1. Question
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
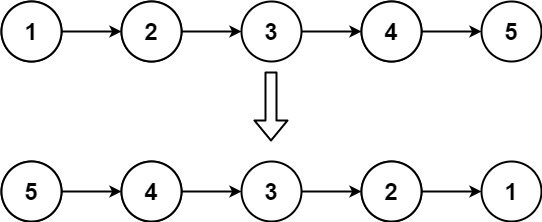
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]Example 2:
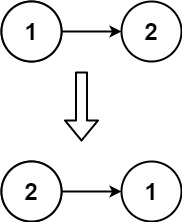
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []2. Thoughts
Make 3 pointers: prev ; current ; next.
next stores the node so that it can be later linked.
current changes the "next" value from the next to the prev so that the link is reveresed.
3. Tips learned
4. My solution
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# List num = 1
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
prev = head
current = head.next
prev.next = None
if current.next == None:
current.next = prev
return current
next = current.next
while True:
# change next dir
current.next = prev
# iterate
prev = current
current = next
if next.next == None:
break
else:
next = next.next
current.next = prev
return current
28/28 cases passed (42 ms)
Your runtime beats 57.54 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 79.26 % of python3 submissions (17.8 MB)5. AI Solution and Improvements
Your implementation for reversing a singly linked list in Python is functional, but there are ways to make it more efficient and cleaner. Let's discuss an improved version of your code.
Improved Solution
The key to simplifying the solution is to use a while loop that iterates through the list once, reversing the pointers as it goes. Here's an improved version of your solution:
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev = None
current = head
while current:
next_node = current.next # Store the next node
current.next = prev # Reverse the link
prev = current # Move prev forward
current = next_node # Move current forward
return prev # At the end, prev will be the new head of the reversed listExplanation
-
Initialize Two Pointers: We use two pointers,
prevandcurrent. Initially,previs set toNone, andcurrentis set to the head of the list. -
Iterating Through the List: We iterate through the list using a while loop until
currentisNone. This means we've reached the end of the list. -
Reversing Links: Inside the loop, we perform the following steps:
- Store
current.nextinnext_nodebefore changingcurrent.next. - Set
current.nexttoprevto reverse the link. - Move
prevtocurrent. - Advance
currenttonext_node.
- Store
-
Return New Head: After the loop ends,
prevwill be pointing to the new head of the reversed list (which was the end of the original list), and we returnprev.
Benefits of the Improved Solution
- Simplicity: The improved solution is simpler and easier to understand.
- Efficiency: It traverses the list only once and doesn't require checking for special cases outside the loop.
- Readability: The code is more concise, making it easier for others to read and understand.
This approach is a standard way to reverse a singly linked list and is widely used due to its simplicity and efficiency.
