Machine learning week 13
Partitioning method
K means clustering
Partitioning method
- 각 클러스터에 하나의 centroid가 있다.
- 각 data point는 가장 가까운 centroid에 할당되고, 같은 centroid에 할당된 data는 하나의 클러스터를 형성한다.
- 클러스터의 개수(K)를 먼저 지정해야 알고리즘 실행할 수 있다.
- 클러스터들은 서로 중첩되지 않는다.
K means clustering 과정
- Set k initial centroids
- 반복
1) 클러스터 생성: 모든 객체 가장 가까운 centroid에 할당
2) 클러스터 centroid 재설정: 클러스터 구성원들 기준으로 centroid 다시 계산
3) 종료 조건 확인: centroid 위치 변하지 X or 할당 결과 변하지 X
초기 centroid 랜덤하게 선택되는데, 초기 설정이 결과에 영향 미칠 수 있다.
Hierarchical method
1. Agglomerative approach (bottom-up)
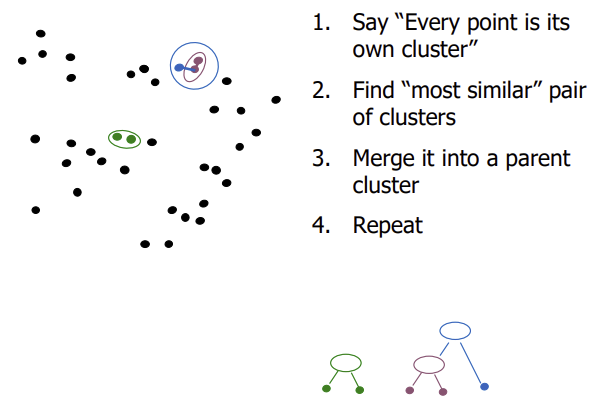
2. Divisive approach (top-down)
DBSCAN
DBSCAN(Density based spatial clustering of applications with noise)
- focuses on using density of points
- DBSCAN은 2개의 hyperparameter(epsilon, minimun number of points) 쓰면서 points 반복
DBSCAN key hyperparameters
- Epsilon
- Minimum number of points
: core point로 간주되기 위해 epsilon 내에 있어야 하는 최소 점 개수
→ 개수 만족 못하면 border point or outlier로 분류
DBSCAN point types
-
Core
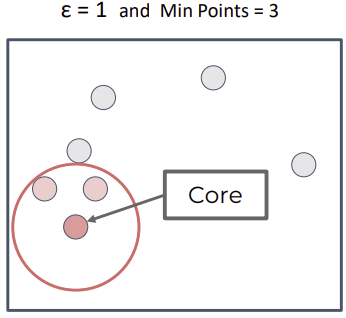
: Points with min. points in epsilon range(자신 포함) -
Border
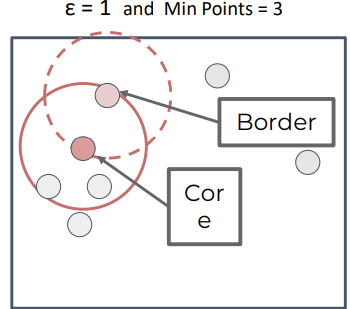
: In epsilon range of core point, but min. num of points 포함하지 않음 -
Outlier
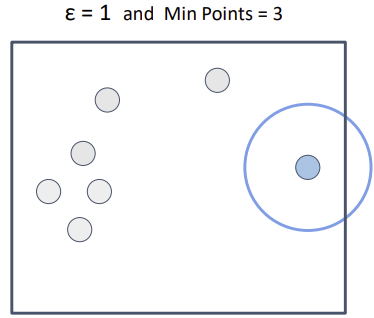
: cluster에 포함 X
Procedure
- Pick a 아직 할당되지 않은 random point
- Determine the point type
- Core point가 발견되고나면, 같은 cluster에 reachable point 다 더하기
- 모든 point가 클러스터에 포함되거나, outlier로 지정될 때까지 반복
DBSCAN vs. K-means
- DBSCAN:
densitybased - K-means:
distancebased
Hyperparameter
-
Increasing
epsilon 커지면 ➡️ more core points ➡️ more border points, less outlier
-
Decreasing
epsilon 작아지면 ➡️ unique clusters
epsilon 값 설정할 때 cluster 개수, relative percentage of outlier 고려해야 함
