
기초부터 쌓아가는 머신러닝 #2
2주차 : pandas 라이브러리 기초 실습
- DataFrame 행, 열 선택 및 필터링 복습
import os import pandas as pd os.listdir('./drive/MyDrive/machine_learning_data') > ['friend.csv'] # 데이터 폴더 src 변수 할당 base_src = './drive/MyDrive/machine_learning_data' # friend.csv 파일 src 변수 할당 friend_src = base_src+"/friend.csv" # friend.csv 불러오기 df = pd.read_csv(friend_src,encoding='utf-8') df.head() > name age job 0 John 20 student 1 Jenny 30 developer 2 Nate 30 teacher 3 Julia 40 dentist 4 Brian 45 manager # index 2번에 해당하는 row 가져오기 df.iloc[2] # Series 형태로 가져옴 >name Nate age 30 job teacher Name: 2, dtype: object # column job에 해당되는 데이터 가져오기(1) df['job'] > 0 student 1 developer 2 teacher 3 dentist 4 manager 5 intern Name: job, dtype: object # column job에 해당되는 데이터 가져오기(2) df.loc[:,'job'] > 0 student 1 developer 2 teacher 3 dentist 4 manager 5 intern Name: job, dtype: object # 슬라이싱 기능을 통해 여러 행 가져오기 df.iloc[[2,3]] # 슬라이싱 기능 사용(x) > name age job 2 Nate 30 teacher 3 Julia 40 dentist df.iloc[2:4] # 슬라이싱 기능 사용(ㅇ) > name age job 2 Nate 30 teacher 3 Julia 40 dentist # "많이 하는 질문!" ```iloc VS loc 뭐가 다른거죠 ?????``` - iloc는 인덱스와 컬럼을 리스트 배열로 선택하는 것! - loc는 인덱스와 컬럼을 문자로 선택하는 것! - 따라서 상황에 맞게 선택하는 것이 중요! # 조건 필터링 걸어서 가져오기 ## 30대 이상만 가져오기 df[df['age']>30] name age job 3 Julia 40 dentist 4 Brian 45 manager ## job이 intern인 사람 가져오기 df[df['job']=='intern'] name age job 5 Chris 25 intern ## 조건 여러개 걸기 30대 이상 40대 이하 (and function) df[(df['age']>=30) & (df['age']<=40)] name age job 1 Jenny 30 developer 2 Nate 30 teacher 3 Julia 40 dentist ## 조건 여러개 걸기 30대 미만 혹은 40대 초과대 초과(or function) df[(df['age']<30) | (df['age']>40)] name age job 0 John 20 student 4 Brian 45 manager 5 Chris 25 intern ## in을 통한 포함 조건 걸기 (이렇게 하면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생) df[df['job'] in ['student','manager']] --------------------------------------------------------------------------- ValueError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-18-56118830d0f6> in <module>() ----> 1 df[df['job'] in ['student','manager']] ValueError: The truth value of a Series is ambiguous. Use a.empty, a.bool(), a.item(), a.any() or a.all(). # 포함 필터링을 사용하고 싶다면 추후에 배울 "apply" 함수를 활용하라. df[df['job'].apply(lambda x : x in ['student','manager'])] name age job 0 John 20 student 4 Brian 45 manager
- DataFrame 행, 열 삭제
import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) ## ['B','C'] 컬럼을 삭제하겠다. axis=0 or 1 => 0:row 방향 , 1:col 방향 df.drop(['B', 'C'], axis=1) > A D 0 0 3 1 4 7 2 8 11 ## ['B','C'] 컬럼을 삭제하겠다 df.drop(columns=['B', 'C']) ## index 0과 1을 삭제하겠다. df.drop([0, 1]) > A B C D 2 8 9 10 11
- DataFrame 행, 열 수정
# friend.csv 불러오기 df = pd.read_csv(friend_src,encoding='utf-8') df.head() > name age job 0 John 20 student 1 Jenny 30 developer 2 Nate 30 teacher 3 Julia 40 dentist 4 Brian 45 manager 5 Chris 25 intern # df를 하나 복사하기(원본 데이터 유지를 위해서) temp = df.copy() # age 컬럼 모든 값 변경 temp['age'] = 20 temp > name age job 0 John 20 student 1 Jenny 20 developer 2 Nate 20 teacher 3 Julia 20 dentist 4 Brian 20 manager 5 Chris 20 intern # 인덱스 2번, 컬럼 age => 15로 바꾸기 temp.loc[2,'age'] = 15 temp > name age job 0 John 20 student 1 Jenny 20 developer 2 Nate 15 teacher 3 Julia 20 dentist 4 Brian 20 manager 5 Chris 20 intern
- DataFrame 그룹 생성
- pandas의 groupby() 연산자를 사용하여 집단, 그룹별로 데이터를 집계 및 요약을 할 수 있다.
