Machine Learning week 10 정리
Does a hyperplane exist that can effectively
separate classes?
- Maximum Margin Classifier
- Support Vector Classifier
- Support Vector Machines
Hyperplane
Hyperplane이란 높은 차원의 공간을 두 부분으로 나누는 subspace으로, 주어진 공간에서 데이터를 분리하는 데 사용된다.
→ N차원 공간에서 hyperlane은 N-1차원의 subspace이다.
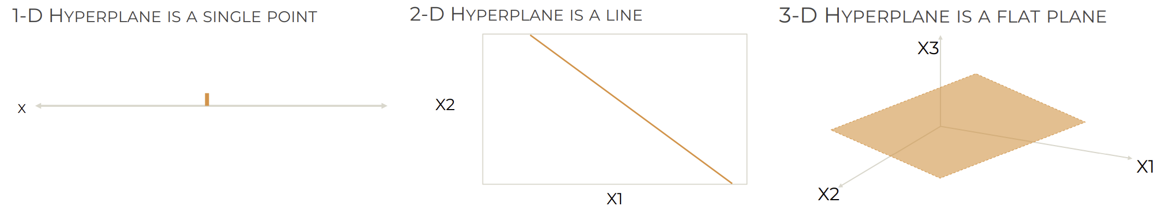
- 3D hyperplane: 2D flat plane
- 2D hyperplane: 1D line
- 1D hyperplane: single point
Maximum Margin Classifier
SVM의 아이디어는 hyperplane으로 클래스를 분리하는 것이다. SVM은 학습한 hyperplane으로, new data point가 어디에 위치하는지에 따라 class를 assign할 수 있다.
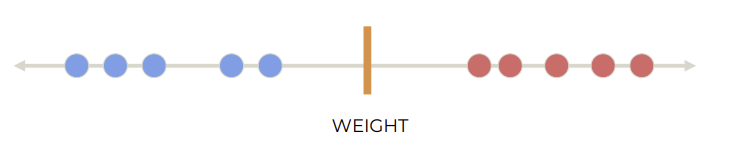
class 나누는 hyperplane 생성
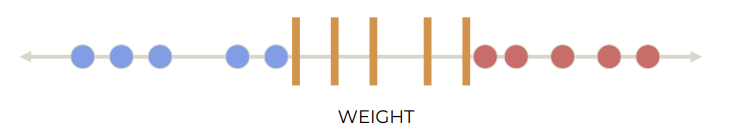
어느 separator가 가장 좋을까?
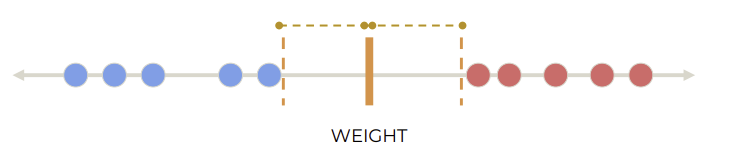
두 클래스 간의 margin을 최대화하는 separator 사용하면 된다.
→ Maximal Margin Classifier
Margin: hyperplane과 가장 가까운 data point 사이의 거리
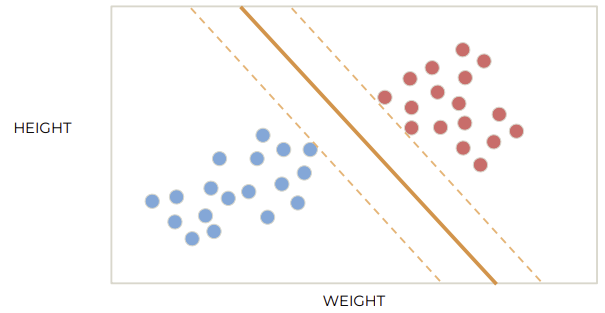
N차원에도 적용 가능하다.

Support vector는 margin 경계에 위치한 data points이다. Hyperplane의 위치는 support vector에 따라 결정된다.
