ch10. Neural Network and Neural Language Models
Neural Networks

input layer, output layer, 두 레이어 간의 weighted sum 이라는 연산 이 존재하면 우리는 NN이라고 함..
근데 사실 hidden layer가 한 층이라도 꼭 있어야함.. 그래야 Neural network 라고함..
Logistic Regression

이론적으로는 NN이지만 실무에서는 NN이라고 얘기하기엔.. 좀 그럼..
그러면 word2vec?
이건 2개의 weighted matrix, 한층의 hidden layer -> NN이라고 할 수 있음
Feedforward Neural Networks

데이터의 흐름이 한 방향으로만 있는 것(역방향, 사이클 x)
- 이전 레이어의 모든 유닛 - 다음 레이어에 있는 모든 유닛과 연결되어있음
- 초기 정의는 맞지만 이제는 아님
- 이 정의는 'fully connected neural networks' 라는게 더 맞는 표현임
- 데이터가 정방향으로만 흐르기만 하면 됨
- fully connected neural network 가 이 안에 속할 수 있음
- hidden layer 가 외부 사용자에게 제공되지 않음
- input, output layer만 보여줌
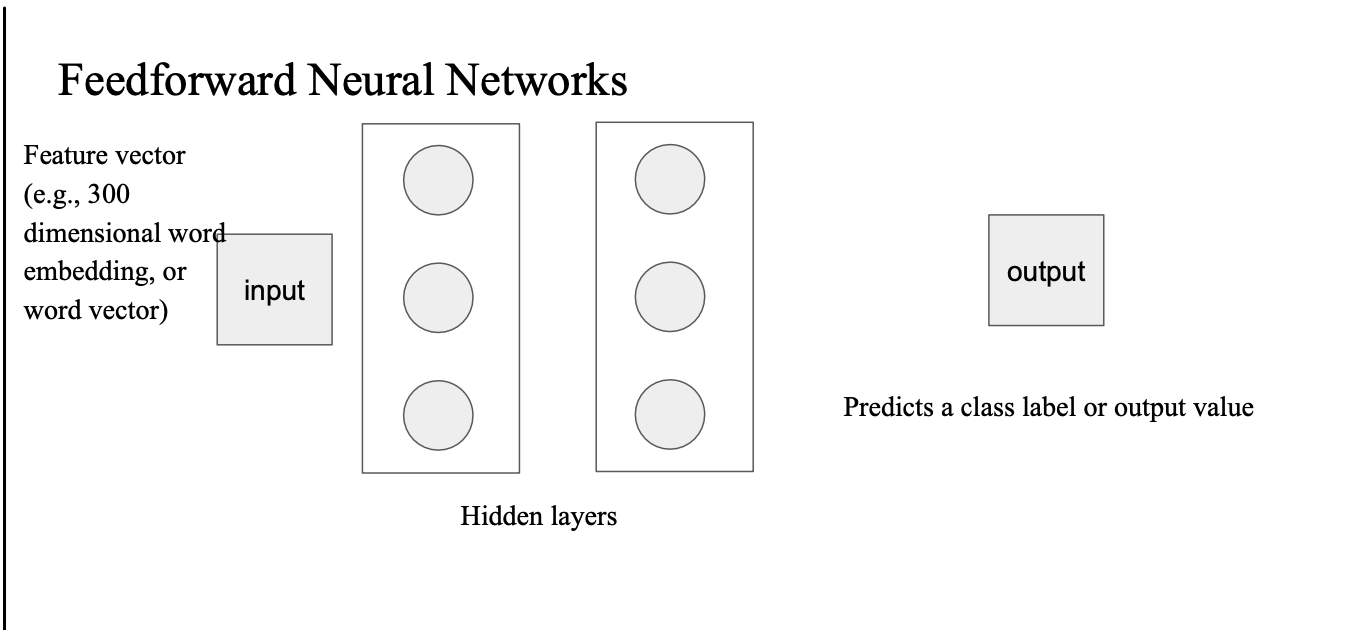
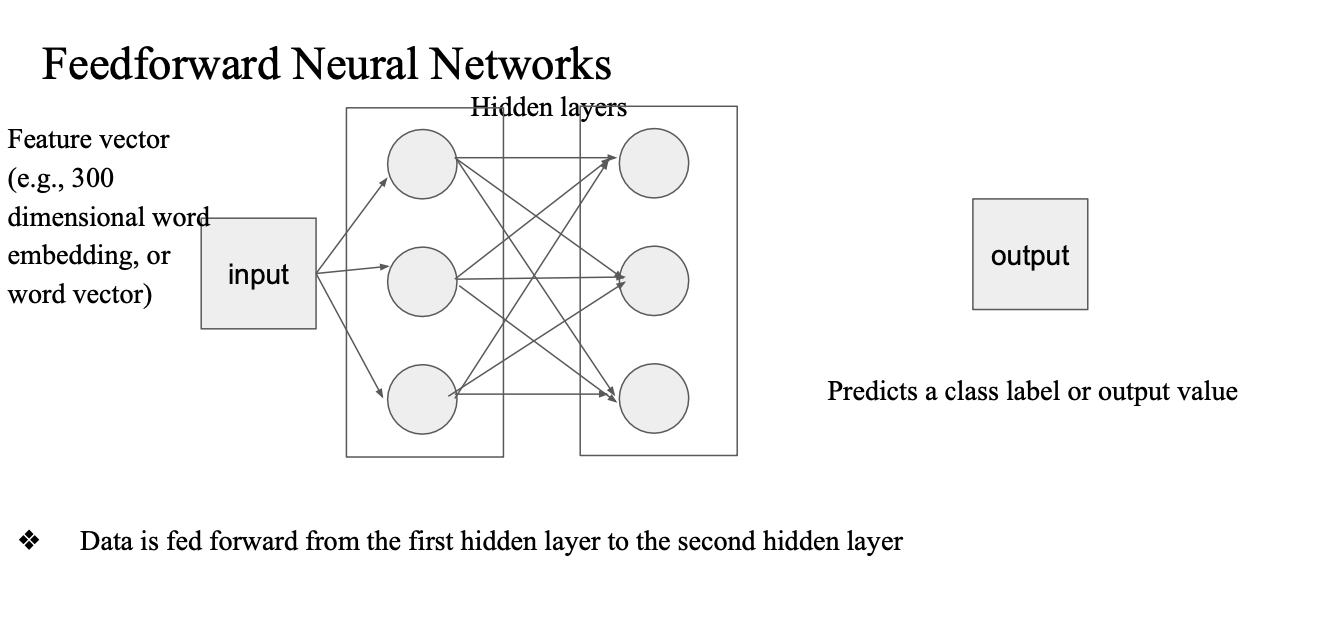
어떤 인풋이 들어옴 -> word vector 가 첫번째 히든 레이어에 프로젝션 된다.
그리고 다음 레이어에 프로젝션된다..
