📦 Lab: IMDB Document Classification
# Convert IMDB dataset in the keras package to be suitable for torch
(imdb_seq_train, imdb_seq_test) = load_sequential(root='data/IMDB')
padded_sample = np.asarray(imdb_seq_train.tensors[0][0])
sample_review = padded_sample[padded_sample > 0][:12]
sample_review[:12]
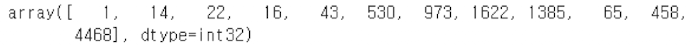
load_sequential() 함수는 IMDB 데이터셋을 불러올 때 각 리뷰를 시퀀스로 표현하며, 이 시퀀스는 최대 500개의 단어로 제한된 패딩(padded)된 형태이다.
즉, 긴 리뷰는 마지막 500단어만 사용되고, 짧은 리뷰는 앞에 0으로 패딩된다.
lookup = load_lookup(root='data/IMDB')
' '.join(lookup[i] for i in sample_review)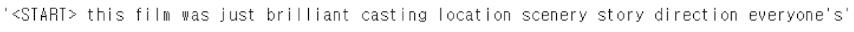
대부분의 리뷰가 매우 짧기 때문에, 이러한 특징 행렬(feature matrix)은 98% 이상이 0으로 채워져 있다.
# Set data
max_num_workers = 10
(imdb_train, imdb_test) = load_tensor(root='data/IMDB')
imdb_dm = SimpleDataModule(imdb_train,
imdb_test,
validation=2000,
num_workers=min(6, max_num_workers),
batch_size=512)
load_tensor()은 IMDB 데이터를 불러오는 함수로, 희소 텐서(sparse tensor) 형식으로 데이터를 로드하여 PyTorch에서 바로 사용할 수 있도록 구성한다.
- BoW(Bag-of-Words) 형식의 데이터처럼 대부분이 0으로 이루어진 텍스트 데이터를 효율적으로 표현할 수 있음
- torch의
TensorDataset형태로 반환되어,SimpleDataModule등에 바로 활용 가능 validation인자를 통해 검증 세트를 분리할 수 있음
즉, 희소한 텍스트 데이터를 torch가 다룰 수 있는 구조로 변환해주는 전처리 역할을 한다.
# Use a two-layer model for our first model.
class IMDBModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size):
super(IMDBModel, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = nn.Linear(input_size, 16)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
self.dense2 = nn.Linear(16, 16)
self.output = nn.Linear(16, 1)
def forward(self, x):
val = x
for _map in [self.dense1,
self.activation,
self.dense2,
self.activation,
self.output]:
val = _map(val)
return torch.flatten(val)# Instantiate our model
imdb_model = IMDBModel(imdb_test.tensors[0].size()[1])
# Show model summary
summary(imdb_model,
input_size=imdb_test.tensors[0].size(),
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params'])

# Use a smaller learning rate for the data
imdb_optimizer = RMSprop(imdb_model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# Define the binary classification module
imdb_module = SimpleModule.binary_classification(imdb_model,
optimizer=imdb_optimizer)
# Set up logger and trainer
imdb_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='IMDB')
imdb_trainer = Trainer(deterministic=True,
max_epochs=30,
logger=imdb_logger,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()])
# Train the model
imdb_trainer.fit(imdb_module, datamodule=imdb_dm)

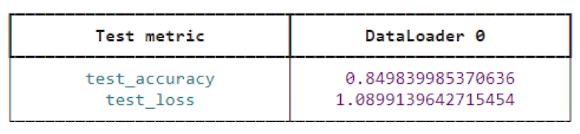
# Evaluate the test error
test_results = imdb_trainer.test(imdb_module,
datamodule=imdb_dm)
test_results