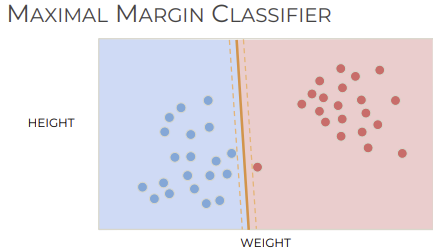
SVC
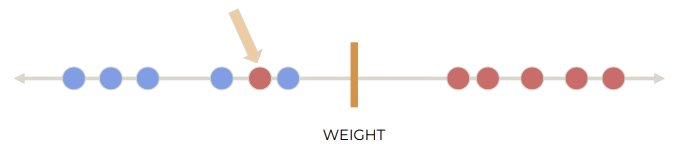
class를 완벽히 나눌 수 없는 경우에는 misclassification을 허용해야 한다.
Separator을 어디에 놓는지에 따라 bias-variance trade off가 있다.
- Bias: 모델이 단순해서 데이터의 complexity 반영 잘 못하는 경우
- Variance: 모델이 데이터의 complexity에 과적합하는 경우
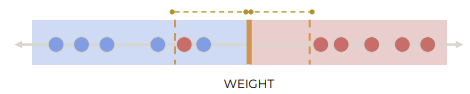
Soft margin: Misclassification 허용하고 hyperplane 정의
Soft margin을 허용하면 다양한 threshold를 설정할 수 있다. Soft margin의 margin 크기를 조정하기 위해 cross validation을 사용할 수 있다. Cross validation은 데이터를 여러번 train, test해서 최적의 파라미터를 찾는 방법이다.
(Hard Margin은 모든 데이터가 완벽히 분리된다고 가정)
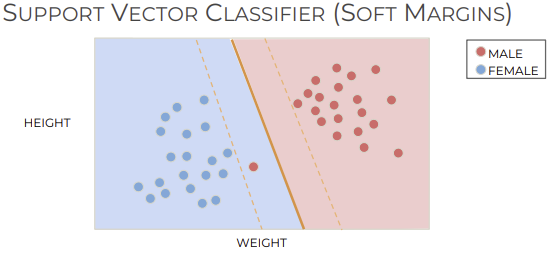
SVM
Misclassification 허용해도 hyperplane 성능 낮은 경우들이 있다.
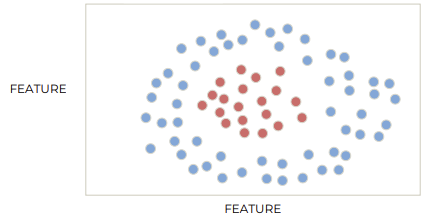
Support Vector Classifier(SVC)는 hyperplane으로 데이터를 선형적으로 분리한다. 하지만 데이터를 선형적으로 분리할 수 없는 경우들이 있다.
Non linear 문제를 해결하기 위해 Support Vector Machine(SVM)을 사용한다. SVM은 데이터를 고차원에 project하여, linear하게 데이터를 분리한다. 이를 위해 kernel을 사용한다.
kernel projection 역할: 저차원에서 복잡한 데이터 구조를 ➡️ 고차원으로 투영 (non linear → linear)
Polynomial kernel
[1-D]
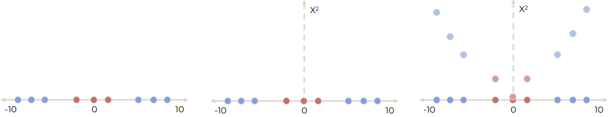
1D가 주어졌을 때, polynomial kernel로 차원으로 확장할 수 있다.
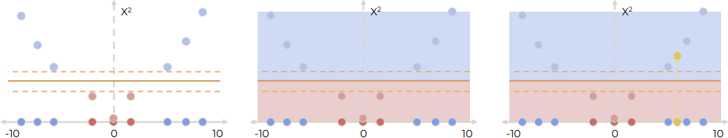
Projection 하고 hyperplane 만든 후에 새로운 data point를 evaluate 할 수 있다.
