FLOps: 플롭스
컴퓨터 성능을 수치로 나타낼 때 주로 사용되는 단위
컴퓨터가 1초동안 수행할 수 있는 부동소수점 연산의 횟수를 기준으로 삼는다.
CPU Architecture 구조에 따라 클럭 당 연산 속도가 다르기 때문에 객관적 성능 비교 시 사용된다.
연산식
FLOPS=cores×clock×cycleFLOPS
Example
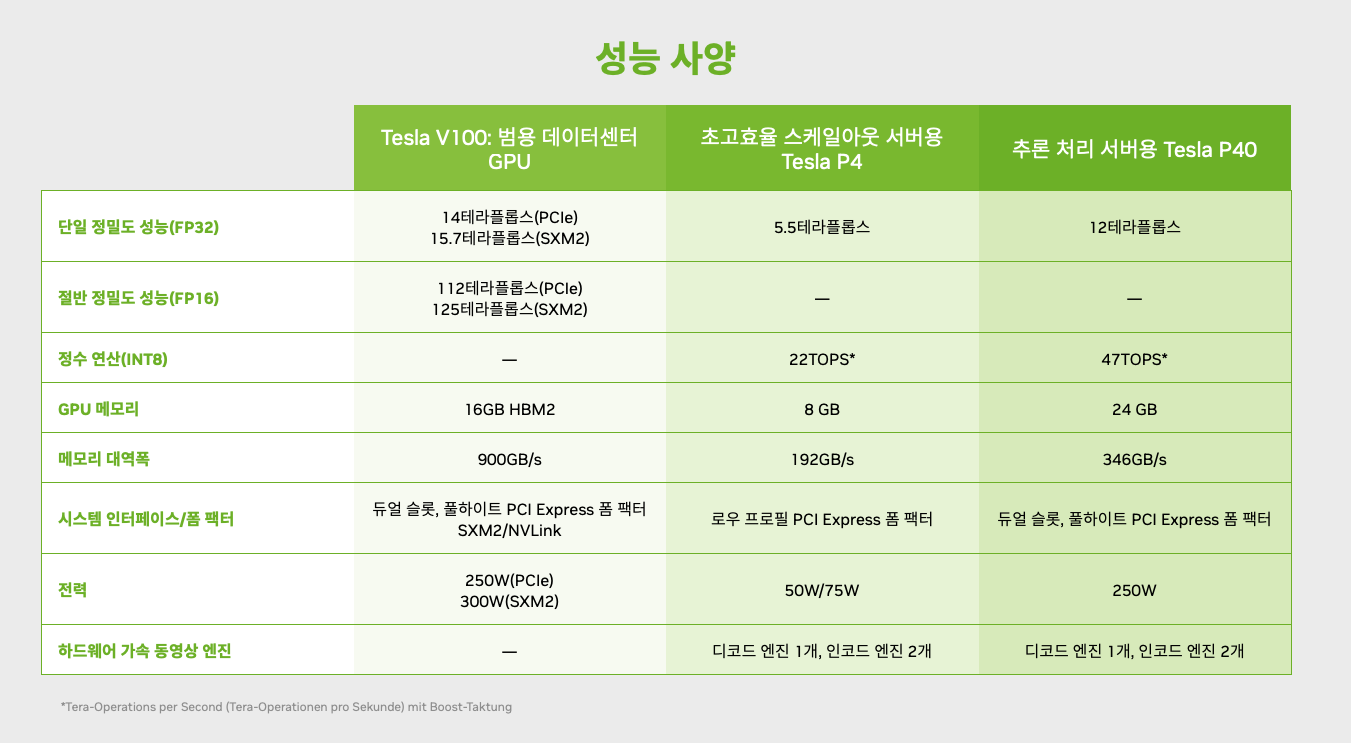
In Deep Learning
플롭스의 본 의미는 1초 당 수행할 수 있는 부동소수점 연산 횟수지만, 딥러닝에서는 실제 연산량에 따른다. 하여 딥러닝에서는 Floating Point Operations로 명명한다.
Linear Layers
MAC: Multiply-Accumulate
MAC=output.shape×input.shape
ADD=output.shape (for bias)
➡️FLOps=2×MAC+ADD
Convolution Layers
3차원 텐서인 경우 H×W×C를 갖는다.
여기서 kernel size 가 K×K일 때, FLOps는 K×K×Cin×Cout×Hout×Wout 이 된다.
N conv OPS=inputh×strideinputw=output2
MAC/filter=kernelsize2×InputChannels×OutputChannels
ADD=OutputChannels (for bias)
➡️FLOps=2×(MAC/filter+N conv OPS)+ADD
G-Ops by DL model
Accuracy와 FLOps 측면에서의 Architecture 비교
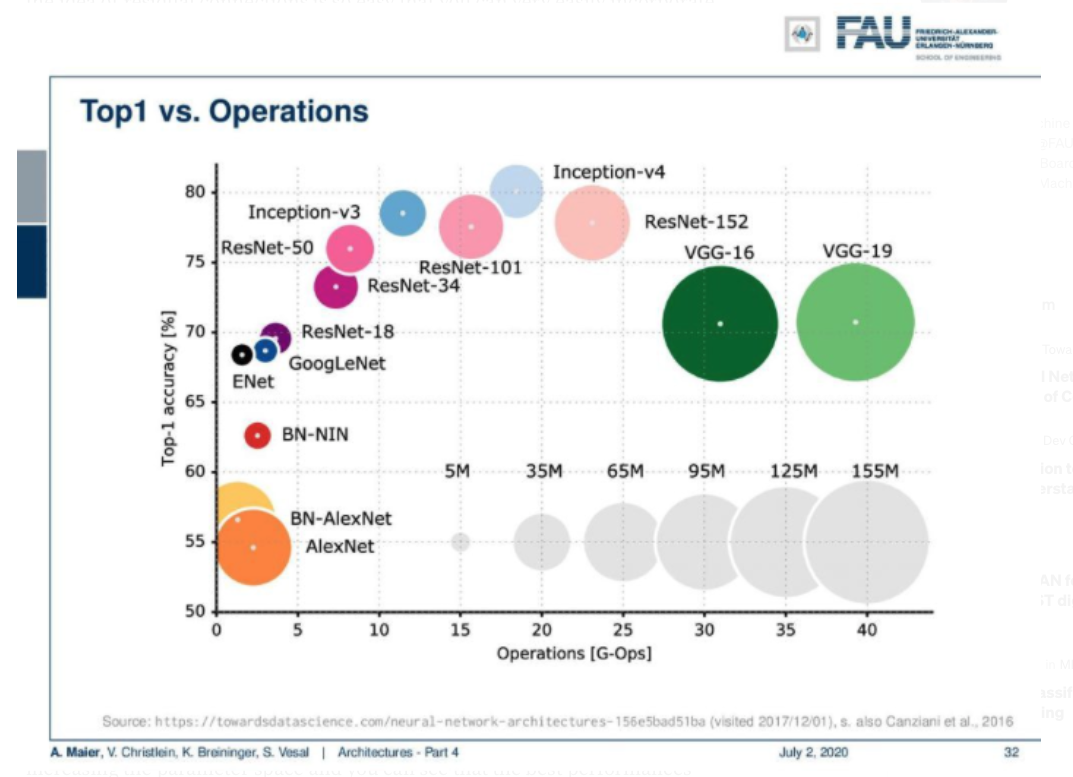
References
wikipedia, FLOps.
Matthijs Hollemans, How fast is my model?, 2018.
Nvidia, Example fig
Andreas Maier, Architectures - Part 4

