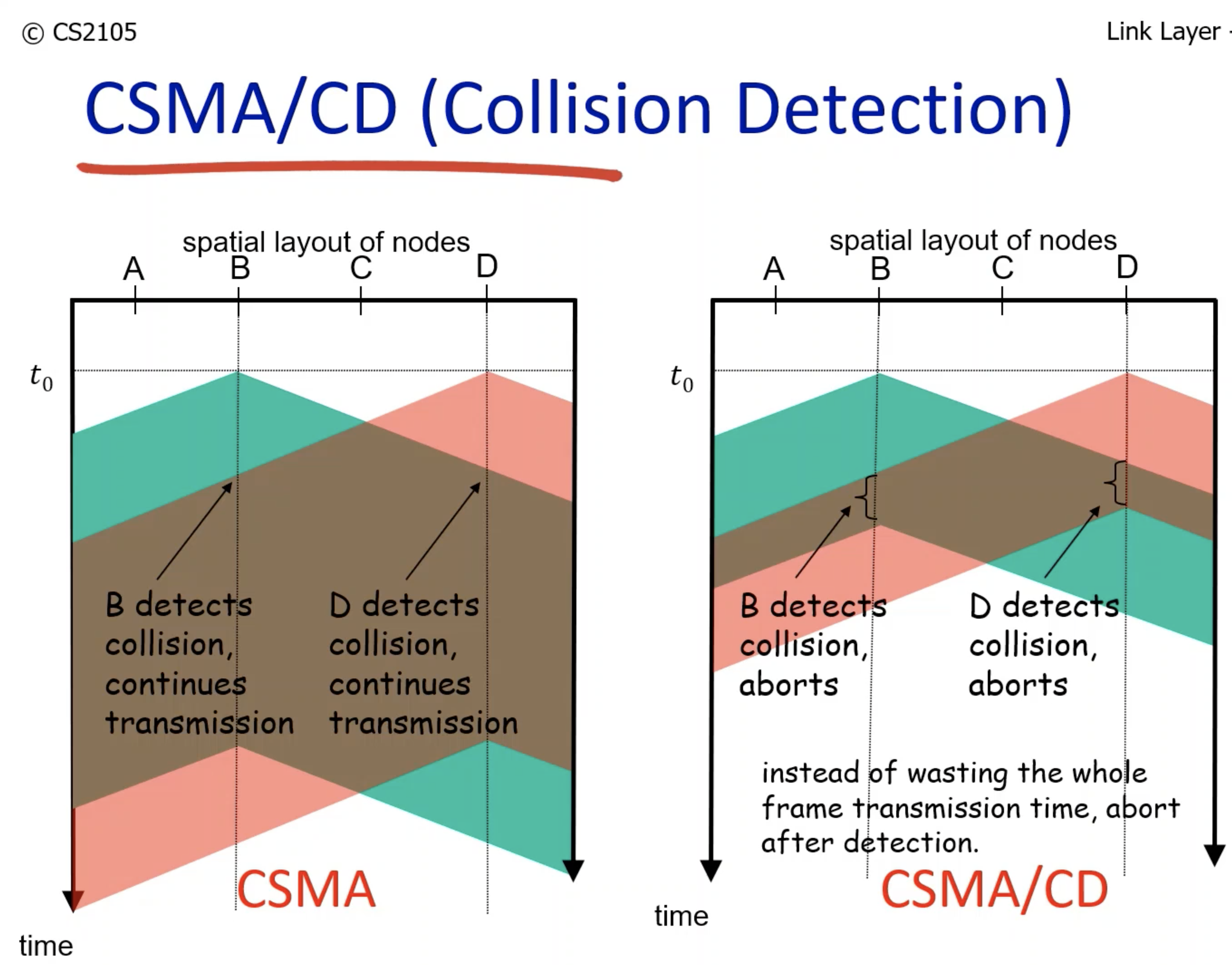
- When collision is detected, the transmission is aborted.