- dataframe을 지정한 그룹으로 나누고, 각 그룹별로 집계합수를 적용하고, 그룹별 집계 결과를 하나로 합치는 과정을 거친다.
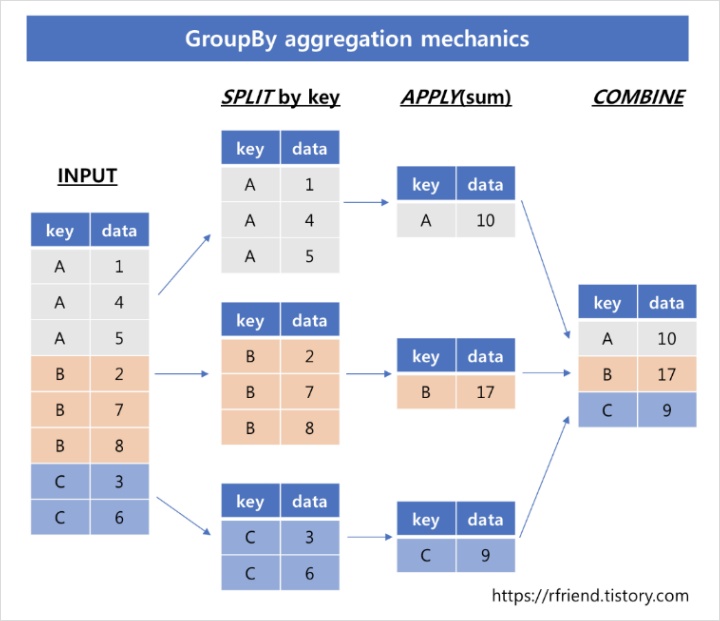
- 데이터 url : https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/149jcCyJFKKG5MFaPNWnYYqM2EkzgRz2P?usp=sharing
abalone_src = base_src+'/abalone.data' abalone_df = pd.read_csv(base_src+'/abalone.data', header=None,sep=',', names=['sex','length','diameter','height', 'whole_weight','shucked_weight','viscera_weight', 'shell_weight','rings']) abalone_df.head() sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.150 15 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.070 7 2 F 0.530 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.210 9 3 M 0.440 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.155 10 4 I 0.330 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.055 7 # 데이터 shape 확인 => 4177개의 데이터와 9개의 변수 abalone_df.shape > (4177, 9) # 데이터 결측값 확인 abalone_df.isnull().sum().sum() > 0 # 기술통계 확인(평균, 편차, 최소값, 25%, 50%, 75%, 최대값) > length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings count 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 4177.000000 mean 0.523992 0.407881 0.139516 0.828742 0.359367 0.180594 0.238831 9.933684 std 0.120093 0.099240 0.041827 0.490389 0.221963 0.109614 0.139203 3.224169 min 0.075000 0.055000 0.000000 0.002000 0.001000 0.000500 0.001500 1.000000 25 % 0.450000 0.350000 0.115000 0.441500 0.186000 0.093500 0.130000 8.000000 50 % 0.545000 0.425000 0.140000 0.799500 0.336000 0.171000 0.234000 9.000000 75 % 0.615000 0.480000 0.165000 1.153000 0.502000 0.253000 0.329000 11.000000 max 0.815000 0.650000 1.130000 2.825500 1.488000 0.760000 1.005000 29.000000 # 전복 성별(M,F,I)에 따라 groupby함수를 통해 집계를 하겠다. ## 그룹별 합계 : grouped.sum() ## 그룹별 평균 : grouped.mean() ## 그룹별 크기 : grouped.size() ### ex) DataFrame[집계 변수].groupby(DataFrame[집계 대상]) grouped = abalone_df['whole_weight'].groupby(abalone_df['sex']) # grouped는 pandas의 SeriesGroupBy object 형태이다. grouped > <pandas.core.groupby.generic.SeriesGroupBy object at 0x7f74f51f3f50> grouped.sum() >sex F 1367.8175 I 578.8885 M 1514.9500 Name: whole_weight, dtype: float64 grouped.mean() >sex F 1.046532 I 0.431363 M 0.991459 Name: whole_weight, dtype: float64 grouped.size() >sex F 1307 I 1342 M 1528 Name: whole_weight, dtype: int64 # 그룹변수 하나가 아닌, 전체 연속형 변수에 대한 집계 abalone_df.groupby(abalone_df['sex']).mean() > length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings sex F 0.579093 0.454732 0.158011 1.046532 0.446188 0.230689 0.302010 11.129304 I 0.427746 0.326494 0.107996 0.431363 0.191035 0.092010 0.128182 7.890462 M 0.561391 0.439287 0.151381 0.991459 0.432946 0.215545 0.281969 10.705497 # 다음과 같이 간단하게 작성할 수 있으며, 위와 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다. abalone_df.groupby('sex').mean() # 새로운 조건에 맞는 변수 추가 abalone_df['length_bool'] = np.where(abalone_df['length']>abalone_df['length'].median(), 'length_long', # True일 경우 'length_short' # False일 경우) abalone_df['length_bool'] >0 length_short 1 length_short 2 length_short 3 length_short 4 length_short ... 