개요
하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝 (랜덤포레스트, xgboost)
📌 문제
심장마비 확률이 높은사람?
- 성별, 나이, 혈압, 콜레스테롤, 공복혈당, 최대 심박수 등의 컬럼이 있음
- 평가: ROC-AUC, 정확도(Accuracy), F1 을 구하시오
- target : output (1:심장마비 확률 높음, 0:심장마비 확률 낮음)
- csv파일 생성 : 수험번호.csv (예시 아래 참조)
id,output 41,0.633 28,0.123 222,0.355
📌 데이터 불러오기
import pandas as pd train = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/MLpractice/heart/heart/2files/train.csv') test = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/MLpractice/heart/heart/2files/test.csv') train.shape, test.shape
📌 EDA
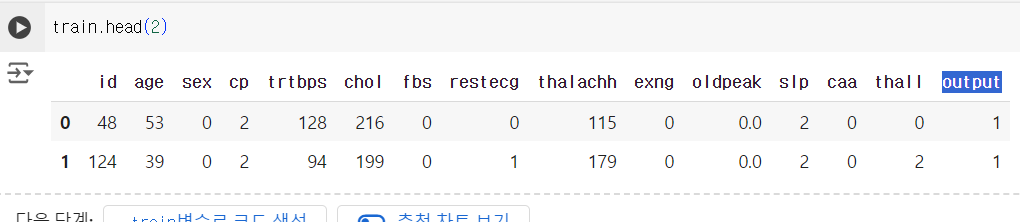
# 타겟 컬럼 (output) 확인 train.head(2)
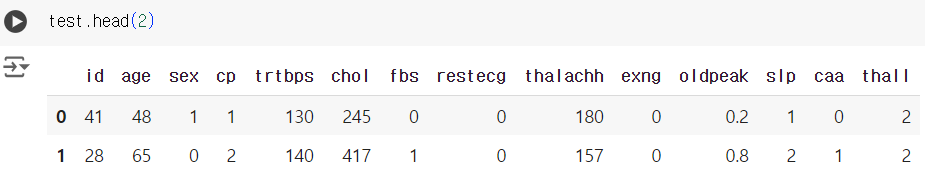
# 테스트 데이터에는 타겟 컬럼이 없다. test.head(2)
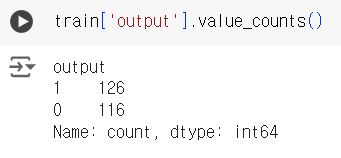
# 타겟 컬럼 값 확인 train['output'].value_counts()
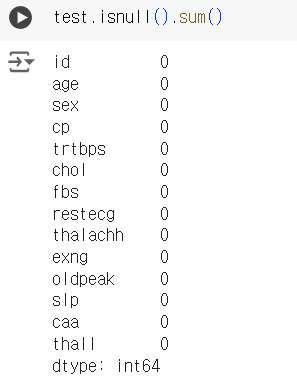
# 결측치 확인 train.isnull().sum()
test.isnull().sum()
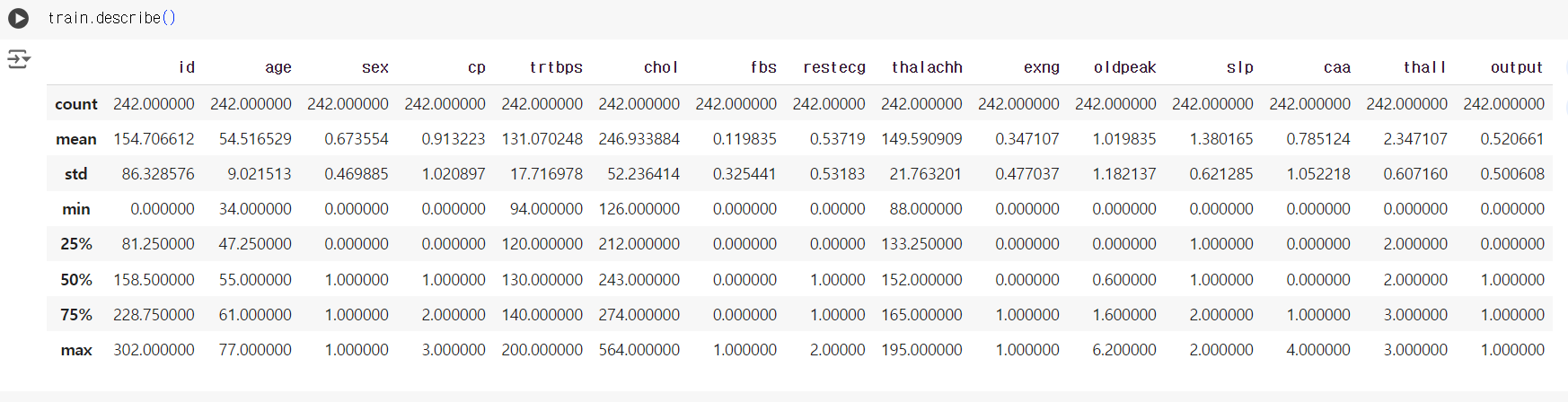
# 기초통계량 확인 train.describe()
# 데이터 형태 확인 train.info()
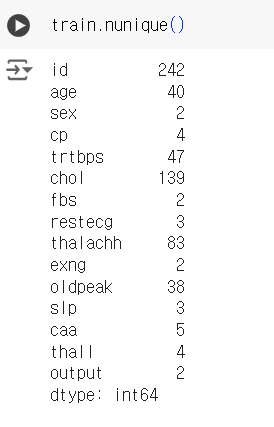
# 데이터 고유값 갯수 확인 train.nunique()
📌 데이터 전처리 및 & 피처엔지니어링
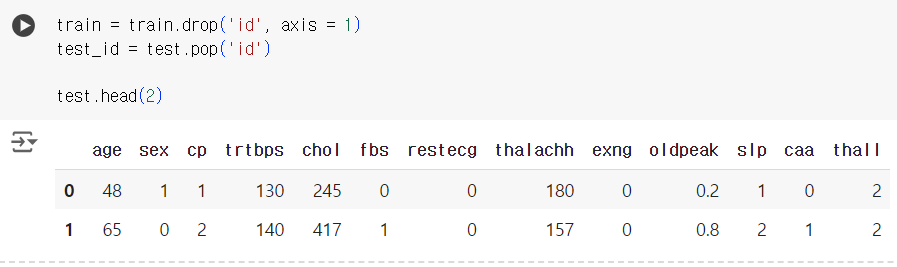
# 과적합 방지를 위해 훈련용 데이터에서는 id 컬럼 제거 # 시험용 데이터에서는 결과물에 제출하기 위해 .pop() 메서드 활용 test_id 에 빼놓기 train = train.drop('id', axis = 1) test_id = test.pop('id') test.head(2)
📌 검증 데이터 분리
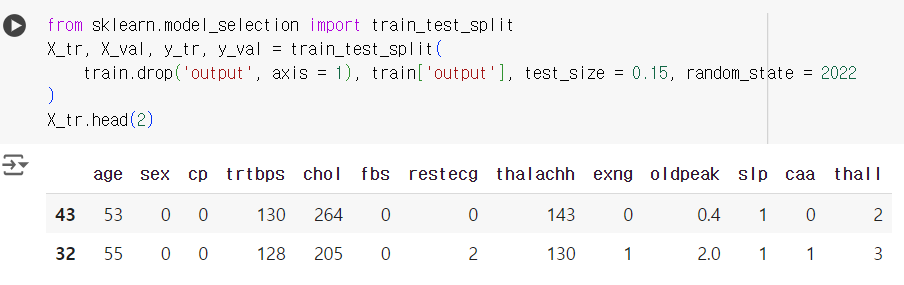
# 데이터 크기가 작기 때문에 15% 정도만 검증용으로 분리 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_tr, X_val, y_tr, y_val = train_test_split( train.drop('output', axis = 1), train['output'], test_size = 0.15, random_state = 2022 ) X_tr.head(2)
📌 모델 및 평가
- 랜덤포레스트: 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝
랜덤 포레스트의 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝은
max_depth (트리의 깊이)와 n_estimators (트리의 갯수)를 조절할 수 있다.
평균적인 조절값 :
max_depth = 3 ~ 12
n_estimators = 100 ~ 1000