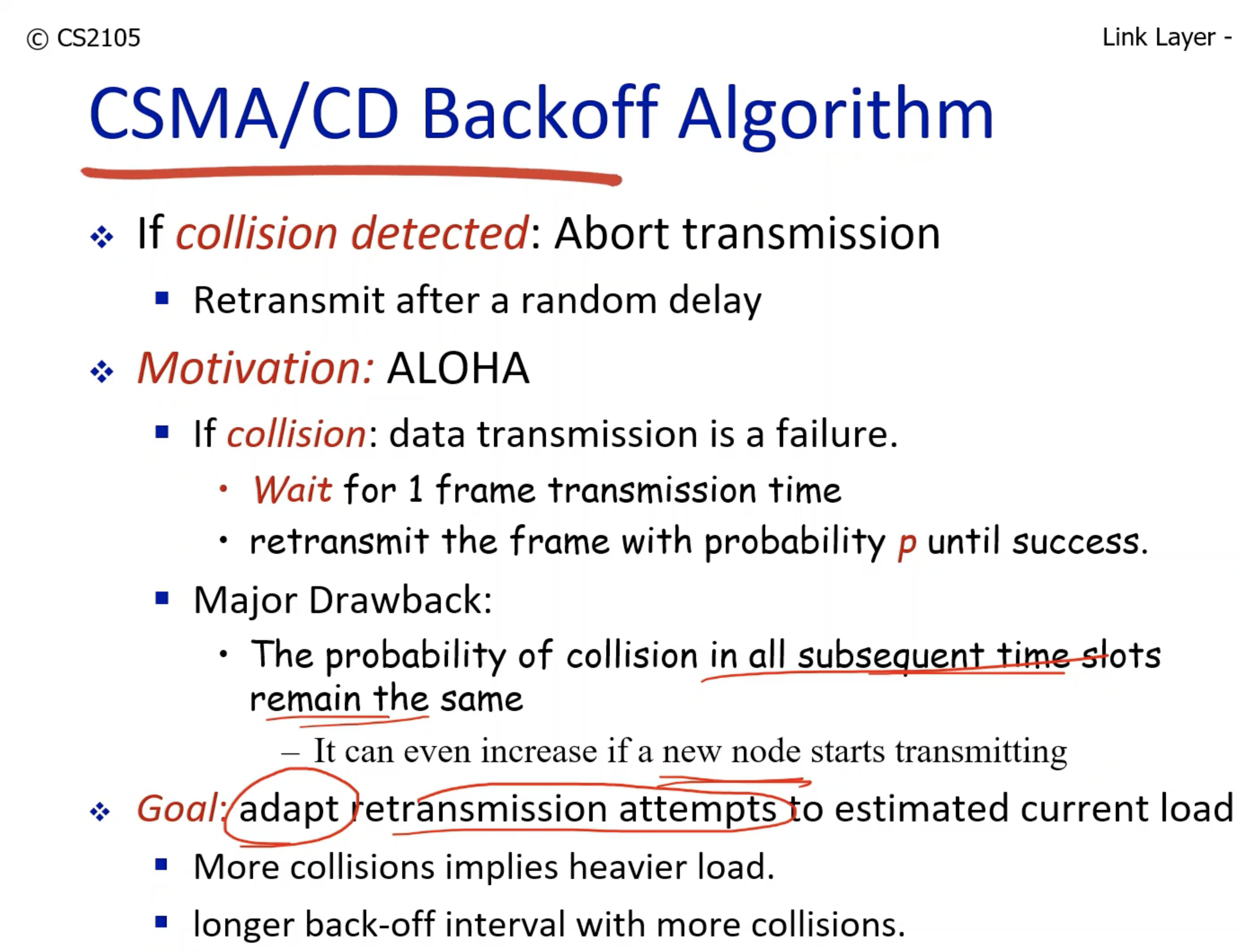
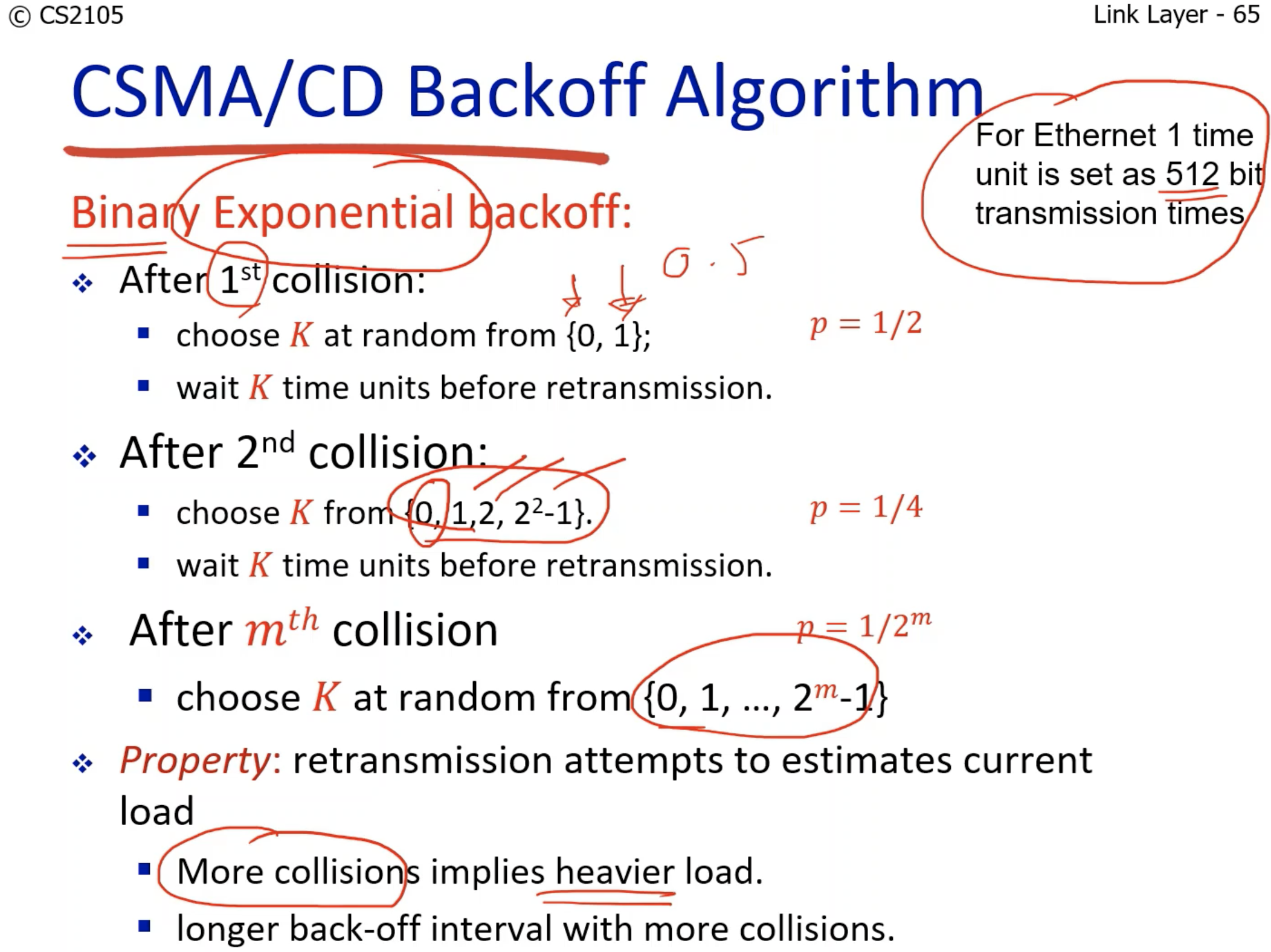
- The time delays of retransmission increases exponentially, and each node gets to pick one of the time delays randomly.

- If the size of the frame is too small, the collision may not be detected by the sending nodes, which causes no retransmission.
- The solution is to set the lower boundary (64 bytes) minimum.
