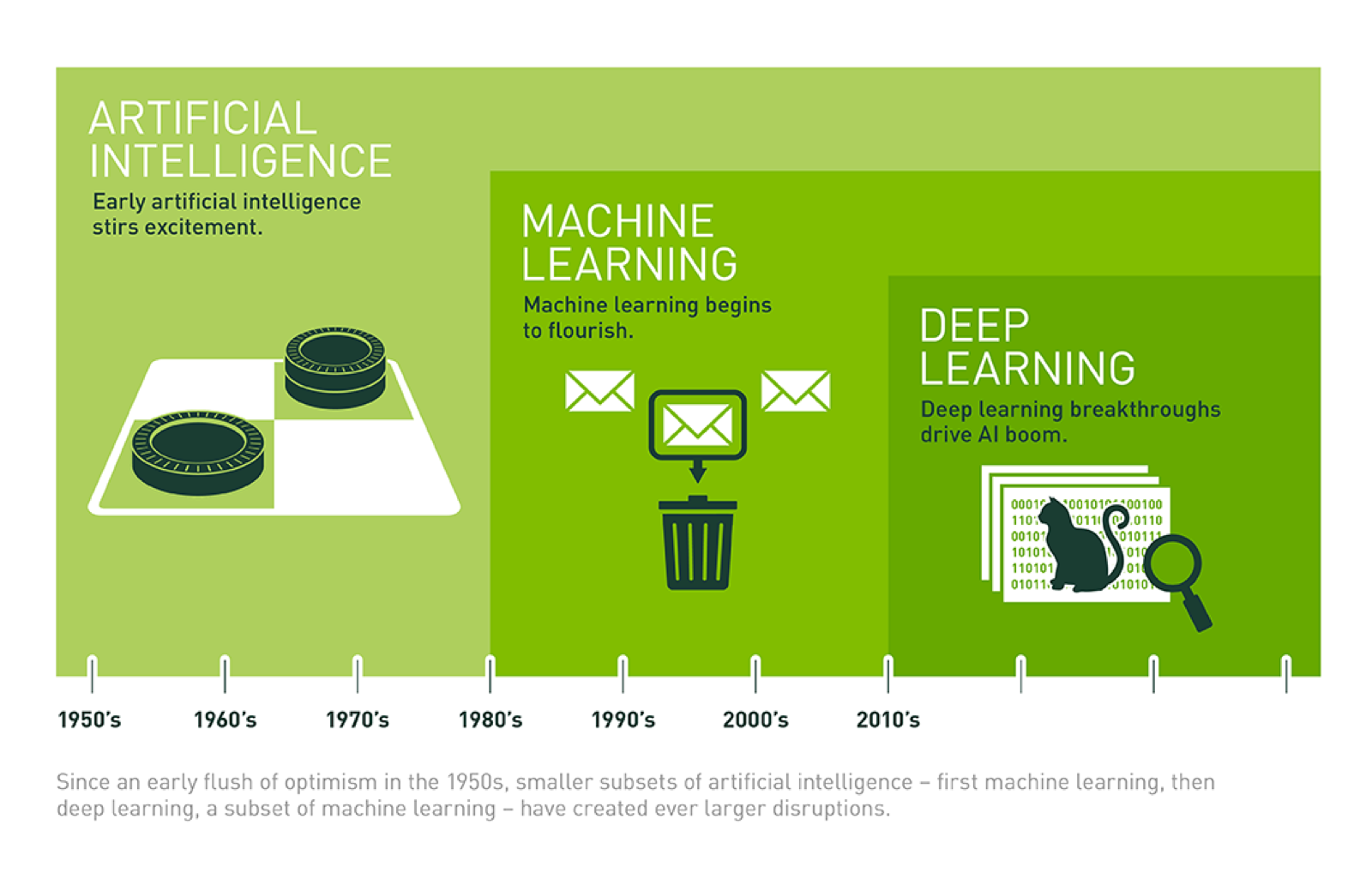
[ ML/DL & AI ] ML & AI 엔지니어링 공부 01 : 쉽게 정리해본 LLM.