4172 length_long 4173 length_long 4174 length_long 4175 length_long 4176 length_long Name: length, Length: 4177, dtype: object # 그룹변수를 2개 이상 선택하여 총계처리 abalone_df.groupby(['sex','length_bool']).mean() > length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings sex length_bool F length_long 0.626895 0.493020 0.169944 1.261330 0.542957 0.276945 0.360013 11.415073 length_short 0.477428 0.373301 0.132632 0.589702 0.240380 0.132311 0.178650 10.521531 I length_long 0.584495 0.452952 0.150957 0.923215 0.402524 0.196912 0.273247 10.585106 length_short 0.402210 0.305893 0.100997 0.351234 0.156581 0.074920 0.104549 7.451473 M length_long 0.623359 0.489291 0.168670 1.255182 0.554312 0.272203 0.351683 11.299172 length_short 0.454875 0.353336 0.121664 0.538157 0.224335 0.118156 0.162141 9.685053 # 더 간결하게 표현한다면. ## 그룹변수('sex','length_bool') 선택 및 집계변수('whole_weight') 평균 abalone_df.groupby(['sex','length_bool'])['whole_weight'].mean() >sex length_bool F length_long 1.261330 length_short 0.589702 I length_long 0.923215 length_short 0.351234 M length_long 1.255182 length_short 0.538157 Name: whole_weight, dtype: float64 #> _'''위 글은 https://rfriend.tistory.com/383의 글을 참고하여 작성되었습니다.'''_
- 중복 데이터 삭제
# 기존 abalone 데이터 활용 abalone_df = pd.read_csv(base_src+'/abalone.data', header=None,sep=',', names=['sex','length','diameter','height', 'whole_weight','shucked_weight','viscera_weight', 'shell_weight','rings']) # 중복된 row를 확인하는 법 abalaone_df.duplicated() >0 False 1 False 2 False 3 False 4 False ... 4172 False 4173 False 4174 False 4175 False 4176 False Length: 4177, dtype: bool # 위와같이 하면 중복된 row를 확인할 수 있지만, # 가시적으로 몇개가 중복되어 있는지 확인하기 어렵다. abalone_df.duplicated().sum() > 0 # 중복 예제 생성을 위해서, 가상으로 중복데이터 생성 ## pd.concat은 2개의 DataFrame을 합치는 함수이다. new_abalone_df = pd.concat([abalone_df,abalone_df.iloc[[0]]],axis=0) new_abalone_df.duplicated() >0 False 1 False 2 False 3 False 4 False ... 4173 False 4174 False 4175 False 4176 False 0 True Length: 4178, dtype: bool # keep='last' 옵션을 통해서 처음으로 중복되는 데이터를 검색 new_abalone_df.duplicated(keep='last') >0 True 1 False 2 False 3 False 4 False ... 4173 False 4174 False 4175 False 4176 False 0 False Length: 4178, dtype: bool # 중복 데이터(row) 삭제 new_abalone_df.drop_duplicates() # 중복 데이터(row) 삭제(첫번째 중복되는 것) new_abalone_df.drop_duplicates(keep='last') # 중복 데이터(column) 조회 new_abalone_df.duplicated('sex') # 중복 데이터(column) 삭제 new_abalone_df.drop_duplicates('sex') # 중복 데이터(column) 삭제(첫번째 중복되는 것) new_abalone_df.drop_duplicates('sex')
- NaN(결측치) 찾아서 다른 값 변경