output layer도 마찬가지로 모든 뉴런에서 받게 됨
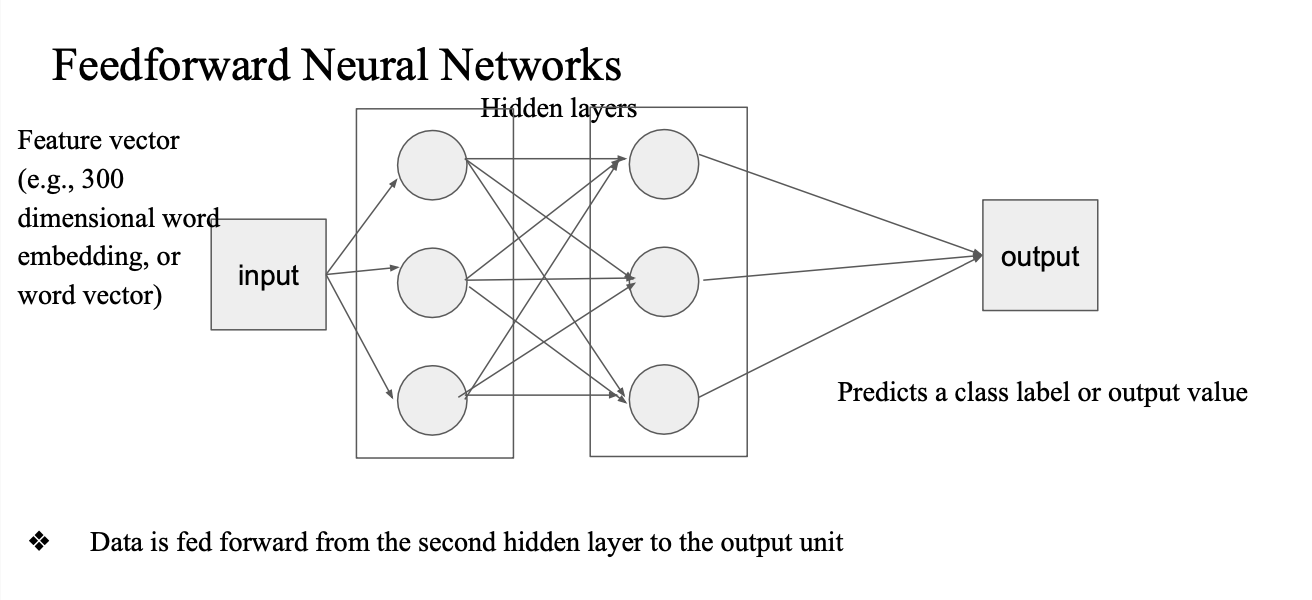
classifier 면 output을 베이스로 얻은 pred 값과 true class label 을 비교해서 loss값 계산 -> back propagation 과정 -> weight 조금씩 수정
python output = model(input) loss = loss_fn(output, target) loss.backward() optimizers.step()
Deep learning

NN에서 hidden layer가 깊어지면...
deep 하다..?
어느정도..?
-> 12층... LLM은 32층...

딥러닝이 성능이 그럼 좋냐?
- 항상 그런건 아니다...
- 데이터가 필요함...
- 각 case 별로 테스트가 필요함
- 왜 그럼 딥런이 모델이 뭐가 좋길래?
- 전통적인 ML알고리즘의 기본 가정 -> 선형분리가 가능하다..
- 이 선을 배우기만 하면 된다...라는 가정임 (단순한 task 에서 잘 할 수 있음)
- 근데 딥러닝에서는 nonlinear function 이 존재
- 비 선형 관계도 학습할 수 있다...
- 그렇지만 복잡한 관계를 배우기 위해서는 데이터가 많이 필요하다..
- feature engineering 단순하고 랜덤하게..