▽쉽게 정리해본 LLM.
목 차
1. LLM이란 무엇인가?
2. LLM의 작동 원리
3. LLM의 파라미터와 모델 크기
4. LLM의 협력 시스템(멀티 에이전트)
5. LLM의 학습과 피드백
6. LLM을 활용한 서비스 구현
1. LLM이란 무엇인가?
정의:
- LLM(Large Language Model)은 자연어 처리(NLP) 기술의 발전으로 인해 가능해진 AI 모델로, 텍스트를 입력받아 이해하고 다시 텍스트로 답변하는 능력을 갖추고 있습니다.
- LLM은 인간과 유사한 수준의 언어 이해와 생성 능력을 제공하며, 다양한 응용 분야에서 활용되고 있습니다.
대표 모델:
-
GPT-4o: OpenAI에서 개발한 최신 모델로, 다양한 언어와 작업을 지원합니다.
- GPT-4o는 이전 모델에 비해 더 많은 파라미터를 가지고 있어, 더 정교한 답변을 제공할 수 있습니다.
-
Claude 3: Anthropic에서 개발한 모델로, 안전성과 정확성을 강조합니다.
- Claude 3는 사용자에게 더 신뢰할 수 있는 답변을 제공하기 위해 설계되었습니다.
-
Grok3: xAI에서 개발한 모델로, 인간의 과학적 발견을 가속화하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
- Grok3는 과학적 문제 해결에 특화된 기능을 제공합니다.
기능.
-
텍스트 생성: 주어진 프롬프트에 따라 문장을 생성합니다.
- 이는 창작물 작성, 번역, 요약 등 다양한 작업에 활용될 수 있습니다.
-
코딩: 코드 작성, 디버깅, 설명 등을 할 수 있습니다.
- LLM은 개발자에게 코드 작성 시 도움을 주며, 코드의 오류를 찾는 데도 유용합니다.
-
이미지 분석: 이미지에 대한 설명을 제공하거나, 이미지와 관련된 질문에 답변할 수 있습니다.
- 이는 이미지 분류, 객체 탐지 등 다양한 컴퓨터 비전 작업에 활용될 수 있습니다.
-
수식 풀이: 수학 문제를 이해하고 풀이 과정을 설명할 수 있습니다.
- 이는 학생들에게 수학 문제 해결에 도움을 줄 수 있습니다.
from openai import OpenAI
# OpenAI API 키 설정
client = OpenAI(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# 모델과 프롬프트 설정
MODEL = "gpt-4o"
prompt = "Hello, how are you?"
# 문장 생성
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=MODEL,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
print("Assistant: " + completion.choices[0].message.content)

2. LLM의 작동 원리
입력과 출력:
-
LLM은 텍스트를 입력받아 이를 토큰화하고, 학습된 데이터를 기반으로 다음 토큰을 예측합니다.
- 이 과정을 반복하여 문장을 생성합니다.
- 예를 들어, 사용자가 "안녕하세요"라는 문장을 입력하면, LLM은 이를 토큰화하여 "안녕", "하", "세", "요"로 나누고, 다음으로 올 수 있는 토큰을 예측합니다.
- 이 과정을 반복하여 문장을 생성합니다.
-
API 호출: LLM은 직접 API를 호출하지 않으며, 실제 호출은 개발자가 코드로 구현해야 합니다.
- 예를 들어, LLM이 특정 기능을 수행하도록 요청할 때, 함수 호출을 통해 이를 구현할 수 있습니다. 이는 LLM이 외부 API나 데이터베이스와 상호작용할 수 있도록 합니다.

RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation):
- 최신 정보를 반영하기 위해 LLM이 대답하기 전에 필요한 자료를 넣어주고, 이를 기반으로 답변하는 기술입니다.
- 이는 LLM이 외부 데이터베이스나 문서에서 정보를 검색하여 답변의 정확성을 높이는 방법입니다.
- 예를 들어, 사용자가 "현재 뉴스"에 대한 질문을 하면,
LLM은 외부 데이터베이스에서 최신 뉴스를 검색하고 이를 기반으로 답변을 생성합니다.
- 예를 들어, 사용자가 "현재 뉴스"에 대한 질문을 하면,
LLM이 아무리 똑똑해도,
이미 학습한 데이터만 가지고 답을 생성하게 된다는 단점이 있습니다.
그럼 최신 뉴스나 사내 문서 같은 정보는 어떻게 불러오는걸까요?
그때 필요한 게 RAG입니다.
외부 데이터베이스에서 필요한 정보를 먼저 검색(Retrieval)하고,
그 정보를 기반으로 답변을 생성(Generation)하는 방식입니다.
이렇게 하면 LLM이 최신 정보도 반영하여 결과를 Return 할 수 있습니다.
즉, LLM이 대답하기 이전에 먼저 대답에 필요한 자료들을 넣어주고,
요약 또는 이를 기반으로 대답하는걸 모두 RAG라고 하는거죠
3. LLM의 파라미터와 모델 크기
파라미터.
- LLM 모델의 크기는 학습한 파라미터의 개수로 나타납니다.
( 8B, 70B 같은 숫자들 == 모델이 학습한 파라미터 개수)- 예를 들어, 8B(8 billion) 파라미터, 70B(70 billion) 파라미터 등이 있습니다.
- 파라미터가 많을수록 모델은 더 많은 데이터를 학습할 수 있어 정교한 답변을 제공할 수 있습니다.

