📕 참고: ROS2로 시작하는 로봇 프로그래밍, topic_service_action_rclpy_example
서비스를 요청(Request)하는 서비스 클라이언트와 응답(Response)하는 서비스 서버에 대해 살펴보고자 한다.
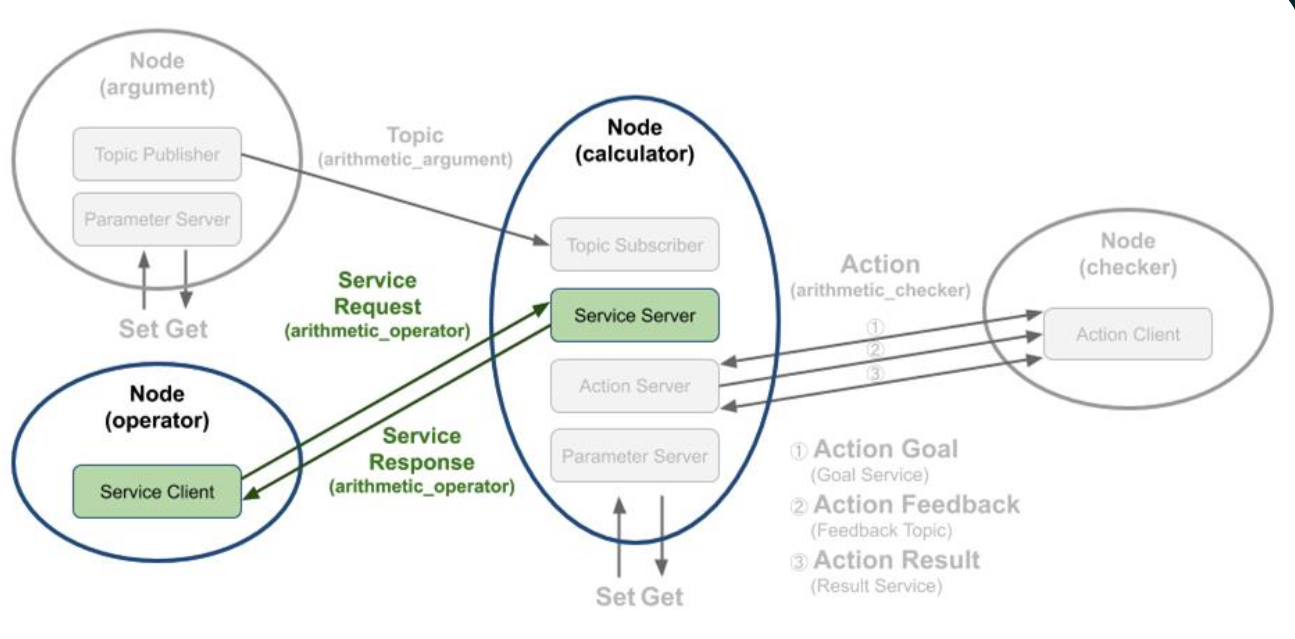
calculator
- 서비스 클라이언트에게 연산자(+,-,*, /) 응답 요청
- operator가 보낸 연산자로 변수 a,b 연산 후 다시 operator에게 수신
operator
- arithmetic_operator 서비스를 통해 calculator에게 연산자(+,-,*, /)를 랜덤으로 보냄
- calculator에게 받은 연산 결과를 터미널에 표시
calculator/서비스 서버 코드
서비스 서버 생성
self.arithmetic_service_server = self.create_service(
ArithmeticOperator,
'arithmetic_operator',
self.get_arithmetic_operator,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
ArithmeticOperator서비스 타입을arithmetic_operator라는 이름의 서비스 서버로 생성ArithmeticOperator는 인터페이스 패키지에srv로 정의되어 있음
서비스 콜백 함수
- 서비스 요청 처리
def get_arithmetic_operator(self, request, response):
self.argument_operator = request.arithmetic_operator
request.arithmetic_operator를 통해 서비스 클라이언트가 보낸 산술연산자를 읽어와 self.argument_operator 에 저장
- 산술 연산 수행
self.argument_result = self.calculate_given_formula(
self.argument_a,
self.argument_b,
self.argument_operator)
self.caculate_given_formula 메서드를 호출하여 self.argument_a,self.argument_b로 연산을 수행하고 self.argument_result에 저장
- 서비스 응답 설정
response.arithmetic_result = self.argument_result
연산 결과를 response.arithmetic_result에 저장하고 response로 반환
- 연산 결과 문자열 출력
self.argument_formula = '{0} {1} {2} = {3}'.format(
self.argument_a,
self.operator[self.argument_operator-1],
self.argument_b,
self.argument_result)
self.get_logger().info(self.argument_formula)
return responseself.get_logger().info 로 저장된 연산 결과를 출력
return response 로 서비스 요청에 대한 응답 제공
연산 함수
def calculate_given_formula(self, a, b, operator):
if operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.PLUS:
self.argument_result = a + b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MINUS:
self.argument_result = a - b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MULTIPLY:
self.argument_result = a * b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.DIVISION:
try:
self.argument_result = a / b
except ZeroDivisionError:
self.get_logger().error('ZeroDivisionError!')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
else:
self.get_logger().error(
'Please make sure arithmetic operator(plus, minus, multiply, division).')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
operator/서비스 클라이언트 코드
Operator 클래스
✔ 서비스 클라이언트 생성
class Operator(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('operator')
self.arithmetic_service_client = self.create_client(
ArithmeticOperator,
'arithmetic_operator')
while not self.arithmetic_service_client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=0.1):
self.get_logger().warning('The arithmetic_operator service not available.')