[2-D]
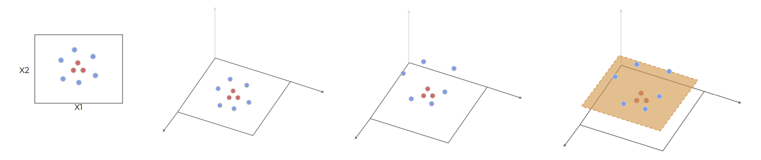
Soft margin으로도 분리가 잘 되지 않는 2D feature space에서도 SVM 사용하면 된다. Kernel transformation으로 2D에서 3D로 projection하고 hyperplane을 만든다.
Mathematics
SVM의 목표: Optimal hyperplane 찾기
→ Hyperplane과 support vector 사이 거리 최대화
일반적인 D 공간에서 hyperplane 식:
- : weight
- : input
SVM은 와 를 학습하여 optimal hyperplane을 찾는다.
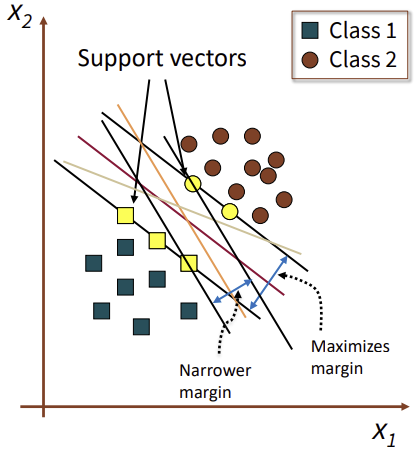
Binary classification에서 잘 분리하는 hyperplane을 찾으려면 objective function을 optimize 해야한다. Objective function은 data point들에 따라 결정된다.
Decision boundary에 가까운 point일수록 misclassified 될 확률이 높다. 따라서 classifier을 만들 때 decision boundary 근처에 있는 support vector에 더 많은 비중을 둬야한다.
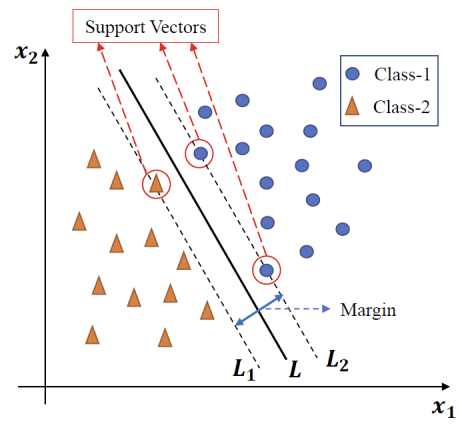
- , : support vector들에 의해 정의된 선(hyperplane)
- Margin: , 사이의 separation(perpendicular distance)
- : decision boundary
Objective: maximize the margin
Support Vector Machine(SVM)은 maximum margin classifier로도 불린다.
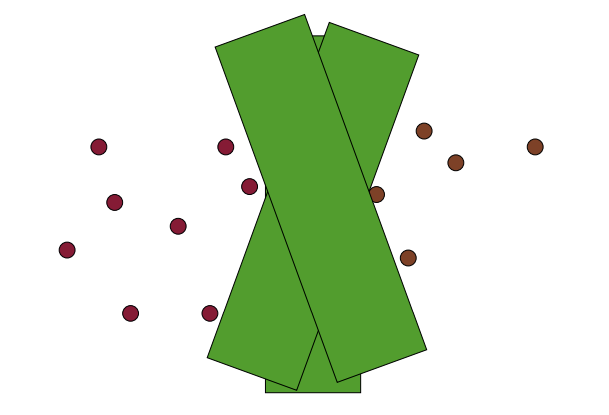