- 모델 크기와 성능: 큰 모델일수록 더 많은 데이터를 학습할 수 있어 정교한 답변을 제공할 수 있지만, 속도와 비용이 부담될 수 있습니다.
- 요즘은 경량 모델을 잘 활용하는 것이 트렌드입니다.
- 경량 모델은 작은 파라미터로도 높은 성능을 제공하며,
빠른 응답 시간과 낮은 비용을 장점으로 합니다.
from openai import OpenAI
# OpenAI API 키 설정
client = OpenAI(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# 모델과 프롬프트 설정
MODEL_1 = "gpt-4o" # 8B 파라미터
MODEL_2 = "gpt-4o-large" # 70B 파라미터
prompt = "What is the difference between AI and ML?"
# 문장 생성
completion_1 = client.chat.completions.create(
model=MODEL_1,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
completion_2 = client.chat.completions.create(
model=MODEL_2,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
print("Model 1 (8B): " + completion_1.choices[0].message.content)
print("Model 2 (70B): " + completion_2.choices[0].message.content)

4. LLM의 협력 시스템(멀티 에이전트)
멀티 에이전트(에이전트 협력):
-
LLM이 혼자서 모든 작업을 처리하는 것이 아니라, 여러 개의 작은 AI(에이전트)가 협력하는 방식입니다.
- 예를 들어, 프론트엔드와 백엔드를 담당하는 에이전트가 협력하여 작업을 수행합니다.
- 각 에이전트는 특화된 작업을 수행하며, 전체 시스템의 성능을 향상시킵니다.
-
속도와 정확성: 이렇게 역할을 나누면 속도도 빠르고, 더 정확한 답변이 가능해집니다.
- 각 에이전트는 자신의 역할에 집중할 수 있어 전체 시스템의 효율성을 높입니다.
import { Agentica } from "@agentica/core";
import typia from "typia";
// Agentica 인스턴스 생성
const agent = new Agentica({
controllers: [
typia.llm.application<ShoppingCounselor>(),
typia.llm.application<ShoppingPolicy>(),
],
});
// 대화 시작
await agent.conversate("I want to buy a MacBook Pro.");

5. LLM의 학습과 피드백
Validation Feedback:
-
LLM이 항상 정답을 말하는 것은 아니므로, 틀린 답변을 줄 수도 있습니다.
-
이를 자동화하여 LLM이 스스로 학습하는 시스템을 만들 수 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, LLM이 제공한 답변을 검증하고, 잘못된 답변에 대해 피드백을 제공하여 모델을 개선합니다.
-
이는 LLM의 성능을 지속적으로 향상시키는 데 도움이 됩니다.
-
피드백 루프
: 사용자로부터 피드백을 받고 이를 모델에 반영하는 과정을 반복하여 LLM의 성능을 개선합니다.- 이는 LLM이 사용자의 요구에 맞춰 점점 더 정확한 답변을 제공할 수 있도록 합니다.
Function Call:
- LLM이 특정 기능을 수행하도록 요청할 때, 함수 호출을 통해 이를 구현할 수 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, 현재 시간을 알려주는 함수 호출을 할 수 있습니다.
- 이를 통해 LLM은 외부 API나 데이터베이스와 상호작용할 수 있습니다.
- 이는 LLM의 활용 범위를 확장하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
from openai import OpenAI
# OpenAI API 키 설정
client = OpenAI(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# 모델과 프롬프트 설정
MODEL = "gpt-4o"
prompt = "What is the capital of France?"
# 문장 생성
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=MODEL,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
# 피드백 반영
if completion.choices[0].message.content != "Paris":
# 피드백을 통해 모델을 개선합니다.
print("Incorrect answer. Providing feedback...")
else:
print("Correct answer!")

6. LLM을 활용한 서비스 구현
OpenAI의 GPT-4o:
- OpenAI의 GPT-4o를 이용하여 Function Call을 구현하는 예시 코드를 제공합니다.
- 이는 LLM이 특정 기능을 수행하도록 요청할 때, 함수 호출을 통해 이를 구현하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
- 예를 들어, GPT-4o를 사용하여 사용자의 질문에 답변하거나,
특정 작업을 수행하는 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, GPT-4o를 사용하여 사용자의 질문에 답변하거나,
Agentica 라이브러리:
- 복잡한 함수의 인자값을 하나하나 스키마로 작성하는 것이 귀찮을 수 있으므로, Agentica 라이브러리를 추천합니다.
- 이 라이브러리를 사용하면 간단한 코드로 챗봇 에이전트를 만들 수 있습니다.
- 이를 통해 LLM의 활용 범위를 확장할 수 있습니다.
- Agentica 라이브러리는 개발자가 쉽게 LLM을 통합하여 다양한 서비스를 구현할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
import openai
# OpenAI API 키 설정
openai.api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
# 모델과 프롬프트 설정
MODEL = "gpt-4o"
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current temperature for provided coordinates in celsius.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"latitude": {"type": "number"},
"longitude": {"type": "number"},
},
"required": ["latitude", "longitude"],
"additionalProperties": False,
},
"strict": True,
},
]
input = [
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Paris today?"},
]
# 함수 호출을 포함한 응답 생성
response = openai.responses.create(
model=MODEL,
input=input,
tools=tools,
)
# 함수 호출 결과 처리
for tool_call in response.output:
if tool_call.type != "function_call":
continue
name = tool_call.name
args = json.loads(tool_call.arguments)
result = get_weather(args["latitude"], args["longitude"])
# 결과를 모델에 반영
input.append(
{
"type": "function_call_output",
"call_id": tool_call.call_id,
"output": str(result),
}
)
# 최종 응답 생성
response2 = openai.responses.create(
model=MODEL,
input=input,
tools=tools,
)
print(response2.output_text)
