1. Question
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:
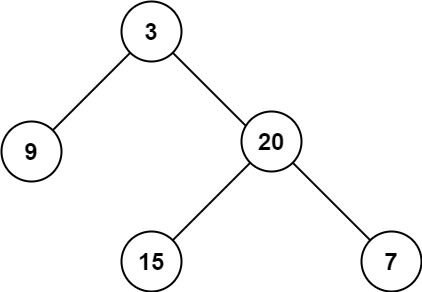
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 22. Thoughts
Use BFS
3. Tips learned
4. My solution
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
visited = []
queue = deque([(root, 1)])
max_depth = 1
while queue:
n, depth = queue.popleft()
if n not in visited:
visited.append(n)
if n.left:
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth + 1)
queue.append((n.left, depth + 1))
if n.right:
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth + 1)
queue.append((n.right, depth + 1))
return max_depth39/39 cases passed (134 ms)
Your runtime beats 5.86 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 79.8 % of python3 submissions (17.8 MB)5. AI Solution and Improvements
Your solution for finding the maximum depth of a binary tree uses a breadth-first search (BFS) approach, which is a valid method. However, there are some improvements that can be made to optimize and simplify your code:
Improved Solution
-
Avoid Using
visitedList: In a tree structure, unlike graphs with cycles, you don't need to keep track of visited nodes. Each node is visited exactly once. -
Simplify Depth Calculation: The depth of the tree can be maintained without explicitly keeping track of it for each node. Instead, you can increment the depth as you go level by level.
Here's the revised code:
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([root])
max_depth = 0
while queue:
max_depth += 1
level_size = len(queue) # Number of nodes at the current level
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return max_depthExplanation
- Queue for BFS: A queue is used to perform a level-order traversal (BFS) of the tree.
- Depth Calculation: The maximum depth is incremented for each level in the tree. At each level, all nodes of that level are processed, and their children are added to the queue for the next level.
- No Need for
visitedList: Since a tree doesn't contain cycles (unlike graphs), there's no need to check if a node has been visited before.
Benefits of the Improved Solution
- Efficiency: The solution is more efficient as it avoids unnecessary checks for visited nodes.
- Simplicity and Readability: The code is simpler and more intuitive, focusing directly on the task of finding the maximum depth using BFS.
