TIL: Python Basics Day 26 - List & Dictionary & DataFrame Comprehensions/ NATO Alphabet
Udemy Python Course
목록 보기
26/62
List Comprehension
-unique to python
-create a new list from an existing list
-Sequences: work with any sequences such as list, string, range, tuple
Before:
For Loop, using empty new_list and .append()
List Comprehenshions:
new_list = [new_item for item in list]
numbers = [1, 2, 3]
new_numbers = [n+1 for n in numbers]
#[2, 3, 4]
name = "Angela"
new_name = [letter for letter in name]
#['A', 'n', 'g', 'e', 'l', 'a']
range(1, 5)
new_range = [num * 2 for num in range(1, 5)]
#[2, 4, 6, 8]Conditional List Comprehension : new_list = [new_item for item in list if test]
e.g. #only add names have four letters
names = ['Alex', 'Beth', 'Caroline', 'Eleanor' ]
short_names = [name for name in names if len(name) < 5]
#short_names = ['Alex', 'Beth']- in this case, new_item and item 's name are same; because we just want a list of items that's passed the condition.
e.g. coverting names into all caps (capital) if length of name longer than five
names = ['Alex', 'Beth', 'Caroline', 'Dave', 'Eleanor', 'Freddie' ]
all_caps = [name.upper() for name in names if len(name) > 5]
#all_caps = ['CAROLINE', 'ELEANOR', 'FREDDIE']task.1
You are going to create a list called result which contains the numbers that are common in both files.
---------------------------<my code>---------------------------
with open("path.txt") as file1:
file1 = open("file1.txt", "r")
file_list = file1.readlines()
file_1 = [int(number.strip()) for number in file_list]
print(file_1)
file2 = open("file2.txt", "r")
file_list_2 = file2.readlines()
file_2 = [int(number.strip()) for number in file_list_2]
print(file_2)
result = [ num for num in file_1 if num in file_2 ]
# Write your code above 👆
print(result)
#[3, 6, 5, 33, 12, 7, 42, 13]
---------------------------Angela's ---------------------------
with open("file1.txt") as file_1:
file_list = file_1.readlines()
with open("file2.txt") as file_2:
file_list_2 = file_2.readlines()
result = [ int(num) for num in file_list if num in file_list_2 ]Dictionary Comprehension
new_dict = {new_key:new_value for item in list}
- create a new dictionary from a list
names = ['Alex', 'Beth', 'Caroline', 'Dave', 'Eleanor', 'Freddie' ]
import random
students_scores = {student:random.randint(1, 100) for student in names}
#{'{'Alex': 3, 'Beth': 43, 'Caroline': 68, 'Dave': 51, 'Eleanor': 15, 'Freddie': 3}
new_dict = {new_key:new_value for (key,value) in dict.items()}
- create a new dictionary by taking an existing dictionary and getting hold of all of the items by using .itmes() method
-split it into key and value and use it to create a new pair
-conditional : new_dict = {new_key:new_value for (key,value) in dict.items() if test}
passed_students = {student:score for (student, score) in students_scores.items() if score > 60 }
#{'Alex': 98, 'Freddie': 90}task.2 string sequence -> dict comprehension
sentence = "What is the Airspeed Velocity of an Unladen Swallow?"
# Don't change code above 👆
# Write your code below:
splitted_word_list = sentence.split()
print(splitted_word_list)
result = { item:len(item) for item in splitted_word_list}
print(result)
#['What', 'is', 'the', 'Airspeed', 'Velocity', 'of', 'an', 'Unladen', 'Swallow?']
#{'What': 4, 'is': 2, 'the': 3, 'Airspeed': 8, 'Velocity': 8, 'of': 2, 'an': 2, 'Unladen': 7, 'Swallow?': 8}task.3 Farenheight
weather_c = {
"Monday": 12,
"Tuesday": 14,
"Wednesday": 15,
"Thursday": 14,
"Friday": 21,
"Saturday": 22,
"Sunday": 24,
}
# 🚨 Don't change code above 👆
# Write your code 👇 below:
def temp_f(temp):
f = (temp * 9/5) + 32
return f
weather_f = {day:temp_f(temp) for (day,temp) in weather_c.items()}
print(weather_f)
#{'Monday': 53.6, 'Tuesday': 57.2, 'Wednesday': 59.0, 'Thursday': 57.2, 'Friday': 69.8, 'Saturday': 71.6, 'Sunday': 75.2}
DataFrame comprehension
Looping through Dictionaries
for (key, value) in student_dict.items():
print(value)Pandas inbuilt loop : iterrows
loop through a dataframe
import pandas
pandas.DataFrame(new_dict)
for (key, value) in new_dict.items():
print(values)loop through rows of a data frame
each rows are pandas series object
for (index_num, row) in data_frame.iterrows():
print(index_num)
print(row.student)Project. NATO Alphabet
read csv file -> turn it into dictionary format using iterrows -> row.labelname -> list comprehension
#TODO 1. Create a dictionary in this format:
#{"A": "Alfa", "B": "Bravo"}
#csvfile.to_dict() doesn't provide the format we want...
data = pandas.read_csv("nato_phonetic_alphabet.csv")
# print(data)
# for (index, row) in data.iterrows():
# print(row.letter)
# print(row.code)
dict_nato = {row.letter:row.code for (index, row) in data.iterrows()}
# print(dict_nato)
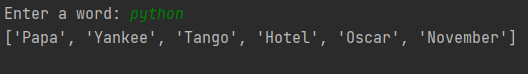
#TODO 2. Create a list of the phonetic code words from a word that the user inputs.
user = input(f"Enter a word: ").upper()
result = [dict_nato[word] for word in user]
print(result)squaring number: 4 squared equals 16. 4**2
You can use join() method to convert list to string in python:
def listToString(s):
s = ['amazing ', 'learn ', 'python']
print(listToString(s))
Source :
list to string python