ArithmeticOperator서비스 타입을arithmetic_operator라는 이름으로 서비스 클라이언트 생성self.arithmetic_service_client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=0.1): 0.1초 간격으로 서비스 서버가 실행되었는지 확인
✔ 서비스 요청 응답
def send_request(self):
service_request = ArithmeticOperator.Request()
service_request.arithmetic_operator = random.randint(1, 4)
futures = self.arithmetic_service_client.call_async(service_request)
return futures
service_request.arithmetic_operator = random.randint(1,4): 1~4까지 임의의 중수를 통해 연산종류 결정(1:+, 2:-, 3:*, 4:/ ).call_async(service_request): 서비스 요청을 비동기 방식으로 응답 처리return futures: 서비스 응답값 반환💡 동기식 응답처리
response = self.arithmetic_service_client.call(service_request)
메인함수
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
operator = Operator()
future = operator.send_request()
user_trigger = True
'''생략'''
operator = Operator:Operator클래스를 인스턴스화하여 노드 생성future = operator.send_request(): 서비스 요청을 보내고 응답값 받기user_trigger = True: 프로그램이 처음 실행될 때 서비스 요청을 보내도록 설정
전체 코드
# Copyright 2021 OROCA
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import random
from ros_study_msgs.srv import ArithmeticOperator
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
class Operator(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('operator')
self.arithmetic_service_client = self.create_client(
ArithmeticOperator,
'arithmetic_operator')
while not self.arithmetic_service_client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=0.1):
self.get_logger().warning('The arithmetic_operator service not available.')
def send_request(self):
service_request = ArithmeticOperator.Request()
service_request.arithmetic_operator = random.randint(1, 4)
futures = self.arithmetic_service_client.call_async(service_request)
return futures
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
operator = Operator()
future = operator.send_request()
user_trigger = True
try:
while rclpy.ok():
if user_trigger is True:
rclpy.spin_once(operator)
if future.done():
try:
service_response = future.result()
except Exception as e: # noqa: B902
operator.get_logger().warn('Service call failed: {}'.format(str(e)))
else:
operator.get_logger().info(
'Result: {}'.format(service_response.arithmetic_result))
user_trigger = False
else:
input('Press Enter for next service call.')
future = operator.send_request()
user_trigger = True
except KeyboardInterrupt:
operator.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
operator.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
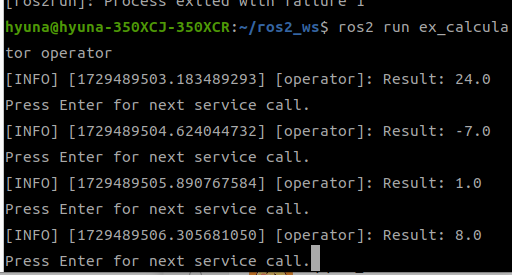
요청이 있을 때마다 연산 결과를 터미널에 표시해주는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