# 랜덤 포레스트 모델 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, f1_score, accuracy_score # max_depth (트리의 깊이) = 3 ~ 12 / n_estimators (트리의 갯수) = 100 ~ 1000 rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state = 2022, max_depth = 5, n_estimators = 200) rf.fit(X_tr, y_tr) pred = rf.predict(X_val) pred_proba = rf.predict_proba(X_val) print(roc_auc_score(y_val, pred_proba[:,-1])) print(f1_score(y_val, pred)) print(accuracy_score(y_val, pred))
- xgboost: 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝 노하우
xgboost 의 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝은
max_depth (트리의 깊이), n_estimators (트리의 갯수), learning_rate (학습률)을 조절할 수 있다.
평균적인 조절값 :
max_depth = 3 ~ 12
n_estimators = 100 ~ 1000
learning_rate = 0.1 ~ 0.01
XGB는 n_estimators에 반비례하여 learning_rate 를 조절해줘야 함.
# XGB from xgboost import XGBClassifier from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, f1_score, accuracy_score # max_depth (트리의 깊이) = 3 ~ 12 / n_estimators (트리의 갯수) = 100 ~ 1000, learning_rate = 0.1 ~ 0.01 # XGB는 트리의 갯수에 반비례하여 learning_rate 를 조정해줘야 한다! xgb = XGBClassifier(random_state = 2022, max_depth = 5, n_estimators = 600, learning_rate = 0.01) xgb.fit(X_tr, y_tr) pred = xgb.predict(X_val) pred_proba = xgb.predict_proba(X_val) print(roc_auc_score(y_val, pred_proba[:,-1])) print(f1_score(y_val, pred)) print(accuracy_score(y_val, pred))
📌 예측 및 csv제출
-
파라미터 조절 및 모델 선택에 따른 평가 지표 비교
랜덤 포레스트 모델


XGB 모델


-
roc_auc_score 기준으로
랜덤 포레스트 모델에서max_depth = 5,n_estimators = 200
파라미터 조절값을 가진 상태의 점수가 가장 높기 때문에,
랜덤 포레스트 모델 및 해당 파라미터 값 선택
test.head(2)
pred_proba = pred_proba = rf.predict_proba(test) pd.DataFrame({'id':test_id, 'output' : pred_proba[:,-1]}).to_csv('00006.csv', index = False) pd.read_csv('00006.csv')
📌 평가(정리)
- 정답 데이터와 비교 : 0.9 이상의 높은 점수를 보여줌 !
y_test = pd.read_csv("/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/MLpractice/heart/heart/2files/y_test.csv") print(roc_auc_score(y_test, pred_proba[:,1]))