# 기존 avalone 데이터는 결측치가 존재하지 않는다. abalone_df.isnull().sum().sum() > 0 # 가상으로 결측치 생성 nan_abalone_df = abalone_df.copy() nan_abalone_df.loc[2,'length'] = np.nan > sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings length_bool 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.0700 7 length_short 2 F NaN 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.2100 9 length_short 3 M 0.440 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.1550 10 length_short 4 I 0.330 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.0550 7 length_short ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4172 F 0.565 0.450 0.165 0.8870 0.3700 0.2390 0.2490 11 length_long 4173 M 0.590 0.440 0.135 0.9660 0.4390 0.2145 0.2605 10 length_long 4174 M 0.600 0.475 0.205 1.1760 0.5255 0.2875 0.3080 9 length_long 4175 F 0.625 0.485 0.150 1.0945 0.5310 0.2610 0.2960 10 length_long 4176 M 0.710 0.555 0.195 1.9485 0.9455 0.3765 0.4950 12 length_long # 결측치를 특정 값으로 채우기 zero_abalone_df = nan_abalone_df.fillna(0) zero_abalone_df > sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings length_bool 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.0700 7 length_short 2 F "0.000" 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.2100 9 length_short 3 M 0.440 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.1550 10 length_short 4 I 0.330 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.0550 7 length_short ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4172 F 0.565 0.450 0.165 0.8870 0.3700 0.2390 0.2490 11 length_long 4173 M 0.590 0.440 0.135 0.9660 0.4390 0.2145 0.2605 10 length_long 4174 M 0.600 0.475 0.205 1.1760 0.5255 0.2875 0.3080 9 length_long 4175 F 0.625 0.485 0.150 1.0945 0.5310 0.2610 0.2960 10 length_long 4176 M 0.710 0.555 0.195 1.9485 0.9455 0.3765 0.4950 12 length_long # 결측치를 결측치가 속한 컬럼의 평균값으로 대체하기 nan_abalone_df.mean() >length "0.523991" diameter 0.407881 height 0.139516 whole_weight 0.828742 shucked_weight 0.359367 viscera_weight 0.180594 shell_weight 0.238831 rings 9.933684 dtype: float64 nan_abalone_df.fillna(nan_abalone_df.mean()) > sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings length_bool 0 M 0.455000 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short 1 M 0.350000 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.0700 7 length_short 2 F "0.523991" 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.2100 9 length_short 3 M 0.440000 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.1550 10 length_short 4 I 0.330000 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.0550 7 length_short ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4172 F 0.565000 0.450 0.165 0.8870 0.3700 0.2390 0.2490 11 length_long 4173 M 0.590000 0.440 0.135 0.9660 0.4390 0.2145 0.2605 10 length_long 4174 M 0.600000 0.475 0.205 1.1760 0.5255 0.2875 0.3080 9 length_long 4175 F 0.625000 0.485 0.150 1.0945 0.5310 0.2610 0.2960 10 length_long 4176 M 0.710000 0.555 0.195 1.9485 0.9455 0.3765 0.4950 12 length_long
- apply 함수 활용
- DataFrame타입의 객체에서 호출가능한 apply함수에 대해 살펴보자.
- 본인이 원하는 행과 열에 연산 혹은 function을 적용할 수 있다.
- 열 기준으로 집계하고 싶은 경우 axis=0
- 행 기준으로 집계하고 싶은 경우 axis=1
abalone_df[['diameter']].apply(np.average,axis=0) >diameter 0.407881 dtype: float64 # 열 기준 집계 abalone_df[['diameter','whole_weight']].apply(np.average,axis=0) >diameter 0.407881 whole_weight 0.828742 dtype: float64 # 행 기준 집계 abalone_df[['diameter','whole_weight']].apply(np.average,axis=1) >0 0.43950 1 0.24525 2 0.54850 3 0.44050 4 0.23000 ... 4172 0.66850 4173 0.70300 4174 0.82550 4175 0.78975 4176 1.25175 Length: 4177, dtype: float64 # 사용자 함수를 통한 집계 ★★★★★ import math def avg_ceil(x,y,z): return math.ceil((x+y+z)/3) abalone_df[['diameter','height','whole_weight']].apply(lambda x : avg_ceil(x[0],x[1],x[2]),axis=1) >0 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 .. 4172 1 4173 1 4174 1 4175 1 4176 1 Length: 4177, dtype: int64 # 문제 1. 사용자 정의 함수 사용 2. ['diameter','height','whole_weight'] 변수 사용 3. 세 변수의 합이 1이 넘으면 True, 아니면 False 출력 후 answer변수에 저장 4. abalone_df에 answer 열을 추가하고 입력
- 컬럼 내 유니크한 값 뽑아서 갯수 확인
# 성별 변수에 포함된 M , I, F가 몇개인지 확인 abalone_df['sex'].value_counts() >M 1528 I 1342 F 1307 Name: sex, dtype: int64 # 성별 변수에 포함된 M , I, F가 몇개인지 확인 및 정렬 abalone_df['sex'].value_counts(ascending=True) >F 1307 I 1342 M 1528 Name: sex, dtype: int64 # 결측값이 있는 경우 abalone_df['sex'].value_counts(dropna=True)
- 두 개의 DataFrame 합치기
# 가상 abalone 1개 row데이터 생성 및 결합 one_abalone_df = abalone_df.iloc[[0]] pd.concat([abalone_df,one_abalone_df],axis=0) > sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings length_bool 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.0700 7 length_short 2 F 0.530 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.2100 9 length_short 3 M 0.440 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.1550 10 length_short 4 I 0.330 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.0550 7 length_short ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4173 M 0.590 0.440 0.135 0.9660 0.4390 0.2145 0.2605 10 length_long 4174 M 0.600 0.475 0.205 1.1760 0.5255 0.2875 0.3080 9 length_long 4175 F 0.625 0.485 0.150 1.0945 0.5310 0.2610 0.2960 10 length_long 4176 M 0.710 0.555 0.195 1.9485 0.9455 0.3765 0.4950 12 length_long 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short # 가상 abalone 1개 col 데이터 생성 및 결합 one_abalone_df = abalone_df.iloc[:,[0]] pd.concat([abalone_df,one_abalone_df],axis=1) >sex length diameter height whole_weight shucked_weight viscera_weight shell_weight rings length_bool sex 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 0.1010 0.1500 15 length_short M 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.0700 7 length_short M 2 F 0.530 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 0.1415 0.2100 9 length_short F 3 M 0.440 0.365 0.125 0.5160 0.2155 0.1140 0.1550 10 length_short M 4 I 0.330 0.255 0.080 0.2050 0.0895 0.0395 0.0550 7 length_short I ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4172 F 0.565 0.450 0.165 0.8870 0.3700 0.2390 0.2490 11 length_long F 4173 M 0.590 0.440 0.135 0.9660 0.4390 0.2145 0.2605 10 length_long M 4174 M 0.600 0.475 0.205 1.1760 0.5255 0.2875 0.3080 9 length_long M 4175 F 0.625 0.485 0.150 1.0945 0.5310 0.2610 0.2960 10 length_long F 4176 M 0.710 0.555 0.195 1.9485 0.9455 0.3765 0.4950 12 length_long M
결론
오늘부로 데이터전처리의 기본 실습이 끝났다. 오늘 배운 것들이 가령 어디에 쓰일지 지금 이해를 못해도 괜찮다. 만약 이 글을 읽은 여러분들이 데이터 전처리를 할 시점이 되었을 때, 오늘 읽었던 내용이 머리에 조금이나마 스쳐지나간다면 오늘의 노력은 정말 의미있고 가치있어 질 것이다.

안녕하세요. 영상 꾸준히 잘보고있습니다.
다름이 아니라 궁금한 점이 있어서 글을 남깁니다.
데이터 결측값 확인할 때 abalone_df.isnull().sum().sum() 을하면 0이 나오던데
저는 4180이 나와서요 이런건 왜그런것인지 왜 다른 것인지가 좀 궁금합니다...!