# Fit a lasso logistic regression model using LogisticRegression() from sklearn
((X_train, Y_train),
(X_valid, Y_valid),
(X_test, Y_test)) = load_sparse(validation=2000,
random_state=0,
root='data/IMDB')
lam_max = np.abs(X_train.T * (Y_train - Y_train.mean())).max()
lam_val = lam_max * np.exp(np.linspace(np.log(1), np.log(1e-4), 50))
logit = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1',
C=1/lam_max,
solver='liblinear',
warm_start=True,
fit_intercept=True)
coefs = []
intercepts = []
for l in lam_val:
logit.C = 1 / l
logit.fit(X_train, Y_train)
coefs.append(logit.coef_.copy())
intercepts.append(logit.intercept_)
coefs = np.squeeze(coefs)
intercepts = np.squeeze(intercepts)
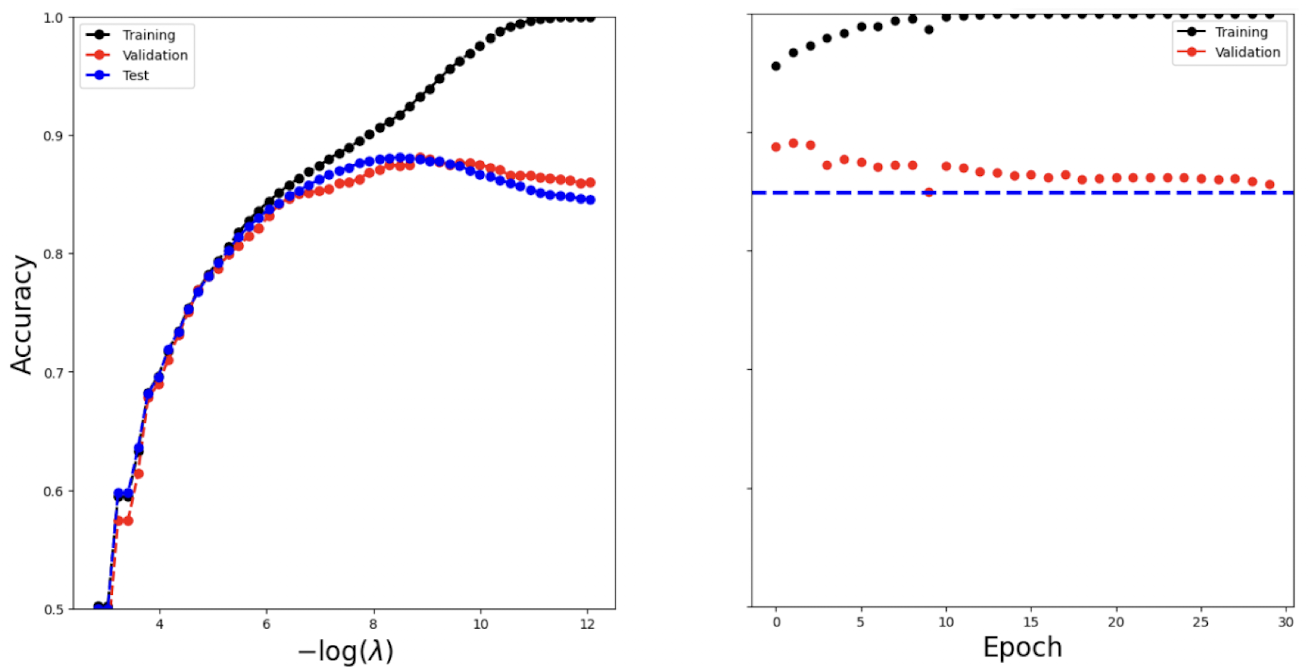
# Make a plot to compare our neural network results with the lasso
%%capture
fig, axes = subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 8), sharey=True)
for ((X_, Y_), data_, color) in zip(
[(X_train, Y_train), (X_valid, Y_valid), (X_test, Y_test)],
['Training', 'Validation', 'Test'],
['black', 'red', 'blue']
):
linpred_ = X_ * coefs.T + intercepts[None, :]
label_ = np.array(linpred_ > 0)
accuracy_ = np.array([np.mean(Y_ == l) for l in label_.T])
axes[0].plot(
-np.log(lam_val / X_train.shape[0]),
accuracy_,
'.--',
color=color,
linewidth=2,
label=data_
)
axes[0].legend()
axes[0].set_xlabel(r'$-\log(\lambda)$', fontsize=20)
axes[0].set_ylabel('Accuracy', fontsize=20)
# Read and plot IMDB results
imdb_results = pd.read_csv(imdb_logger.experiment.metrics_file_path)
summary_plot(
imdb_results,
axes[1],
col='accuracy',
ylabel='Accuracy'
)
axes[1].set_xticks(np.linspace(0, 30, 7).astype(int))
axes[1].set_ylabel('Accuracy', fontsize=20)
axes[1].set_xlabel('Epoch', fontsize=20)
axes[1].set_ylim([0.5, 1])
axes[1].axhline(
test_results[0]['test_accuracy'],
color='blue',
linestyle='--',
linewidth=3
)
fig
# Cleanup
del(imdb_model, imdb_trainer, imdb_logger,
imdb_dm, imdb_train, imdb_test)
📦 Lab: RNN for Document Classification
# Fit a simple LSTM RNN for sentiment prediction
imdb_seq_dm = SimpleDataModule(
imdb_seq_train,
imdb_seq_test,
validation=2000,
batch_size=300,
num_workers=min(6, max_num_workers)
)
class LSTMModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size):
super(LSTMModel, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, 32)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(
input_size=32,
hidden_size=32,
batch_first=True
)
self.dense = nn.Linear(32, 1)
def forward(self, x):
val, (h_n, c_n) = self.lstm(self.embedding(x))
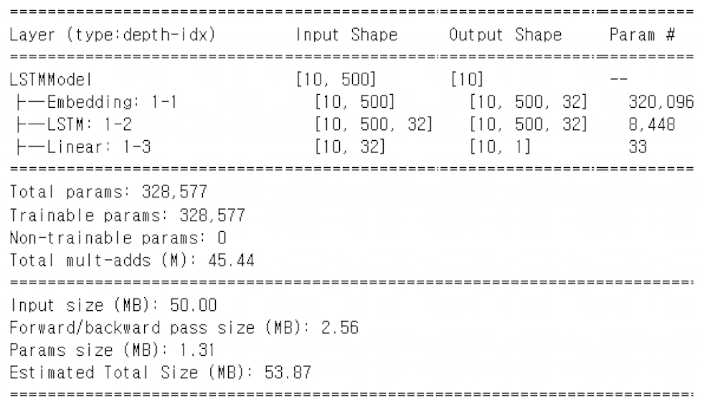
return torch.flatten(self.dense(val[:, -1]))nn.Embedding(10003, 32)의 경우 파라미터 수는: 임베딩 행렬의 크기
lstm_model = LSTMModel(X_test.shape[-1])
summary(
lstm_model,
input_data=imdb_seq_train.tensors[0][:10],
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params']
)
lstm_module = SimpleModule.binary_classification(lstm_model)
lstm_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='IMDB_LSTM')
lstm_trainer = Trainer(
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=20,
logger=lstm_logger,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()]
)
lstm_trainer.fit(
lstm_module,
datamodule=imdb_seq_dm
)
 ```
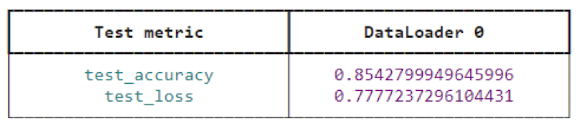
lstm_trainer.test(
lstm_module,
datamodule=imdb_seq_dm
)
```
```
lstm_trainer.test(
lstm_module,
datamodule=imdb_seq_dm
)
```
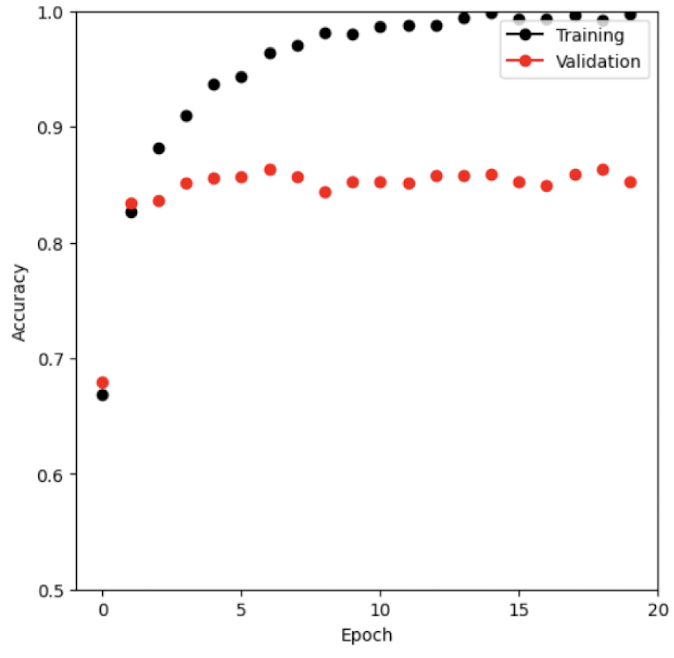
lstm_results = pd.read_csv(lstm_logger.experiment.metrics_file_path)
fig, ax = subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 6))
summary_plot(
lstm_results,
ax,
col='accuracy',
ylabel='Accuracy'
)
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, 20, 5).astype(int))
ax.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax.set_ylim([0.5, 1])
# Cleanup
del(
lstm_model,
lstm_trainer,
lstm_logger,
imdb_seq_dm,
imdb_seq_train,
imdb_seq_test
)
📦 Lab: RNN for Time Series Prediction
# Load and standardize the data
NYSE = load_data('NYSE')
cols = ['DJ_return', 'log_volume', 'log_volatility']
X = pd.DataFrame(
StandardScaler(with_mean=True, with_std=True)
.fit_transform(NYSE[cols]),
columns=NYSE[cols].columns,
index=NYSE.index
)
# Set up the lagged versions of the data
for lag in range(1, 6):
for col in cols:
newcol = np.zeros(X.shape[0]) * np.nan
newcol[lag:] = X[col].values[:-lag]
X.insert(len(X.columns), f"{col}_{lag}", newcol)
X.insert(len(X.columns), 'train', NYSE['train'])
X = X.dropna()
Y, train = X['log_volume'], X['train']
X = X.drop(columns=['train'] + cols)
X.columns
# Fit a simple linear model and compute the R2 on the test data
M = LinearRegression()
M.fit(X[train], Y[train])
M.score(X[~train], Y[~train])
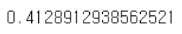
X_day = pd.merge(
X,
pd.get_dummies(NYSE['day_of_week']),
on='date'
)
M.fit(X_day[train], Y[train])
M.score(X_day[~train], Y[~train])
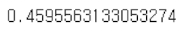
# To fit the RNN, we must reshape the data
ordered_cols = []
for lag in range(5,0,-1):
for col in cols:
ordered_cols.append('{0}_{1}'.format(col, lag))
X = X.reindex(columns=ordered_cols)
X.columns
X_rnn = X.to_numpy().reshape((-1, 5, 3))
X_rnn.shape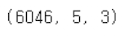
# Define the RNN Model
class NYSEModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NYSEModel, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN(3, 12, batch_first=True)
self.dense = nn.Linear(12, 1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
val, h_n = self.rnn(x)
val = self.dense(self.dropout(val[:, -1]))
return torch.flatten(val)
nyse_model = NYSEModel()
# Form the training dataset
datasets = []
for mask in [train, ~train]:
X_rnn_t = torch.tensor(X_rnn[mask].astype(np.float32))
Y_t = torch.tensor(Y[mask].astype(np.float32))
datasets.append(TensorDataset(X_rnn_t, Y_t))
nyse_train, nyse_test = datasets
# Inspect the summary
summary(nyse_model,
input_data=X_rnn_t,
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params'])
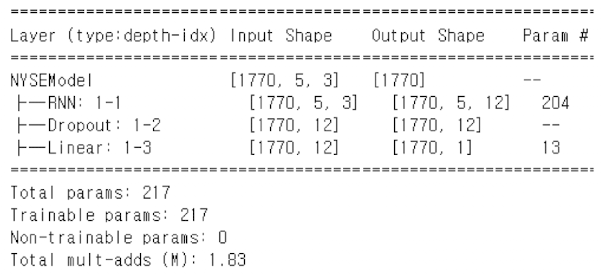
# Put the two datasets into a data module
nyse_dm = SimpleDataModule(nyse_train,
nyse_test,
num_workers=min(4, max_num_workers),
validation=nyse_test,
batch_size=64)
for idx, (x, y) in enumerate(nyse_dm.train_dataloader()):
out = nyse_model(x)
print(y.size(), out.size())
if idx >= 2:
break

nyse_optimizer = RMSprop(nyse_model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
nyse_module = SimpleModule.regression(nyse_model,
optimizer=nyse_optimizer,
metrics={'r2': R2Score()})
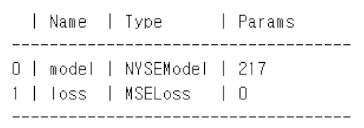
nyse_trainer = Trainer(deterministic=True,
max_epochs=200,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()])
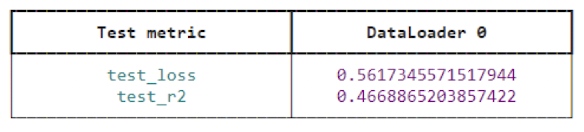
nyse_trainer.fit(nyse_module, datamodule=nyse_dm)
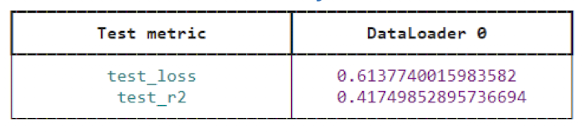
nyse_trainer.test(nyse_module, datamodule=nyse_dm)
# Fit a nonlinear AR model using the feature set X_day
# that includes the day_of_week indicators.
datasets = []
for mask in [train, ~train]:
X_day_t = torch.tensor(
np.asarray(X_day[mask]).astype(np.float32)
)
Y_t = torch.tensor(
np.asarray(Y[mask]).astype(np.float32)
)
datasets.append(TensorDataset(X_day_t, Y_t))
day_train, day_test = datasets
day_dm = SimpleDataModule(
day_train,
day_test,
num_workers=min(4, max_num_workers),
validation=day_test,
batch_size=64
)
# Define AR Model
class NonLinearARModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NonLinearARModel, self).__init__()
self._forward = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(20, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(32, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return torch.flatten(self._forward(x))
nl_model = NonLinearARModel()
nl_optimizer = RMSprop(nl_model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
nl_module = SimpleModule.regression(
nl_model,
optimizer=nl_optimizer,
metrics={'r2': R2Score()}
)
nl_trainer = Trainer(
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=20,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()]
)
nl_trainer.fit(nl_module, datamodule=day_dm)
nl_trainer.test(nl_module, datamodule=day_dm)