SVM에서 margin을 최대화하려는 목적
= 더 두꺼운 decision boundary를 만듦
= margin 두껍게
= 선택할 수 있는 hyperplane 개수 제한
= hyperplane 위치할 수 있는 공간 감소
= hyperplane 선택지 줄어들수록 모델의 복잡도(or capacity) 감소
⇒ overfitting 방지, generalization ↑
Linear Classifiers
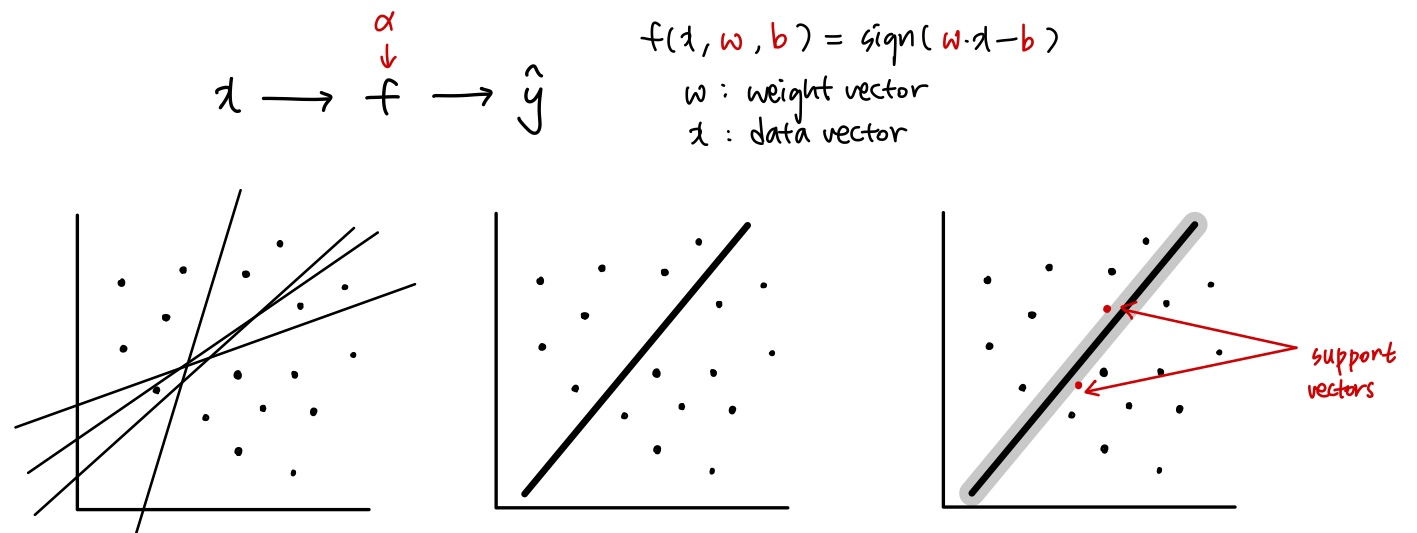
Linear classifier 식:
- : data point
- : weight vector (hyperplane의 방향 정의)
- : hyperplane의 절편
sign은 data point가 hyperplane을 경계로 어디에 위치하는지 결정한다.
경계의 경우의 수가 많은데, hyperplane을 설정할 때 margin을 최대화하는 것이 SVM의 목표이다.
Linear classifier의 margin은 boundary가 data point와 닿기 전까지 확장될 수 있는 최대 width로 정의된다.
Maximum Margin Linear Classifier는 가장 넓은 margin을 가지는 linear classifier이다. 이는 가장 단순한 형태의 SVM으로, LSVM(Linear Support Vector Machine)으로도 불린다. LSVM = Linear SVM
Large margin decision boundary
hyperplane L 식:
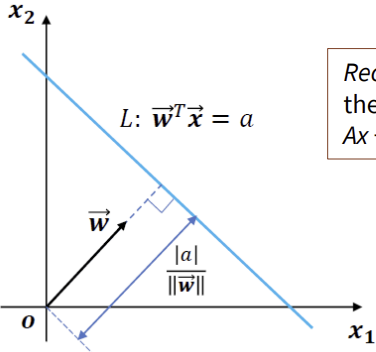
- : hyperplane에 수직인 벡터 (법선 벡터)
- x: data point
- a: hyperplane의 절편
임의의 점 가 hyperplane L에 대해 수직으로 떨어진 거리:

