📦 Lab: Single Layer Network on Hitters Data
# Hitters data
Hitters = load_data('Hitters').dropna()
n = Hitters.shape[0]
print(n) # > 263
# Set up the model matrix and the response
model = MS(Hitters.columns.drop('Salary'), intercept=False)
X = model.fit_transform(Hitters).to_numpy()
Y = Hitters['Salary'].to_numpy()
# Split the data into test and training
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(
X, Y, test_size=1/3, random_state=1
)# Fit the linear model and evaluate the test error
hit_lm = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, Y_train)
Yhat_test = hit_lm.predict(X_test)
print(np.abs(Yhat_test - Y_test).mean()) # > 259.7152883314631
# Fit the lasso using sklearn
# Encode a pipeline with two steps: we first normalize
# the features using a StandardScaler() transform, and
# then fit the lasso without further normalization.
scaler = StandardScaler(with_mean=True, with_std=True)
lasso = Lasso(warm_start=True, max_iter=30000)
standard_lasso = Pipeline(steps=[
('scaler', scaler),
('lasso', lasso)
])
# Create a grid of values for λ
X_s = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
n = X_s.shape[0]
print(n)
lam_max = np.fabs(X_s.T.dot(Y_train - Y_train.mean())).max() / n
print(lam_max)
param_grid = {
'alpha': np.exp(np.linspace(0, np.log(0.01), 100)) * lam_max
}
print(param_grid)
# Perform cross-validation using this sequence of λ
cv = KFold(10, shuffle=True, random_state=1)
grid = GridSearchCV(
lasso,
param_grid,
cv=cv,
scoring='neg_mean_absolute_error'
)
grid.fit(X_train, Y_train)
trained_lasso = grid.best_estimator_
Yhat_test = trained_lasso.predict(X_test)
print(np.fabs(Yhat_test - Y_test).mean()) # > 257.23820107995# Make a class and object for Hitters data
class HittersModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size):
super(HittersModel, self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.sequential = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_size, 50),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.4),
nn.Linear(50, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.flatten(x)
return torch.flatten(self.sequential(x))
hit_model = HittersModel(X.shape[1])
summary(
hit_model,
input_size=X_train.shape,
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params']
)
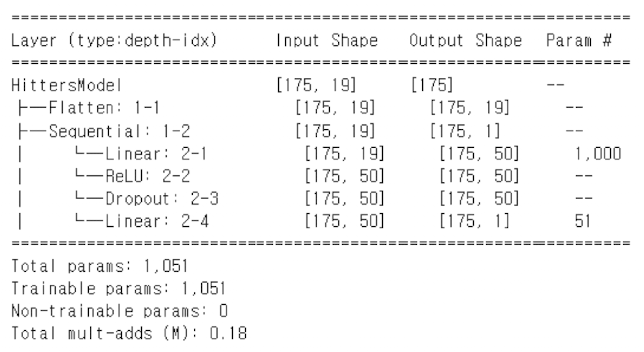
self.sequential 객체는 4개의 연산(map)으로 구성된 모델이다.
첫 번째는 Hitters 데이터의 19개 특성을 50차원으로 변환하는 선형 계층(linear layer)으로,
가중치 50×19개 + 바이어스 50개 = 총 1,000개의 파라미터가 사용된다.
그 다음으로는
ReLU활성화 함수- 40%의 드롭아웃(dropout)
- 마지막으로 1차원으로 줄이는 선형 계층(50개 가중치 + 1개 바이어스)
이 모든 것을 합치면 학습 가능한 파라미터 수는 50×19 + 50 + 50 + 1 = 1,051개이다.
# Transform our training data into a form for torch
X_train_t = torch.tensor(X_train.astype(np.float32))
Y_train_t = torch.tensor(Y_train.astype(np.float32))
hit_train = TensorDataset(X_train_t, Y_train_t)
# Transform our test data into a form for torch
X_test_t = torch.tensor(X_test.astype(np.float32))
Y_test_t = torch.tensor(Y_test.astype(np.float32))
hit_test = TensorDataset(X_test_t, Y_test_t)
# Provide a helper function SimpleDataModule() in ISLP to live on different GPU machines
max_num_workers = rec_num_workers()
hit_dm = SimpleDataModule(hit_train, hit_test,
batch_size=32,
num_workers=min(4, max_num_workers),
validation=hit_test)
# Use the SimpleModule.regression() method
hit_module = SimpleModule.regression(hit_model,
metrics={'mae': MeanAbsoluteError()})
# Log our results via CSVLogger() within ‘logs/hitters’
hit_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='hitters')
# Train our model using the Trainer() object
hit_trainer = Trainer(deterministic=True,
max_epochs=50,
log_every_n_steps=5,
logger=hit_logger,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()])
hit_trainer.fit(hit_module, datamodule=hit_dm)

SGD에서는 매 스텝마다 32개의 훈련 샘플을 랜덤하게 선택해 gradient를 계산한다.
전체 데이터가 175개이고 batch size가 32이므로, 한 에폭(epoch)은 약 5.5개의 SGD 스텝으로 구성된다.
→ 즉, 1 epoch = 전체 데이터를 한 번 처리하는 데 필요한 미니배치 횟수.
# Evaluate performance on our test data
hit_trainer.test(hit_module, datamodule=hit_dm)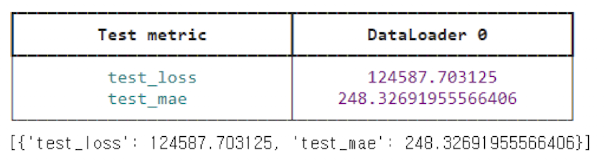
hit_results = pd.read_csv(hit_logger.experiment.metrics_file_path)
print(hit_results)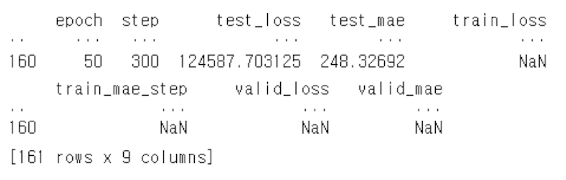 ```python
# Simple generic function to produce this plot
def summary_plot(results, ax, col='loss',
valid_legend='Validation',
training_legend='Training',
ylabel='Loss', fontsize=20):
for (column, color, label) in zip([f'train_{col}_epoch', f'valid_{col}'],
['black', 'red'],
[training_legend, valid_legend]):
results.plot(x='epoch',
y=column,
label=label,
marker='o',
color=color,
ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
return ax
```python
# Simple generic function to produce this plot
def summary_plot(results, ax, col='loss',
valid_legend='Validation',
training_legend='Training',
ylabel='Loss', fontsize=20):
for (column, color, label) in zip([f'train_{col}_epoch', f'valid_{col}'],
['black', 'red'],
[training_legend, valid_legend]):
results.plot(x='epoch',
y=column,
label=label,
marker='o',
color=color,
ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
return ax
```python
# Simple generic function to produce this plot
def summary_plot(results, ax, col='loss',
valid_legend='Validation',
training_legend='Training',
ylabel='Loss', fontsize=20):
for (column, color, label) in zip([f'train_{col}_epoch', f'valid_{col}'],
['black', 'red'],
[training_legend, valid_legend]):
results.plot(x='epoch',
y=column,
label=label,
marker='o',
color=color,
ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
return ax
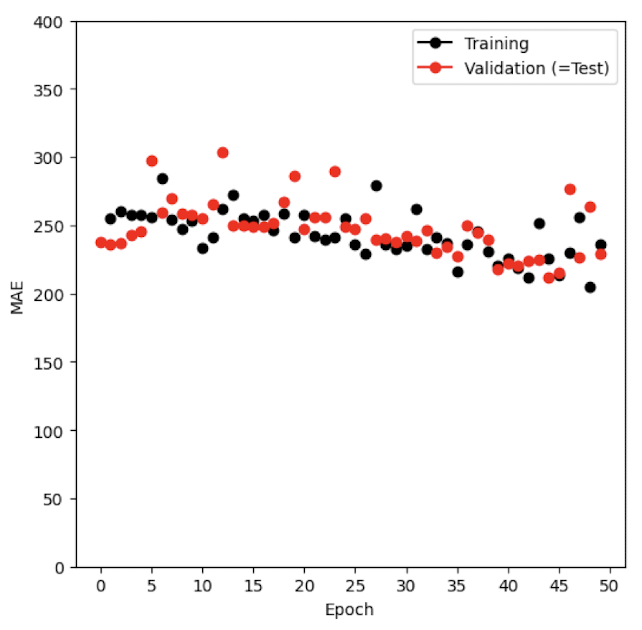
# Delete all references to the torch objects
del(Hitters,
hit_model, hit_dm,
hit_logger,
hit_test, hit_train,
X, Y,
X_test, X_train,
Y_test, Y_train,
X_test_t, Y_test_t,
hit_trainer, hit_module)📦 Lab: Multilayer Network on the MNIST Digit Data
# MNIST() function within torchvision.datasets retrieves the training and test data sets
(mnist_train, mnist_test) = [
MNIST(
root='data',
train=train,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
for train in [True, False]
]
mnist_train

학습 데이터에는 60,000장의 이미지가 있고, 테스트 데이터에는 10,000장이 있다. 각 이미지는 28×28 크기의 픽셀 행렬로 저장되어 있다.
# Form a data module from training and test datasets
mnist_dm = SimpleDataModule(
mnist_train,
mnist_test,
validation=0.2,
num_workers=max_num_workers,
batch_size=256
)
for idx, (X_, Y_) in enumerate(mnist_dm.train_dataloader()):
print('X: ', X_.shape)
print('Y: ', Y_.shape)
if idx >= 1:
break

X는 각 배치마다 256개의 이미지를 담고 있으며, 각 이미지는1×28×28 크기의 텐서입니다.
# Specify our neural network.
class MNISTModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MNISTModel, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.4)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.3)
)
self._forward = nn.Sequential(
self.layer1,
self.layer2,
nn.Linear(128, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self._forward(x)
✅ MNISTModel 구조 설명
-
입력: 각 이미지는 크기
1×28×28의 회색조 이미지
→ 첫 번째 계층에서 이를 1차원 벡터(784차원) 로 flatten함. -
1층 (Layer 1):
784 → 256차원으로 선형 변환ReLU활성화Dropout(0.4)로 40% 뉴런 무작위 제거
-
2층 (Layer 2):
256 → 128차원으로 선형 변환ReLU활성화Dropout(0.3)로 30% 뉴런 무작위 제거
-
출력층:
128 → 10차원으로 선형 변환
→MNIST의 클래스 수인0~9총 10개 클래스에 대한 로짓(logits) 출력
# Check that the model produces output of expected size based on our existing batch X_ above.
mnist_model = MNISTModel()
mnist_model(X_).size()
# > torch.Size([256, 10])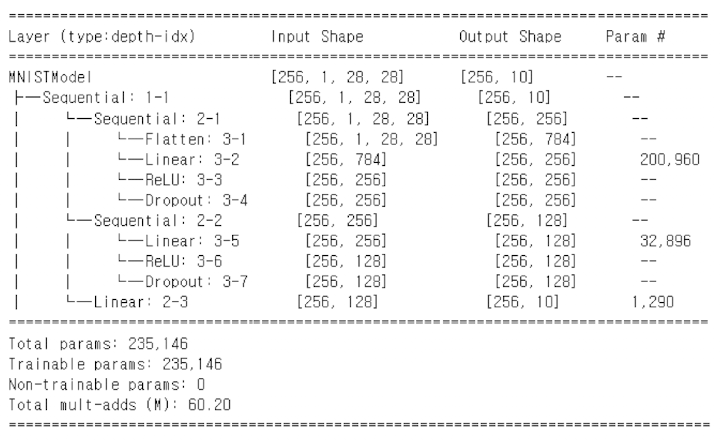
# SimpleModule.classification() method uses the cross-entropy loss function instead of mean squared error
mnist_module = SimpleModule.classification(mnist_model, num_classes=10)
mnist_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='MNIST')
# Supply training data, and fit the model
mnist_trainer = Trainer(
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=30,
logger=mnist_logger,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()]
)
mnist_trainer.fit(mnist_module, datamodule=mnist_dm)
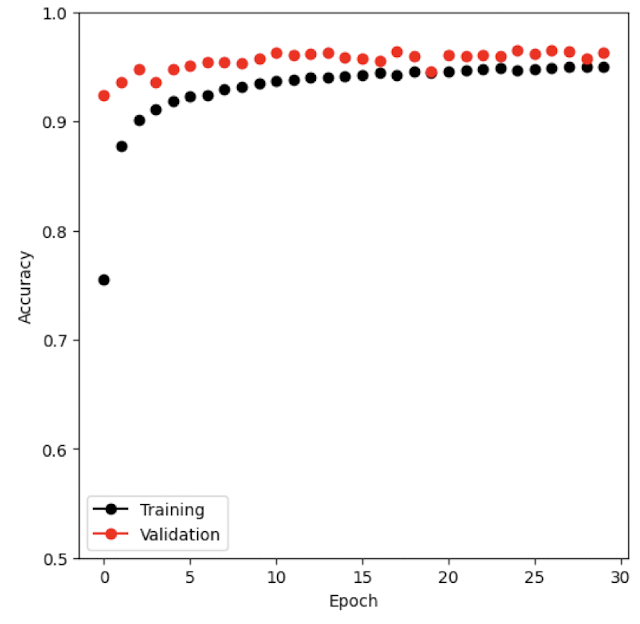
# Display accuracy across epochs.
mnist_results = pd.read_csv(mnist_logger.experiment.metrics_file_path)
fig, ax = subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 6))
summary_plot(
mnist_results,
ax,
col='accuracy',
ylabel='Accuracy'
)
ax.set_ylim([0.5, 1])
ax.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, 30, 7).astype(int))
# Evaluate the accuracy using the test() method
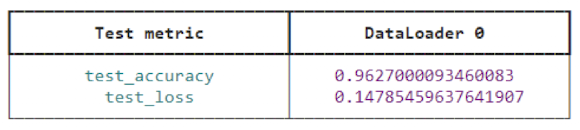
mnist_trainer.test(mnist_module, datamodule=mnist_dm)
# Multiclass logistic regression
class MNIST_MLR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MNIST_MLR, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(784, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
mlr_model = MNIST_MLR()
mlr_module = SimpleModule.classification(mlr_model, num_classes=10)
mlr_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='MNIST_MLR')
mlr_trainer = Trainer(
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=30,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()]
)
mlr_trainer.fit(mlr_module, datamodule=mnist_dm)

# Fit the model just as before and compute the test
mlr_trainer.test(mlr_module, datamodule=mnist_dm)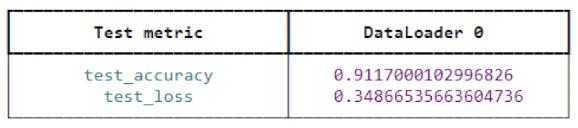
# Delete some of the objects
del (
mnist_test, mnist_train, mnist_model, mnist_dm,
mnist_trainer, mnist_module, mnist_results,
mlr_model, mlr_module, mlr_trainer
)