- 근데 딥러닝에서는 nonlinear function 이 존재

장단점이 있음
Nueral Language Models
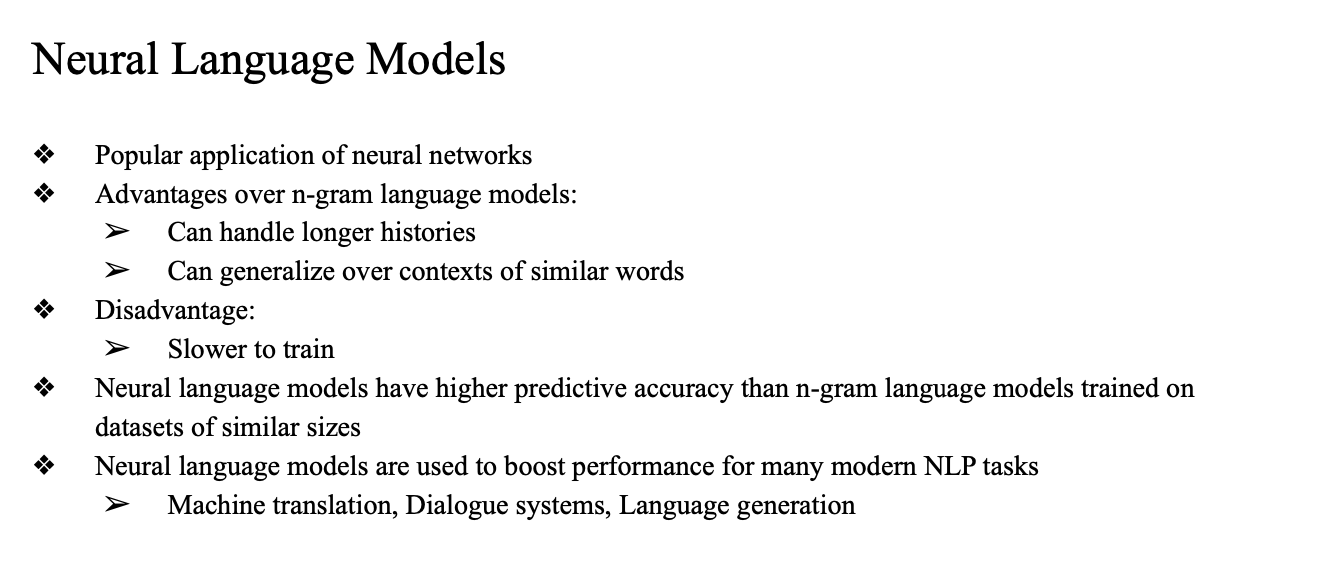
이전까지는 (n-gram LM)prob을 어떤 corpus 가 존재한다고 했을 때 모두 계산해두고 이 결과를 모델로 썼던 건데
이제는 어떤 모델을 가지고 훈련을 시켜서 sentence prob 을 구할때 NLM을 써보자..
language model 이라는건 현실에 존재하는 언어를 유사하게 따라하고 싶은 것
Feedforward Neural Language Model

- "a b c d e" 문장이 있을때
- 전체 vocab : a, b, c, d, e, f ...
- a b c 가 나왔을 대 e 보다 d가 나올 확률을 더 높이는 것
- 이런 관계를 다 배우는 것
- next word prediction
- language model objective
- 지식 주입의 목적
- model architecture:
- nn.Embedding
- 단어 인덱스를 고정 차원 벡터로 변환
- (Flatten)
- 여러 단어의 임베딩 벡터를 하나의 벡터로 이어붙임 (배치 프로세싱을 안한다면)
- nn.Linear(히든레이어)
- 임베딩 벡터 shape을 다음 레이어에 매핑하기
- nn.Linear(출력층)
- hidden representation → vocab 크기만큼의 로짓
- 예를들면, 출력 [1, vocab_size]
- 간단하게 2개의 hidden
- transformer가 12층이 쌓일 수도 있음
- 마지막에선느 Loss
- crossEntropyLoss
- 모델 출력 [1, vocab_size] 와 정답 인덱스(Gold Label) [1] 비교해서 loss 계산
- crossEntropyLoss
- nn.Embedding
nn.Embedding -> (Flatten) -> nn.linear(히든레이어) -> nn.linear(출력층) -> Loss(crossEntropyLoss)
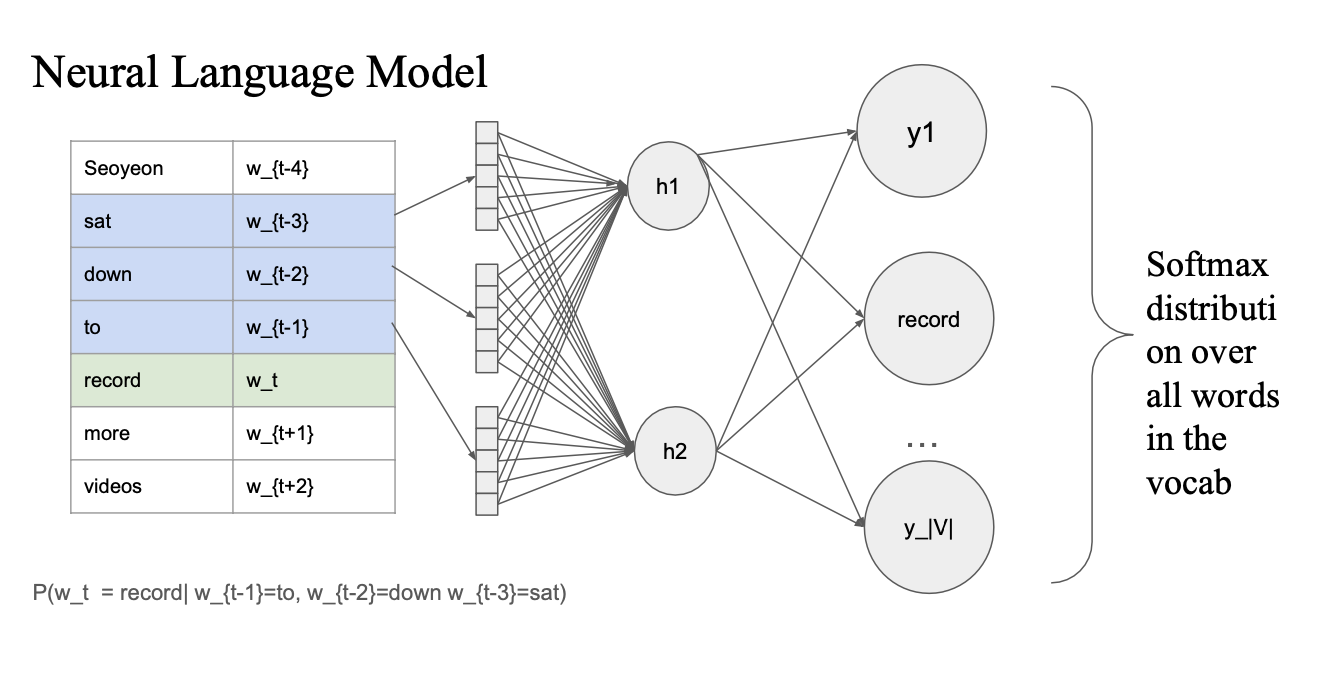
context word (previous word) 가 있었을때
hidden layer 의 input으로 주면 -> vocab word 중에 record 가 가장 높은 값을 갖게끔...
softmax를 취해서 vocab distribution 을 구한다음에 record에 해당하는 부분을 gold label 1 로 설정해서 training...

- pretrained 된 word2vec을 쓸것이냐..?
- 이게 보통 더 좋긴함
Feedforward Neural Language Model Example
training data:
- you need a data
- i neea a data
vocab = [you, need, a, data, i], window size = 3, embedding_dim = 50, 1st hidden layer dim = 150 이라면,
- possible input-output pairs = (you need a) -> data, (i need a) -> data
- shape of the weight matrix for the nn.Embedding?
- [5, 50] ([vocab, embedding_dim])
- output of nn.Embedding
- [3, 50] -> (flatten) -> [1, 150] (no batch processing, and for 1st hidden layer)
- shape and output vector of 1st hidden layer
- [150, 150], [1, 150]
- shape and output vector of 2nd hidden layer
- [150, 5], [1, 5]
- vocab size = 5
- [150, 5], [1, 5]
- two inputs of nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- prediction [1, 5] -> 모델의 logits
- gold label [5] -> 정답 word(여기서는 data)의 vocab 인덱스 -> [3]
criterion(pred_logits, target_index)- you need a, data
